Influence of Reading Behavior of Entrepreneurs on Their Entrepreneurial Performance: Empirical Study of Chongqing
,
College of Economics and Management, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
1 Introduction
Cultural level and national quality of a country are closely connected with reading level of the country. The national average reading is an indicator for measuring the national reading level. According to survey data of the UNESCO, the annual average reading of Israel was 12.9 books and ranked the first place in the world, while the world annual average reading was 6.88 books. However, according to the 11th national reading survey, the national annual average reading of paper books in China was 4.77, and the annual average reading of e-books was 2.48. Although the annual average reading is rising in recent years, there is still a great gap with the world average level. According to analysis of Xu Guosheng, the president of Chinese Academy of Press and Publication, in the context of encouraging entrepreneurial activities, citizens should fully realize the importance of reading for personal promotion. In the entrepreneurial process, reading behavior of entrepreneurs has great significance and influence on their entrepreneurial performance. Minniti (2001) held that entrepreneurial learning is the process of enterprise learning and acquiring knowledge, and using the knowledge to make effective decisions, while Slater.F (1990) stated that customer demands are gradually diversified and individualized, enterprises should improve their ability of searching, spreading and using information, so as to realize survival and development. Researches of domestic and foreign scholars manifest that reading behavior of entrepreneurs is of utmost importance to their development. Besides, the influence of reading is hidden but comprehensive. However, Wright. M (2009) believed that reading behavior of entrepreneurs may not play a positive role in entrepreneurial performance, some reading actions may play an adverse role in entrepreneurial performance. Bruderl. J (1992) contended that reading behavior of entrepreneurs has no significant influence on entrepreneurial performance.
In the context of energetically encouraging innovation and entrepreneurial activities, there are very few researches about the relation between reading behavior and entrepreneurial performance. Thus, we built corresponding theoretical system, analyzed different values and functions of different reading behavior, divided reading behavior of entrepreneur, and finally came up with pertinent recommendations.
2 Study method and data collection
2.1DataacquisitionandsamplesIn this study, we selected 200 entrepreneurs of new enterprises in one-hour economic circle of Chongqing and carried out a questionnaire. Before formal survey in a large area, we randomly selected 20 entrepreneurs of new enterprises to make preliminary survey, to improve the questionnaire. In formal survey, we collected 180 copies of questionnaire, the response rate was 90%. In these 180 copies, 152 ones were valid (84.4%). Statistical information of this survey indicated that: as for the sex, the male entrepreneurs accounted for 64%, consistent with current entrepreneurial situations of Chongqing in recent years; as for the educational level, most entrepreneurs (76%) had the junior middle school education; as for the age, entrepreneurs in 30-40 years old accounted for 80% of all entrepreneurs; as for development stages, most enterprises (59%) were still at the developing stage; as for the scale, most enterprises (51%) had total assets of 0.3 million to 1 million, conforming to characteristics of central and western enterprises.
2.2Measurementofindicators
2.2.2Reading behavior indicators. Some indicators of reading behavior are based on the library science, while some indicators are based on actual entrepreneurial environment of Chongqing and our understanding of entrepreneurs at the preliminary survey. In our opinion, any reading behavior is the reading of certain media by reading subjects in certain reading environment. This depicts three dimensions of reading behavior: reading subjects, reading media, and reading environment. Since each dimension includes specific indicators, we adopted the expert evaluation method in quantitative process of empirical analysis, and made analysis and evaluation of indicators of reading behavior, as listed in Table 1.
2.2.2Entrepreneurial performance indicators. In this study, we employed methods proposed by Venkatraman (1986) and Murphy (1996), and divided entrepreneurial performance of new enterprises into survival indicators and financial indicators. To meet the requirement of quantitative indicators, we screened on this basis and finally determined entrepreneurial performance indicators, as listed in Table 1.
Table1Readingbehaviorandentrepreneurialperformanceindicatorsystem
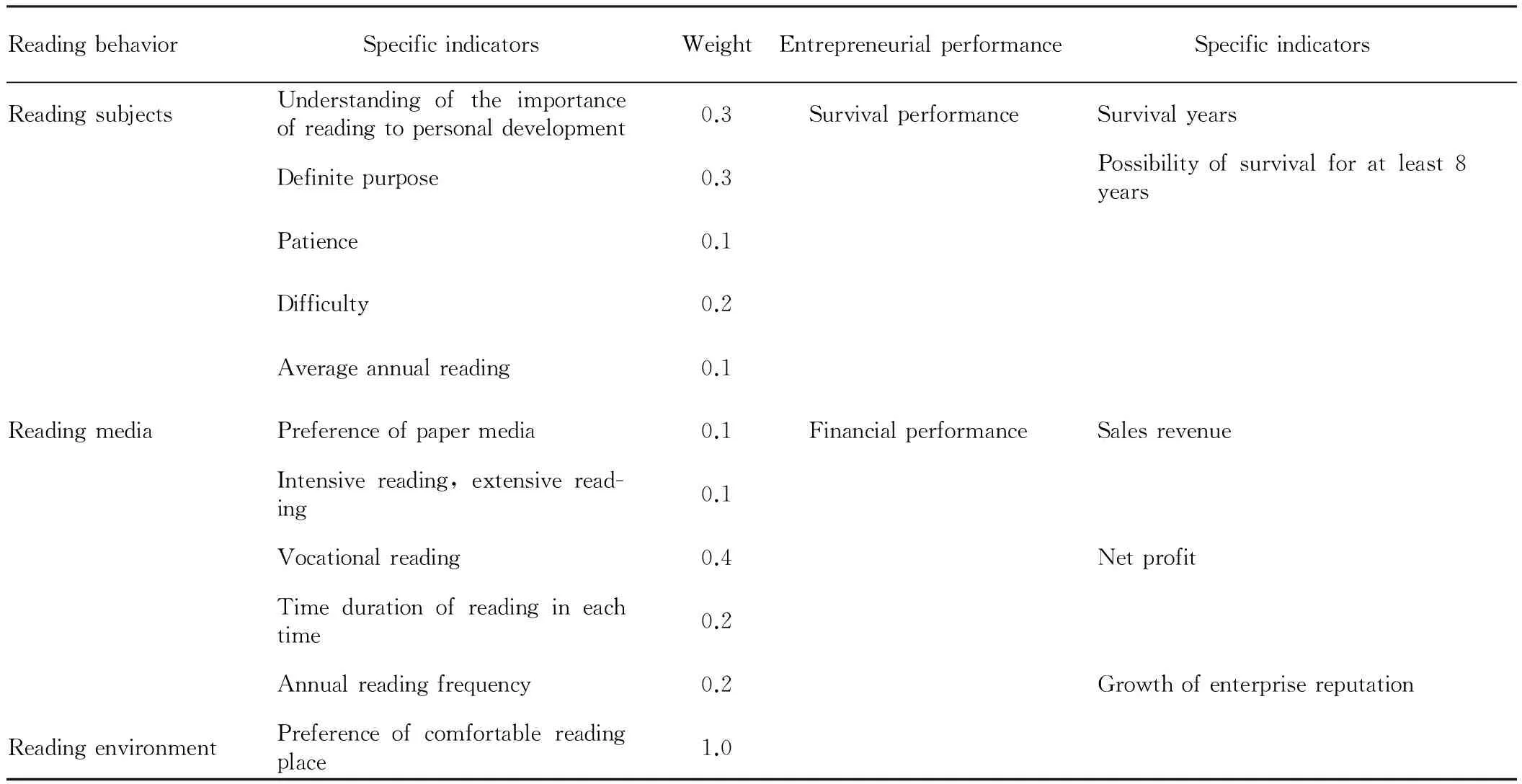
ReadingbehaviorSpecificindicatorsWeightEntrepreneurialperformanceSpecificindicatorsReadingsubjectsUnderstandingoftheimportanceofreadingtopersonaldevelopment0.3SurvivalperformanceSurvivalyearsDefinitepurpose0.3Possibilityofsurvivalforatleast8yearsPatience0.1Difficulty0.2Averageannualreading0.1ReadingmediaPreferenceofpapermedia0.1FinancialperformanceSalesrevenueIntensivereading,extensiveread-ing0.1Vocationalreading0.4NetprofitTimedurationofreadingineachtime0.2Annualreadingfrequency0.2GrowthofenterprisereputationReadingenvironmentPreferenceofcomfortablereadingplace1.0
2.3StudymethodsIn the empirical test of survival performance and financial performance, we established Probit regression model to test "possibility of survival for at least 8 years"; we built OLS regression model to test dependent variables "survival years", "sales revenue" and "profit"; in the empirical test of financial performance, because "enterprise reputation" is numerical variable (5 for very high, 4 for high, 3 for general, 2 for low, and 1 for very low), we built Ordered Probit regression model to conduct test. Form of these three models is as follows:
y*=βx+ε
whereY=0,y*≤0
Y=βx+ε
3 Result analysis
From Table 2, we can know that (i) reading media has significantly positive promotion on survival years of entrepreneurial enterprises (α= 2.7997,p= 0.036), while reading subjects and reading environment have negative effect, indicating that reading media can significantly increase survival years of entrepreneurial enterprises. (ii) Reading media has significantly positive promotion on possibility of survival for at least 8 years of entrepreneurial enterprises (α= 4.2294,p= 0), while reading subjects and reading environment have negative effect, indicating that reading media can significantly increase possibility of survival for at least 8 years of entrepreneurial enterprises. (iii) Age of entrepreneurs has positive effect on possibility of survival for at least 8 years, such function is manifested as "reverse U shape", indicating growth of age of entrepreneurs can significantly increase survival years and sustained operation of enterprises at early stage, but when it increases to certain level, such effect will decline. Possible reasons: upgrade and update of products and innovation of technologies are rapid. With growth of age, learning ability of entrepreneurs gradually declines, while satisfying demands of customers is one of the most important tasks. Knowledge obtained by entrepreneurs can not make their products completely satisfy customer demands and win market acceptance, or win any advantage in competitive market, which is not favorable for sustained survival and development of enterprises.
According to Table 3, (i) reading environment plays significantly positive role in sales revenues and profit of enterprises (α=23.9516,p=0), while reading subjects and reading media have negative effect, indicating that more comfortable reading environment can significantly increase sales revenues and profit of entrepreneurial enterprises. Possible reasons: comfortable reading environment, such as library and coffee shop, creates elegant and ordered reading atmosphere and the auxiliary material conditions provide convenience for enterprises reading there. Comfortable reading environment contains collective reading behavior (reading club) and has certain hidden supervision mechanism, so as to increase the reading efficiency of entrepreneurs. (ii) Reading media exerts significantly positive effect on social reputation of entrepreneurial enterprises (α=1.7273,p=0), while the role of reading subjects is relatively weak (α=0.0904,p=0.286), and reading environment plays adverse role (α=-1.5786,p=0), indicating that reading media can significantly strengthen social reputation of entrepreneurial enterprises, and reading subjects can enhance social reputation of entrepreneurial enterprises to a certain extent. Possible reasons: in the process of entrepreneurs creating or improving social reputation, reading brings different value perception to different interested parties. From reading media, it can be seen that whether entrepreneurs have sustained learning ability, whether they actively cultivate innovation awareness, different interested parties establish understanding and acceptance of entrepreneurs through judgment of these factors, so as to directly influence social reputation of enterprises.
Table2Regressionresultsofenterprisesurvivalperformancemodel
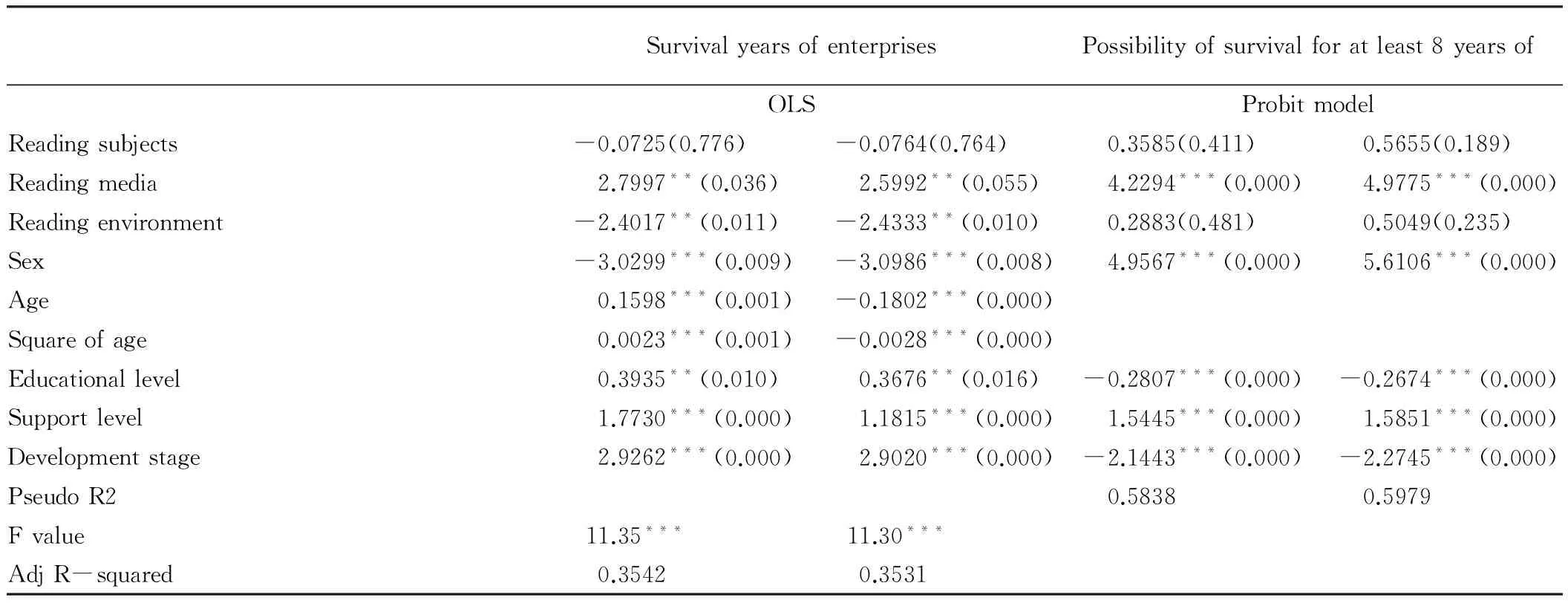
SurvivalyearsofenterprisesPossibilityofsurvivalforatleast8yearsofOLSProbitmodelReadingsubjects-0.0725(0.776)-0.0764(0.764)0.3585(0.411)0.5655(0.189)Readingmedia2.7997**(0.036)2.5992**(0.055)4.2294***(0.000)4.9775***(0.000)Readingenvironment-2.4017**(0.011)-2.4333**(0.010)0.2883(0.481)0.5049(0.235)Sex-3.0299***(0.009)-3.0986***(0.008)4.9567***(0.000)5.6106***(0.000)Age0.1598***(0.001)-0.1802***(0.000)Squareofage0.0023***(0.001)-0.0028***(0.000)Educationallevel0.3935**(0.010)0.3676**(0.016)-0.2807***(0.000)-0.2674***(0.000)Supportlevel1.7730***(0.000)1.1815***(0.000)1.5445***(0.000)1.5851***(0.000)Developmentstage2.9262***(0.000)2.9020***(0.000)-2.1443***(0.000)-2.2745***(0.000)PseudoR20.58380.5979Fvalue11.35***11.30***AdjR-squared0.35420.3531
Note: results were obtained through Stata12.0 and parenthetic values were P value. *, **, and***signify 10%, 5% and 1% significance level respectively.
Table3Regressionresultsofenterprisefinancialperformancemodel
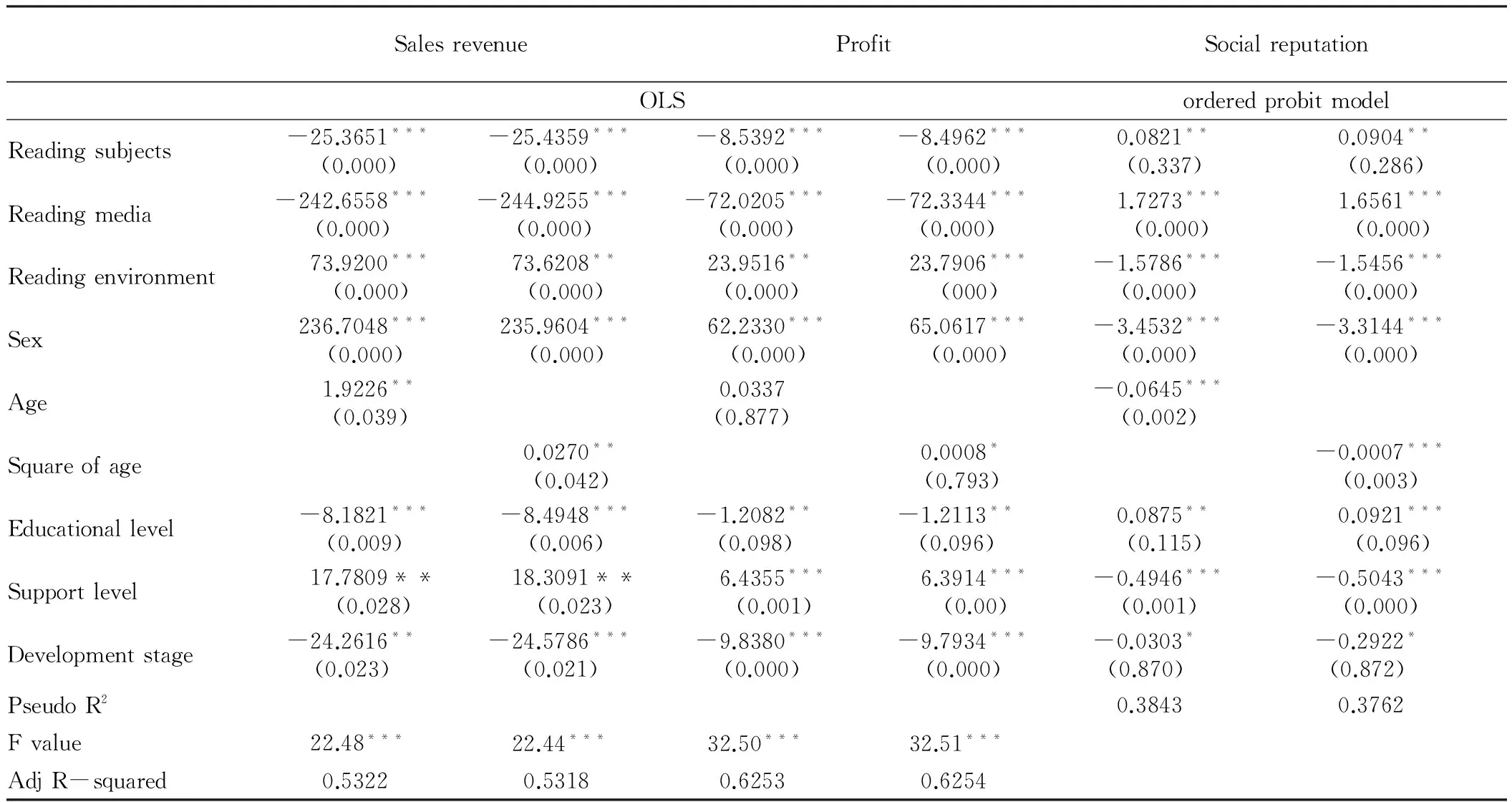
SalesrevenueProfitSocialreputationOLSorderedprobitmodelReadingsubjects-25.3651***(0.000)-25.4359***(0.000)-8.5392***(0.000)-8.4962***(0.000)0.0821**(0.337)0.0904**(0.286)Readingmedia-242.6558***(0.000)-244.9255***(0.000)-72.0205***(0.000)-72.3344***(0.000)1.7273***(0.000)1.6561***(0.000)Readingenvironment73.9200***(0.000)73.6208**(0.000)23.9516**(0.000)23.7906***(000)-1.5786***(0.000)-1.5456***(0.000)Sex236.7048***(0.000)235.9604***(0.000)62.2330***(0.000)65.0617***(0.000)-3.4532***(0.000)-3.3144***(0.000)Age1.9226**(0.039)0.0337(0.877)-0.0645***(0.002)Squareofage0.0270**(0.042)0.0008*(0.793)-0.0007***(0.003)Educationallevel-8.1821***(0.009)-8.4948***(0.006)-1.2082**(0.098)-1.2113**(0.096)0.0875**(0.115)0.0921***(0.096)Supportlevel17.7809**(0.028)18.3091**(0.023)6.4355***(0.001)6.3914***(0.00)-0.4946***(0.001)-0.5043***(0.000)Developmentstage-24.2616**(0.023)-24.5786***(0.021)-9.8380***(0.000)-9.7934***(0.000)-0.0303*(0.870)-0.2922*(0.872)PseudoR20.38430.3762Fvalue22.48***22.44***32.50***32.51***AdjR-squared0.53220.53180.62530.6254
4 Conclusions
This study elaborated entrepreneurial performance of entrepreneurs, divided entrepreneurial performance into survival performance and financial performance, which is helpful for better understanding the effect of reading behavior on entrepreneurial performance. From different perspective of reading behavior, namely, reading subjects, reading media and reading environment, the effect of reading behavior on entrepreneurial performance is different. Firstly, reading media can significantly increase survival years of entrepreneurial enterprises. Secondly, reading media can significantly increase possibility of survival for at least 8 years of entrepreneurial enterprises. Thirdly, reading media can significantly strengthen social reputation of entrepreneurial enterprises, and reading subjects can enhance social reputation of entrepreneurial enterprises to a certain extent.
From the above analysis, our conclusions mainly lie in following aspects: functions of reading subjects, reading media and reading environment are different. We divided entrepreneurial performance into survival performance and financial performance. Besides, we further analyzed influence of reading behavior on survival performance and financial performance. This will break the simple understanding of "reading behavior of entrepreneurs having certain positive effect on entrepreneurial performance", in hope of providing theoretical basis for fully understanding the effect of reading behavior on entrepreneurial performance of enterprises. It should be noted that our data were collected from some enterprises of Chongqing, which will reduce randomness of data to a certain extent and make our study have certain regional limitation. In future, it is expected to make further pertinent survey, to test universality of our conclusions. In addition, we mainly interviewed entrepreneur. In future, it is recommended to study entrepreneurial teams, and study their reading behavior and influence of different reading behavior on entrepreneurial performance, so as to provide guidance for entrepreneurial teams.
[1] FU LY. A study on the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation, entrepreneurial learning and new venture performance[D] .Nanjing:Nanjing University of Finance & Economics, 2012.(in Chinese).
[2] Wright M. The extent and nature of opportunity identification of experienced entrepreneurs[J].Journal of Business Venturing, 2009, 24(2):99-115.
[3]Bruderl J. Dynamic career models of inequality research[J]. Sociological Methods & Research, 1992,21(1):3-24.
[4] Slater F. The effect of market orientation on business profitability[J]. Journal of Marketing,1990,54(3):20-37.
[5] ZHAO WH, LI DM. Effect of entrepreneur's prior knowledge on entrepreneurial performance: Moderating effect of environmental dynamism[J].Technology Economics,2014(8):33. (in Chinese).
[6] YU SZ. Review of entrepreneurial performance[J].Foreign Economies & Management,2013(2):35.(in Chinese).
[7] FU LYL. A study on the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation, entrepreneurial learning and new venture performance[D] .Nanjing:Nanjing University of Finance & Economics, 2012.(in Chinese).
[8] DING YF. Study on the relationship between exploration-exploitation organizational learning and entrepreneurial performance[D] .Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006. (in Chinese).
[9] LI XX. Research on the evolution of national reading behaviour and its countermeasures in the digital age[D] .Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2013.(in Chinese).
[10] ZHU XM. Empirical analysis on the relationship among resource availability, EO and new venture’s performance[J] .Studies in Science of Science, 2008, 26(3): 589-596. (in Chinese).
[11] CHEN LC. Effects of entrepreneur’s human capital and social capital on establishment and development of new ventures[J]. Technology Economics, 2009, 28(8): 22. (in Chinese).
[12] GAN LM, PAN H, LIU JJ. Studies in technological knowledge management of the corporation[J].Studies in Science of Science,2003,21(2):201-204.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2016年5期
Asian Agricultural Research2016年5期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Is It Worthwhile for Farmers to Grow Grain?—A Study of Farmers’ Behavior of Growing Grain
- Establishment of Chinese Agricultural Brand Value Scale and Study of Its Reliability and Validity Based on Customer Value
- How to Develop Chinese Rural Tourism in the Context of New Urbanization?
- Chinese Customers’ WTP for Legal Digital Music Downloading
- High Standard Capital Farmland Construction Based on Grain Security
- Research on the Brand Construction of Agritourism Enterprise in Chongqing
