Current Situation and Development Trends of Pharmaceutical Market in China
WANG Shu-ling, LI Xuan(SchoolofBusinessAdministration,ShenyangPharmaceuticalUniversity,Shenyang110016,China)
Current Situation and Development Trends of Pharmaceutical Market in China
WANG Shu-ling, LI Xuan
(SchoolofBusinessAdministration,ShenyangPharmaceuticalUniversity,Shenyang110016,China)
Objective To discuss the current situation of pharmaceutical market and to predict its development trends in China. Methods Multiple methods were adopted: Firstly, data were collected from internet and through document survey method. Secondly, SWOT methods was used to analyze Chinese pharmaceutical market from four aspects, including advantages, disadvantages, opportunities and threats. Finally comparative analysis methods were used in both R&D investment and market concentration. Results and Conclusion Pharmaceutical market in China lacks of inter-disciplinary talents, and its supervision system is imperfect. Based on the situation of pharmaceutical market, a prediction is made concerning its international status, consumption structure, enterprise situation and its key development areas.
pharmaceutical market; current situation; development trend
In recent years, with the economic growth and the increase of health expenditure, China has entered an aging society, and the expanding coverage of medical insurance has become the driving force for the development of Chinese pharmaceutical industry. In 2003, the output of Chinese pharmaceutical industry reached 310.3 billion yuan and it exceeded 866.7 billion yuan in 2008[1]. In 2013, the output was expected to reach 2255.6 billion yuan[2], and the compound annual growth rate was 19 percent. The average growth rate of Chinese pharmaceutical industrial output was 22 percent, which was faster than GDP growth. As can be seen from Figure 1, China’s pharmaceutical industry, despite the challenges from the national policies and other factors, has been developing rapidly in recent years.
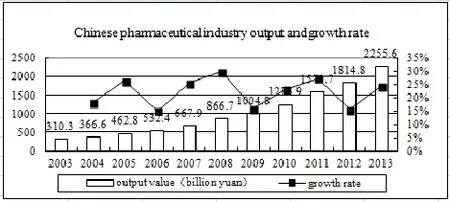
Figure 1 Gross output value of Chinese pharmaceutical industry
1 Situation of China’s pharmaceutical market
1.1 Situation of Chinese medicine production
By the end of 2008, China’s enterprises had produced more than 1500 kinds of pharmaceutical raw materials. The output of penicillin, vitamin C and other medicines were ranked first in the world. A large number of natural medicines, such as berberine and colchicine, have been mass produced and widely used in China. In addition, more than 40 kinds of vaccines can be produced to prevent 26 kinds of virus and bacteria. And the annual production exceededmore than 1 billion doses[3]. The continuous growth of output value and the expanding of the production scale show that China has become the world’s largest producer and exporter of raw medicines.

Figure 2 Quantity variations of Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers
As is shown in Figure 2, the number of Chinese pharmaceutical manufacturers was 4875 in 2013[4]and the number rose by more than 1000 compared to that in the year 2004 (3731[5]). The number fluctuated in the year 2003, 2006 and 2010 due to the renewal of drug production licenses and the implementation of new GMP certification standards. The number of enterprises in 2003, 2006 and 2010 decreased slightly but the overall trend was on the rise and the scale of the enterprises was expanding. The total output value of pharmaceutical industry in 2013 was 2255.6 billion yuan, which was six times more than that in the year 2004 (366.6 billion yuan). In 2013, China approved 106 kinds of new drugs, which showed that the technology and production processes of pharmaceutical enterprises were greatly improved. The main business income of the chemical pharmaceutical industry (including chemical materials production and chemistry preparation production) amounted to 955.08 billion yuan, an increase of 14.8 percent, and it became the main pillar of China’s pharmaceutical industry. Traditional Chinese medicine industry developed steadily and its business income reached 632.44 billion yuan in 2013. At the same time, bio pharmaceutical and medical device industries also developed quickly[2].
1.2 The situation of Chinese medicine circulation
By the end of 2013, the main business income of China’s pharmaceutical circulation enterprises had reached 987.3 billion yuan, an increase of 17 percent. And the total profit was 20.2 billion yuan, an increase of 16 percent. The sales of pharmaceutical wholesale enterprises and pharmaceutical retail enterprises amounted to 562 billion yuan and 741.5 billion yuan respectively, accounting for 43.1 percent and 56.9 percent[6].
In the past ten years, the number of both pharmaceutical retailers and wholesalers kept increasing and the sales of pharmaceutical circulation industry were rising year after year (see Figure 3 and Table 1). Affected by the 2012 version of GSP, the number of retailers and wholesalers declined slightly, but the overall development was good. In 2013, the main business income of the top 100 pharmaceutical wholesalers accounted for 64.3 percent of the drug market, an increase of 0.3 percent compared to the previous year. The top three accounted for 29.7 percent, an increase of 0.9 percent over the previous year[6]. Large chain pharmacies, such as Nep-star drug store, Dashenlin pharmacy and LBX pharmacy, developed rapidly and Nep-star drug store alone had 3007 stores. Now China’s pharmaceutical enterprises are moving towards the direction of a large scale and centralization which shows a good trend of development.
1.3 The situation of drug use in China
As is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, Chinese total health expenditure amounted to 3166.15 billion yuan and the average health expenditure per person was 2326.8 yuan in 2013. From 2003 to 2013, the number of Chinese medical institutions increased from 0.806 million to 0.962 million. The average health expenditure per person was quadrupled in a decade from 509.5 yuan to 2326.8 yuan[7], which indicated that health awareness was enhanced and a large number of people started to spend more money on health care. The increase of drug expenditure and the number of medical institutions does not mean the enhancement of drug use. In fact we still have many problems of drug use. For instance, patients do not take medicines according to drug directions, and they think highly of doctors’ advice rather than the drugs, in addition, essential drugs in the catalogue of hospital have low rate of use, and they abuse antibiotic.
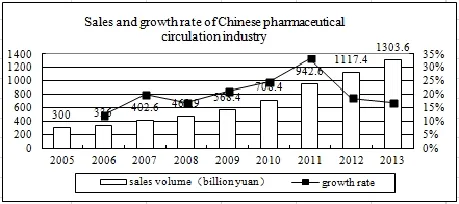
Figure 3 Sales of Chinese pharmaceutical circulation industry
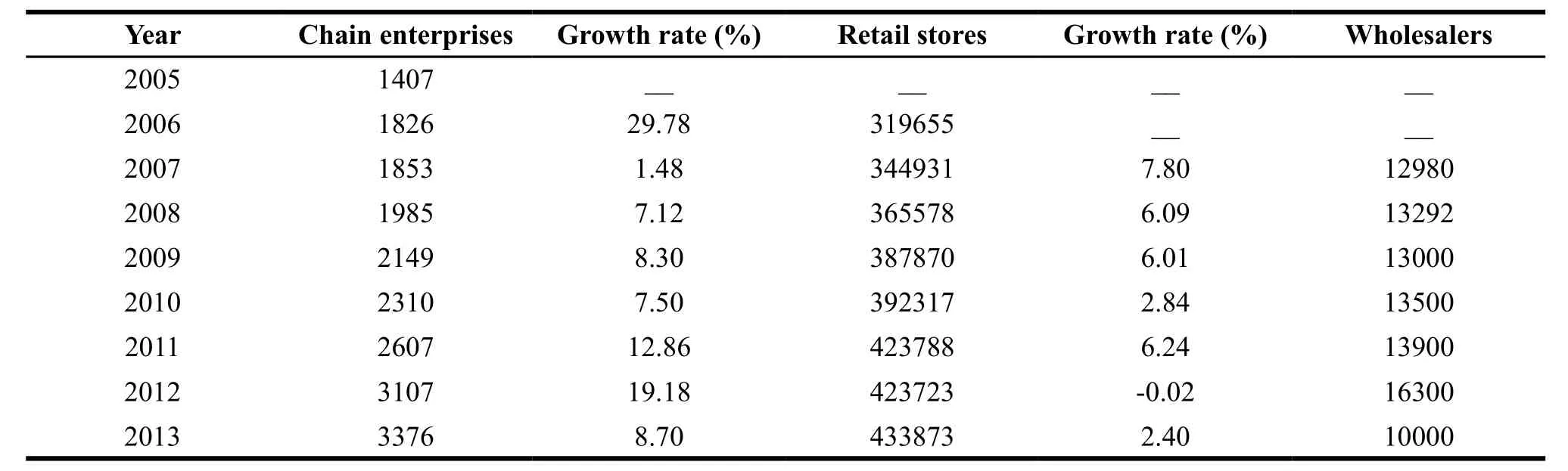
Table 1 Quantity variation of Chinese pharmaceutical trading enterprises

Figure 4 Quantity variations of Chinese medical institutions
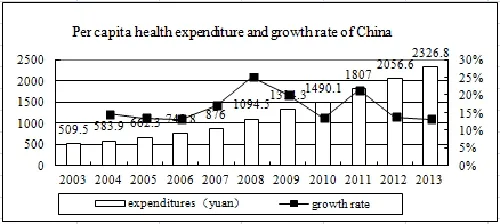
Figure 5 Per-capita health expenditure of China
1.4 Importation and exportation of Chinese medicine
In 2012, the total value of importation and exportation of Chinese pharmaceutical products reached $80.95 billion, an increase of 10.5 percent over the previous year. The exports reached $47.6 billion, an increase of 6.9 percent, while importation reaching $33.35 billion, an increase of 15.9 percent. China’s trade surplus was $14.25 billion with a decrease of 9.5 percent[8].
The export of traditional Chinese medicine accounted for the second trade in recent years, Because of the rising price of raw materials, such as Chinese herb medicine, traditional Chinese medicine industry has become the second largest pharmaceutical industry. The exportation of chemical pharmaceutical products (including two categories of chemical raw materials and chemical agent) deviates from the normal price. The main reason is that chemical raw materials accounts for a large proportion (>80%) of the total exportation and their prices falls significantly. It reflects that China’ pharmaceutical industry is entering a critical period of transformation as it is losing its traditional competitiveness, such as price, and it is also faced with the sluggish market in the world, especially in Europe and the United States.
2 SWOT analysis of China’s pharmaceutical market
In the above paragraphs, data on production, circulation, utilization, importation and exportation of Chinese medicine were collected. In order to specify reasons for the changes, SWOT analysis method is used to analyze the present situation of China’s pharmaceutical market, as is shown in Table 2.

Table 2 SWOT analysis of China’s pharmaceutical market
Pharmaceutical industry is greatly affected by the national policy. The introduction of a series of positive policies has laid a solid foundation for the development of China’s pharmaceutical market. In 2012, some China’s enterprises were appointed to produce the essential drugs of small dosage. It promoted the merger and reorganization of enterprises. The 2013 version of essential drug list required that the second-class hospitals should use essential drugs first, which not only provided the foundation for the growth of drug use but also greatly increased the proportion of the use of essential drugs. New policies on drug bidding, purchasing and other related policies, such as “Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Deepening the Health Care System Reform”and “Plan for the Development of China’s Pharmaceutical Circulation Industry (2011–2015)”, made good plans for drug production, circulation and sales. These policies are good for the development of China’s pharmaceutical industry.
At the end of 2008, there were over 159.89 million people older than 60, about 12 percent of the total population, which showed that China entered the aging society[9]. The increasing chronic patients led to a huge demand for drugs, health service and health care that would promote the expansion of China’s pharmaceutical market. From 2014, more than 440 kinds of patented drugs in the West would expire, bringing a great chance for China’s generics market[10]. In order to control cost, pharmaceutical enterprises in developed countries will gradually transfer their chemical raw medicine to other countries, which promote the development of China’s API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) market and improve the production technology of Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises. China, as a country where the Western pharmaceutical industries will flush in, can obtain a larger share in the international market.
Low market concentration has become the biggest problem hindering the development of Chinese pharmaceutical industry. By the end of 2012, there had been 4700 raw medicine and preparation manufacturers in China, but the sales that exceeded 10 billion yuan accounted for less than 0.5 percent of the total market. Compared with the 2000 pharmaceutical enterprises of America, the number of China’s pharmaceutical enterprises is big, but the scale is small. Generally speaking, the top ten global pharmaceutical enterprises account for 18 percent of sales revenue for R&D investment, while R&D investment in China accounts for only 2 percent[5]. Due to the shortage of funds and technology, most of China’s pharmaceutical enterprises are unwilling to carry out in-depth research, which results in the products with low technological content. Though the current situation of China’s pharmaceutical exportation is optimistic, we still follow the traditional pattern of importation and exportation. Limited by the policies of antidumping and countervailing from U.S.A, India, Europe and other countries, few China’s enterprises can enter the highend medical market, which reflects the irrational structure of importation and exportation.
China has become the largest producer of chemical raw medicine and preparations. Meanwhile, the exportation of preparations continues to grow. But the proportion of preparations exportation is less than 5 percent of the total exportation[11](4.23 percent in 2010, 4.88 percent in 2011). The condition that multinational enterprises play a dominant role in the preparation market weakens the competitive power of China’s pharmaceutical enterprises. Influenced by the mainstream monopoly market, China’s pharmaceutical enterprises are still in the low-end of the global industrial chain. There are other problems as well. For example, RMB appreciation increases the outlet pressure and the improved environmental standards add cost to enterprises. If we can address these problems, China can achieve substantial development.
3 Problems in China’s pharmaceutical market
3.1 The scarcity of compound talents
China has a large number of pharmaceutical and management talents, but there is a small pool of people with the multidisciplinary knowledge and compound background. And people who are familiar with foreign regulations and speak English skillfully in the international pharmaceutical trade are desperately needed. In contrast, India has both large numbers of talents familiar with international trade rules and the advantage of language, making it ahead of China in the international market. Therefore, it is important and urgent for China to cultivate a group of compound talents for further development in overseas markets[12]. To attract and retain talents, China’s enterprises should offer competitive salary and benefits. Another way is to cooperate with universities to attract domestic and foreign talents to stay in the team.
3.2 Low innovation ability and R&D investment lead to low-tech
As to innovation ability and R&D investment, there is a big gap between China’s pharmaceutical enterprises and the enterprises in developed countries though China’s enterprises have an advantage of labor cost. Conversely, low innovation ability and R&D investment will directly lead to plenty of low-tech and low-profit products. This condition intensifies and eventually makes China’s pharmaceutical enterprises far from international highend market. In addition to increasing R&D investment and intensifying technical reform, China’s pharmaceutical enterprises can cooperate with research organizations, universities and other pharmaceutical enterprises at home and abroad to change the situation. Through outsourcing, patent licensing, joint ventures and other methods, China’s enterprises can participate in the international cooperation to improve their own strengths.
3.3 Low industrial concentration and cluster effect
In 2011, the top ten China’s pharmaceutical enterprises had a 15.2 percent market share while the top three of wholesalers and retailers accounted for 26.7 percent, 5.5 percent respectively. Compared with the share of 52.3 percent, 96 percent, 73 percent of America[13], the industrial concentration in China was low. Because of the disorderly competition in China’s pharmaceutical market, the problem of low industrial concentration will exist for a long time.
Pharmaceutical industry is a knowledge-intensive and high-tech industry, while most of China’s pharmaceutical enterprises rely heavily on foreign capital. To pursue low cost, enterprises are often located near the origin of raw materials without distributing around research institutions and universities. It is difficult for China’s enterprises to form the pharmaceutical industrial cluster on the level of knowledge and technology. There are large numbers of pharmaceutical enterprises, circulation enterprisesand retail enterprises in China but the scale is small and the distribution is scattered. Until now, there is no internationally competitive pharmaceutical enterprise in China. Additionally, the inherent geographical and historical reasons as well as different industrial policies in China lead to the low industrial concentration.
3.4 Drug administration system and pharmaceutical logistics system should be improved
“The Twelfth Five-year Plan of China’s Drug Safety”determined the goal of the government is to promote China’s drug electronic supervision system. In addition to supervising the process of production and operation, China’s drug electronic supervision system will monitor the production and procurement plan for special drugs, such as narcotic drugs and psychotropic drugs. In the near future, the supervision system will connect with relevant departments and enterprises’ systems. Therefore, it is necessary to develop the drug electronic supervision system.
“CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Deepening the Health Care System Reform” clearly stated that the government should standardize the order of drug production and circulation, develop the modern pharmace utical logistics and promote the integration of enterprises. Chinese government encouraged pharmaceutical production enterprises, circulation enterprises and retail enterprises to form a large medical logistics center so that they could manage the logistics operation system. Finally the system helped to improve the efficiency of drug circulation and reduce the logistic cost[14].
4 Developing trend of China’s pharmaceutical market in future
As is shown in Figure 1, the average growth rate of China’s pharmaceutical industrial output was 22 percent. It can be estimated that in the year 2018 China’s pharmaceutical industrial output will reach 6090 billion yuan. The expansion of pharmaceutical market will inevitably promote the rapid development of the whole industry chain. Based on the analysis of data, we can see the developing trend of China’s pharmaceutical market has the following four aspects.
4.1 China will become the production center of the global pharmaceutical industry
Nowadays, an increasing number of pharmaceutical enterprises in developed countries transfer their production to developing countries such as China and India. The outsourcing of products in the pharmaceutical industry makes the emerging pharmaceutical market develop rapidly. On one hand, large multinational companies hope to control cost and outsource their non-core business to the low-cost enterprises in developing countries when their patents become expired. On the other hand, these lowcost enterprises also hope to take the chance to enter the international market by making generic drugs. As the main force of the emerging pharmaceutical market, China will become the production center of pharmaceutical transfer in the future.
4.2 New changes in drug consumption
With the improvement of national medical coverage, the medication demand of children and elderly will increase greatly. It will be popular for pharmaceutical enterprises to produce suitable formulations and specifications for them in the future. The probability of people suffering from infectious diseases and digestive diseases decreases, while the prevention of suffering from malignant tumor, cardiovascular diseases and chronic diseases will be stressed. And some preventive health care and self medication will be developed quickly. With the implementation of categorized management of drugs and health care reform, medicines with high efficiency and low price will continue to have large market share and the trend will be further intensified.
4.3 Mergers and reorganizations accelerate, and enterprises develop toward large-scale
As competition intensifies in the pharmaceutical industry, the low-end products can’t meet the need of China’s pharmaceutical market anymore. Enterprises making low value-added products, such as raw materials and medical accessories, should be transferred urgently. Compared with API market, preparation market with a large-scale can get more profits. It is a fact that China’s pharmaceutical market will transfer from API market to preparation market. Facing the intense fierce competition, large API manufacturers begin to move downstream, such as preparation and pharmaceutical industry. At the same time, pharmaceutical enterprises will extend to the upstream industry. The tough competition will definitely decrease the number of pharmaceutical enterprises, but it will expand the scale of some enterprises. Finally, the small-scale and high-cost enterprises and retail companies will merge with firms of large scale and high efficiency.
4.4 Preparation and bio-pharmaceutical industry will be favored
In 2011, the NDRC (national development and reform commission) promulgated the “Catalog for the Guidance of Industrial Structure Adjustment” which encouraged the development and production of new drugs with independent intellectual property rights and promoted the application of modern pharmaceutical technology. In 2012, “The Development of Generic Name of Chemical Pharmaceutical Industry” was promulgated which supported enterprises to produce drugs with expired patent. It promoted the development of leading preparation enterprises as well. “The Twelfth Five-year Plan” also clarified that biomedicine was the core of bio-industry and bio-industry was included in the national strategic emerging industries. These support policies will prompt the pharmaceutical enterprises to insist on the traditional manufacturing, and they should transfer to the production of preparation and biological medicine in the future. Both the preparation and bio-pharmaceutical industries are in line with the government’s plan and the national development strategy. They are the areas of hot pursuit for pharmaceutical industry.
In conclusion, China’s pharmaceutical market still has a lot of problems, such as low R&D investment, low technology, low market centralization, chaotic drug circulation, insufficient pharmaceutical compound talents, high drug price and others. China’s pharmaceutical industry should improve itself in many aspects, such as scientific research, marketing management and core competitiveness. With the strong support of Chinese government, China’s pharmaceutical market will have a bright future.
[1] The Variation of Chinese Pharmaceutical Industrial Output Between 2001 and 2009 [EB/OL]. http://www.askci.com/data/ viewdata193404.html, 2011-06-13.
[2] Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Economic Performance Analysis of Pharmaceutical Industry in 2013 [R]. 2014-04-02.
[3] The State Council Information Office. The Supervision Situation of Chinese Drug Safety [G]. 2008-07-18.
[4] China Food and Drug Administration. Annual Report on the Food and Drug Administration in 2013 [R]. 2014-12-23.
[5] Southern Medical Economic Research Institute. Analysis Report on the Development Trend of Pharmaceutical Industry in 2013 [EB/OL]. http://www.doc88.com/p-2972990993603.html. 2013-02-02.
[6] Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China Department of Market Supervision. Statistical Analysis Report of Medicine Circulation Industry in 2013 [R]. 2014-06-25.
[7] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China’s Health and Family Planning Programs Developed Statistical Bulletin in 2013 [R]. 2014-05-30.
[8] ZENG Liang-liang. Medicine Importation and Exportation is Expected to Grow 12% This Year [N]. Economic Information, 2013-02-08.
[9] Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Report on the Development of Civil Affairs in 2008 [R]. 2009-05-22.
[10] LI Xue-feng. Viagra’s Patent Expired, Making Domestic Enterprises Scramble For it [N]. China Pharmaceutical News, 2013-07-23.
[11] ZOU A-luo, CHEN Yong-fa. SWOT Analysis of the Exportation of Chinese Chemical Medicine [J]. Journal of Frontiers of Medicine, 2012, 2 (7): 363-364.
[12] LIU Guo-en. Development Report of the Chinese Pharmaceutical Industry in 2010 [M]. Beijing: Sciences Press, 2010: 46-49.
[13] GUO Chun-li. The Present Situation and Problems of Drug Circulation System in China [J]. China Economic and Trade Herald, 2013, (30): 53-57.
[14] LI Xiao-ming. Discussion on the Development of Modern Medical Logistics under the Policy of Health Reform [J]. Capital Medicine, 2009, 16 (16): 9.
Author’s information: WANG Shu-ling, Associate professor. Major research area: Retail pharmacy. Tel: 13998302138, E-mail: lingyi50@163.com
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Risk Reviews of Preclinical Pharmaceutical Studies on Traditional Chinese Medicine Injection
- Risks and Risk Control Measures of in vivo Genotoxicity Test in New Drug R&D
- Regional Studies of Bio-pharmaceutical Industry in China
- GMP Regulations in China: Problems and Countermeasures
- Analysis and Evaluation of Measures for the Administration of Medical Device Registration
- Australian PBS and Its Enlightenment to Drug Price Reform in China

