光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中的应用①
刘海泉,王增春,王强,任自刚,熊巍,王俊杰
光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中的应用①
刘海泉,王增春,王强,任自刚,熊巍,王俊杰
目的探讨光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中应用的可行性。方法选择50例拟在静脉麻醉联合吸入麻醉下行颈椎手术的患者,随机分成使用光学窥喉镜气管插管组(A组)和光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜气管插管组(AF组)。观察两组插管时间、一次插管成功率、插管期间血流动力学改变及插管相关并发症情况。结果A组插管时间显著长于AF组(P<0.001)。A组一次插管成功率低于AF组(P<0.05)。两组在气管插管期间血流动力学改变及插管相关并发症方面无显著性差异(P>0.05)。结论光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜可安全、有效地应用于颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中。
颈椎损伤;光学窥喉镜;纤维支气管镜;气管内插管
[本文著录格式]刘海泉,王增春,王强,等.光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中的应用[J].中国康复理论与实践,2015,21(6):713-716.
CITED AS:Liu HQ,Wang ZC,Wang Q,et al.Application of Airtraq®optical laryngoscope combined with bronchofibroscope for endotracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine injury[J].Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian,2015,21(6):713-716.
光学窥喉镜能够降低颈部活动受限患者的气管插管难度[1-3]。但由于光学窥喉镜的沟槽是固定的,有时即使是经验丰富的麻醉医生也需要花费一定时间调整窥喉镜的置入点,而且一旦遇到患者声门位置过高,有时导致插管失败[4]。
纤维支气管镜的头端可以灵活转动,当窥喉镜不能正对声门导致插管困难时,借助纤维支气管镜可转动的头端能够轻易找到声门。
我们拟通过观察光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中的应用,探讨这种方法的可行性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
2007年1月~2014年10月收入北京博爱医院骨关节康复科、脊柱脊髓外科或脊柱脊髓功能重建科并在静吸复合全麻下接受手术的颈椎损伤患者50例,其中男性39例,女性11例;年龄16~75岁;体重50~88 kg。
所有患者术前常规禁食8 h,禁饮6 h。患者入室后建立静脉通道,常规监测无创血压(non-invasive blood pressure,NIBP)、心电图(electrocardiogram, ECG)、脉搏血氧饱和度(pulse blood oxygen saturation, SPO2)。面罩辅助呼吸下行麻醉诱导,方案是咪唑安定0.04 mg/kg、丙泊酚2 mg/kg、维库溴铵0.1 mg/kg或罗库溴铵0.6 mg/kg、芬太尼2 μg/kg或舒芬太尼0.4 μg/kg、地塞米松10 mg。面罩正压通气3 min后实施经口气管插管术。男性患者选择7.5-ET导管,女性患者选择7.0-ET导管。
将纳入患者按照拟手术次序依次编号1~50,利用EXCEL软件中函数“RAND()”命令制作一组随机数字并与手术编号对应。将所得的随机数字按照降序排列,重新排列后的数字第1~25位属于光学窥喉镜气管插管组,即A组,第26~50位属于光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜气管插管组,即AF组)。
A组按照常规光学窥喉镜插管法将气管导管经口腔置入到气管内的合适位置。AF组先将光学窥喉镜(Airtraq®,氧瞬得®)置入口腔,通过光学窥喉镜的窥孔看见声门后,沿其沟槽先将纤维支气管镜置入气管内,然后将气管导管沿纤维支气管镜置入到气管中合适的位置。
每次实施气管插管时如果操作时间超过3 min,则停止操作,改由面罩正压通气1 min后再继续实施操作,插管时间重新计算,并将观察项目“一次性插管成功率”记为“0次”。
实施气管插管的麻醉医师为高年主治医师(固定为2人),能够熟练使用纤维支气管镜和实施气管插管术。所有患者均采用静脉麻醉联合吸入麻醉维持麻醉深度直至手术结束。
1.2 观察指标
观察两组的插管时间(intubation time,IT)、一次插管成功率(success rate of single intubation,SRSI)、插管期间血流动力学改变及插管相关并发症发生的情况。
1.3 统计学分析
2 结果
A组中有4例患者插管时间超过3 min仍没有成功,经面罩重新正压通气后改为在光学窥喉镜联合纤维支气管镜下实施气管插管,没有被纳入最后的统计。
两组患者的一般情况无显著性差异(P>0.05)。A组插管时间显著长于AF组(P<0.001)。A组一次插管成功率低于AF组(P<0.05)。见表1。
两组在气管插管期间血流动力学改变方面无显著性差异(P>0.05)。见表2和表3。
两组在插管相关并发症方面无显著性差异(P>0.05)。见表4。
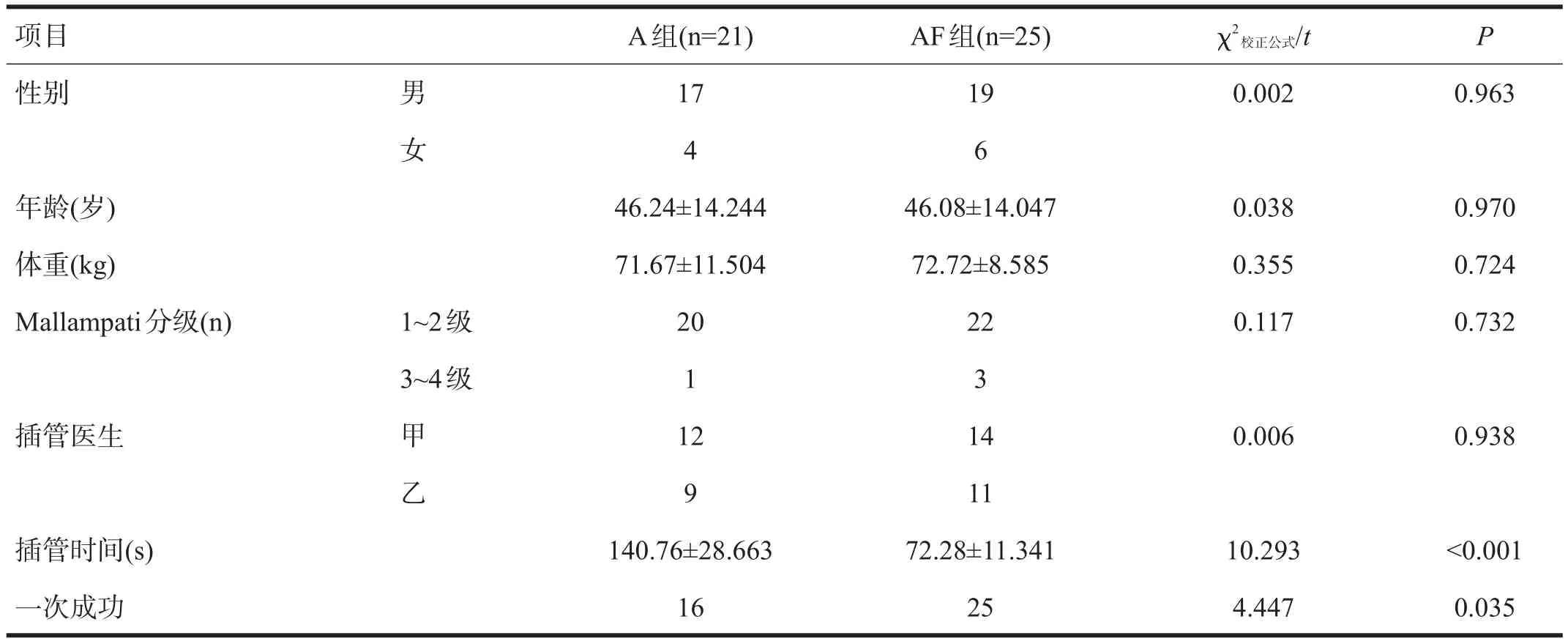
表1 两组患者一般资料比较(n)

表2 两组患者的MAP比较(mmHg)

表3 两组患者的HR比较(min-1)

表4 两组插管相关并发症发生情况(n)
3 讨论
顺利的气管插管能够降低心血管意外、组织损伤、缺氧等并发症,尤其对危重患者更为重要[5-7]。
目前有许多能够帮助麻醉医生降低气管插管术难度的手段,其中光学窥喉镜的作用尤为突出[8-9]。光学窥喉镜不需调整口、咽、喉三轴线就可以看到声门,因此在插管过程中需要较少的力量就可以完成插管,对颈椎损伤患者能够起到很好的保护作用。
由于这种装置的沟槽是固定的,遇到特殊病例时,在引导气管导管时常常会出现不能正对声门而导致插管失败或延长插管时间的情况[10],并且在反复调整光学窥喉镜以对准声门的过程中容易造成口咽部损伤。如果将这种装置与纤维支气管镜联合使用,就有可能克服它的缺陷。而且,由于沟槽的导向作用也能够避免单独使用纤维支气管镜容易“迷失”方向的缺陷。
本研究中,我们将这种装置与纤维支气管镜联合使用,借助于纤维支气管镜可转动的头端,使得光学窥喉镜相对固定的沟槽也变得“灵活”,以满足麻醉医生轻易将气管导管置入声门,并减少光学窥喉镜在口咽部的移动或转动从而减少对口咽部的损伤。
本研究结果显示,将光学窥喉镜与纤维支气管镜联合应用时,插管时间显著缩短,一次插管成功率提高,说明这种方法在颈椎损伤患者气管插管术中是安全、有效的。
绝大多数困难在气道通过术前评估都能够得到预测,因此,掌握多种管理困难气道和处理紧急情况的方法有助于患者的安全[11-22]。目前国内在困难气道管理方面有很多的经验及报道[23-26],麻醉医生可以根据自己的情况及医院的条件加以选择。
[1]Durga P,Yendrapati C,Kaniti G,et al.Effect of rigid cervical collar on tracheal intubation using Airtraq(®)[J].Indian J Anaesth,2014,58(4):416-422.
[2]Ni J,Luo L,Wu L,et al.The Airtraq laryngoscope as a first choice for parturients with an expected difficult airway[J].Int J ObstetAnesth,2014,23(1):94-95.
[3]Ali QE,Amir SH,Siddiqui OA,et al.Airway management in severe post-burn contracture of the neck using Airtraq:A case series[J].Indian JAnaesth,2013,57(6):620-622.
[4]Saracoglu KT,Eti Z,Gogus FY.Airtraq optical laryngoscope: advantages and disadvantages[J].Middle East J Anaesthesiol, 2013,22(2):135-141.
[5]Noppens RR.Airway management in the intensive careunit[J].Acta Clin Croat,2012,51(3):511-517.
[6]Divatia JV,Khan PU,Myatra SN.Tracheal intubation in the ICU:Life saving or life threatening?[J].Indian J Anaesth, 2011,55(5):470-475.
[7]Aziz MF,Healy D,Kheterpal S,et al.Routine clinical practice effectiveness of the Glidescope in difficult airway management:an analysis of 2,004 Glidescope intubations,complications,and failures from two institutions[J].Anesthesiology, 2011,114(1):34-41.
[8]Selde W,English K,Heffelfinger M,et al.Successful airtraq use in an air medical transport system[J].Air Med J,2014,33 (6):331-334.
[9]Dhonneur G,Zraier S,Sebbah JL,et al.Urgent face-to-face tracheal re-intubation using Video-Airtraq in ICU patients placed in the sitting position[J].Intensive Care Med,2014,40(4): 625-626.
[10]Saracoglu KT,Acarel M,Umuroglu T,et al.The use of Airtraq laryngoscope versus Macintosh laryngoscope and fiberoptic bronchoscope by experienced anesthesiologists[J].Middle East JAnaesthesiol,2014,22(5):503-509
[11]Asai T.Monitoring during difficult airway management[J].J Anesth,2014,28(1):87-93.
[12]De Jong A,Futier E,Millot A,et al.How to preoxygenate in operative room:healthy subjects and situations"at risk"[J]. Ann FrAnesth Reanim,2014,33(7-8):457-461.
[13]Dedmon MM,Rogers DJ,Hartnick CJ.Management of the difficult pediatric airway with endotracheal intubation via telescopic guidance[J].Laryngoscope,2014,124(3):785-788.
[14]Durbin CG Jr.,Bell CT,Shilling AM.Elective intubation[J]. Respir Care,2014,59(6):825-846.
[15]Janiszewski A,Paslawski R,Skrzypczak P,et al.The use of a plastic guide improves the safety and reduces the duration of endotracheal intubation in the pig[J].J Vet Med Sci,2014,76 (10):1317-1320.
[16]Kallio PJ,Cox AE,Pagel PS.Utility of preoperative anesthesia clinic videoendoscopy for airway management planning[J]. Anesth Pain Med,2014,4(4):e19776.
[17]Karalapillai D,Darvall J,Mandeville J,et al.A review of video laryngoscopes relevant to the intensive care unit[J].Indian J Crit Care Med,2014,18(7):442-452.
[18]Kristensen MS,Teoh WH,Graumann O,et al.Ultrasonography for clinical decision-making and intervention in airway management:from the mouth to the lungs and pleurae[J].Insights Imaging,2014,5(2):253-279.
[19]Liou JY,Chow LH,Chan KH,et al.Successful anesthetic management of a patient with thyroid carcinoma invading the trachea with tracheal obstruction,scheduled for total thyroidectomy[J].J Chin MedAssoc,2014,77(9):496-499.
[20]Liu L,Yue H,Li J.Comparison of three tracheal intubation techniques in thyroid tumor patients with a difficult airway:a randomized controlled trial[J].Med Princ Pract,2014,23(5): 448-452.
[21]Long E,Sabato S,Babl FE.Endotracheal intubation in the pediatric emergency department[J].Paediatr Anaesth,2014,24 (12):1204-1211.
[22]Mellanby E,Podmore BM,McNarry AF.Safety in the emergency situation:the airway-a theatre team approach[J].J Perioper Pract,2014,24(5):112-117.
[23]郝景宇,赵尤美.可视喉镜联合纤维支气管镜引导气管插管在困难气道患者中的应用[J].河北医科大学学报,2013,34 (4):472-473.
[24]翁建东,李斌,费建平,等.Glide Scope视频喉镜联合纤维支气管镜用于双腔支气管插管的临床体会[J].海南医学,2013, 24(21):3222-3223.
[25]陈美银,万宗明,徐朴,等.纤维支气管镜联合Glidescope视频喉镜用于经鼻气管插管的观察[J].皖南医学院报,2014,33 (5):440-442.
[26]杨改生,薛晓东,夏舒萌,等.Airtraq可视喉镜和Macintosh喉镜在困难气管插管中的对比应用[J].徐州医学院学报,2012, 32(1):10-13.
Application of Airtraq®Optical Laryngoscope Combined with Bronchofibroscope for Endotracheal Intubation in Patients with Cervical Spine Injury
LIU Hai-quan,WANG Zeng-chun,WANG Qiang,REN Zi-gang,XIONG Wei,WANG Jun-jie
1.Capital Medical University School of Rehabilitation Medicine,Beijing 100068,China;2.Department of Anesthesiology,Beijing Bo'ai Hospital,China Rehabilitation Research Center,Beijing 100068,China
Objective To explore the application of Airtraq®optical laryngoscope combined with bronchofibroscope for endotracheal intubation(EI)in patients with cervical spine injury(CSI).Methods 50 patients with CSI undergoing spine surgery under combined general anesthesia were randomly assigned to two groups,group A(n=25)received EI by using Airtraq®optical laryngoscope and group AF(n=25) received EI by usingAirtraq®optical laryngoscope combined with bronchofibroscope.The intubation time(IT),success rate of single intubation(SRSI),hemodynamic changes in endotracheal intubation,and complications related to EI were observed.Results IT was significantly longer in groupAthan in groupAF(P<0.001),and SRSI was significantly lower than in groupA in groupAF(P<0.05).There was no significant difference in hemodynamic changes in EI and complications related to EI between two groups(P>0.05).Conclusion Airtraq®optical laryngoscope combined with bronchofibroscope would be safely and effectively used for EI in patients with CSI.
cervical spine injury;optical laryngoscope;bronchofibroscope;endotracheal intubation
10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2015.06.016
R681.5
A
1006-9771(2015)06-0713-04
2015-01-04
2015-02-12)
1.首都医科大学康复医学院,北京市100068;2.中国康复研究中心北京博爱医院麻醉科,北京市100068。作者简介:刘海泉(1976-),男,河北廊坊市人,主治医师,主要研究方向:临床麻醉与疼痛。通讯作者:王强,男,浙江杭州市人,主任医师。E-mail: 13801032889@163.com。

