2型糖尿病患者高血糖状态对肾功能的影响
杨淑芝
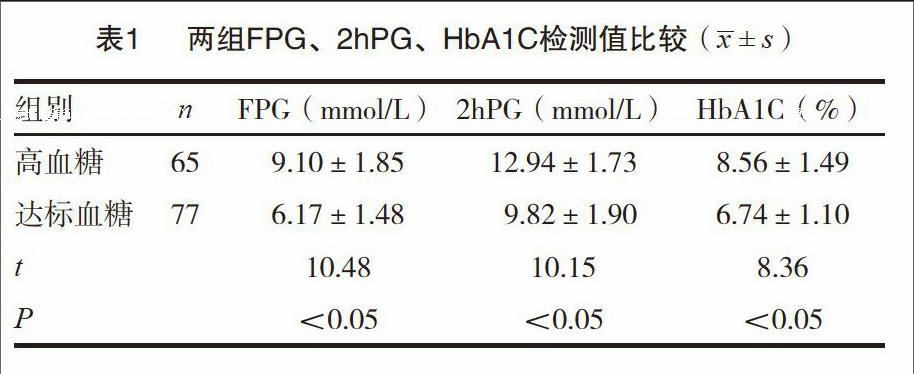

[摘要] 目的 探讨2型糖尿病患者高血糖状态对肾功能的影响。 方法 选择我院2013年10月~2014年5月收治的142例2型糖尿病患者为研究对象,根据血糖状态分为高血糖状态组[空腹血糖(FPG)≥7.0 mmol/L、餐后2h血糖(2h PG)≥11.1 mmol/L)]65例和达标血糖状态组(FPG<7 mmol/L、2hPG<11.1 mmol/L)77例,观察两组患者的FPG、2hPG、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1C)测定值以及尿微量白蛋白(尿mALB)、尿β2-微球蛋白(尿β2-MG)水平。 结果 高血糖状态患者的FPG、2hPG、HbA1C分别为(9.10±1.85)mmol/L、(12.94±1.73)mmol/L、(8.56±1.49)%,显著高于达标血糖状态患者的(6.17±1.48)mmol/L、(9.82±1.90)mmol/L、(6.74±1.10)%,组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);高血糖状态患者的肾功能指标尿mALB、β2-MG分别为(32.60±2.94)mmol/L、(0.45±0.06)mmol/L,均显著高于达标血糖状态患者的(28.92±2.35)mmol/L、(0.38±0.05)mmol/L,组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 2型糖尿病患者高血糖状态对肾功能具有不良影响,显著降低患者的尿mALB、β2-MG水平,应积极降血糖治疗、防止肾脏并发症。
[关键词] 2型糖尿病;高血糖;肾功能
[中图分类号] R587.1 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 2095-0616(2015)18-152-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of renal function of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hyperglycaemia state. Methods From October 2013 to May 2014 in our hospital, 142 cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients were selected as the objects in this study, they were divided into hyperglycemia state group [fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥7.0 mmol / L, 2h postprandial glucose (2hPG) ≥11.1 mmol / L)] and standard glucose state group (FPG<7 mmol / L, 2 h PG <11.1 mmol / L) groups, the patients'FPG, 2 h PG, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) measured values and microalbuminuria (urinary mALB), urinary β2- microglobulin (urinary β2-MG) levels of two groups were compared. Results The FPG, 2hPG, HbA1C of hyperglycemia state group were (9.10±1.85) mmol/L, (12.94±1.73) mmol/L, (8.56±1.49)%, significantly higher than (6.17±1.48) mmol/L, (9.82±1.90)mmol/L, (6.74±1.10)% of standard glucose state group, there were significant differences between two groups (P<0.05); the urine mALB, β2-MG of hyperglycemia state group were (32.60±2.94) mmol/L, (0.45±0.06) mmol/L, significantly higher than (28.92±2.35)mmol/L, (0.38±0.05) mmol/L of standard glucose state group, there were significant differences between two groups (P<0.05). Conclusion Hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes has an adverse effect on the renal function state, can significantly reduce the patients' urinary mALB, β2-MG levels, should actively hypoglycemic treatment to prevent renal complications.
[Key words] Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Hyperglycemia; Renal function
2型糖尿病已经成为现代临床备受关注的疾病之一,糖尿病的危害主要是其可以引发多种慢性并发症,肾病即为其中一种,如何做到更好地防治糖尿病并发症,对相关实验指标的监测为主要临床重要依据[1-2]。2型糖尿病患者的高血糖状态到底对肾功能存在怎样的影响,笔者借助本研究收集相关病例资料,并进行整理报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择我院2013年10月~2014年5月收治的142例2型糖尿病患者为研究对象,根据血糖状态分为高血糖状态[空腹血糖(FPG)≥7.0mmol/L、餐后2h血糖(2hPG)≥11.1mmol/L)]和达标血糖状态(FPG<7mmol/L、2hPG<11.1mmol/L)两组,高血糖状态组65例中,男37例,女28例;年龄38~74岁,平均(51.2±3.4)岁;2型糖尿病病程6个月~15年,平均(4.1±1.0)年。达标血糖状态组77例中,男42例,女35例;年龄36~72岁,平均(50.9±3.5)岁;2型糖尿病病程8个月~16年,平均(4.3±1.2)年。入选研究的所有患者均排除酮症酸中毒及其他影响糖代谢的疾病。两组患者的年龄、性别、病程间差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。endprint

