钡餐、CT及胃镜应用于胃癌诊断的对比分析
仲其山 仲晓军 周涛


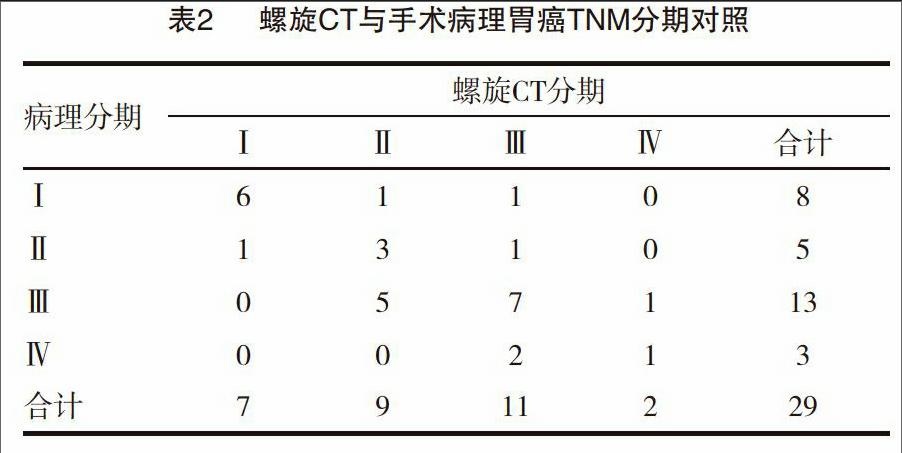
[摘要] 目的 比较钡餐、CT及胃镜应用于胃癌诊断的临床应用价值。方法 研究对象为2012年1月~ 2014年12月来我院就诊的胃癌患者41例,均用CT检查、上消化道钡餐造影、纤维胃镜检查。CT检查用飞利浦Brilliance16排CT,钡餐造影用SMEW数字胃肠机,胃镜检查用奥林巴斯电子胃镜。结果 CT、钡餐、胃镜检出率(97.56%、87.80%、95.12%)比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),CT、胃镜分型敏感性高于钡餐(82.92%,78.04% vs. 48.78%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),CT的分型敏感性与胃镜比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。CT检查胃癌TNM分期的准确率为58.62%。 结论 CT、钡餐、胃镜三种检测方法在胃癌检出率方面差异不大,CT、胃镜在分型敏感性方面优于钡餐,CT在胃癌分期方面具有重要的临床意义,为最佳治疗方案的制定提供有价值的参考依据,可提升手术方案的可靠性及准确性。
[关键词] 胃癌;钡餐;CT;胃镜
[中图分类号] R735.2 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 2095-0616(2015)19-190-04
[Abstract] Objective To compare the clinical application value of barium meal, CT and gastroscopy in the application of the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Methods 41 patients with gastric cancer from January 2012 to December 2014 in our hospital were selected as the subjects, all patients were given CT(used by Philips Brilliance 16-slices CT), upper gastrointestinal barium meal(used by SMEW digital gastrointestinal machine), gastroscopy examination(used by Olympus electronic gastroscope).Results The detection rate of CT, barium meal, gastroscopy were 97.56%, 87.80%, 95.12%, the difference was not statistically significant(P>0.05), the typing sensitive of CT, gastroscopy were higher than barium meal (82.92%, 78.04% vs. 48.78%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), and the difference was not statistically significant in the typing sensitive between CT and gastroscopy (P>0.05). The accuracy rate of TNM staging of gastric cancer by CT examination was 58.62%. Conclusion CT, barium meal, gastroscopy of three detection methods is not very different in the detection rate of gastric cancer, the typing sensitive of CT, gastroscopy are superior to barium meal, CT has important clinical significance in the staging of gastric cancer, and can provide valuable reference for the development of optimal treatment regimen, improve the reliability and accuracy of surgical plan.
[Key words] Gastric cancer; Barium meal; CT; Gastroscopy
胃癌是一种临床最常见的消化道恶性肿瘤,好发于40~60岁,可以发生在任何部位,以胃窦、小弯及贲门区常见,对人们的生命和健康均造成严重威胁[1]。胃癌无明显临床症状,易被其他症状误导,大部分胃癌患者确诊时已属于中晚期,错过了最佳治疗时机[2]。近年来,随着医学技术的不断进步,CT诊断技术日益完善,螺旋CT在胃癌的检查中广泛应用,准确率及可靠性均明显提高,螺旋CT检查能对胃癌病变组织进行准确定性及定位,因而能对患者预后和手术治疗效果进行准确判断[3]。我们收集了本院2012年1月~ 2014年12月经病理检查证实为胃癌的患者资料41例,探讨钡餐、CT及胃镜综合应用与胃癌检查的应用价值,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
研究对象为2012年1月~2014年12月来我院就诊的胃癌患者41例,所有患者均经手术和病理证实,男23例,占56.09%, 女18例,占43.91%,年龄最小15岁,最大76岁,平均(52.7±8.9)岁。病程最短3个月,最长9个月,平均(3.6±0.5)个月。病灶位置:胃窦部10例,占24.39%,胃体部13例,占31.70%,胃底贲门部8例,占19.51%,胃窦及胃体部4例,占9.75%,胃体及胃底贲门部6例,占14.63%。主要症状:食欲不佳17例,上腹隐痛33例, 呕吐21例, 黑便8例、消瘦29例。endprint

