SPECT/MRI双模态显像剂的制备及其性质研究
王 晓,崔海平,史旭东,梁积新,孙钰林,申一鸣,沈浪涛,*
(1.中国原子能科学研究院国家同位素工程技术研究中心,北京 102413;2.原子高科股份有限公司,北京 102413)
王 晓1,2,崔海平1,2,史旭东1,2,梁积新1,孙钰林2,申一鸣1,2,沈浪涛1,2,*
(1.中国原子能科学研究院国家同位素工程技术研究中心,北京 102413;2.原子高科股份有限公司,北京 102413)
摘要:为制备纳米材料SPION-DMSA及其标记物,探讨该标记物作为SPECT/MRI双模态显像剂的可能性,本工作先采用高温热解法合成了SPION,然后用DMSA包覆获得SPIONDMSA并进行各种表征。用99Tcm标记SPION-DMSA得到,并对该标记物进行荷U87 MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠的生物分布和显像研究。实验结果表明,SPION-DMSA具有超顺磁性,99Tcm标记率大于98%。在血液中清除较快,在肝脏中的摄取较高。与在小鼠体内的生物分布差异较大。在肿瘤中并没有明显的摄取。SPION-DMSA和的MRI和SPECT显像结果表明,SPIONDMSA和的肿瘤被动靶向作用有限。因此,对于荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠,还不是一种理想的SPECT/MRI双模态显像剂。
关键词:超顺磁氧化铁纳米颗粒;二巯基丁二酸;99Tcm;SPECT/MRI双模态显像剂
医学影像是现代医学的重要工具。磁共振成像(MRI)和单光子发射计算机断层成像(SPECT)已在临床得到了广泛应用。MRI没有电离辐射,具有极好的软组织反差、很高的空间分辨率(<1 mm),能提供解剖、生理和代谢等信息,但灵敏度较低(10-3~10-5mol/L)。SPECT具有很高的灵敏度(10-10~10-11mol/L),但空间分辨率较低(5~12 mm),且有一定的电离辐射[1-2]。当前将两种或多种影像技术融合是影像技术发展的趋势之一。SPECT/MRI既可提供检测对象功能和代谢方面的变化,又能在亚毫米水平上提供组织信息的一系列生物参数及三维结构成像和高分辨率信息[3]。SPECT显像依赖于发射γ光子的放射性药物。同样,为了获得最佳的反差效果,MRI成像也往往需要使用磁共振造影剂。SPECT/MRI技术的发展与SPECT/MRI双模态显像剂的研发进展密切相关[4]。
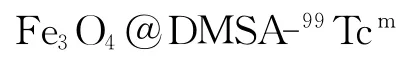

1 实验材料
1.1 仪器及试剂
WGL-230 B型真空干燥箱,天津泰斯特仪器有限公司;高纯水器,美国Millipore公司;IRAffinity-1傅里叶变换红外光谱仪,日本SHIMADAZU公司;JEM2100F透射电镜,日本电子株式会社;Nano ZS动态光散射纳米粒度分析仪,英国Malvern公司;BKT-4500Z振动样品磁强计,美国Quantum Design公司;1470自动γ计数器,芬兰Perkin Elmer公司;CRC-15 R放射性活度计,美国Capintec公司;AR-2000薄层扫描仪,德国Eckert Ziegler公司;NanoScan SPECT/CT,匈牙利MEDISO公司;7.0 T小动物磁共振成像仪,美国Varian公司。
乙酰丙酮铁,纯度98%,百灵威公司;1,2-十六烷二醇,纯度98%,TCI公司;油酸,分析纯,阿拉丁试剂公司;油胺,纯度90%,Adamasbeta公司;meso-2,3-二巯基丁二酸,纯度98%,Adamas-beta公司;Na99TcmO4淋洗液,原子高科股份有限公司。其他化学试剂均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 实验动物
昆明小白鼠,雌性,重约18~20 g,一级,由中国医学科学院肿瘤研究所提供。动物模型:取4~5周龄Balb/c雌性裸鼠,右前肢腋下接种5×106个U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤细胞,肿瘤平均直径达到8~10 mm时用于实验,SPF级,由中国医学科学院肿瘤研究所提供。
2 实验方法
2.1 SPION-DMSA的合成
SPION-DMSA的合成路线示于图1。
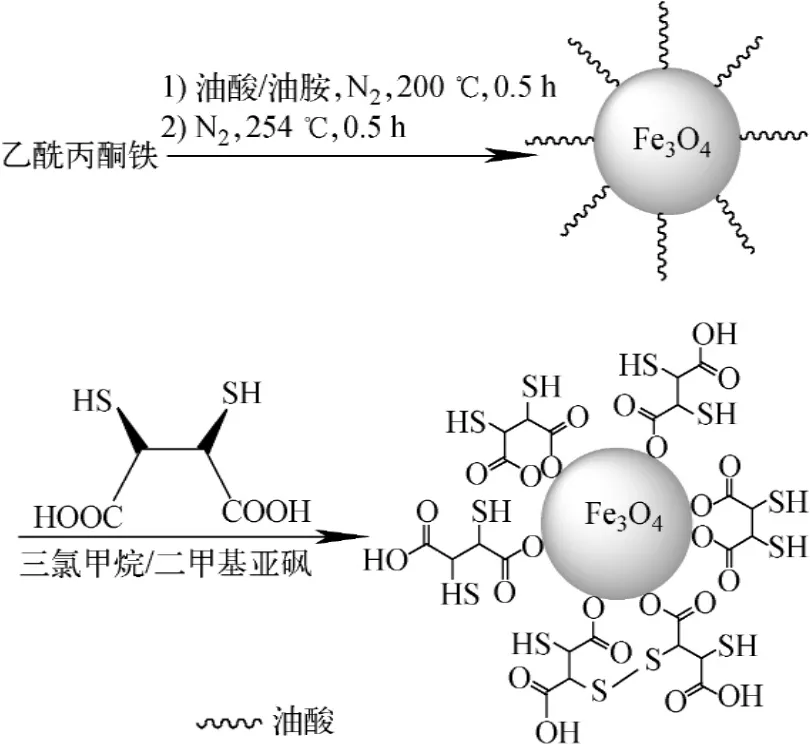
图1 SPION-DMSA合成路线Fig.1 Synthetic route of SPION-DMSA
称取2 mmol乙酰丙酮铁放入三口烧瓶中,加入10 mmol 1,2-十六烷二醇、6 mmol油酸、6 mmol油胺和20 m L苯醚,通N2保护并用磁力搅拌,先加热至200℃回流30 min,继续升温至254℃并回流30 min,然后,移除加热源,待溶液自然冷却至室温后加入40 m L无水乙醇,于离心机中以3 500 r/min离心20 min,沉淀用乙醇洗涤2~3次,置真空干燥箱中干燥,得到黑色粉末0.15 g。
称取100 mg SPION,并加入10 m L三氯甲烷和50μL三乙胺,与含10 m L二甲基亚砜的50 mg DMSA混合,于油浴中加热至60℃并机械搅拌18 h,离心后沉淀物用乙醇洗涤3次。沉淀物中加入10 m L乙醇和50μL三乙胺,与含10 m L二甲基亚砜的50 mg DMSA混合,于油浴中加热至60℃并机械搅拌18 h,离心后沉淀用乙醇洗涤,并重复3次。向沉淀中加入10 mL蒸馏水,振荡后透析48 h,过0.22μm膜,得SPION-DMSA。
样品和产物的扫描电镜(TEM)分析:将SPION和SPION-DMSA分别溶于己烷和水中,滴在铜网上,自然干燥,观察形貌及大小分布。动态光散射(DLS)分析:将合适浓度的样品溶液倒入石英比色皿中,用633 nm的He/Ne激光进行扫描测定。磁性VSM的测定:将固体样品装入约7 mm的棉签管中,两端封口后于样品舱中进行测试。红外光谱(FT-IR)分析:取少量的固体粉末与KBr混合后压片进行FG-IR分析。
2.299Tcm的标记与质控分析

2.3 体外稳定性
取标记率达到95%以上的标记物0.1 mL,分别与0.9 mL生理盐水、10%人血清白蛋白混合,振荡摇匀,室温下静置,分别于0.5、1、2、4、6 h取样,用TLC法检测标记物的放化纯度。
2.4 生物分布与显像
取荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠9只,随机分成3组,每组3只,经尾静脉注射0.1 mL标记物(约0.74 MBq),于注射后0.5、2、4 h分别摘眼球取血,继而断颈处死并解剖,取心、肝、脾、肺、肾、胃、肠、肉、骨、脑、瘤等称重,用γ计数器测定放射性计数,经衰变校正后,计算每克组织的百分注射剂量率(%ID/g)及肿瘤与正常组织的摄取比T/NT。
取荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠4只,随机分成2组,每组2只,一组经尾静脉注射0.1 m L标记物(约37.0 MBq),于给药后0.5 h和4 h进行SPECT显像。另一组经尾静脉注射同样量的未标记物SPION-DMSA,于给药后0.5 h和4 h进行MRI显像。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 SPION-DMSA的表征
SPION、SPION-DMSA和DMSA的红外光谱如图2所示。图2曲线a中592 cm-1处的宽峰对应Fe—O键的振动;2 920 cm-1和2 848 cm-1处的峰分别对应油酸中—CH2基团的不对称和对称伸缩振动。这表明SPION表面被油酸覆盖。在图2曲线b中仍存在592 cm-1处的峰,但强度有所减弱,2 920 cm-1和2 848 cm-1处峰则变得很微弱,而在1 606 cm-1和1 386 cm-1处的峰明显是DMSA中—COO基团的不对称和对称伸缩振动所致。这充分说明DMSA已被成功地包覆在SPION表面,DMSA可能通过—COO螯合在SPION表面[15-16]。SPION-DMSA的可能结构如图1所示。
SPION和SPION-DMSA的TEM图像如图3所示。图3a显示,SPION纳米颗粒大小均匀,呈球形,粒径约为4 nm。由图3b可见,SPION-DMSA的粒径明显增大,且粒径分布较不均匀,约在60~100 nm之间。SPIONDMSA粒径增大可能是因为DMSA在SPION上包覆并且DMSA之间发生了S—S分子间的交联[17]。

图2 SPION、SPION-DMSA和DMSA的红外光谱Fig.2 FT-IR spectra of SPION,SPION-DMSA and DMSA

图3 SPION(a)和SPION-DMSA(b)的TEM图像Fig.3 TEM images of SPION(a)and SPION-DMSA(b)
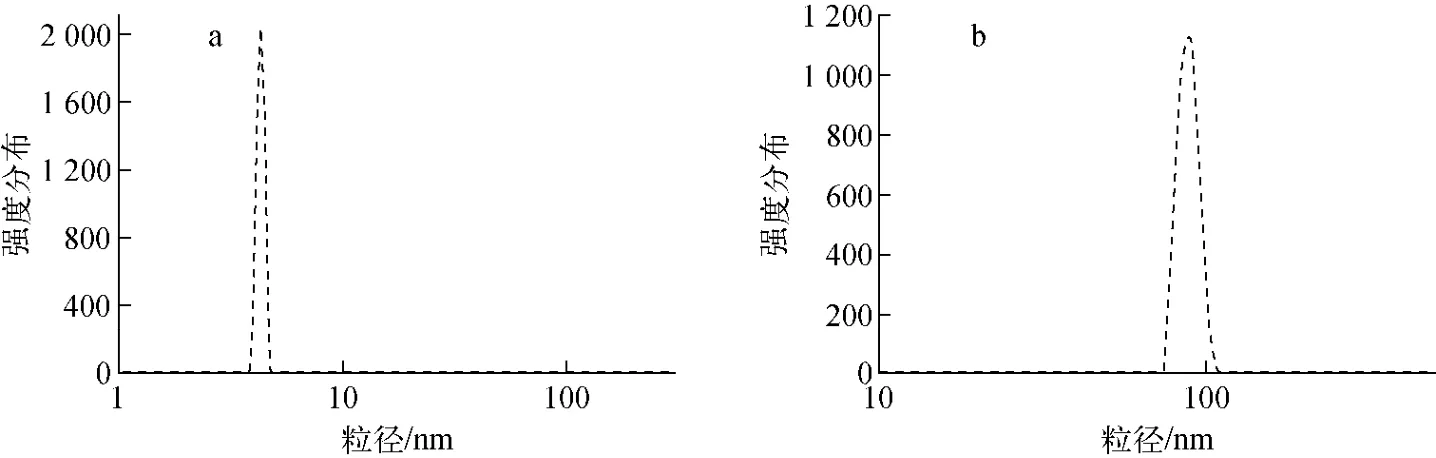
图4 SPION(a)和SPION-DMSA(b)的水合动力学直径分布Fig.4 Hydrodynamic size distribution of SPION(a)and SPION-DMSA(b)
在溶液状态中,SPION和SPION-DMSA的DLS结果如图4所示。强度权重的DLS显示均为单峰,即两种纳米粒子的粒径大小分别集中在约4nm和80nm处,该结果与TEM结果相互印证。
SPION和SPION-DMSA的磁性分析如图5所示。图5的磁滞回线表明,随着外加磁场强度的增大,纳米粒子的磁化强度也随之增大,当外加磁场强度增大到一定值(10 000Oe)时,磁化强度增速趋缓,逐渐达到磁饱和。SPION和SPION-DMSA的饱和磁化强度分别为54.6和26.0emu/g。SPION-DMSA的饱和磁化强度优于文献[14]的报道。由于DMSA包覆层的存在,虽然SPION-DMSA的饱和磁化强度较SPION明显减小,但剩磁和矫顽力几乎可忽略不计,因此,所制得的SPION-DMSA仍具有良好的超顺磁性。SPION-DMSA可作为下一步构筑SPECT/MRI双模态影像剂的良好平台。
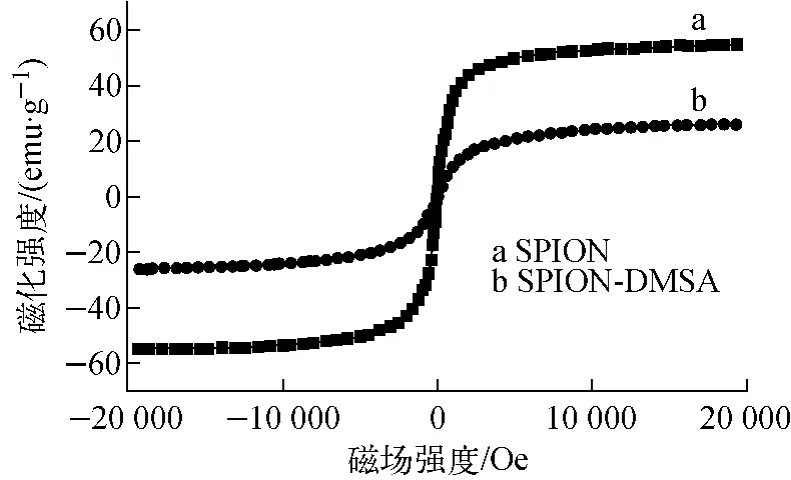
图5 SPION和SPION-DMSA的磁滞回线Fig.5 Hysteresis loops of SPION and SPION-DMSA
3.299Tcm的标记与质控分析
3.3 体外稳定性

图6 SPION-DMSA-99Tcm的TLC色谱Fig.6 TLC chromatography ofSPION-DMSA-99Tcm
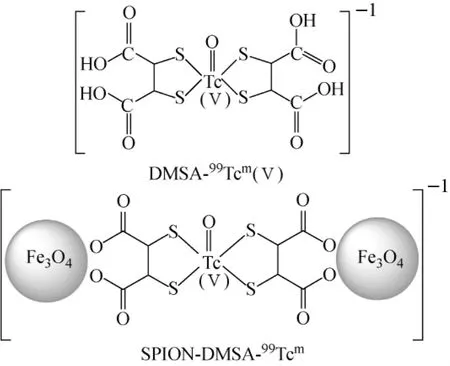
图7 DMSA-99Tcm(Ⅴ)和SPION-DMSA-99Tcm的可能结构Fig.7 Possible structures of DMSA-99Tcm(Ⅴ)and SPION-DMSA-99Tcm
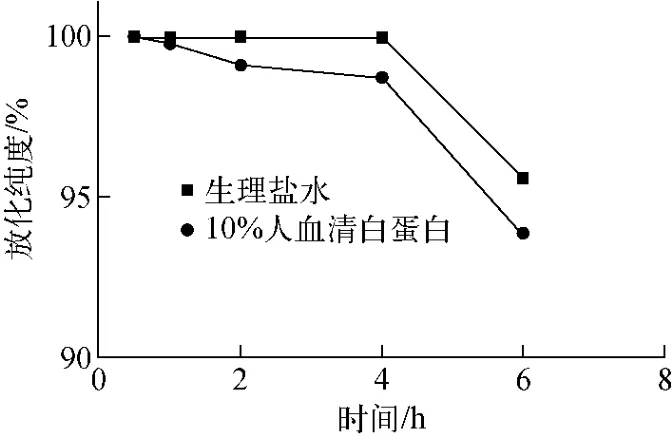
图8 SPION-DMSA-99Tcm体外稳定性Fig.8 In vitro stability ofSPION-DMSA-99Tcm
3.4 生物分布与显像
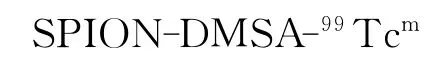
表1 SPION-DMSA-99Tcm在荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠体内的生物分布(±s,n=3)Table 1 Biodistribution of SPION-DMSA-99Tcmin nude mice bearing U87MG human glioma
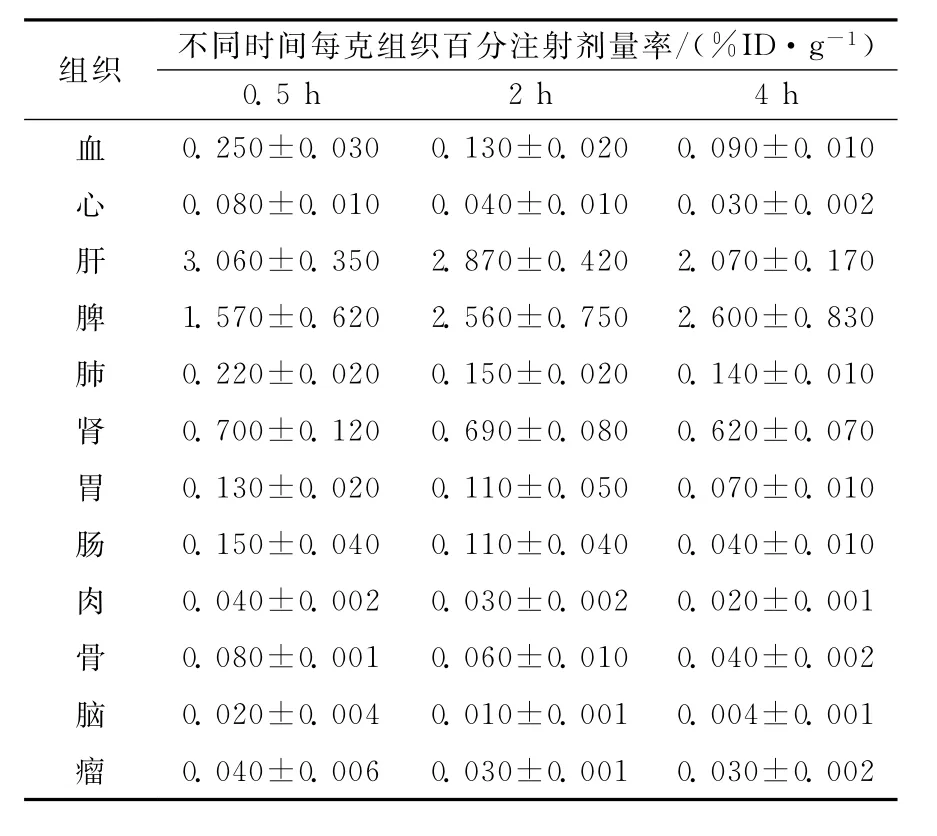
表1 SPION-DMSA-99Tcm在荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠体内的生物分布(±s,n=3)Table 1 Biodistribution of SPION-DMSA-99Tcmin nude mice bearing U87MG human glioma
组织不同时间每克组织百分注射剂量率/(%ID·g-1)0.5 h 2 h 4 h血0.250±0.030 0.130±0.020 0.090±0.010心0.080±0.010 0.040±0.010 0.030±0.002肝3.060±0.350 2.870±0.420 2.070±0.170脾1.570±0.620 2.560±0.750 2.600±0.830肺0.220±0.020 0.150±0.020 0.140±0.010肾0.700±0.120 0.690±0.080 0.620±0.070胃0.130±0.020 0.110±0.050 0.070±0.010肠0.150±0.040 0.110±0.040 0.040±0.010肉0.040±0.002 0.030±0.002 0.020±0.001骨0.080±0.001 0.060±0.010 0.040±0.002脑0.020±0.004 0.010±0.001 0.004±0.001瘤0.040±0.006 0.030±0.001 0.030±0.002


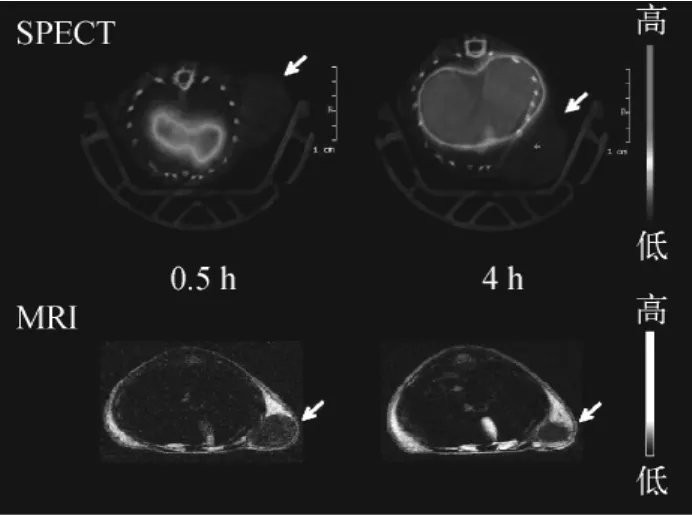
图9 荷U87MG人脑神经胶质瘤裸鼠的SPECT和MRI图像Fig.9 SPECT and MRI images of nude mice bearing U87MG human glioma
超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子在MRI成像中为T2造影剂。从图9的MRI图像可见,在注射SPION-DMSA 4 h后肿瘤部位略有变暗,表明肿瘤部位有微弱摄取,SPION-DMSA可作为一种MRI造影剂。
在肿瘤组织中,由于血管生成非常迅速,肿瘤脉管的完整性较差,此外,大多数肿瘤具有较差的淋巴引流系统,因此,在血流中的大分子或纳米材料,如SPION进入肿瘤组织较进入正常组织更容易,而它们一旦进入肿瘤组织,就难以回到循环系统中,这使得大分子或纳米材料从血管进入肿瘤后在肿瘤组织中能滞留较长的时间。这就是大分子或纳米材料在肿瘤组织中的增强通透性和滞留效应,即EPR效应[27]。但在本研究中并未观察到明显的EPR效应。影响EPR效应的因素是多方面的,如肿瘤的异质性等[28],还有待进一步研究。
4 结论

为了进一步提高SPECT/MRI双模态影像剂在肿瘤中的摄取,在后续的研究中,考虑引入合适的多肽或抗体等靶向分子,使99Tcm标记的SPION显像剂具有主动靶向的功能,以期进一步改善SPECT和MRI的图像质量,制备出更为理想的肿瘤SPECT/MRI双模态影像剂。
参考文献:
[1] BONEKAMP D,HAMMOUD D A,POMPER M G.Molecular imaging:Techniques and current clinical applications[J].Applied Radiology,2010,39(1):10-21.
[2] PYSZ M A,GAMBHIR S S,WILLMANN J K.Molecular imaging:Current status and emerging strategies[J].Clinical Radiology,2010,65(7):500-516.
[3] HAMAMURA M J,HA S,ROECK W W,et al.Development of an MR-compatible SPECT system(MRSPECT)for simultaneous data acquisition[J].Physics in Medicine and Biology,2010,55(6):1 563-1 575.
[4] BOUZIOTIS P,TSOTAKOS T,STAMOPOULOS D,et al.Radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles as dual-modality SPECT/MRI and PET/MRI agents[J].Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry,2012,12(23):2 694-2 702.
[5] LAURENT S,FORGE D,PORT M,et al.Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles:Synthesis,stabilization,vectorization,physicochemical characterizations,and biological applications[J].Chemical Reviews,2008,108(6):2 064-2 110.
[6] MADRU R,KJELLMAN P,OLSSON F,et al.99mTc-labeled superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for multimodality SPECT-MRI of sentinel lymph nodes[J].The Journal of Nuclear Medicine,2012,53(3):459-463.
[7] LU A H,SALABAS E L,SCHUTH F.Magnetic nanoparticles:Synthesis,protection,functionalization,and application[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2007,46(8):1 222-1 244.
[8] SAMANTA B,YAN H,FISCHER N O,et al.Protein-passivated Fe3O4nanoparticles:Low toxicity and rapid heating for thermal therapy[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry,2008,18(11):1 204-1 208.
[9] APOSHIAN H V,MERSHON M M,BRINKLEY F B,et al.Anti-lewisite activity and stability of meso-dimercaptosuccinic acid and 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid[J].Life Science,1982,31(19):2 149-2 156.
[10]HOET P,BUCHET J P,DECERF L,et al.Clinical evaluation of a lead mobilization test using the chelating agent dimercaptosuccinic acid[J].Clinical Chemistry,2006,52(1):88-96.
[11]RAMAMOORTHY N,SHETYE V,PANDEY P M,et al.Preparation and evaluation of99mTc(Ⅴ)-DMSA complex:Studies in medullary carcinoma of thyroid[J].European Journal of Nuclear Medicine,1987,12(12):623-628.
[12]ESER L E,PELIN O K.The role of Tc-99m(Ⅴ)DMSA scintigraphy in the diagnosis and follow-up of lung cancer lesions[J].Annals of Nuclear Medicine,2007,21(5):275-283.
[13]KIM J S,YOON T J,YU K N,et al.Toxicity and tissue distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in mice[J].Toxicologial Science,2006,89(1):338-347.
[14]FATAHIAN S,SHAHBAZI-GAHROUEI D,POULADIAN M,et al.Biodistribution and toxicity assessment of radiolabeled and DMSA coated ferrite nanoparticles in mice[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry,2012,293(3):915-921.
[15]CHEN Z P,ZHANG Y,ZHANG S,et al.Preparation and characterization of water-soluble monodisperse magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via surface double-exchange with DMSA[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2008,316(1-3):210-216.
[16]JUN Y W,HUH Y M,CHOI J,et al.Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2005,127(16):5 732-5 733.
[17]MEJIAS R,PEREZ-YAGUE S,GUTIERREZ L,et al.Dimercaptosuccinic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for magnetically guided in vivo delivery of interferon gamma for cancer immunotherapy[J].Biomaterials,2011,32(11):2 938-2 952.
[18]IKEDA I,INOUE O,KURATA K.Preparation of various Tc-99m dimercaptosuccinate complexes and their evalution as radiotracers[J].Journal of Nuclear Medicine,1977,18(12):1 222-1 229.
[19]HORIUCHI K,SAJI H,YOKOYAMA A.p H sensitive properties of Tc(Ⅴ)-DMS:Analytical and in vitro cellular studies[J].Nuclear Medicine and Biology,1998,25(7):689-695.
[20]BANERJEE T,SINGH A K,SHARMA R K,et al.Labeling efficiency and biodistribution of technetium-99m labeled nanoparticles:Interference by colloidal tin oxide particles[J].International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2005,289(1):189-195.
[21]FATAHIAN S,SHAHBAZI D,POULADIAN M,et al.Preparation and magnetic properties investigation of Fe3O4nanoparticles99mTc labeled and Fe3O4nanoparticles DMSA coated[J].Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures,2011,6(3):1 161-1 165.
[22]BANDOLI G,NICOLINI M,MAZZI U,et al.Synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of tetraethylammonium bis[1,2-di(carbomethoxy)etane-1,2-dithiolato]oxotechnetate(Ⅴ)[J].Transition Metal Chemistry,1984,9(4):127-129.
[23]LING D,HYEON T.Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications[J].Small,2013,9(9-10):1 450-1 466.
[24]GARCIA M P,PARCA R M,CHAVES S B,et al.Morphological analysis of mouse lungs after treatment with magnetite-based magnetic fluid stabilized with DMSA[J].Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2005,293(1):277-282.
[25]RAMAMOORTHY N,SHETYE S V,PANDEY P M,et al.Preparation and evaluation of99mTc(Ⅴ)-DMSA complex:Studies in medullary carcinoma of thyroid[J].European Journal of Nuclear Medicine,1987,12(12):623-628.
[26]CHAUHAN U P S,BABBAR A,KASHYAP R,et al.Evaluation of a DMSA kit for instant preparation of99mTc(Ⅴ)-DMSA for tumour and metastasis scintigraphy[J].International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation,Part B:Nuclear Medicine and Biology,1992,19(8):825-830.
[27]MAEDA H.Tumor-selective delivery of macromolecular drugs via the EPR effect:Background and future prospects[J].Bioconjugate Chemistry,2010,21(5):797-802.
[28]LAMMERS T,KIESSLING F,HENNINK W E,et al.Drug targeting to tumors:Principles,pitfalls and(pre-)clinical progress[J].Journal of Controlled Release,2012,161(2):175-187.
中图分类号:O615.4
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1000-6931(2015)09-1557-08
doi:10.7538/yzk.2015.49.09.1557
收稿日期:2014-05-05;修回日期:2014-06-09
作者简介:王 晓(1986—),女,山西运城人,博士研究生,放射性同位素技术专业
通信作者:*沈浪涛,E-mail:shenlt@yahoo.com

WANG Xiao1,2,CUI Hai-ping1,2,SHI Xu-dong1,2,LIANG Ji-xin1,SUN Yu-lin2,SHEN Yi-ming1,2,SHEN Lang-tao1,2,*
(1.National Isotope Center of Engineering and Technology,China Institute of Atomic Energy,Beijing 102413,China;2.Atom Hi-Tech Co.,Ltd.,Beijing 102413,China)
Abstract:Nanoparticle SPION-DMSA and its radiolabeledwere prepared in order to investigate the possibility ofas a SPECT/MRI dual-modal imaging agent.SPION was synthesized by a hydrothermal process,and then coated with DMSA to afford SPION-DMSA.SPION-DMSA was characterized by means of various methods.was obtained by labeling with99Tcm.The data of biodistribution and the SPECT and MRI images were acquired after injectinginto the nude mice bearing U87MG human glioma in various intervals.The results show that SPION-DMSA exhibits super-magnetic properties.Thelabeling yield ofwas more than 98%.is cleared from the blood quickly and has higher uptake in the liver.There was a big difference of biodistributions betweenandin the nude mice.The uptake ofin tumor is not obvious.The results of imaging made by MRI and SPECT using SPION-DMSA andrespectively show that the tumor passive targeting of SPION-DMSA andis limited.Therefore,is not an ideal SPECT/MRI dualmodal imaging agent for the nude mice bearing U87MG human glioma.
Key words:super-magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle;DMSA;99Tcm;SPECT/MRI dualmodal imaging agent

