温州市成人原发性肾小球疾病病理类型构成比20年演变
叶腾,吕吟秋,陈波,李凡凡,陈孝倩,黄朝兴
(温州医科大学附属第一医院 肾内科,浙江 温州 325015)
·论 著·
温州市成人原发性肾小球疾病病理类型构成比20年演变
叶腾,吕吟秋,陈波,李凡凡,陈孝倩,黄朝兴
(温州医科大学附属第一医院 肾内科,浙江 温州 325015)
目的:探讨温州市成人原发性肾小球疾病(PGD),包括原发性肾病综合征(PNS)病理类型分布的流行病学特征。方法:回顾性分析我院肾内科病理室2000-2013年14年间经肾活检诊断的成人(≥18岁)PGD患者3 392例(资料完整)的流行病学特点,并与1993-1999年我院肾活检诊断的553例PGD作比较。结果:①2000-2013年间肾活检诊断PGD共3 392例,中位年龄为37(29,48)岁,男女比例为1∶1。PGD以IgA肾病(IgAN)最多,占59.5%,其次分别为膜性肾病(MN)和微小病变型肾小球疾病(MCD),分别占16.5%和12.4%。IgAN在青年组、中年组分别占47.6%和41.2%;老年前期组和老年组合计以MN最常见,占46.6%。②与1993-1999年肾活检病例比较,2000-2013年PGD中最显著的改变是MN的比率明显提高(从7.2%提高到16.5%)。1 067例PNS以MN最常见,占38.7%,其次分别为MCD(占38.3%)、IgAN(占13.0%)和局灶性节段性肾小球硬化症(FSGS)(占6.2%)。结论:近14年来PGD仍以IgAN居首,但MN的比率有明显上升趋势,后者已成为成人PNS最常见的病理类型。在前后两个时期肾活检指征基本未变的情况下,肾活检PGD构成比的演变可能与实际发病率的改变有关。
原发性肾小球疾病;病理类型;肾活检;流行病学
原发性肾小球疾病(primary glomerular diseases,PGD)在我国肾穿刺活检诊断肾脏疾病谱中占最大比率[1-4]。正确认识PGD各种病理类型分布的流行病学特点对于疾病防治具有重要的指导意义。本课题组曾于2000年报道1993-1999年间553例温州地区PGD病理类型分布及流行病学特点[5],随着时间的推移,温州市成人PGD疾病谱的构成是否发生了变化需要进一步研究探讨。因此,笔者回顾性分析温州市近20年成人PGD流行病学数据及其动态演变,以期在预防医学方面起指导作用。
1 资料和方法
1.1 一般资料 2000年1月-2013年12月在我院肾内科肾脏病理室制片并获得经肾活检诊断成人(≥18岁)PGD患者3 392例。其中已剔除继发性肾小球疾病(secondary glomerular diseases,SGD)和遗传性肾病(hereditary nephropathy,HERN)及因标本量不足而不能明确诊断者。 肾活检组织样本主要来自我院及温州市二级以上医院。临床病理资料基本完整。根据肾穿刺时的年龄分为青年组(18~34岁)1 433例,中年组(35~49岁)1 278例,老年前期组(50~64岁)480例,老年组(≥65岁)201例。
1.2 肾活检 B超定位,用国产Menghin穿刺针行经皮肾穿刺负压抽吸法获得肾组织。
1.3 病理检查 所有肾穿刺组织常规行光镜、免疫荧光检查,其中68.0%的病例还做了电镜检查。方法同本课题组以往的报道[5]。
1.4 病理诊断标准 主要参照WHO(1995年)肾小球疾病组织学分型修订方案和2001年在全国肾活检病理诊断研讨会上拟定的肾活检病理诊断标准指导意见[6]进行病理分型。需要指出的是,本研究将IgA肾病(IgA nephropathy,IgAN)归为PGD。免疫荧光检查以IgA弥漫系膜区颗粒状沉积为主,光镜表现为肾小球轻微病变,电镜检查见广泛足突融合,未见系膜区电子致密物,临床上表现为肾病综合征,诊断为微小病变型肾小球疾病(minimal change disease,MCD)伴IgA沉积,归为MCD。系膜增生性肾小球肾炎(mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis,MsPGN)指非IgA-系膜增生性肾小球肾炎。本研究把C1q肾病、纤维样肾小球病、脂蛋白肾病、C3肾小球病、 III型胶原肾小球病和纤维连接蛋白肾小球病均归入PGD的“其他类型”。
1.5 其他定义 肾病范围蛋白尿:指尿蛋白>3.0 g/24 h不伴血浆白蛋白<30 g/L。原发性肾病综合征(primary nephrotic syndrome,PNS):包括肾病范围蛋白尿,并排除继发性和遗传性疾病。
1.6 统计学处理方法 采用SPSS16.0软件进行统计分析。计量资料采用M(P25,P75)表示。计数资料的分析用x2检验。以双侧P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 成人PGD的人口学特征 2000-2013年间PGD 3 392例中男1 721例,占50.7%,女1 671例,占49.3%,男∶女=1∶1。PGD的中位年龄为37(29,48)岁,青年组在PGD所有年龄段中所占的比率最高,为42.2%。
2.2 成人PGD病理类型分布特点
2.2.1 成人PGD病理类型分布:病理类型分布按检出率高低排列依次为IgAN、膜性肾病(membranous nephropathy,MN)、MCD、局灶节段性肾小球硬化(focal segmental glomeruloselerosis,FSGS)、MsP-GN、局灶增生性肾炎(focal proliferative glomerulonephritis,FGN)、增生硬化性肾炎(proliferative sclerotic glomerulonephritis,PSGN)和硬化性肾炎(sclerotic glomerulonephritis,SGN)、新月体肾炎(crescentic glomerulonephritis,CreGN)、膜增生性肾小球肾炎(membrano-prolif-erative glomerulone-phritis,MPGN)、毛细血管内增生性肾炎(endocapillary proliferative glomerulo-nephritis,EnPGN),其他类型9例(占0.3%),包括C1q肾病3例,纤维样肾小球病2例,脂蛋白肾病、C3肾小球病、 III型胶原肾小球病及纤维连接蛋白肾小球病各1例。详见表1。与1993-1999年间553例PGD[5]比较,2000-2013年间MN的检出率明显升高,MsPGN所占比率明显减少,IgAN仍是最常见的病理类型,并继续呈上升趋势,其余病理类型均无明显变化,见表2。
2.2.2 成人PGD患者各种病理类型的年龄分布特征:IgAN患者的高发年龄段为青年组,随年龄增加其检出率依次降低;MCD的高发年龄段为青年组,在中年组降低,但是到老年前期和老年组又出现一个小高峰;MN患者随年龄增加其检出率依次升高,以老年前期+老年组(占46.6%)最多见;MCD、MN、IgAN在各年龄组之间分布差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),见表1。
2.3 成人PNS病理类型分布特点
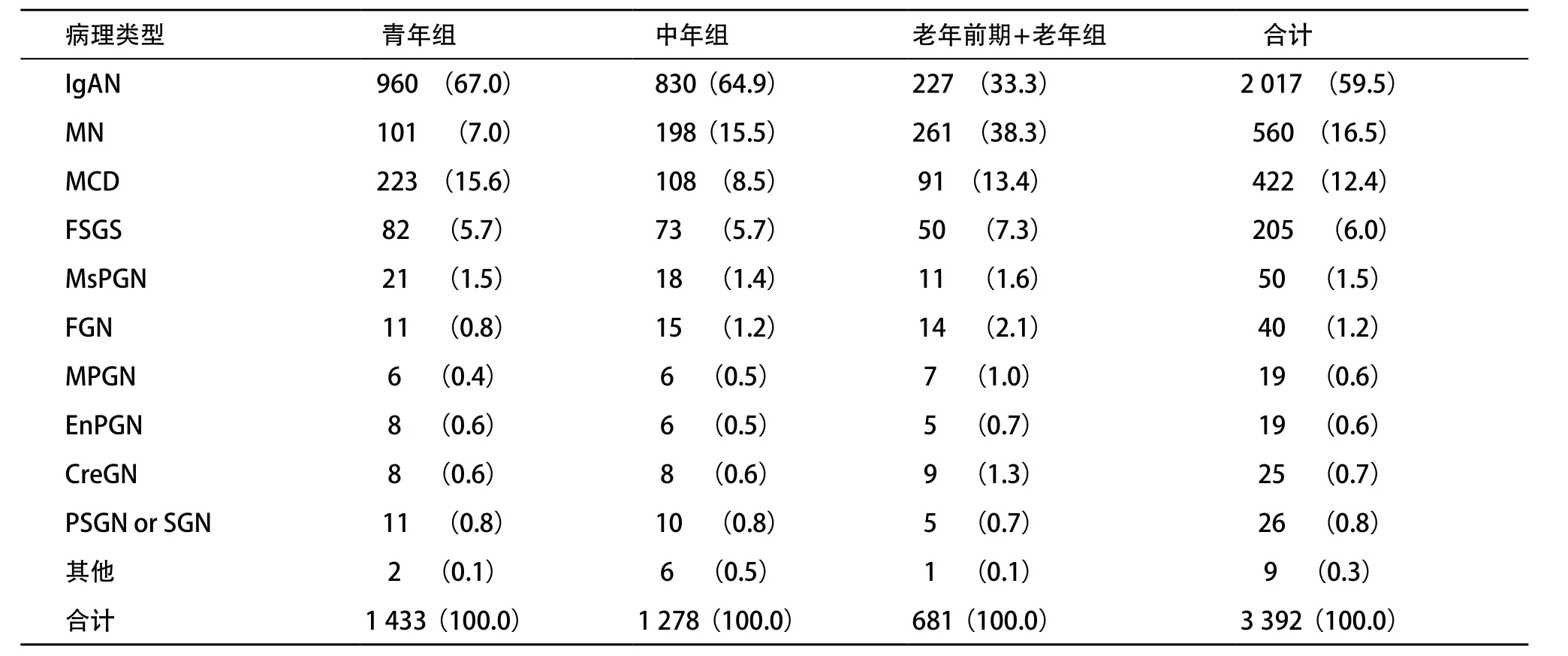
表1 2000-2013年成人PGD的病理类型以及年龄分布 n(%)
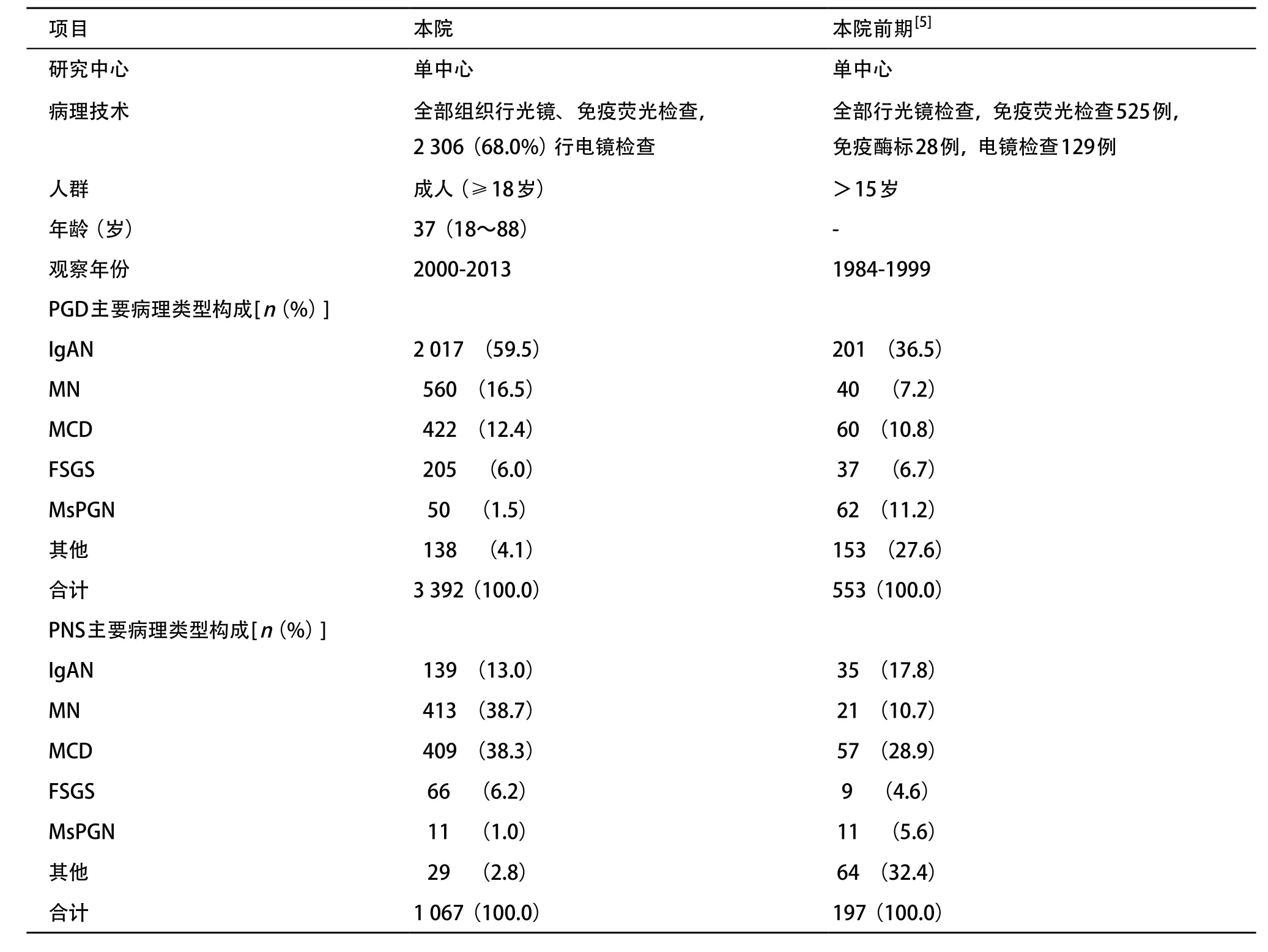
表2 本院2个时期成人PGD和PNS的病理类型比较
2.3.1 PNS病理类型分布及演变:2000-2013年成人PNS 1 067例,中位年龄为40(28,55)岁。病理类型分布按检出率高低排列依次为MN、MCD、IgAN、FSGS、MsPGN、FGN、MPGN、EnPGN和CreGN。其他类型包括C1q肾病、纤维样肾小球病、C3肾小球病、I I I型胶原肾小球病各1例。见表3。与1993-1999年比较,在2000-2013年时期PNS构成比中MN上升至第一位,而IgAN退居于第三位,见表2。
2.3.2 成人PNS不同年龄段病理类型的分布特征:青年组以MCD最常见,占54.1%,其次是MN和IgAN,分别占19.4%和16.4%;中年组以MN最常见,占41.2%,其次是MCD和IgAN,分别占20.9%和16.9%;老年前期+老年组也以MN最常见,占59.9%,其次是MCD和IgAN,分别占26.6%和4.9%,见表3。
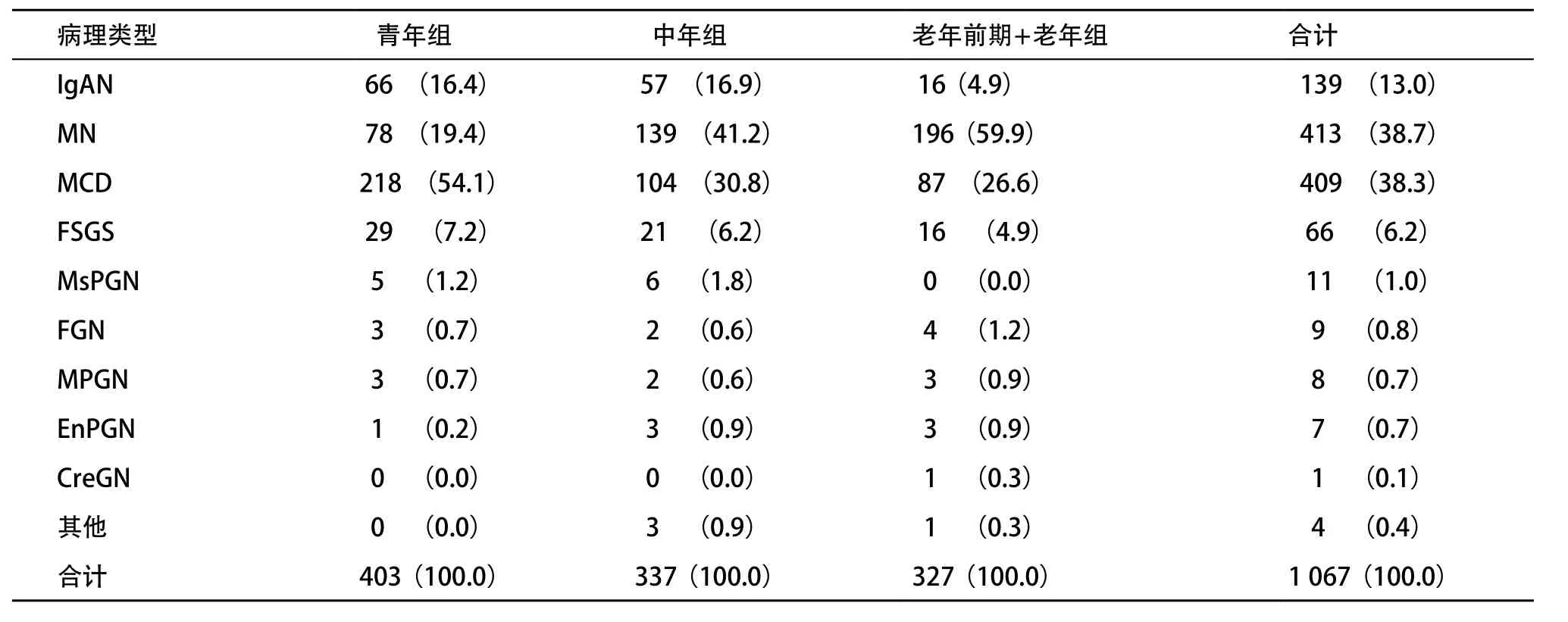
表3 2000-2013年成人PNS的病理类型以及年龄分布 n(%)
3 讨论
本研究显示,IgAN是温州地区最常见的PGD病理类型(占59.5%),对比2000年报道IgAN检出率为36.5%[5],2007年报道为49.8%[7],提示IgAN的检出率在逐渐上升,这个增长趋势在我国南方的刘志红等[2]和北方的王海燕等[9]研究中也可见到。本研究还显示,IgAN是青中年组PGD的最常见病理类型,提示IgAN是青中年人群PGD一级预防的最主要对象。
本研究最突出的发现是MN在PGD中的所占比率(占16.5%)明显提高。这与我院1993-1999年[5]所占的比率(占7.2%)比较,及与我院1999-2007年[7]全部电镜检查的PGD中MN所占比率(占12.1%)比较,呈明显的上升趋势。上海瑞金医院分析了1997-1999年和2009-2011年成人PGD肾活检病理类型,前3年MN仅占6.48%,而后3年MN则高达22.79%[8]。MN在PGD的所占比率逐年升高的现象在北大一院报道[9]中也可见到。本研究显示,在老年前期+老年组,MN是PGD最常见病理类型,其所占比率明显高于其他PGD病理类型,提示MN已成为老年PGD的最主要防治对象。
本研究还显示,MN在成人PNS中的比率已超过MCD,跃居PNS的首位,高达38.7%,这高于北大一院(占29.5%)的报道[9]。MN在成人PNS中的比率较高,在意大利(占44.1%)[10]、日本(占33.8%)[11]、韩国[4](占25.7%)和西班牙[12](占22.9%)也有相似报道。我们认为,造成MN检出率上升的可能原因为:①本资料3 392例PGD中有电镜检查2 306例(占68.0%),电镜检查技术的应用可提高早期MN的检出率;②本组PNS患者平均中位年龄为40(28,55)岁,由于MN发病高峰年龄在40岁以上,故本组患者年龄偏大可能是其影响因素之一;③本组MN在青年组PGD中和青年组PNS中分别占第3位和第2位,以及上述MN在PGD的所占比率升高的现象,可能与MN的实际发病率增加有关。
本研究显示MsPGN的检出率明显降低,这与近年国内[2,9]资料显示MsPGN比率呈明显下降的趋势一致。此外,近14年来FSGS的检出率变化不大,分别占PGD和PNS的6.0%和6.2%,这也与国内多数大中心研究[2,8-9]的结果相似。
研究资料表明,肾脏病的病理类型构成与地区、种族、性别、社会经济环境有一定的关系[13-15],仅依赖肾活检资料判断其流行病学特点存在一定的局限性,如病例的来源(包括肾活检指征的掌握、对象的区域来源和人口学特征等)和诊断水平(采用的病理技术和病理诊断标准)等变异均会影响到病理类型分布的统计结果。但是,通过分析温州市成人原发性肾小球疾病谱20年来的疾病构成及其变化特点,笔者认为不能排除其中某些病理类型构成比的演变来自实际发病率改变的可能性。
[1] Simon P, Ramee MP, Boulahrouz R, et al. Epidemiologic data of primary glomerular diseases in western France[J]. Kidney Int, 2004, 66(3): 905-908.
[2] Li LS, Liu ZH. Epidemiologic data of renal diseases from a single unit in China: analysis based on 13,519 renal biop-sies[J]. Kidney Int, 2004, 66(3): 920-923.
[3] Sugiyama H, Yokoyama H, Sato H, et al. Japan Renal Biopsy Registry: the first nationwide, web-based, and prospective registry system of renal biopsies in Japan[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2011, 15(4): 493-503.
[4] Chang JH, Kim DK, Kim HW, et al. Changing prevalence of glomerular diseases in Korean adults: a review of 20 years of experience[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2009, 24(8): 2406-2410.
[5] 黄朝兴, 许菲菲, 吕吟秋, 等. 温州地区肾小球疾病病理类型分布及流行病学特点[J]. 温州医学院学报, 2000, 30(4): 267-270.
[6] 邹万忠. 肾活检病理诊断标准指导意见[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2001, 17(4): 270-275.
[7] 姜淑英, 黄朝兴, 吕吟秋, 等. 电镜检查对原发性肾小球疾病患者肾活检病理类型构成的影响[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2007, 23(11): 703-704.
[8] Pan X, Xu J, Ren H, et al. Changing spectrum of biopsyproven primary glomerular diseases over the past 15 years: a single-center study in China[J]. Contrib Nephrol, 2013, 181: 22-30.
[9] Zhou FD, Zhao MH, Zou WZ, et al. The changing spectrum of primary glomerular diseases within 15 years: a survey of 3331 patients in a single Chinese centre[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2009, 24(3): 870-876.
[10] Gesualdo L, Di PAM, Morrone LF, et al. The Italian experience of the national registry of renal biopsies[J]. Kidney Int, 2004, 66(3): 890-894.
[11] Yokoyama H, Taguchi T, Sugiyama H, et al. Membranous nephropathy in Japan: analysis of the Japan Renal Biopsy Registry (J-RBR)[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2012, 16(4): 557-563.
[12] Arias LF, Henao J, Giraldo RD, et al. Glomerular diseases in a Hispanic population: review of a regional renal biopsy database[J]. Sao Paulo Med J, 2009, 127(3): 140-144.
[13] Briganti EM, Dowling J, Finlay M, et al. The incidence of biopsy-proven glomerulonephritis in Australia[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2001, 16(7): 1364-1367.
[14] Polito MG, de Moura LA, Kirsztajn GM. An overview on frequency of renal biopsy diagnosis in Brazil: clinical and pathological patterns based on 9,617 native kidney biopsies [J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2010, 25(2): 490-496.
[15] Rychlik I, Jancova E, Tesar V, et al. The Czech registry of renal biopsies. Occurrence of renal diseases in the years 1994-2000[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2004, 19(12): 3040-3049.
(本文编辑:丁敏娇)
The renal pathologic types of adult primary glomerular diseases in Wenzhou: an analysis of evolution in20 years
YE Teng, LV Yinqiu, CHEN Bo, LI Fanfan, CHEN Xiaoqian, HUANG Zhaoxing. Department of Nephrology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, 325015
Objective: To investigate the renal pathologic types of adults’ primary glomerular diseases (PGD) including primary nephrotic syndrome (PNS), and the changing spectrum in 20 years in Wenzhou. Methods: Totally 3 392 adult (≥18 years of age) cases of biopsy-proven primary glomerular diseases diagnosed in the period of 2000 to 2013 in the Department of Nephrology of our hospital were retrospectively investigated, the renal pathologic types of all cases were analyzed and another 553 PGD cases diagnosed in the period of 1993 to 1999 in the same department were analyzed as control. Results: ①All of the 3 392 cases of PGD patients, the median age was 37 (29, 48)y, male:female ratio=1:1. The leading PGD was IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (accounts for 59.5%), followed by membranous nephropathy (MN) (accounts for 16.5%) and minimal change disease (MCD) (accounts for 12.4%). MN was the most frequent finding in early stage of the elderly and elderly patients (accounts for 46.6% totally), whereas in young and middle-aged adults, IgAN was the commonest (accounts for 47.6% and 41.2%, respectively). ②Compared with those diagnosed in the period of 1993-1999, the incidence rate of MN was two-fold increased in 2000-2013 (accounts for 16.5% and 7.2%, respectively). Among 1 067 cases of PNS diagnosed in 2000-2013, the dominant renal histopathological finding was MN (accounts for 38.7%), followed by MCD (accounts for 38.3%), IgAN (accounts for 13.0%) and focal segmental glomerular sclerosis (FSGS, accounts for 6.2%). Conclusion: IgAN remains the commonest renal pathologic type of PGD which is correspondence with our previous study. MN become predominant among PNS and increases significantly in recent years. Without the change of indications for renal biopsy, the evolution of renal pathologic types in PGD over the past 20 years is probably related to the actual change of the kidney diseases in Wenzhou.
primary glomerular diseases; pathologic types; renal biopsy; epidemiology
R692.6
A
10.3969/j.issn.2095-9400.2015.08.007
2014-11-20
叶腾(1989-),女,浙江永嘉人,硕士生。
黄朝兴,主任医师,Email:huangzhaoxing@medmail. com.cn。

