肾细胞癌中鸟嘌呤核苷酸解离抑制因子2的表达及意义
赵波 李颖毅

[摘 要] 目的:探讨肾细胞癌组织中鸟嘌呤核苷酸解离抑制因子2(RhoGDI2)的表达及其与临床病理因素关系。方法:选择2010年1月至2014年8月期间60例肾细胞癌患者为研究对象;检测癌及癌旁组织RhoGDI2表达,分析RhoGDI2的表达与肾细胞癌临床病理关系。结果:肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2的表达水平高于癌旁组织,肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2表达的阳性率(70.0%)显著高于癌旁组织(38.3%),差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.1175,P=0.0005);肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2的表达与病理分期、分化程度、淋巴结转移、肿瘤大小有显著相关性(P<0.05)。结论:RhoGDI2在肾细胞癌中呈高表达;肾细胞癌中RhoGDI2的表达参与了肾细胞癌的发病、转移和进展。
[关键词] 肾细胞癌;鸟嘌呤核苷酸解离抑制因子2;病理
中图分类号:R737.11 文献标识码: B 文章编号:2095-5200(2015)05-122-03
[Abstract] Objective: To study expression of guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitory factor 2 in renal cell carcinoma and the correlation with clinical pathology. Methods: 60 cases of renal cell carcinoma patients were selected as the research object.The expression of RhoGDI2, and the correlation with clinical pathology in renal cell carcinoma were made for statistical analysis. (1)From Jan. 2010 to Aug. 2014, immunohistochemistry was used to assess the expression of RhoGDI2 in 60 pairs of renal cell carcinoma tissues and adjacent pancreatic tissues, and its correlation with clinicopathological features was also analyzed. Results: RhoGDI2 expression level in renal cell carcinoma tissues was higher than the tissue adjacent to carcinoma. Positive rate (70.0%) of RhoGDI2 expression in renal cell carcinoma tissue was significantly higher than tissue adjacent to carcinoma (38.3%), and the difference was statistically significant (χ2=12.1175,P=0.0005). RhoGDI2 expression in renal cell carcinoma tissue were significantly correlated with pathological staging, degree of differentiation, lymph node metastasis, tumor size (P<0.05). Conclusion: RhoGDI2 is highly expressed in renal cell carcinoma; The expression of RhoGDI2 is involved in the pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma, metastasis and progress in renal cell carcinoma.
[Key words] Renal cell carcinoma; Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitory factor 2; Pathology
肾细胞癌由肾实质泌尿小管上皮系统起源,病理类型以透明肾细胞癌、乳头状肾细胞癌、嫌色细胞性肾细胞癌为主。以50~70岁年龄段人群为肾细胞癌高发人群,其发病率仅次于膀胱癌,恶性程度较高,患者预后亦较差[1-2];肾细胞癌病因尚不明确,流行病学研究数据显示,其发病与遗传、吸烟、肥胖等因素有关,男性发病率明显高于女性[3-4]。鸟嘌呤核苷酸解离抑制因子2(RhoGDI2)为重要肿瘤转移相关基因[5],在恶性肿瘤中可呈异常表达,在机体肿瘤转移及进展过程中起重要作用[6-7],但有关RhoGDI2在肾细胞癌组织中表达与肾细胞癌临床病理关系国内较少。本研究通过检测肾细胞癌中RhoGDI2表达,旨在探讨RhoGDI2在肾细胞癌发生、转移和进展中可能作用。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2010年1月至2014年8月期间被我院收治60例肾细胞癌患者为研究对象,患者年龄42~80岁,平均(57.2±4.16)岁,男38例,女22 例,体重指数为(21.59±3.10 )kg/m2。60例肾细胞癌患者均经手术病理证实为肾细胞癌,符合肾细胞癌诊断标准[8]。排除近3个月内接受靶向治疗、放化疗者;严重精神疾病者;肺结核者;免疫性疾病者;急性感染者;其他系统恶性肿瘤;过度饮酒者;资料缺失;未完成随访者。按照病理分期,I期12例,II期48例。取相邻癌旁组织为对照组。本研究获我院伦理委员会审核批准,并经患者签署知情同意书。
1.2 免疫组化方法
术中取直径5~8 mm标本,中性福尔马林保存。石蜡块切成4?m厚标本,经孵育、染色,高倍镜下观察。判定按照细胞染色强度:无染色0 分,淡黄色 1 分,棕黄色 2 分,深褐色 3 分。染色细胞阳性率:0 分为阴性;小于 25%判定为 1 分;25%与 50%之间为 2 分;50%与 70%之间为 3 分;大于 75%为 4 分。得分为 0 即阴性,2~3 即弱阳性,4~5 分即中等阳性,6~7 分即强阳性[6]。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 17.0软件,计数资料采用χ2检验,病理参数间统计执行person χ2检验,等级资料采用秩和检验;P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 肾细胞癌、癌旁组织中RhoGDI2表达
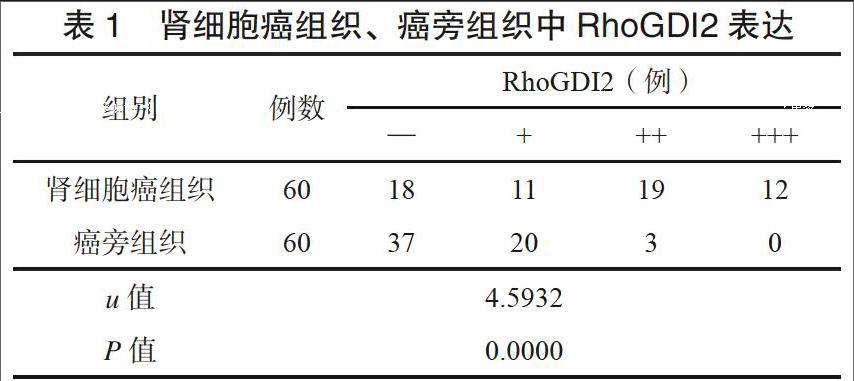
肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2表达水平高于癌旁组织,数据见表1。肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2阳性率(70.0%)显著高于癌旁组织(38.3%),差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.1175,P=0.0005)。
2.2 RhoGDI2在肾细胞癌组织中表达与病理关系
对肾细胞癌中RhoGDI2表达进行相关因素分析,如表2结果显示,RhoGDI2表达与肾细胞癌分期、分化程度、出现淋巴结转移、肿瘤大小相关。与性别、年龄等因素无明显相关关系。
3 讨论
研究报道,RhoGDI2在呼吸系统肿瘤、消化系统肿瘤等恶性肿瘤发生及进展中起一定作用,在上述恶性肿瘤组织中RhoGDI2可出现异常激活和异常表达[9-11]。肾细胞癌发病机制复杂,可由多种因素诱发;Xu等[12]研究显示,泌尿系统疾病中RhoGDI2表达水平可出现异常增强现象。Li等[13]研究发现,RhoGDI2表达与恶性肿瘤患者预后及转移密切相关,在其中可能起一定促进作用。本研究组免疫组化检测结果显示,肾细胞癌中RhoGDI2表达水平高于癌旁组织。本研究亦进一步探讨了肾细胞癌中RhoGDI2表达与患者临床病理相关性。研究结果显示,肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2表达与肾细胞癌病理分期、淋巴结转移、分化程度、肿瘤大小有关(P<0.05)。提示RhoGDI2表达与肾细胞癌临床病理密切相关,上述指标表达在肾细胞癌进展中亦起一定作用。该结果与Yi等[14]研究报道一致,Yi等认为RhoGDI2参与肾细胞癌发生、转移和进展可能机制之一是RhoGDI2在抑制机体免疫功能同时,促进肿瘤血管生成及细胞增殖。
另有学者研究认为:RhoGDI2参与肾细胞癌进展另一种可能机制为:RhoGDI2通过上调基质金属蛋白酶2(MMP2)表达参与肾细胞癌进展及肿瘤细胞增殖和转移[15]。恶性肿瘤组织中RhoGDI2 mRNA及MMP2 mRNA检测水平明显高于癌旁组织,而相关性显示,RhoGDI2及MMP2表达之间呈现正相关,表明RhoGDI2及MMP2可能共同参与了恶性肿瘤发病及进展。
本研究结果表明,肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2高表达,后期可进一步探讨肾细胞癌组织中RhoGDI2表达与其他生化标志物关系及其可能调控作用,以进一步探讨RhoGDI2在肾细胞癌发病及进展中可能机理。
参 考 文 献
[1] 朱致晖,谷江,张永春,等.斯钙素蛋白1下调钙离子及缺氧诱导因子1α水平调控肾癌细胞抗缺氧增殖平衡[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2014,43(5):528-534.
[2] 张伟,李玉军,鲁青,等.多房性囊性肾细胞癌临床病理特点[J].中华病理学杂志,2014,(11):723-727.
[3] 标准·方案·指南--美国国立综合癌症网络肾癌指南2015. V.3版更新解读[J].中国全科医学,2015,(12):1430-1430.
[4] 郑振东.NCCN 肾癌指南2015.V.3版更新解读[J].浙江医学,2015,(5):353-353,356.
[5] Cho HJ, Baek KE, Park SM, et al. RhoGDI2 expression is associated with tumor growth and malignant progression of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2009,15(8):2612-2619.
[6] Liu S, Cui H, Li Q, et al. RhoGDI2 is expressed in human trophoblasts and involved in their migration by inhibiting the activation of RAC1. Biol Reprod, 2014,90(4):88.
[7] Gildea JJ, Seraj MJ, Oxford G, et al. RhoGDI2 is an invasion and metastasis suppressor gene in human cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2002,62(22):6418-6423.
[8] 胡林昆,张学峰,魏雪栋,等.肾嫌色细胞癌33例临床分析[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2014,35(2):91-94.
[9] Stevens EV, Banet N, Onesto C, et al. RhoGDI2 antagonizes ovarian carcinoma growth, invasion and metastasis[J]. Small GTPases, 2011,2(4):202-210.
[10] Mack NA, Georgiou M. The interdependence of the Rho GTPases and apicobasal cell polarity[J]. Small GTPases, 2014,5(2):1-16.
[11] Cho H J, Park S M, Kim I K, et al. RhoGDI2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via induction of Snail in gastric cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2014,5(6):1554-1564.
[12] Xu R, Dong Y, Wang L, et al. TAT-RhoGDI2, a novel tumor metastasis suppressor fusion protein: expression, purification and functional evaluation[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2014,98(23):9633-9641.
[13] Li X, Wang J, Zhang X, et al. Overexpression of RhoGDI2 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012,19(1):145-153.
[14] Yi B, Hu Y, Qin G, et al. Depletion of RhoGDI2 expression inhibits the ability of invasion and migration in pancreatic carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2014,34(1):205-212.
[15] Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Richards D, et al. EGF promotes invasion by PANC-1 cells through Rac1/ROS-dependent secretion and activation of MMP-2[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009,379(2):445-450.

