连续饲喂转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对2个世代鹌鹑生长发育的影响
李泽阳冯京海周 明张敏红常 玉(1.安徽农业大学动物科技学院,合肥30036;.中国农业科学院北京畜牧研究所,动物营养学国家重点实验室,北京100193)
连续饲喂转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对2个世代鹌鹑生长发育的影响
李泽阳1,2冯京海2∗周 明1∗∗张敏红2常 玉2
(1.安徽农业大学动物科技学院,合肥230036;2.中国农业科学院北京畜牧研究所,动物营养学国家重点实验室,北京100193)
摘 要:本试验旨在研究连续饲喂转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对2个世代鹌鹑生长发育的影响。选取健康的1日龄日本鹌鹑(Coturnix japonica)402羽随机分成2组,每组3个重复,每个重复67羽,雌雄混养。2组分别为转基因组和非转基因组,分别饲喂含转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因或非转基因糙米的饲粮,35日龄时从各组中分别挑选健康的体重相近的鹌鹑72羽,平均分成6个重复,每个重复3羽雄性9羽雌性,分别继续饲喂2种饲粮,饲养至91日龄。2个组85~91日龄所产的蛋分别孵化,孵化出的子代鹌鹑分别继续饲喂2种饲粮,分组及饲养管理与亲代相同。结果表明:转基因糙米中的粗蛋白质、粗脂肪、粗纤维等营养成分的含量与非转基因糙米没有显著差异(P>0.05);与非转基因组相比,转基因组亲代和子代鹌鹑的平均日采食量、平均日增重和料重比均无显著差异(P>0.05);2代鹌鹑的肝脏、心脏、睾丸和卵巢等器官指数也与非转基因组无显著差异(P>0.05)。结果表明,连续2个世代采食含转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米的饲粮对日本鹌鹑的生长发育没有显著影响。
关键词:转基因;糙米;Cry1Ab/1Ac;鹌鹑;生长发育
∗∗通信作者:周 明,教授,硕士生导师,E⁃mail:aauzhouming@163.com
转苏云金芽胞杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis,Bt)基因(包括Cry1Ab、Cry1A和Cry1Ab/1Ac等基因)作物可在茎、叶、种子等部位表达外源杀虫蛋白,该蛋白质具有高度专一性,能与昆虫肠道上皮细胞膜上的特异受体蛋白发生专一性结合,造成细胞渗透压改变,上皮细胞膜穿孔,进而导致昆虫死亡,故能有效防治鳞翅目、双翅目、鞘翅目等虫害[1-4]。水稻是重要的粮食作物[5-6],早在20世纪80年代,国内外就开展了转Bt基因水稻的培育[7-14]、安全性评价和营养价值差异等工作[15-17]。研究发现,连续90 d饲喂转Cry1C基因水稻[17]、转Cry1Ab基因水稻[18]或转CryAb/CryAc基因水稻[19]对大鼠采食量、体增重和料重比(F/G)等指标无显著影响。但也有试验表明,连续90 d饲喂转Cry1Ab基因糙米显著增加雄鼠的睾丸指数[20]。连续42 d喂转Cry1Ab基因糙米“Bt110”显著提高肉鸡采食量、日增重和F/G[21-22],其原因可能是2种饲粮组成不同,而非引入的外源基因。此外,研究人员还评价了转Bt基因水稻对动物血液生理生化、外源基因残留和肠道微生物等方面的影响[23-28]。上述研究工作主要针对转Bt基因水稻的亚急性安全评价,评价周期一般在90 d以内,不能完全反映转Bt基因水稻的长期影响。
华中农业大学自行培育出“华恢1号”和“Bt汕优63”2种转Bt基因水稻,经过系统的安全评价研究,于2009年获得农业部颁发的转基因生物安全证书。由于水稻是人类的主粮之一,人们还是担心长期食用转基因水稻是否会产生未知的不利影响。因此,本试验连续2个世代饲喂转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米,观察转Bt基因水稻对鹌鹑生长发育的长期影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验动物与试验设计
亲代鹌鹑:选择健康、体重相近的1日龄日本鹌鹑402羽,随机分成2个组,每组3个重复,每个重复67羽,雌雄混养。分别饲喂含有转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因和非转基因亲本糙米的饲粮,自由采食和饮水。13日龄称重,更换喂料器,记录采食量,35日龄称重,从各组中挑选健康的、体重相近的鹌鹑72羽,平均分成6个重复,每个重复3羽雄性、9羽雌性。采用3层阶梯式笼养,35日龄更换产蛋料,自由饮水和采食,每天光照16 h,试验至91日龄结束。
子代鹌鹑:选取不同组亲代鹌鹑85~91日龄所产的蛋分别孵化,孵化出的子代鹌鹑分别继续饲喂含有转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因和非转基因亲本糙米,分组及饲养管理与亲代相同。
1.2 试验饲粮
糙米和豆粕为主要原料,参照NRC(1994)推荐的鹌鹑营养需要配制试验饲粮(表1)。转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因水稻及其传统亲本水稻(表2)由华中农业大学提供。试验前分别对2种水稻及豆粕进行Cry1Ab/1Ac基因特异性片段扩增,结果表明,仅转基因水稻含有375 bp的阳性目标片段。
1.3 测定指标及方法
1.3.1 糙米及饲料营养成分
参照张丽英[29]的方法测定糙米及饲料中粗蛋白质、水分、粗脂肪、粗纤维、粗灰分含量等。
1.3.2 生长性能和器官指数
因雏鹑体型小,12日龄前需将饲料均匀撒在垫纸上饲喂,饲料消耗量无法准确记录,从13日龄开始使用小型自动喂料器,以重复为单位准确记录13~35日龄的给料量和剩料量。计算平均日增重(ADG)、平均日采食量(ADFI)和F/G。36日龄开始以重复为单位记录每周耗料量。91日龄禁食24 h后,每重复挑选雄性和雌性鹌鹑各2只,颈部放血处死后记录各器官重量,计算器官指数。
1.4 数据处理与统计分析
试验数据采用SAS 9.1.3软件进行t检验分析,P<0.05为差异显著,各组试验数据以“平均值±标准误”表示。

表1 试验饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础)Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of experimental diets(air⁃dry basis) %

续表1
2 结果与分析
2.1 转基因糙米与传统亲代糙米营养成分比较
从表2可以看出,转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因与非转基因糙米的粗蛋白质、粗脂肪、粗纤维等常规营养成分的含量无显著差异(P>0.05)。从表1可以看出,含有转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因和非转基因糙米的2种饲粮粗蛋白质、粗脂肪、粗纤维等常规营养成分的含量也无显著差异(P>0.05)。

表2 转基因和非转基因糙米的营养水平(风干基础)Table 2 Nutrient levels of genetically modified and non⁃genetically modified rice(air⁃dry basis) %
2.2 转基因糙米对亲代鹌鹑生长性能的影响
由表3可以看出,2个组亲代鹌鹑13~35日龄及36~91日龄的ADFI、ADG和F/G没有显著差异(P>0.05),91日龄时,2个组雌性和雄性鹌鹑的平均体重没有显著差异(P>0.05)。可见转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对亲代鹌鹑生长性能没有显著影响。

表3 转基因糙米对亲代鹌鹑生长性能的影响Table 3 Effects of genetically modified rice on growth performance of quails in parental generation
2.3 转基因糙米对亲代鹌鹑器官指数的影响
由表4可以看出,饲喂91日龄转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对亲代雄性和雌性鹌鹑心脏、肝脏、肌胃、腺胃以及睾丸或卵巢等器官指数无显著影响(P>0.05)。
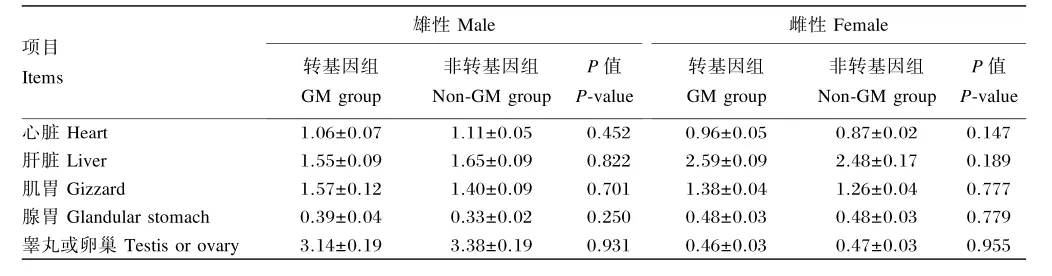
表4 转基因糙米对91日龄亲代鹌鹑器官指数的影响Table 4 Effects of genetically modified rice on organ indexes of quails in parental generation at age of 91 days %
2.4 转基因糙米对子代鹌鹑生长性能的影响
由表5可以看出,2个组子代鹌鹑13~35日龄及36~91日龄的ADFI、ADG和F/G没有显著差异(P>0.05),91日龄时,2组雌性和雄性鹌鹑的平均体重没有显著差异(P>0.05)。可见连续饲喂2世代转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对鹌鹑的生长性能没有显著影响。
2.5 转基因糙米对子代鹌鹑器官指数的影响
由表6可以看出,连续饲喂2个世代转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米对子代雄性和雌性鹌鹑心脏、肝脏、肌胃、腺胃以及睾丸或卵巢等器官指数无显著影响(P>0.05)。
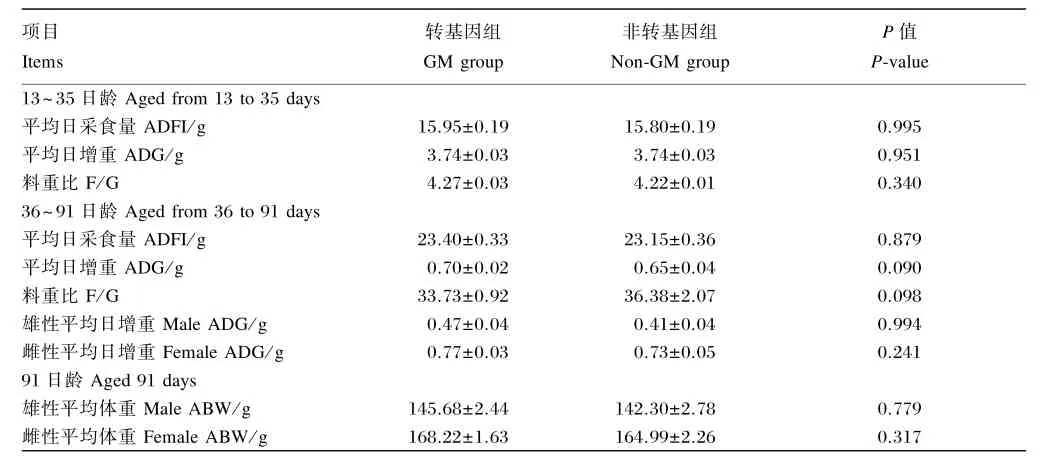
表5 转基因糙米对子代鹌鹑生长性能的影响Table 5 Effects of genetically modified rice on growth performance of quails in filial generation

表6 转基因糙米对91日龄子代鹌鹑器官指数的影响Table 6 Effects of genetically modified rice on organ indexes of quails in filial generation at age of 91 days %
3 讨 论
水稻是人类的主要粮食作物,也是重要的饲料原料。转Bt基因水稻经过人工导入外源基因能够稳定表达杀虫蛋白,有效抗病虫害,提高水稻产量,人们担心外源Bt基因导入引起水稻营养成分等变化。本研究表明,转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因水稻与其非转基因亲本水稻之间在营养成分含量上无显著差异。Cao等[15]对比了转Cry1Ab基因糙米T1c⁃19与其非转基因亲本糙米“明恢63”的各项营养成分含量,也未见显著差异。Wang等[16]发现转Cry1Ab基因的水稻“克螟稻I”与其非转基因亲本水稻“秀水11”粗蛋白质、脂肪和氨基酸含量没有显著差异。但王军[21]的研究结果显示,转基因水稻“Bt110”与非转基因亲本水稻“秀水110”之间粗蛋白质和氨基酸含量存在显著差异。Schrøder等[20]同样对比了“克螟稻I”和“秀水11”(与Wang等[16]所用材料相同,仅种植时间和地点不同),发现2种水稻粗蛋白质、氨基酸和矿物质含量存在微小但显著的差异,作者认为2种水稻营养成分的差异可能是由于水稻种植时间和地点不同造成的正常的生物学变异,而非外源基因导入造成。
转Bt基因作物所表达的杀虫蛋白具有高度的特异性[1-4],由于哺乳动物和禽类肠道内为酸性环境且不存在特异性的受体[30],因此理论上对人类以及动物安全,但人们担心由于外源Bt基因的导入产生未知的不利影响。王忠华等[18]用转Cry1Ab基因水稻“克螟稻2号”饲喂SD大鼠90 d,发现其对大鼠采食量、日增重和F/G等无显著影响。Wang等[26]用转基因水稻TT51饲喂大鼠90 d的结果也表明转基因水稻不影响大鼠的生长发育,大量试验也表明转Bt基因水稻不影响小鼠等动物生长发育[25,30-31]。但杜红方[22]发现饲喂转Cry1Ab基因糙米“Bt110”42 d显著提高肉仔鸡耗料量、体增重,王军[21]的研究结果也与之类似,认为可能是由于2种饲粮组成不同,而非外源基因引入导致肉鸡生长性能的提高。上述研究主要针对转Bt基因水稻的亚急性安全评价,评价周期一般在90 d以内,不能完全反映转Bt基因水稻的长期影响。本试验连续2个世代饲喂转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米,发现对鹌鹑体增重、F/G、器官指数等指标均未产生显著影响。Flachowsky等[32]用转Bt基因玉米Bt176连续饲喂鹌鹑10个世代,每世代持续12周,也未发现长期饲喂转Bt基因玉米对鹌鹑生长发育产生任何不利影响。Wang等[26]的2世代饲养试验结果显示,转Cry⁃Ab/CryAc基因糙米TT51对大鼠的生长发育也没有显著影响。
4 结 论
转Cry1Ab/1Ac基因糙米中的粗蛋白质、粗脂肪、粗纤维、粗灰分、干物质等营养成分的含量与传统亲本糙米相比无显著差异。连续饲喂2个世代对鹌鹑的生长速度及器官指数无显著影响。
参考文献:
[1] SANAHUJA G,BANAKAR R,TWYMAN R M,et al.Bacillus thuringiensis:a century of research,devel⁃opment and commercial applications[J].Plant Bio⁃technology Journal,2011,9(3):283-300.
[2] SHAO Z Z,CUI Y L,LIU X L,et al.Processing of δ⁃endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.kurstaki HD⁃1 in Heliothis armigera Midgut juice and the effects of protease inhibitors[J].Journal of Invertebrate Patholo⁃gy,1998,72(1):73-81.
[3] KNIGHT P J K,CRICKMORE N,ELLAR D J.The receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(c)delta⁃en⁃dotoxin in the brush border membrane of the lepidop⁃teran Manduca sexta is aminopeptidase N[J].Molecu⁃lar Microbiology,1994,11(3):429-436.
[4] BETZ F S,HAMMOND B G,FUCHS R L.Safety and advantages of Bacillus thuringiensis⁃protected plants to control insect pests[J].Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology,2000,32(2):156-173.
[5] VAN NGUYEN N,FERRERO A.Meeting the chal⁃lenges of global rice production[J].Paddy and Water Environment,2006,4(1):1-9.
[6] RAO Y C,DONG G J,ZENG D L,et al.Genetic anal⁃ysis of leaffolder resistance in rice[J].Journal of Ge⁃netics and Genomics,2010,37(5):325-331.
[7] TORIYAMA K,ARIMOTO Y,UCHIMIYA H,et a1.Transgenic rice plants after direct gene transfer into protoplasts[J].Nature Biotechnology,1988,6(9):1072-1074.
[8] ZHANG W,WU R.Efficient regeneration of transgen⁃ic plants from rice protoplasts and correctly regulated expression of the foreign gene in the plants[J].Theo⁃retical and Applied Genetics,1988,76(6):835-840.
[9] 谢道昕,范云六,倪王冲.苏云金芽孢杆菌杀虫基因导入中国栽培水稻品种中花11号获得转基因植株[J].中国科学,1991(8):830-834.
[10] FUJIMOTO H,ITOH K,YAMAMMOTO M,et al.In⁃sect resistant rice generated by introduction of a modi⁃fied δ⁃endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis[J].Nature Biotechnology,1993,11(10):1151-1155.
[11] WÜNN J,KLÖTI A,BURKHARDT P K,et al.Trans⁃genic indica rice breeding line IR58 expressing a syn⁃thethic cry1A(b)gene from Bacillus thuringiensis provide effective insect pest control[J].Biotechnolo⁃gy,1996,14(2):171-176.
[12] WU C,FAN Y,ZHANG C,et al.Transgenic fertile ja⁃ponica rice plants expressing a modified cry1A(b)gene resistant to yellow stem borer[J].Plant Cell Re⁃ports,1997,17(2):129-132.
[13] 舒庆尧,叶恭银.转基因水稻“克螟稻”选育[J].浙江农业大学学报,1998,24(6):579-580.
[14] 张志罡,李勇,朱兆洲.Cry1Ab杀虫蛋白在转Bt水稻中的表达及在害虫体内的积累动态[J].中国植保科学,2010,30(7):10-13.
[15] CAO S S,HE X Y,XU W T,et al.Safety assessment of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis rice T1c⁃19 in sprague⁃dawly rats from metabonomics and bacterial profile perspectives[J].IUBMB Life,2012,64(3):242-250.
[16] WANG Z H,WANG Y,CUI H R,et al.Toxicological evaluation of transgenic rice flour with a synthetic cry1Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2002,82(7):738-744.
[17] TANG X M,HAN F T,ZHAO K,et al.A 90⁃day diet⁃ary toxicity study of genetically modified rice T1C⁃1 expressing Cry1C protein in sprague dawley rats[J].PLoS One,2012,7(12):e52507.
[18] 王忠华,王茵,崔海瑞,等.Bt水稻“克螟稻”稻米毒理性评价研究初报[J].中国农业科学,2002,5 (12):1487-1492.
[19] WANG E H,YU Z,HU J,et al.Effects of 90⁃day feeding of transgenic Bt rice TT51 on the reproductive system in male rats[J].Food and Chemical Toxicolo⁃gy,2013,62:390-396.
[20] SCHRØDER M,POULSEN M,WILCKS A,et al.A 90⁃day safety study of genetically modified rice ex⁃pressing Cry1Ab protein(Bacillus thuringiensis tox⁃in)in Wistar rats[J].Food and Chemical Toxicolo⁃gy,2007,45(3):339-349.
[21] 王军.转基因糙米在肉仔鸡日粮中的安全性初探[D].硕士学位论文.杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2006.
[22] 杜红方.转基因水稻作为肉仔鸡饲粮原料的安全性评价[D].博士学位论文.北京:中国农业科学院,2006.
[23] 熊燕飞,覃铜城,陈超,等.转Bt基因水稻对雄性小白鼠体内酶活性的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2011,50(24):5200-5205.
[24] 曹正辉,王占彬,顾宪红.转Bt基因糙米中外源蛋白质和外源基因在生长猪体内的残留及对组织器官的损伤[J].动物营养学报,2014,26(7):1908-1915.
[25] 张珍誉,刘立军,张琳,等.转Bt基因稻谷对小鼠的亚慢性毒性实验[J].毒理学杂志,2010,24(2):126-129.
[26] WANG E H,YU Z,HU J,et al.A two⁃generation re⁃production study with transgenic Bt rice TT51 in Wist⁃ar rats[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,65:312-320.
[27] YUAN Y F,XU W T,LUO Y B,et al.Effects of ge⁃netically modified T2A⁃1 rice on faecal microflora of rats during 90 day supplementation[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2011,91(11):2066-2072.
[28] YUAN Y,XU W,HE X,et al.Effects of genetically modified T2A⁃1 rice on the GI health of rats after 90⁃day supplement[J].Scientific Reports,2013,3:1962.
[29] 张丽英.饲料分析及饲料质量检测技术[M].北京:中国农业大学出版社,2003:45-75.
[30] MCCLINTOCK J T,SCHAFFER C R,SJOBLAD R D.A comparative review of the mammalian toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis⁃based pesticides[J].Pesticide Science,1995,45(2):95-105.
[31] JIANG L X,YANG L T,ZHANG H B,et al.Interna⁃tional collaborative study of the endogenous reference gene,Sucrose Phosphate Synthase(SPS),used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of genetically modified rice[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(9):3525-3532.
[32] FLACHOWSKY G,HALLE I,AULRICH K.Long term feeding of Bt⁃corn⁃a ten⁃generation study with quails[J].Archives of Animal Nutrition,2005,59 (6):449-451.
Effects of Feeding Transgenic Rice Containing Cry1Ab/1Ac Gene on Growth and Development in Two Generations of Quails
LI Zeyang
1,2
FENG Jinghai
2∗
ZHOU Ming
1∗∗
ZHANG Minhong
2
CHANG Yu
2
(责任编辑 陈 燕)
(1.College of Animal Science and Technology,Anhui Agricultural University,Hefei 230036,China;2.State Key Laboratory of Animal Nutrition,Institute of Animal Science,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100193,China)
∗Contributed equally
∗∗Corresponding author,professor,E⁃mail:aauzhouming@163.com
Abstract:A two⁃generation feeding trial was conducted to study the effects of transgenic rice containing Cry1Ab/1Ac gene on growth and development in Japanese quails(Coturnix japonica).Four hundred and two 1⁃day⁃old Japanese quails were randomly divided into 2 groups with 3 replicates per group and 67 quails per replicate.The 2 groups were genetically modified and non⁃genetically modified(non⁃GM)groups,and quails in these 2 groups were fed diets with genetically modified rice containing Cry1Ab/1Ac gene and non⁃genetically modified(non⁃GM)rice,respectively.At age of 35 d,seventy⁃two healthy quails with similar body weight from each group were selected and randomly divided into 2 groups with 6 replicates per group,each replicate contained 9 female quails and 3 male quails,and quails in different groups were continued to feed with the 2 di⁃ets.The duration of each generation was 91 d and the eggs of first generation in the period at 85 to 91 d of age were hatched for the next generation.The experimental design and management of the second generation was the same as the first generation.The results showed that there was no significant difference in nutrient compo⁃nent contents in the genetically modified rice compared with the non⁃GM rice(P>0.05).The results of aver⁃age daily gain(ADG),average daily feed intake(ADFI)and the ratio of feed to gain(F/G)of quails in each generation showed no significant difference in each generation between different groups(P>0.05).Com⁃paring with the non⁃GM group,the indexes of liver,heart,testis and ovary of quails in each generation be⁃tween the 2 groups were not significantly different.The results suggest that consuming genetically modified rice containing Cry1Ab/1Ac gene for consecutive two generations has no significant effect on growth and develop⁃ment in quails.[Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2015,27(7):2168⁃2175]
Key words:genetically modified;rice;Cry1Ab/1Ac;quails;growth and development
作者简介:李泽阳(1990—),男,安徽芜湖人,硕士研究生,研究方向为动物营养生态。E⁃mail:xmyglzy@126.com∗同等贡献作者
基金项目:国家科技重大专项子课题(2012ZX08011001⁃005);中国农业科学院科技创新工程(ASTIP-IAS07)
收稿日期:2015-02-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006⁃267x.2015.07.022
文章编号:1006⁃267X(2015)07⁃2168⁃08
文献标识码:A
中图分类号:S816.41;S839

