原发性局灶节段性肾小球硬化患者血清可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体检测及其诊断价值
刘国勇,贺理宇,石艳,易法云,肖国球,杨青,佘建,徐海琴,龙庆
原发性局灶节段性肾小球硬化患者血清可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体检测及其诊断价值
刘国勇,贺理宇,石艳,易法云,肖国球,杨青,佘建,徐海琴,龙庆
目的探讨血清可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体(suPAR)水平检测对于诊断原发性局灶节段性肾小球硬化(FSGS)的价值。方法选取常德市职业技术学院附属第一医院于2011年1月—2014年1月收治的临床病理资料完整的103例肾病综合征(NS)患者,包括34例原发性膜性肾病(MN)患者(MN组)、30例原发性FSGS患者(FSGS组)、26例原发性微小病变型肾病(MCD)患者(MCD组)和13例IgA肾病患者(IgAN组)。检测4组患者血清中suPAR水平,并分析FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平与患者临床资料的关系;通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分析suPAR诊断FSGS、MN、MCD的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)、灵敏度和特异度。结果4组患者性别构成、血红蛋白、血清清蛋白、肌酸酐、24 h尿蛋白定量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。4组患者年龄、肾小球滤过率(GFR)、suPAR水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。FSGS组患者GFR低于MN组、MCD组和IgAN组,MN组患者GFR低于MCD组和IgAN组(P<0.05);FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平高于MN组、MCD组和IgAN组(P<0.05);MN组患者血清suPAR水平与MCD组和IgAN组患者比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平与年龄和肌酸酐呈正相关(P<0.05),与GFR呈负相关(P<0.05);血清suPAR水平与性别、血红蛋白、血清清蛋白、24 h尿蛋白定量无直线相关性(P>0.05)。suPAR诊断FSGS的AUC为0.723〔95%CI(0.702,0.769)〕,而suPAR诊断MCD和MN的AUC分别为0.455〔95%CI(0.382,0.486)〕和0.493〔95%CI(0.425,0.538)〕。suPAR诊断FSGS的临界值为3 542 ng/L,其灵敏度为79%,特异度为78%。结论血清suPAR水平>3 542 ng/L对FSGS的诊断具有较大指导意义,suPAR有望成为辅助诊断FSGS的血清标志物。
肾小球硬化症,局灶节段性;可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体;肾病,脂性;肾小球肾炎,膜性
刘国勇,贺理宇,石艳,等.原发性局灶节段性肾小球硬化患者血清可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体检测及其诊断价值[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(30):3682-3685.[www.chinagp.net]
Liu GY,He LY,Shi Y,et al.Examination of suPAR serum level in patients with primary focal segmental glomerular sclerosis and its diagnostic value[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(30):3682-3685.
原发性局灶节段性肾小球硬化(focal segmental glomurular sclerosis,FSGS)是成人肾病综合征(nephrotic syndromes,NS)的常见病因之一[1],是由Rich[2]在1957年首次描述的一个病理形态学诊断名词,指累及部分肾小球毛细血管的非炎症性硬化性疾病。临床多表现为大量蛋白尿、高度水肿和高脂血症。快速准确地对FSGS做出诊断对于能否正确有效治疗十分关键,然而FSGS的诊断面临诸多困难,目前诊断FSGS主要依靠肾穿刺活检术,尚无标准的生化诊断方法,而肾穿刺活检术禁忌证和并发症较多且对机体造成不利影响,不易被患者接受。造成FSGS诊断困难的重要原因之一是FSGS与膜性肾病(membranous nephropathy,MN)和微小病变型肾病(minimal change disease,MCD)临床表现相似,均以蛋白尿和足细胞病变为突出症状且均能导致成人NS的发生,因此鉴别诊断MCD和MN是FSGS诊断的难点。最近有研究报道,在FSGS患者血清中检测到可溶性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物受体(soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor,suPAR)表达异常并认为其可能通过损伤足细胞引发FSGS[3],suPAR有望成为快捷准确诊断FSGS的一种血清标志物[4]。本研究入组103例NS患者,检测FSGS患者血清suPAR水平,探讨suPAR在FSGS诊断中的价值。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象选取常德市职业技术学院附属第一医院于2011年1月—2014年1月收治的24 h尿蛋白定量>3.5 g/24 h,血清清蛋白<30 g/L,高脂血症和水肿等临床表现明显的103例NS患者。所有患者经肾穿刺活检病理诊断,包括34例原发性MN患者(MN组)、30例原发性FSGS患者(FSGS组)、26例原发性MCD患者(MCD组)和13例IgA肾病患者(IgAN组)。原发性FSGS患者均符合诊断标准[5]:肾穿刺活检光镜下有肾小球毛细血管袢的管腔闭塞、足细胞突起消失及绒毛样变性、肾小管萎缩、免疫荧光下IgM和C3阳性、电镜检查可见硬化节段基底膜皱缩、毛细血管腔狭窄或闭塞。患者有下列情况之一者除外:(1)合并药物或感染相关小管间质性肾炎;(2)继发性肾小球疾病:如糖尿病肾病、高血压肾损害、肥胖相关肾损害、有机溶剂肾损害等;(3)中毒、创伤、感染、手术相关急性肾脏损伤;(4)其他:终末期肾脏疾病、多囊肾、肾移植、肿瘤、肝硬化、活动性感染等。本研究由本院伦理委员会讨论并通过,患者签署知情同意书。
1.2 血标本收集患者于肾穿刺活检当天取空腹静脉血5 ml,在4℃条件下,以2 000×g离心15 min,取上清液储存于-80℃待用。
1.3 研究方法详细记录患者一般情况和临床化验指标,包括性别、年龄、血红蛋白、血清清蛋白、肾功能(肌酐、24 h尿蛋白定量等)、肾小球滤过率(glomerular filtration rate,GFR)等。GFR通过CKDEPI公式[6]进行估算;suPAR的检测使用suPARnostic®ELISA试剂盒,步骤严格参照试剂盒说明书进行。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0软件对所有数据进行统计学分析,正态分布计量资料以(±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用q检验;计数资料比较采用χ2检验;相关性采用Pearson相关分析;通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分析suPAR诊断FSGS、MN和MCD的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)、灵敏度和特异度。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 4组患者临床资料比较4组患者性别构成、血红蛋白、血清清蛋白、肌酐、24 h尿蛋白定量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。4组患者年龄、GFR、suPAR水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。FSGS组患者GFR低于MN组、MCD组和IgAN组,MN组患者GFR低于MCD组和IgAN组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平高于MN组、MCD组和IgAN组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);MN组患者血清suPAR水平与MCD组和IgAN组患者比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1)。
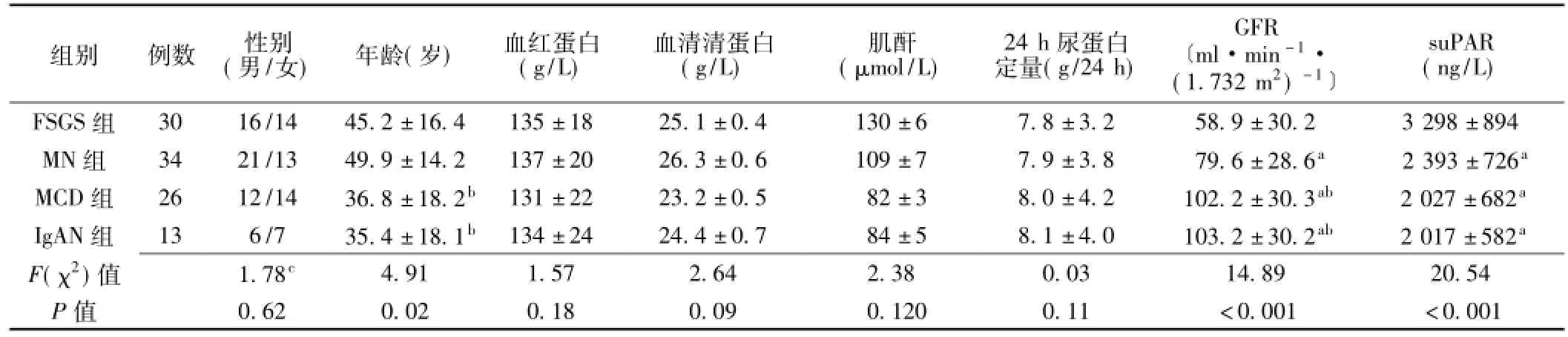
表1 FSGS组、MN组、MCD组和IgAN组患者临床资料比较Table 1 Comparison of clinical data among FSGSgroup,MN group,MCD group and IgAN group
2.2 FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平与临床资料的关系FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平与年龄和肌酐呈正相关(P<0.05),与GFR呈负相关(P<0.05);血清suPAR水平与性别、血红蛋白、血清清蛋白、24 h尿蛋白定量无直线相关性(P>0.05,见表2)。
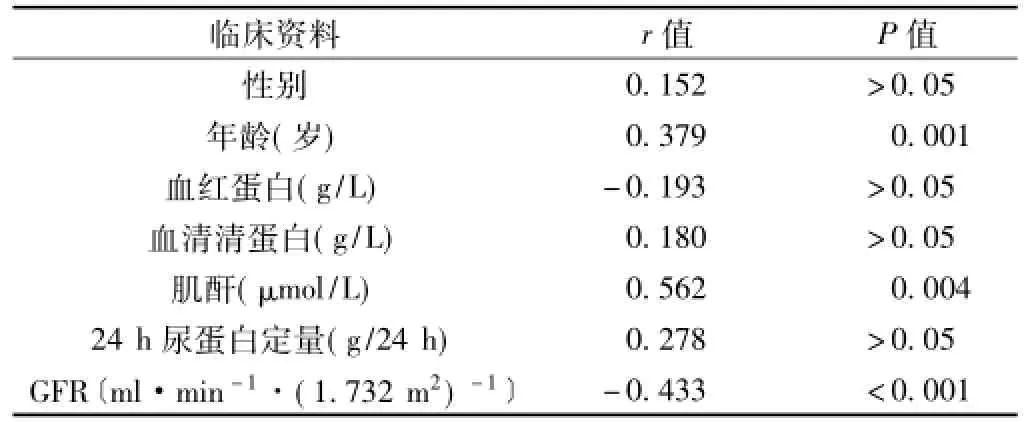
表2 FSGS组患者suPAR水平与临床资料的相关性分析Table 2 Correlation between SuPAR levels and clinical data in patients with FSGS
2.3 suPAR诊断FSGS的价值suPAR诊断FSGS的AUC为0.723〔95%CI(0.702,0.769)〕,而suPAR诊断MCD和MN的AUC分别为0.455〔95%CI (0.382,0.486)〕和0.493〔95%CI(0.425,0.538)〕。suPAR诊断FSGS的临界值为3 542 ng/L,其灵敏度为79%,特异度为78%;而suPAR诊断MN的灵敏度和特异度分别为35%、42%,诊断MCD的灵敏度和特异度分别为42%、48%(见图1)。
3 讨论
FSGS为儿童及成人多种肾脏疾病持续进展至终末期肾病最多见的病理改变,也是肾移植后复发最常见的原因[6]。近年来FSGS的发生率明显增加,而其发病机制仍然不明确,有观点认为水溶性肾小球通透性改变是主要的致病因素[7]。原发性FSGS患者以中青年为主,临床表现为高血压、蛋白尿、血尿、肾功能异常。FSGS、MCD和MN是以大量蛋白尿发病的常见肾小球疾病,3者在临床表现上具有高度的相似性,组织水平上也均表现为足细胞病变[8]。尿激酶受体(uPAR)是纤溶系统中的一个多功能受体,包含由糖基化磷脂酰肌醇锚定的3个结构域,在中性粒细胞、吞噬细胞、活性T细胞、内皮细胞和癌细胞等细胞中表达,可作为尿激酶和其他一些跨膜蛋白的受体,通过与其配体结合介导纤溶酶原的活化、信号传递、细胞黏附和细胞转移等多种生理功能。当uPAR从细胞表面脱落释放进入外周血循环中即成为suPAR。suPAR已被证实在肿瘤的生长、浸润和转移过程中发挥着重要作用[7]。同时有文献报道,suPAR在人类FSGS和尿蛋白动物模型中发挥重要作用[9]。
目前有不少关于原发性FSGS患者血清suPAR的报道。本研究检测所有患者血清suPAR水平与Huang等[10]报道的中国人群suPAR水平接近,但均低于国外相关报道水平[11],可能由于suPAR与人群种族分布有关。本研究发现,FSGS组、MN组、MCD组患者血清中suPAR水平分别为(3 298±894)ng/L、(2 393 ±726)ng/L、(2 027±682)ng/L,均高于正常人群的1 739 ng/L[10];FSGS组患者血清suPAR水平高于MN组和MCD组,而后两组血清中suPAR水平无差异。有研究将血清suPAR具有诊断意义的临界值设置为3 000 ng/L[3],本研究FSGS患者中有24例(80.0%)超过该值。本研究还显示,血清suPAR水平不仅与肾脏疾病类型有关,而且与年龄和肾功能有关,与有关报道结果一致[12]。
本研究发现,血清suPAR水平与GFR呈负相关。有关suPAR和GFR的研究也较多,有学者指出,suPAR分子量约22 kDa,能通过肾小球滤过屏障排出体外,当肾脏受损时,suPAR无法及时排出,在体内积累,可解释suPAR与GFR之间呈负相关的原因[13]。24 h尿蛋白定量是影响FSGS的重要因素之一,为肾功能不全和肾小管病变的危险因素,有研究认为,24 h尿蛋白定量与NS预后有一定相关性[9]。本研究提示,血清suPAR水平与24 h尿蛋白定量无直线相关性。本研究进一步通过比较suPAR诊断不同类型肾脏疾病发现,suPAR诊断FSGS的AUC(0.723)均高于MN(0.493)、MCD(0.455),且通过ROC曲线分析血清suPAR水平用于诊断FSGS的灵敏度和特异度较理想,血清suPAR>3 542 ng/L时,其诊断FSGS的灵敏度为79%、特异度为78%,其对于诊断FSGS具有较高的可信性。
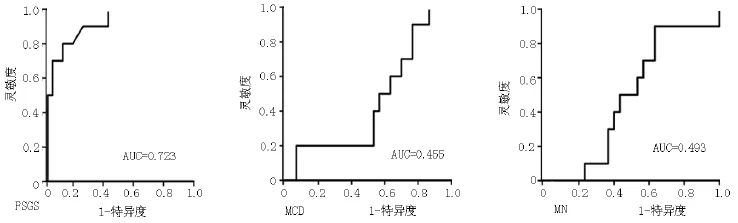
图1 suPAR诊断FSGS、MCD和MN的ROC曲线Figure 1 ROC curve of suPAR for diagnosing FSGS,MCD and MN
综上所述,本研究提示,原发性FSGS患者血清suPAR水平高于MN和MCD患者,血清suPAR>3 542 ng/L对FSGS诊断有一定的提示作用。但受限于本研究样本例数有限,suPAR能否作为鉴别诊断原发性FSGS的血清标志物仍需要进一步深入研究。有研究报道在MN或MCD患者血清中一些因子的高表达,如Garin等[14]报道血清CD80在MCD患者中明显升高而在FSGS患者中无此现象。因此结合多项指标,如suPAR、CD80、血管生成素样蛋白4[15]、肌营养不良蛋白聚糖[16]等,或许可提高对患者NS类型的诊断正确率。
[1]Donald A,Molony MD,Jonathan C,et al.Management of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in adults:minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis[M].Oxford:Wiley-Blackwell,2009:149-157.
[2]Rich AR.A hitherto undescribed vulnerability of the juxtamedullary glomeruli in lipoid nephrosis[J].Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp,1957,100(4):173-186.
[3]Wei C,El Hindi S,Li J,et al.Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis[J].Nat Med,2011,17 (8):952-960.
[4]Cara-Fuentes G,Wei C,Segarra A,et al.CD80 and suPAR in patients with minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis:diagnostic and pathogenic significance[J].Pediatr Nephrol,2014,29(8):1363-1371.
[5]D'Agati VD,Fogo AB,Bruijn JA,et al.Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis:a working proposal[J].Am J Kidney Dis,2004,43(2):368-382.
[6]Levey AS,Stevens LA,Schmid CH,et al.A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J].Ann Intern Med,2009,150 (9):604-612.
[7]Haas M,God frin Y,Oberbauer R,et al.Plasma immunadsorption treatment in patients with primary focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant,1998,13(8): 2013-2016.
[8]Li LS,Liu ZH.Epidemiologic data of renal diseases from a single unit in China:analysis based on 13,519 renal biopsies[J].Kidney Int,2004,66(3):920-923.
[9]Wei C,Möller CC,Altintas MM,et al.Modification of kidney barrier function by the urokinase receptor[J].Nat Med,2008,14(1): 55-63.
[10]Huang J,Liu G,Zhang YM,et al.Plasma soluble urokinase receptor levels are increased but do not distinguish primary from secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis[J].Kidney Int,2013,84(2):366-372.
[11]Zhan LB,Xie B,Hua F,et al.Research on diagnostic value of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor,procalcitonin on ventilator-associated pneumonia and ventilator-associated thacheobronchitis[J].Chinese Journal of General Practice,2015,13(6):914-915,918.(in Chinese)占林兵,谢波,华锋,等.SuPAR、PCT对呼吸机相关肺炎和呼吸机相关气管支气管炎诊断价值的研究[J].中华全科医学,2015,13(6):914-915,918.
[12]Maas RJ,Wetzels JF,Deegens JK.Serum-soluble urokinase receptor concentration in primary FSGS[J].Kidney Int,2012,81(10):1043-1044.
[13]Wada T,Nangaku M,Maruyama S,et al.A multicenter cross-sectional study of circulating soluble urokinase receptor in Japanese patients with glomerular disease[J].Kidney Int,2014,85(3): 641-648.
[14]Garin EH,Mu W,Arthur JM,et al.Urinary CD80 is elevated in minimal change disease but not in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis[J].Kidney Int,2010,78(3):296-302.
[15]Clement LC,Avila-Casado C,MacéC,et al.Podocyte-secreted angiopoietin-like-4 mediates proteinuria in glucocorticoid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome[J].Nat Med,2011,17(1):117-122.
[16]Giannico G,Yang H,Neilson EG,et al.Dystroglycan in the diagnosis of FSGS[J].Clin J Am Soc Nephrol,2009,4(11): 1747-1753.
Examination of suPAR Serum Level in Patients With Primary Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis and Its Diagnostic Value
LIU Guo-yong,HE Li-yu,SHI Yan,et al.Department of Urology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Changde Vocational Technical College,Changde 415000,China
Objective To investigate the value of the examination of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR)serum level in the diagnosis of primary focal segmental glomerular sclerosis(FSGS).Methods The study enrolled 103 NS patients who were admitted into the First Affiliated Hospital of Changde Vocational Technical College from January 2011 to January 2014,including 34 patients with membranous nephropathy(MN group),30 patients with primary FSGS(FSGS group),26 patients with minimal change disease(MCD group)and 13 IgA nephropathy(IgAN group).The serum level of suPAR was tested,and the relation between serum level of suPAR and patients' clinical data were investigated.By ROC curves,the study analyzed the AUC,sensitivity and specificity of suPAR diagnosing FSGS,MN and MCD.Results The four groups were not significantly different in gender composition,hemoglobin,serum albumin,creatinine and 24 h urine protein(P>0.05).The four groups were significantly different in age,GFR and suPAR(P<0.05).FSGS group was lower than MN group,MCD group and IgAN group in GFR,and MN group was lower than MCD group and IgAN group in GFR(P<0.05);FSGS group was higher than MN group,MCD group and IgAN group in suPAR serum level(P<0.05);MN group was not significantly different from MCD group and IgAN group in suPAR serum level(P>0.05).The serum suPAR level of FSGS group was positively correlated with age and creatinine(P<0.05)and was negatively correlated with GFR(P<0.05);suPAR serum level had no correlation with gender,hemoglobin,seryn albumin and 24 h urine protein(P>0.05).The AUC of suPAR diagnosing FSGS was0.723〔95%CI(0.702,0.769)〕,and AUC of suPAR diagnosing MCD and MN was 0.455〔95%CI (0.382,0.486)〕and 0.493〔95%CI(0.425,0.538)〕respectively.The critical value of suPAR diagnosing FSGS was3 542 ng/L,and the sensitivity and specificity were 79%and 78%respectively.Conclusion The serum level of suPAR>3 542 ng/L has important diagnosis value,and suPAR has the potential to become a serum marker for the diagnosis of FSGS.
Glomerulosclerosis,focal segmental;Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor;Nephrosis,lipoid;Glomerulonephritis,membranous
R 692.6
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.30.011
2015-03-21;
2015-07-13)
(本文编辑:李婷婷)
湖南省常德市科技局重点资助项目(2012ZX08)
415000,湖南省常德市职业技术学院附属第一医院肾内科(刘国勇,石艳,易法云,肖国球,杨青,佘建,徐海琴,龙庆);中南大学湘雅二医院肾脏病研究所(贺理宇)
刘国勇,415000,湖南省常德市职业技术学院附属第一医院肾内科;E-mail:liuguoyong2012@126.com

