Aesthetic evaluation of yardang landforms landscape:the Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park example
RuiJie Dong ,ZhiBao Dong
1.College of Tourism and Environment Science,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi'an,Shaanxi 710062,China
2.Key Laboratory of Desert and Desertification,Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Lanzhou,Gansu 730000,China
1 Introduction
Yardang landforms belong to geological vestige landscape composed of yardang ridge(steep hill,highland,tableland,monadnock)and yardang trough(valley,lowland,trench,depression,gutter,valley,corridor).These landforms are located in arid areas,formed from mega fluviolacustrine deposits being acted upon by wind erosion or jointly with water erosion along vertical rock cracks.
Yardang landforms are precious heritage,with exquisite scenery of aeolian landforms,reflecting high aesthetic value(Donget al.,2011;Guoet al.,2012;Wuet al.,2012a,b).There are numerous documents on the qualitative descriptions of yardang appearance,such as the yardang landforms possess the beauty in magnitude,vicissitude,color,status,form,and mystery(Jiang,2004;Peng,2010;Guoet al.,2012;Wuet al.,2012b).The word "Devil City" vividly describes the characteristics of oddity,danger,solitude,and antiquity of yardang landforms.Unfortunately,there are few quantitative aesthetics analyses on yardang landforms landscape.In this paper,we provide a comprehensive aesthetic evaluation method for the geologic wonders of yardang landforms landscape.
2 Yardang landforms landscape
2.1 Yardang interpretation
"Yardang"(of Uyghur),means steep earth hummock,a kind of wind erosion landform in dry areas.Most aeolian geomorphologists source "yardang" to the Turkic language(Uyghur belongs to the branch of the Turkic language).In fact,the professional vocabulary of"yardang" was named from the Uyghur language in the Lop Nor region of northwestern China(Hedin,1903).
"Yardang landforms" are defined in both its broad and narrow senses(Niuet al.,2011).In the narrow sense,yardang is the wind-erosion landforms with streamline and long-ridge as the main type,formed during the Tertiary(i.e.,Late Tertiary)of incomplete consolidation deposits(e.g.,lacustrine clay sediments).These deposits were acted upon by wind and flood events,distributed in extreme arid or arid regions,with large distributional range and developing scale.In the broad sense,yardang includes all long ridge-shaped wind-erosion landforms,developed from various lithologic deposits of different times,and is predominantly shaped by wind force.In terms of force,yardang landforms are formed from fluviolacustrine deposits in arid areas,being shaped by external forces,usually by wind erosion,water erosion,or their combination(Xia,2007).In addition,rainfall erosion,weathering,and gravity collapse are also the forming causes of yardang landforms(Dong,2011).However,wind erosion plays a predominate role,thus yardang landforms are commonly attributed to the type of wind-erosion landforms(Blackwelder,1934;Hagedorn,1971;Fox and McDonald,1973;Ward and Ronald,1984;Wu,1987,2003;Gutiérrez-Elorzaet al.,2002;Xie and Yang,2006;Wang and Hasi,2009;Dong,2011).For example,Wu(1987,2003)regards yardang as a catch-all term of wind-erosion mound and wind-erosion depression(groove)developing in bedrock or unconsolidated deposits,and high mound being elongated and arranged parallel to the predominate wind direction.At present,yardang landforms are nearly synonymous with wind-erosion landforms in geography.
2.2 Features of yardang landforms
Viewed from the tourism landscape aspect,yardang landforms belong to the wind-erosion geologic landscape of forest-like pillars(Xie and Yang,2006).Yardang ridges and depressions are the main feature of yardang landforms(Blackwelder,1934).
A typical yardang possesses the characteristics of"flat top and steep slope".A well-developed yardang has streamline or ribbon-like structure,and the length-width ratio is 3:1 or 4:1(Hagedorn,1971;Fox and McDonald,1973;Ward and Ronald,1984;Dong,2011),becoming larger with the change of lithology,wind power,wind direction,and time.The depression is narrow "U" type groove,with the bottom becoming flat and the groove being gradually eroded to be wider.On the groove bottom,some regions are covered with sand,or exposed to the hard clay layer(Wang and Hasi,2009).
There is obvious contrast in color between yardang ridge and groove:yardang ridge is interlaced with smaller lacustrine sediments and sands,showing the light color(light-brown color,or light-yellow color);yardang groove,as well as the surrounding Gobi is composed of coarse sands and gravels of the dark color.
2.3 Aesthetic value of yardang landscape
The aesthetic characteristics of yardang landforms is a multidimensional combination of spatial dimensions,temporal visitation,enjoyment perspective,enlightenment,and even culture.Yardang landforms have a splendid combination of landscape beauty in terms of tourism perspective.
3 Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park
Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park(40º25'36"N–40º33'10"N,93º00'00"E–93º13'30"E)is located 185 km northwest of Dunhuang City in Gansu Province,China.Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park,founded in 2001,contains the largest concentration of yardang landforms with mature geological formations.This region is highly regarded in a colorful natural landscape,with a seemingly endless geological structure maze.
The main body of yardang landforms group of the geo-park is also known as Sanlongsha yardang or Shule River yardang group in west of Yumen Gate.The geo-park is 25 km from east to west,18 km from north to south,with an altitude of 810–970 m,covering an area of 398 km2,in the northeast end of Kumtagh Desert,part of the Lop Nor region.
The scenic area of the geo-park is divided into two regions(Figure 1):in northern area,yardang landforms are concentrated and continuously distributed at nearly an east-west trend(NNE10°–SW190°);in southern area,yardang landforms types are dominated by wind-erosion valley,monadnock,pillar,and mushroom formations,rocking stone,deflation hollow,ventifact and so on,all sparsely distributed at a general trend of east-west(ESE95°–WNW275°).
4 Evaluation on aesthetic value of yardang landscape
4.1 Elements of landscape unit
Yardang ridge and trough are the basic elements of the yardang landforms system.The monomer or their combination show wide variety of scenery,having rhythmic characteristics.On the whole,the landscape units in yardang landforms area can be summed up into three basic types:(1)patch(plaque body):singly distributed yardang body and residual hill;(2)corridor(narrow strip):yardang sparse group or dense group;(3)matrix(basic domain component):black Gobi.
4.2 Spatial structure of landscape
The spatial landscape group is the rhythmic combination of various landscapes in particular natural geographical environment,reflecting the different landscapes in space and time(Xie and Zheng,2001).The aesthetics of yardang landscape can be appreciated at the levels from microscopic to macroscopic.That is,yardang landscape has the sceneries of micro-structural(close-up),middle-structural(foreground),and macro-structural(distant background)(Figures 2–4).

Figure 1 Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park(northern and southern areas)(Google Earth);dotted yellow line marking yardang rank

Figure 2 Close-up of yardang landforms landscape
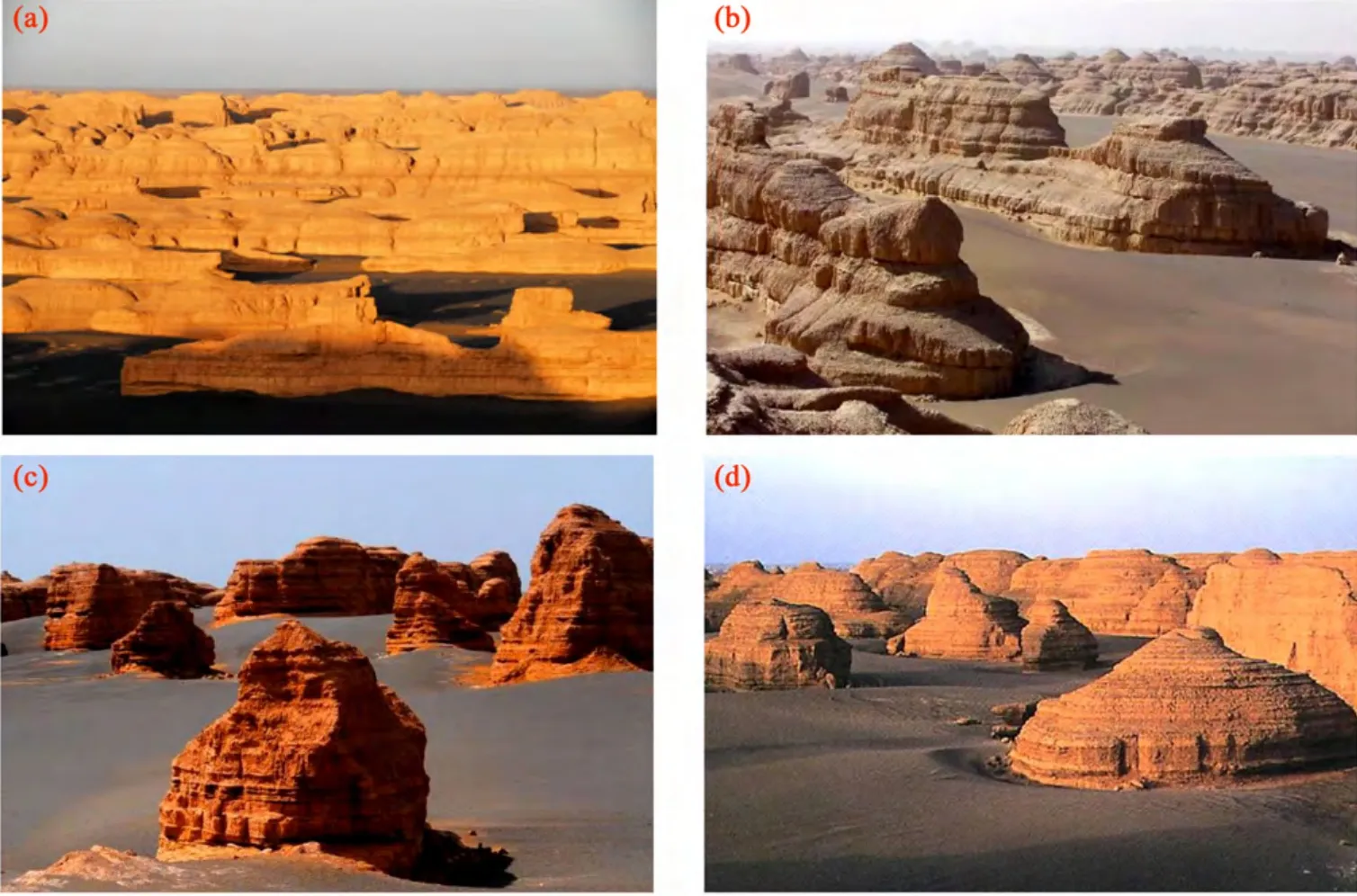

Figure 4 Distant background of yardang landforms landscape
4.3 Aesthetic degree evaluation of landscape
The "Yardang Landscape Aesthetics Comprehensive Evaluation Method" has been constructed by referring to"Stone Forest Landscape Aesthetics Comprehensive Evaluation Method"(Xie and Zheng,2001),combined with approaches of systematic investigation and analysis,and expert assessment.
4.3.1 Evaluation factors
For tourism consideration,the scenery of middle-structural(foreground)is the main body.Based on the landscape characteristics of single yardang body,residual hill,yardang sparse group and dense group,the following representative indices are screened to evaluate the esthetic value of yardang landscapes,and each index is assessed at three levels for scores(Table 1).
4.3.2 Weights of landscape and aesthetic evaluation
Table 2 illustrates the weights of the aforementioned four yardang foreground landscapes,obtained from experts' grading and questionnaire methods.
The northern and southern scenic regions of Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park are matched with 800m×800m grid network,and the score of each grid(f)is given according to Table 1.
First,the aesthetic value of each landscape is calculated by

whereFnis aesthetic value of landscapes;fn-iis score of each evaluation factor.
The evaluation results for Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park are(Table 3):for dense group and sparse group,44≤Fn≤50(first grade),38≤Fn≤43(second grade),30≤Fn≤37(third grade),Fn<30(fourth grade);for single body and residual hill,31≤Fn≤35(first grade),23≤Fn≤30(second grade),19≤Fn≤22(third grade),Fn<19(fourth grade).
Second,the general beauty degree of yardang landforms is calculated by

whereLQis beauty degree of yardang landforms;Fiis aesthetic value of each landscape dense group;qiis the corresponding weight.

Table 1 Evaluation indices and their scores of yardang landforms landscape
The evaluation results of yardang landforms beauty degree for the Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park are(Table 3):40≤LQ≤45(first grade),31≤LQ≤39(second grade),25≤LQ≤30(third grade),LQ<24(fourth grade).
Based onLQvalues,we obtained the distribution pattern of Dunhuang yardang landforms beauty degree(Figure 5).Among the first grade of landscape aesthetics,the proportions for dense group,sparse group,single body,and residual hill are 54%,25%,18%,3%,respectively.For details,the dense group,sparse group,and single body respectively occupy 39%,9%,and 10% in the north scenic region;15%,16%,and 8% in the south scenic region.The first and second grades of general beauty degree are the core of Dunhuang Yardang Geo-park,with values of 42 and 37,and occupying 29% and 22% in order.The fourth grade,with a lower aesthetic value of 21,occupies 37%.It is worthwhile to note that the residual hills account for 49%,most of them are located at the periphery of the geo-park.These obvious empty scenery phenomena suggest that the yardang landscapes have been experiencing serious degradation,arousing considerable protection while developing yardang landscapes.

Table 2 The weights of aesthetic degree for different types of yardang landforms landscape
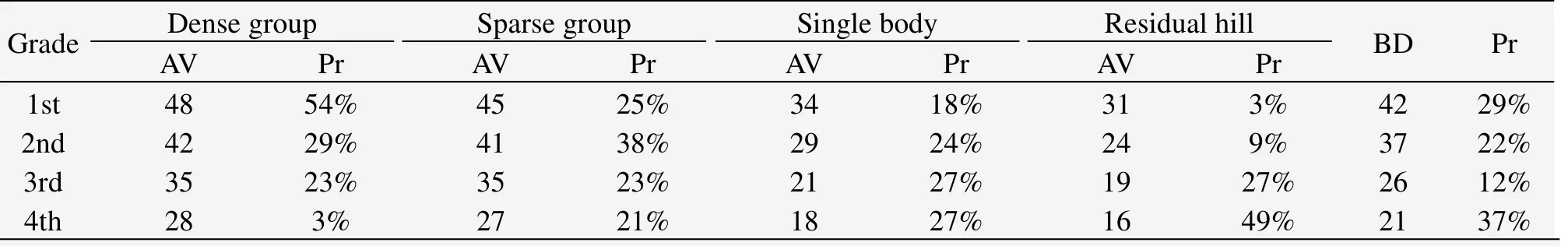
Table 3 Aesthetic value and beauty degree of Dunhuang yardang landforms landscape

Figure 5 The spatial pattern of beauty degree of yardang landforms landscape in Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park
5 Conclusions
Dunhuang yardang landforms landscape has the typical characteristics of natural landscapes,with high aesthetic value and important scientific research significance.The aesthetic evaluation method on Dunhuang yardang landforms landscape provided in this paper can not only calculate the aesthetic value of an individual yardang body,but also compare the landscape beauty degree among different regions.The grade classification offers the basis of protecting Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park.
Northwestern China houses large-area high-grade yardang landforms,highly important for arid desert tourism resources.These yardang landforms landscapes are unique and irreplaceable,and have the potential to join the World Heritage List.
Yardang bodies are mostly distributed in forms of dots and lines,and are easily destroyed from wind and water erosion,possessing vulnerability.It is strongly recommended that it is very important to regulate the tourist behavior through the legislation and protect yardang landforms landscape by adopting various measures,so as to promote the healthy and sustainable development of yardang landforms landscape tourism.
This research was supported by fund project from professor for "Yangtze River Scholar" of the Ministry of Education(No.801813).
Blackwelder VT,1934.Yardangs.Geological Society of America Bulletin,45(1):159–166.
Dong ZB,2011.Kumtagh Desert Aeolian Geomorphology.Beijing:Science Press,pp.292–301.
Dong ZB,Qu JJ,Qian GQ,et al.,2011.The Kumtagh Desert aeolian geomorphology regionalization.Journal of Desert Research,31(4):805–814.
Fox RW,Mc Donald AT,1973.Introduction of Fluid Mechanics.New York:Wiley.
Guo F,Wu JG,Wang X,et al.,2012.Feasibility study on declaration of the world natural heritage for China yardang landforms.Journal of Desert Research,32(3):655–660.
Gutiérrez-Elorza M,Desir G,Gutiérrez-Santolalla F,2002.Yandangs in the semiarid central sector of the Ebro Depression(NE Spain).Germorphology,44(1/2):155–170.
Hagedorn H,1971.Untersuchungen uber Relieftypen arider Raume an Beispielen aus dem Tibesti-Gebirge und seiner Umgebung.Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie,11(S1):1–271.
Hedin S,1903.Central Asia and Tibet.New York Seribners.
Jiang HZ,2004.Eco-geological tourism value of yardang landforms:Devil City,Hami,Xinjiang,as an example.Journal of Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals,(suppl.):9–10.
Niu QH,Qu JJ,Li XZ,et al.,2011.Review and prospect of research progress on yardang geomorphology.Advances in Earth Science,26(5):516–527.
Peng YX,2010.Evaluation of core competitiveness based on tourist benefit of the Geopark:Cui Huashan,Yuntai Mountain and Hukou for patients.Ph.D.Dissertation,pp.124–126.
Wang S,Hasi,2009.Study on wind erosion landform and process.Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,31(1):100–105.
Ward AW,Ronald G,1984.Evolution of the yardangs at Rogers lake,California.Bull of Geological Society of America,95:829–837.
Wu JF,Guo F,Wang X,et al.,2012a.Tourism development of Kumtagh Desert aeolian landforms heritage.Journal of Desert Research,32(4):1163–1168.
Wu JF,Wang X,Guo F,et al.,2012b.Evaluation on the aesthetic value of Kumtagh Desert aeolian landform heritage.Journal of Desert Research,32(5):1451–1456.
Wu Z,1987.Aeolian Geomorphology.Beijing:Science Press,pp.81–84.
Wu Z,2003.Aeolian Geomorphology and Sand Control Engineering.Beijing:Science Press.
Xia XC,2007.Lop Nor in China.Beijing:Science Press,pp.66–68.
Xie HZ,Yang SY,2006.Geological landscape of forest pillars forms the types and distribution.Geology and Resources,15(1):78–80.
Xie NG,Zheng XZ,2001.Aesthetic value evaluation on Yunnan stone forest landscape.Geographical Research,20(5):518–519.
 Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions2015年3期
Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions2015年3期
- Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions的其它文章
- The characteristics of oasis urban expansion and drive mechanism analysis:a case study on Ganzhou District in Hexi Corridor,China
- Characterizing changes in ecosystem service values in China's eastern Loess Plateau
- Elemental composition and its environmental significance for the varicolored hills in the northern foothills of the Qilian Mountains of Sunan Yugur Autonomous County,China
- Characterizing stand structure in a spruce forests:effects of sampling protocols
- Biomass and water partitioning in two age-related Caragana korshinskii plantations in desert steppe,northern China
- Comparative studies on leaf epidermal micromorphology and mesophyll structure of Elaeagnus angustifoliaL.in two different regions of desert habitat
