家兔结肠袋状收缩研究进展
杨自仙,陈继红,谭诗云,罗和生,Jan D Huizinga
1.武汉大学人民医院消化内科,湖北 武汉430060;2.麦克马斯特大学健康科学学院医学系,加拿大 安大略省 汉密尔顿L8S4L8
家兔结肠因具有类似人结肠袋的结构而备受结肠动力研究者关注。结肠袋状收缩较复杂,至今机制不明。
1 家兔结肠袋解剖及组织学特征
家兔结肠分为四个不同区域[1],前三个区域组成近端结肠,第四个区域为远端结肠。第一个区域长约10 cm,有结肠外层纵行肌聚成三条纵行的结肠带,结肠带之间的肠壁呈许多囊状膨出,形成特征性结肠袋。第二个区域长约20 cm,只有一条结肠带,也只有结肠的一侧有结肠袋。第三个区域是肠纽,长约4 cm,分隔近端结肠与远端结肠[2]。这是一段较厚的结肠,整个结肠圆周上聚集着大量的神经节细胞。许多生理学家和药理学家都认为家兔的纵形肌尤其是肠纽在许多方面是一种独特的腑脏肌,其与肠道的其他肌肉大不相同,如家兔的回肠。第四个区域则为远端结肠,长80 ~100 cm,大多数肠内容物混合及水和电解质吸收都发生在近端结肠,而推进粪便排泄的力量主要集中在远端结肠[4]。
家兔的结肠袋类似于人衣服上外翻的口袋,沿着结肠的长径排列,向外凸出3.0 ~3.5 mm[3](见图1)。从管腔的结构来看,结肠袋是较深的空腔,它被结肠带之间折叠的横肌阻断。结肠袋的横断面平坦且向外袋状突出的深浅度不一致,厚度与环形肌的厚度相近。在静息状态下,结肠被约100 μm 厚度的主结肠带固定,结肠带的横截面图显示肌细胞呈不规律的波浪状排列[3]。Bayliss 等[5]指出,结肠袋的每一次膨胀都是由收缩环沿着结肠逐渐移动产生的,其中可能同时出现一些推进性蠕动波,推动粪球向前移动,可以促进肠内容物前进达10 ~12 cm。如果因为各种原因导致粪球的前进受阻,结肠就会加强蠕动以推动粪球前进,这种状态也不会因为前面所产生的蠕动波的到来而停止。给予结肠的某部位一个能够产生兴奋性收缩的局部刺激,可以使收缩的初速度为1 cm,之后传播2 ~3 cm,最后像蠕动波一样慢慢减弱,但是这种下行传递很难证明。Dinning 等[6]在结肠袋上标记,标记的位置并没有随移动改变,认为这些可能是参与连接结构的固定点,但是Lentle 等[7]研究称这些标记随运动推进。可能是两人所作标记的位置不同导致结果不同。
2 结肠袋状收缩特征
1972 年,McKirdy[8]首次提到,兔子的远端结肠存在有节奏地自发性收缩。通过记录纵形肌和环形肌机械活动,证实远端结肠存在巨大收缩(giant contractions,GCs)和部分性收缩(phasic contractions)。
Ehrlein 等[1]认为在近端结肠有袋状收缩(haustral activity)、节段性运动(segmental activity)和集团蠕动(mass peristalsis)3 种截然不同的运动模式参与粪便形成。结肠袋环形肌收缩形成袋状收缩,能产生逆向蠕动波,结肠袋内推进性收缩形成袋内收缩,但环形肌收缩的本质尚未阐明[4,7,9]。节段性运动就是分隔肠道消化物形成粪球,并迫使其缓慢地向远端移动。结肠袋运动则是滚动运动(rolling movement)(见图2),产生逆向蠕动波。集团蠕动转运消化道产物[4]。
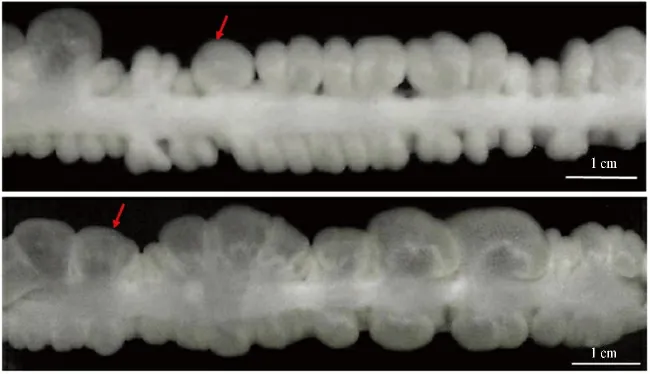
图1 家兔近端结肠袋状收缩外面观Fig 1 The picture of haustral contraction of rabbit proximal colon

图2 家兔近端结肠时空图 A:基础状态下近端结肠袋状收缩和推进性收缩时空图;B:给予TTX(0.2 μmol/L)干预后近端结肠收缩时空图。环形肌收缩产生微小波沿结肠前后传播相当长一段距离,形成“滚动运动”。TTX(0.2 μmol/L)阻断推进性收缩,对结肠袋收缩没有作用Fig 2 Spatiotemporal maps of rabbit proximal colon A:the spatiotemporal map of the control haustral contractions and propagating contractions in the proximal colon in basal conditions;B:the spatiotemporal map after adding TTX (0.2 μmol/L).Ripples induced by the contractions of circular muscle would move a long distance,which were called rolling movement. TTX (0.2 μmol/L)can inhibit propagating contractions,but it had no effect on the contraction of haustral
具有完整环形平滑肌的动物或人类,其远端结肠推进消化道产物有3 种不同的运动模式[10]:节律性相位性收缩(rhythmic phasic contractions)、巨大迁移性收缩(giant migrating contractions,GMCs)和强直收缩(tonic contractions)。GMCs 是高振幅、低频率、推动长距离收缩的方式[11]。节段性收缩的特点是高频率、低振幅和相对较高的基调。相位性收缩的振幅和频率在近端结肠和远端结肠没有差别。
Benabdallah 等[12]认为体外实验中家兔近、中、远端结肠的自发性机械活动存在两种类型的收缩:低振幅、高频率的位相性收缩(phasic contractions)和高振幅、低频率的GCs,且这两种收缩模式在结肠的各个部位不存在差异。GMCs 和GCs 之间的基本区别是前者为神经源性的而后者为肌原性起源。与GCs 相比,GMCs 更容易受到六甲铵和毒蕈碱阿托品的影响[9-12]。
2008 年,基于时空图所记录的径向和纵向运动,Lentle 等[7]提出家兔的近端结肠展示了4 种不同类型的收缩活动,即集团蠕动(mass peristalsis)、快速位相性收缩(fast phasic contraction)、袋状推进性运动(haustral progression)和微小波(ripples),且前两种运动模式跨越整段近端结肠,而袋状运动和微小波仅局限在环形收缩的某一点。这与上述报道发现只有两个或三个类型的收缩活动形成了鲜明的对比。
3 家兔结肠袋状收缩肌源性和神经源性支配
家兔的结肠运动模式受肌源性和神经源性交互支配,但是人们至今尚不清楚结肠各个区域的运动机制[3]。交感神经是结肠运动功能的重要调节器[13]。交感神经兴奋对肠道产生的抑制作用主要通过抑制神经节功能或是直接作用于肠道平滑肌[14]。在肠腔内任何一处施加压力都能通过交感神经抑制肠壁的紧张活动[15]。而副交感神经兴奋能刺激结肠的收缩活动[16],近端和远端的类胆碱能神经是等价的,远端结肠兴奋性主要被类胆碱能神经系统激活,抑制性神经节细胞兴奋远端结肠,需要更深入地研究来明确其抑制作用[17]。人在行迷走神经切断术后能防止增加餐后结肠的能动性[18],而破坏骨盆神经后则能够抑制结肠的能动性[19]。六甲铵(100 μmol/L)和河豚毒素(TTX 0.6 μmol/L)可以抑制神经活动。而肌源性的微小波不会被河豚毒素阻断[6]。研究证明大鼠肌源性的长距离样收缩运动(like long distance contractions,LDCs-like)在TTX 作用下仍然存在(见图3)[20]。肌源性收缩活动存在于环形肌的收缩活动中,且这种收缩活动贯穿于整个结肠,具有顺向性和逆向性双向性运动。近端结肠神经源性肌活动存在于缓慢地推进性复合运动中,而这种多重环形肌收缩产生的顺向性传播的结肠移动性复合波通常开始在结肠带的过渡区域。在只有一条结肠带的近端结肠区域,六甲铵能阻断神经起源的自发性机械运动[6]。
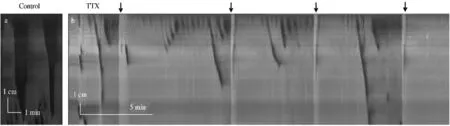
图3 TTX 对大鼠结肠LDCs-like 的影响 A:基础状态LDC,加TTX 前时空图;B:加TTX 后时空图。TTX 可以阻断LDC,同时诱导LDCs-like 产生Fig 3 Effect of TTX on LDCs-like of rat colon A:control LDC,the spatiotemporal map befor adding TTX;B:the spatiotemporal map after adding TTX (0.2 μmol/L),TTX can abolish LDC and induce rhythmic LDCs-like
4 与人类结肠的相似之处及对人结肠动力研究的意义
家兔的结肠与人类十分相近,它拥有与人类结肠相似的结肠外层纵肌聚成3 条纵行的结肠带及结肠带之间的肠壁上呈囊状膨出的特征性结构—结肠袋。组织学上,尽管家兔的降结肠与人类不同,其有一个完整的纵肌层,但是家兔的这一具有结肠带的近端结肠与人类相似[17]。电活动记录人类和家兔的ICC 起搏细胞结肠肌肉组织反应特性和肌肉组织具有类似的特性[21]。基于Rao 等[22-24]的工作,美国神经胃肠病与动力学会(NGM)总结了人结肠的7 种运动模式:孤立的压力波、推进性压力波、高幅推进性收缩(high amplitude propagated contractions or pressure sequences,HAPCs)、自发性压力波、逆向压力波、周期性压力波(3 次/min)、周期性直肠运动活性(3 次/min)。人们也曾用过类似肛门测压的装置生动地记录了家兔近端结肠的某些运动方式[1],且在人类的结肠也可以观察到[25]。人们认为这些动物的运动模式和健康受试者存在某种联系[26]。目前人结肠测压仍处于起步阶段,利用家兔与人类结肠的相似性,认识家兔的运动模式,阐明其运动机制对人结肠动力的研究具有指导性意义。
综上所述,我们了解了家兔的解剖结构及结肠袋在运动中的作用,探讨了不同家兔结肠袋状运动模式,阐述了神经支配对结肠运动的影响。动物结肠与人类结肠的相似性研究,展示了家兔结肠袋状运动研究的广阔前景,对人类消化道研究具有重大意义。但是,目前为止,我们对家兔结肠袋状运动研究仍存在诸多矛盾及分歧,未来需要我们更进一步的研究。
[1] Ehrlein HJ,Reich H,Schwinger M. Colonic motility and transit of digesta during hard and soft faeces formation in rabbits[J]. J Physiol,1983,338:75-86.
[2] Ruckebusch Y,Fioramonti J. The Fusus coli of the rabbit as a pacemaker area[J]. Experientia,1976,32(8):1023-1024.
[3] Gabella G. The taenia of the rabbit colon,an elastic visceral muscle[J].Anat Embryol (Berl),1983,167(1):39-51.
[4] Snipes RL,Clauss W,Weber A,et al. Structural and functional differences in various divisions of the rabbit colon [J]. Cell Tissue Res,1982,225(2):331-346.
[5] Bayliss WM,Starling EH. The movements and the innervation of the large intestine[J]. J Physiol,1900,26(1-2):107-118.
[6] Dinning PG,Costa M,Brookes SJ,et al. Neurogenic and myogenic motor patterns of rabbit proximal,mid,and distal colon[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2012,303(1):G83-G92.
[7] Lentle RG,Janssen PW,Asvarujanon P,et al. High-definition spatiotemporal mapping of contractile activity in the isolated proximal colon of the rabbit[J]. J Comp Physiol B,2008,178(3):257-268.
[8] McKirdy HC. Functional relationship of longitudinal and circular layers of the muscularis externa of the rabbit large intestine[J]. J Physiol,1972,227(3):839-853.
[9] Costa M,Dodds KN,Wiklendt L,et al. Neurogenic and myogenic motor activity in the colon of the guinea pig,mouse,rabbit,and rat[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2013, 305 (10 ):G749-G759.
[10] Sarna SK. Molecular,functional and pharmacological targets for the development of gut promotility drugs[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2006,291(4):G545-G555.
[11] Gonzalez A,Sarna SK. Neural regulation of in vitro giant contractions in the rat colon[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2001,281(1):G275-G282.
[12] Benabdallah H,Messaoudi D,Gharzouli K. The spontaneous mechanical activity of the circular smooth muscle of the rabbit colon in vitro[J]. Pharmacol Res,2008,57(2):132-141.
[13] Garry RC,Gillespie JS. The responses of the musculature of the colon of the rabbit to stimulation,in vitro,of the parasympathetic and of the sympathetic outflows[J]. J Physiol,1955,128(3):557-576.
[14] Wienbeck M,Christensen J. Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat[J]. Gastroenterology,1971,61(4):470-478.
[15] Kreulen DL,Szurszewski JH. Reflex pathways in the abdominal prevertebral ganglia:evidence for a colo-colonic inhibitory reflex[J]. J Physiol,1979,295:21-32.
[16] Roman C,Gonella J. Extrinsic control of digestive tract motility[J].Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract,1981,chapt 9:289-333.
[17] Snape WJ Jr,Shiff S. Neurohumoral control of colonic motility in the rabbit[J]. Am J Physiol,1983,245(4):G582-G588.
[18] Connell AM,McKelvey ST. The influence of vagotomy on the colon[J].Proc R Soc Med,1970,63 Suppl:7-9.
[19] Devroede G,Arhan P,Duguay C,et al. Traumatic constipation[J].Gastroenterology,1979,77(6):1258-1267.
[20] Chen JH,Zhang Q,Yu Y,et al. Neurogenic and myogenic properties of pan-colonic motor patterns and their spatiotemporal organization in rats[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(4):e60474.
[21] Huizinga JD,Stern HS,Chow E,et al. Electrophysiologic control of motility in the human colon[J]. Gastroenterology,1985,88(2):500-511.
[22] Rao SS,Sadeghi P,Beaty J,et al. Ambulatory 24-hour colonic manometry in slow-transit constipation[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2004,99(12):2405-2416.
[23] Hervé S,Savoye G,Behbahani A,et al.Resultsof 24-h manometric recording of colonic motor activity with endoluminal instillation of bisacodyl in patients with severe chronic slow transit constipation[J].Neurogastroenterol Motil,2004,16(4):397-402.
[24] Rao SS,Sadeghi P,Batterson K,et al. Altered periodic rectal motor activity:a mechanism for slow transit constipation[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil,2001,13(6):591-598.
[25] Rao SS. Biofeedback therapy for constipation in adults[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2011,25(1):159-166.
[26] Cook IJ,Furukawa Y,Panagopoulos V,et al. Relationships between spatial patterns of colonic pressure and individual movements of content[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2000,278(2):G329-G341.

