m icroRNA联合PET-CT对头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的诊断价值
许彤,阎慧丽,许挺
山东大学附属省立医院 a.耳鼻喉科;b.内分泌科;c.影像科,山东 济南250021
m icroRNA联合PET-CT对头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的诊断价值
许彤a,阎慧丽b,许挺c
山东大学附属省立医院 a.耳鼻喉科;b.内分泌科;c.影像科,山东 济南250021
目的 探讨一种新型microRNA试剂盒联合正电子发射断层/计算机断层扫描(PET/CT)对头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的诊断价值。方法 选取40例行全身PET/CT检查的头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后病例,提取外周血标本,应用包含4种m icroRNAs的试剂盒诊断肿瘤术后转移,并与病理诊断结果进行比较,分析两种检查方法及联合检查的敏感性、特异性及准确性。结果 40例病例中,28例经病理诊断为头颈部鳞状细胞癌转移。m icroRNA试剂盒诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的灵敏度为96.43%,特异度为83.33%,准确度为92.50%;PET/CT诊断的灵敏度为89.29%,特异度为91.67%,准确度为90.00%;两者联合诊断的灵敏度为100%,特异度为83.33%,准确度为95.00%。结论 PET/CT诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的特异性较m icroRNA试剂盒高,而敏感性不足,m icroRNA试剂盒对PET/CT诊断具有补充作用,两者联合应用是诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的更为理想的方法。
头颈部鳞状细胞癌;正电子发射断层/计算机断层扫描;m icroRNA;肿瘤标志物
头颈部鳞状细胞癌(Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer,HNSCC)是世界第六大肿瘤,占每年世界范围内650,000新发癌症病例的6%[1-5]。头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者中,约有30%~50%的病例手术后复发或转移[6],其生存时间与是否转移密切相关,因此早期发现复发和转移病灶对及时治疗意义重大。常规影像学检查手段(如B超、CT、MRI等)具有一定的局限性,作为CT和核医学分子影像设备的结合,PET/CT检查可辅助诊断术后转移,发现潜在病灶,为更早发现病灶提供可能,但仍然会出现误诊或漏诊;同时,由于PET/CT价格较为昂贵,限制了其临床应用。而外周血microRNA,因其灵敏度高、稳定性好、创伤性小,在肿瘤诊断中的应用也越来越受到关注。本研究选取40例头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后病例,行PET/CT检查的同时,采集外周血,应用自行研发的microRNA试剂盒检测,旨在探讨microRNA试剂盒联合PET/CT在头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移中的诊断价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
选择2007年1月~2014年2月于山东省立医院医学影像中心诊治的40例头颈部鳞状细胞癌患者。其中,男28例,女12例,年龄35~76岁,平均(49.5±8.9)岁。舌鳞状细胞癌10例,口底鳞状细胞癌8例,喉鳞状细胞癌5例,鼻腔鼻窦癌7例,牙龈癌4例,唇癌3例,下咽癌3例。所有患者均于本研究开始前于山东省立医院行原发癌及对应淋巴清扫术,术后时间6~39个月,平均16个月;患者因术后查体、自觉不适、临床怀疑肿瘤转移等原因,于山东省立医院影像中心行PET/CT检查。所有病例均在PET/CT检查前取血清样本。
1.2 仪器与方法
1.2.1 PET/CT检查
采用Discovery Lightspeed PET/CT机,嘱患者检查前空腹4~6 h,控制血糖≤7.0 mmol/L,在安静、避光、平卧状态下,以3.7~5.55 MBq(0.10~0.15 mCi)/kg体重注射显影剂。50~60 min后,采用三维采集及飞行时间(Time of Flight,TOF)采集技术,确定扫描部位,检查范围自头顶至大腿中部,共6~7个床位,每床位3 min,并对CT数据进行衰减校正,采用迭代法获得全身各方位重建的融合图像。采用半定量方法进行诊断,即最大标准摄取值(SUVmax)>2.5作为判断阳性的标准。对初次检查发现病变的部位于注射药物后2 h进行延迟扫描,同时排除正常生理性摄取。
1.2.2 microRNA试剂盒检查
microRNA试剂盒包含4种microRNA的反转录-聚合酶链反应(Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction,RT-PCR)引物,分别为:miR155、miR324、miR23a、miR181。引物设计参照文献,引物合成由上海生工生物技术公司完成。采用mirVana miRNA提取试剂盒(美国Ambio公司),miRcute miRNA cDNA第一链合成试剂盒(中国天根生化公司),miRcute miRNA荧光定量检测试剂盒(中国天根生化公司),MJMini梯度PCR仪(美国Biorad公司),IQ5 PCR实时荧光定量检测系统(美国Biorad公司)。
所有患者均于PET/CT检查前采集静脉外周血,外周血经3000 r/min离心,将分离出的血清置-80 ℃冰箱保存待测,按照miRVana PARIS试剂盒的使用说明书进行血清总RNA的提取。提取的总RNA进行下一步的反转录,配制反应体系,充分混匀后进行反转录。反应总体积为20μL,反应条件设定为95 ℃,10 min;95 ℃,15 s;60 ℃,1 min;40个循环。以5S rRNA为内参,miRNA的表达量表示为F= 2-ΔΔct,计算公式为:-ΔΔct=ΔctmicroRNA-Δct5SrRNA。以4种miRNA试剂盒检测结果中有任意不小于三种miRNA表达上调作为阳性判断标准。
1.3 临床诊断方法
所有患者均随访3个月,由2位副主任以上医师采用双盲法进行诊断。根据以下条件诊断肿瘤是否转移:①再次手术或活检病理证实肿瘤转移;②超声、CT、MRI或后续PET/CT等影像学检查发现新发病灶或病灶增大;④临床治疗过程及病情发展。
1.4 统计分析
采用SPSS 18.0软件进行统计分析。以临床最终诊断为金标准,计算PET/CT、microRNA试剂盒及联合检查诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的灵敏度、特异度、准确度。计算公式:准确度=(真阳性+真阴性)/(真阳性+假阴性+真阴性+假阳性)×100%;特异度=真阴性/(真阴性+假阳性)×100%;灵敏度=真阳性/(真阳性+假阴性)×100%。
2 结果
2.1 临床诊断结果
40例病例中,28例经临床诊断为肿瘤术后转移,其中15例经组织病理学证实,13例经其他影像学检查及随访确诊;另12例病例至2014年6月1日未发现肿瘤转移。
2.2 PET/CT检查结果
40例病例中,26例经PET/CT检查为阳性,其中1例结合临床诊断为不相关炎症,25例结合临床诊断为肿瘤转移(图1);14例阴性,其中3例结合临床诊断为肿瘤转移,11例至2014年6月1日未发现肿瘤转移(表1)。
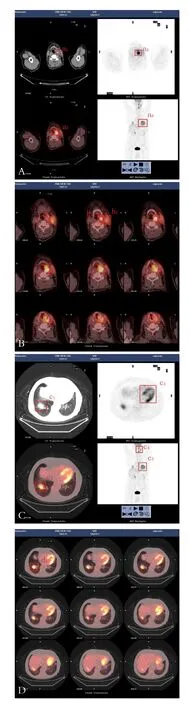
图1 PET/CT影像
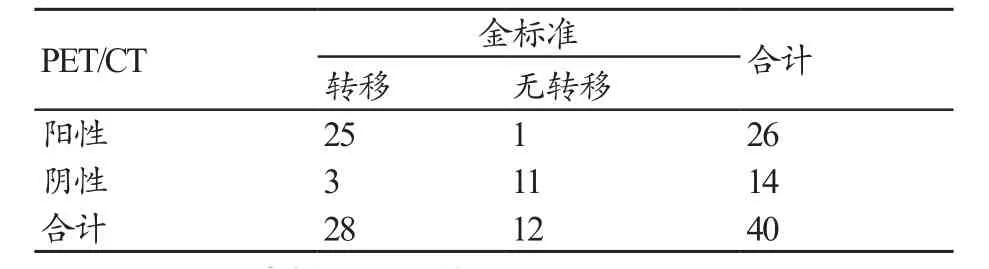
表1 PET/CT检查结果
2.3 m icroRNA试剂盒检查结果
40例病例中,29例经microRNA试剂盒检测为阳性,其中27例结合临床诊断为肿瘤转移,2例至2014年6月1日未发现肿瘤转移;11例阴性,其中1例结合临床诊断为肿瘤转移,10例至2014年6月1日未发现肿瘤转移(表2)。
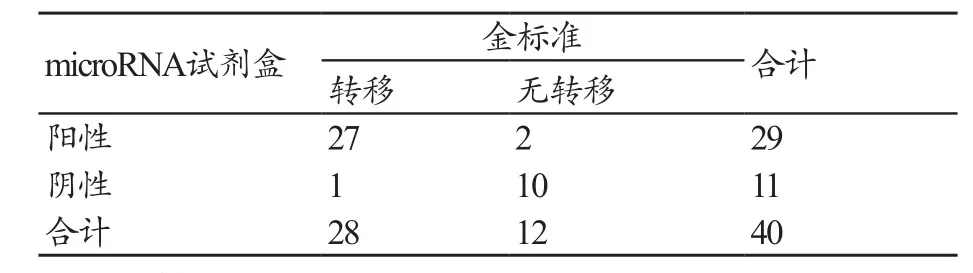
表2 m icroRNA试剂盒检查结果
2.4 PET/CT联合m icroRNA试剂盒检查结果
两种方法有一种为阳性时判断为阳性,同时为阴性时判断为阴性。28例结合临床诊断为术后转移;10例为PET/CT阴性且microRNA试剂盒阴性(表3)。
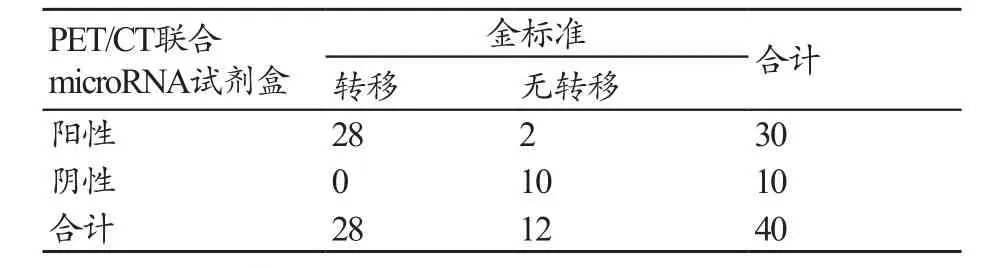
表3 PET/CT联合microRNA试剂盒检查结果
2.5 统计分析结果
以临床最终诊断为金标准,应用公式计算得,PET/CT诊断的灵敏度为89.29%,特异度为91.67%,准确度为90.00%;microRNA试剂盒诊断的灵敏度为96.43%,特异度为83.33%,准确度为92.50%;两者联合诊断的灵敏度为100%,特异度为83.33%,准确度为95.00%。
3 讨论
PET/CT与传统CT、MRI等的成像原理不同,它是将解剖成像、葡萄糖代谢及功能显像融合在一起的分子影像技术,反映组织和病灶区域糖代谢的差异[7-9]。分析图像时,解剖及代谢的统一是确诊的立足点,但在日常诊断工作中,具有空间分辨率较低等缺点,经常会遇到解剖及代谢不统一的情况,给诊断带来了不确定因素[10-11]。本研究中,以临床最终诊断为金标准,PET/CT诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移的灵敏度为89.29%,特异度为91.67%,准确度为90.00%,仍存在着假阳性、假阴性的误判断。同时,由于PET/CT价格较为昂贵,限制了其临床应用。
微小RNAs(microRNAs,miRNAs)是一类全长为19~25个核糖核苷酸的非编码调控单链小分子RNA,由一段具有发卡环结构的单链RNA前体剪切后生成,通过与目标mRNA分子的3’-端非编码区域(3-UTR)互补配对,抑制目标mRNA的翻译,实现转录后水平的表达调控。根据miRBase数据库,现已发现的miRNAs达9500多个,大量研究发现microRNA与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关。同时,近年来的研究发现,外周血miRNAs不仅具有稳定的物理、化学状态,且其在肿瘤患者中的表达量与正常人明显不同,越来越多的文献报道其作为一种特异的肿瘤标志物的价值。大量研究证明,外周血miRNAs在前列腺癌、胃癌、肺癌、结直肠癌和乳腺癌等发生的早期即有明显的改变。
在头颈鳞癌的发生、发展、治疗及预后等方面,microRNAs同样起着重要作用,国内外学者也做了大量相关研究。2009年Wong等[12]通过qRT-PCR技术分析了4种舌癌,结果发现早期舌癌患者与进展性舌癌患者血液中的miR-184含量均明显增高。而手术切除原发灶后,miR-184含量明显下降。2010年Liu等[13]报道,口腔鳞癌患者血液中miR-31表达上调,并且与年龄等因素相关。同时,在手术切除肿瘤后,表达明显下降。同年,Lin等[14]也发现,miR-24在口腔鳞癌患者的血液中过表达。2011年,Yang等[15]发现组织与血液中miR-181的过表达与口腔鳞癌患者淋巴结转移、不良预后有密切相关性。2012年,Maclellan[16]通过对原位癌等高风险口腔病损患者的血清进行研究,发现有15种miRNAs明显上调,而5种miRNAs(miR-16、let-7b、miR-338-3p、miR-223、miR-29a)明显下调。本研究选取4种microRNA(miR-155、miR-324、miR-23a、miR-181)组成试剂盒,分析其在诊断头颈鳞癌术后转移中的应用价值。结果表明,其灵敏度为96.43%,特异度为83.33%,准确度为92.50%,较PET/CT更为灵敏,而特异性不足。
本研究将microRNA试剂盒与PET/CT联合应用,诊断头颈部鳞状细胞癌术后转移,以任意一项阳性即判断为转移,两项检查均为阴性判断为无转移,特异性虽未提高,但其敏感性、准确度明显增加,是比较理想的检查手段,对于指导再次手术或化疗、放疗后随访有重要意义。
[1]Jemal A,Bray F,Center MM,et al.Global cancer statistics[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2011,61(2):69-90.
[2]Davison JM,O zonoff A,Im sande HM,et al.Squamous cell carcinoma of the palatine tonsils:FDG standardized uptake value ratio as a biomarker to differentiate tonsillar carcinoma from physiologic uptake[J].Radiology,2010,255(2):578-585.
[3]Imsande HM,Davison JM,Truong MT,et al.Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT as a predictive biomarker of outcome in patients w ith head-and-neck non-squamous cell carcinoma[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol,2011,197(4):976-980.
[4]Dibble EH,Alvarez AC,Truong MT,et al.18F-FDG metabolic tumor volume and total glycolytic activity of oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer:adding value to clinical staging[J].J Nucl Med,2012,53(5):709-715.
[5]Paidpally V,Chirindel A,Lam S,et al.FDG-PET/CT imaging biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinom a[J].Imaging Med,2012,4(6):633-647.
[6]Gupta T,M aster Z,Kannan S,et al.Diagnostic performance of post-treatment FDG PET or FDG PET/CT imaging in head and neck cancer:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging,2011,38(11):2083-2095.
[7]Curry JM,Sprandio J,Cognetti D,et al.Tumor m icroenvironment in head and neck squam ous cell carcinom a[J].Sem in Oncol,2014,41(2):217-234.
[8]Kim JY,Lee SW,Kim JS,et al.Diagnostic value of neck node status using 18F-FDG PET for salivary duct carcinoma of the major salivary glands[J].J Nucl Med,2012,53(6):881-886.
[9]Tatci E,Ozmen O,Gokcek A,et al.18F-FDG PET/CT rarely provides additional information other than primary tumor detection in patients w ith pulmonary carcinoid tumors[J].Ann Thorac Med,2014,9(4):227-231.
[10]Ye S,W ang W L,Zhao K.F-18 FDG hyperm etabolism in mass-form ing focal pancreatitis and old hepatic schistosom iasis w ith granulomatous inflammation m isdiagnosed by PET/CT imaging[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2014,7(9):6339-6344.
[11]Heusch P,Sproll C,Buchbender C,et al.Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound,18F-FDG-PET/CT,and fused 18F-FDGPET-M R im ages w ith DW I fo r the detection o f cervical lymph node metastases of HNSCC[J].Clin Oral Investig,2014,18(3):969-978.
[12]W ong TS,Ho WK,Chan JY,et al.M ature m iR-184 and squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue[J].Scientific World Journal,2009,9:130-132.
[13]Liu CJ,Kao SY,Tu HF,et al.Increase of m icroRNA m iR-31 level in plasma could be a potential marker of oral cancer[J].Oral Dis,2010,16(4):360-364.
[14]Lin SC,Liu CJ,Lin JA,et al.m iR-24 up-regulation in oral carcinom a:positive association from clinical and in vitro analysis[J].Oral Oncol,2010,46(3):204-208.
[15]Yang CC,Hung PS,W ang PW,et al.m iR-181 as a putative biomarker for lymph-node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Oral Pathol Med,2011,40(5):397-404.
[16]Maclellan SA,Law son J,Baik J,et al.Differential expression of m iRNAs in the serum of patients w ith high-risk oral lesions[J].Cancer Med,2012,1(2):268-274.
App lication Value of Combination Value of M icro-RNA and PET-CT in Diagnosis of Postoperative M etastasis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancers
XU Tonga, YAN Hui-lib, XU Tingc
a. Departm ent o f O to laryngo logy;b. Department of Endocrinology;c. Department of Imaging, Shandong Prov incia l Hosp ita l A ffiliated to Shandong University, Jinan Shandong 250021, China
Ob jective To discuss the application value of positron em ission tomography/computed tomography(PET/CT)and m icro-RNA in diagnosis of post-operative metastasis of head and neck squamous cell cancers. Methods A ltogether 40 patients w ith surgical history of head and neck cancer simultaneously underwent the examination of PET/CT in combination w ith a micro-RNA kit that was comprised four micro-RNAs. The results were compared w ith the final diagnosis so as to analyze the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of these two diagnosis methods. Results Of those 40 cases, 28 were found w ith metastases of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as was diagnosed pathologically. The sensitivity, specifi city and accuracy of the m icro-RNA kit for diagnosis of metastasis were 96.43%, 83.33% and 92.50%. While, those of PET/CT were 89.29%, 91.67% and 90.00%, respectively. Promisingly, those by the detection of PET/CT combined w ith the micro-RNA kit were 100%, 83.33% and 95.00%. Conc lusion PET/CT showed higher specificity and lower sensitivity in assessment of postoperative metastasis of head and neck cancers than those by the m icro-RNA kit. The m icro-RNA kit detection may be used as a supplementary tool to PET/CT exam ination. Combined use of the two exam inations was an ideal strategy for detecting the metastases of head and neck cancers.
head and neck squamous cell cancer;positron em ission tomography/computed tomography;micro-RNA;tumor markers
R739.91;R814.42
B
10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2015.10.014
1674-1633(2015)10-0051-04
2015-03-02
2015-04-02
山东省科技发展计划(2014GSF1181)。
许挺,主管护师。
通讯作者邮箱:d594251@163.com

