D&M模型在医疗卫生信息领域应用分析*
徐 雯 刘加林 黎 勇 鄂琪敏
(四川大学华西医院/华西临床医学院医学信息学教研室 成都610041)
D&M模型在医疗卫生信息领域应用分析*
徐 雯 刘加林 黎 勇 鄂琪敏
(四川大学华西医院/华西临床医学院医学信息学教研室 成都610041)
检索中国知网、维普、万方、Ovid-Medline、SCI、EI、EMBASE、SpringerLink数据库中D&M模型在医疗卫生信息领域应用相关文献,对纳入文章的参考文献进行手工检索,进行提取分析。讨论各评价指标之间的关系及模型实际应用情况,指出D&M模型是医疗卫生信息系统效果评价的有效工具,但其本身的评价维度还有待完善。
D&M模型(信息系统成功模型);评价;应用
1 引言
信息社会的发展和医院现代化管理模式的需求,使医院信息系统已成为医院运行和管理过程中不可或缺的一部分。建设和使用信息系统是为了提高医疗质量及其安全性,但衡量系统的使用效果是否达到了预期值,这就需要人们对其做出评价[1-4]。
D&M模型又称信息系统成功模型,是美国学者Delone与Mclean于1992年提出的信息系统评价模型。该模型使用6个维度评价信息系统,具体包括系统质量、信息质量、系统使用、用户满意、个人影响和组织影响。Delone等在研究过程中,综合理论界对此模型的大量讨论后,在2003年提出了改进的D&M模型,在改进模型中加入了新的维度即服务质量,把个人和组织的影响整合为净收益[5]。我国医疗卫生领域的信息系统发展较晚,对信息系统的评价处于起步阶段,没有较完善的评价体系。本文从研究阶段及维度对D&M模型进行多角度分析,从而归纳出模型的优缺点,为我国医疗卫生领域信息系统的评价提供借鉴。
2 方法与结果
2.1 方法
检索中国知网(CNKI)、维普(VIP)、万方、Ovid-Medline、SCI、EI、EMBASE、SpringerLink数据库。鉴于信息系统成功模型在1992年提出,因此本研究检索的起始日期定为1992年1月,终止日期为2013年11月。检索策略是基于文章的标题和摘要的关键词,中文关键词包括信息系统成功、信息系统与成功模式;英文关键词包括Delone and mclean或Delone and Mclean information system success,限定为医疗卫生信息领域。初步检索完成后,通过手工检索相关的参考文献进行完善。通过对关键词的检索,剔除非英文和非中文文献,共得到相关文献181篇,其中54篇来自SCI、60篇来自SpringerLink、23篇来自EI、14篇来自Ovid-Medline、17篇来自EMBASE、7篇来自CNKI、1篇来自万方、1篇来自VIP、4篇来自参考文献中的相关文章。然后通过Endnote文献管理工具对纳入的文献进行筛选:(1)对重复的文章进行筛选,得到文献49篇。(2)对标题和摘要进行排除,剩下33篇文献。(3)对剩下的文献进行全文评价,最终纳入23篇文献。
2.2 结果
提取的证据,见表1,表2。在表3中,列出了纳入文献中关于模型研究分析维度的频次。对于D&M模型的各个维度,每个作者在分析时都有着不同的侧重点。
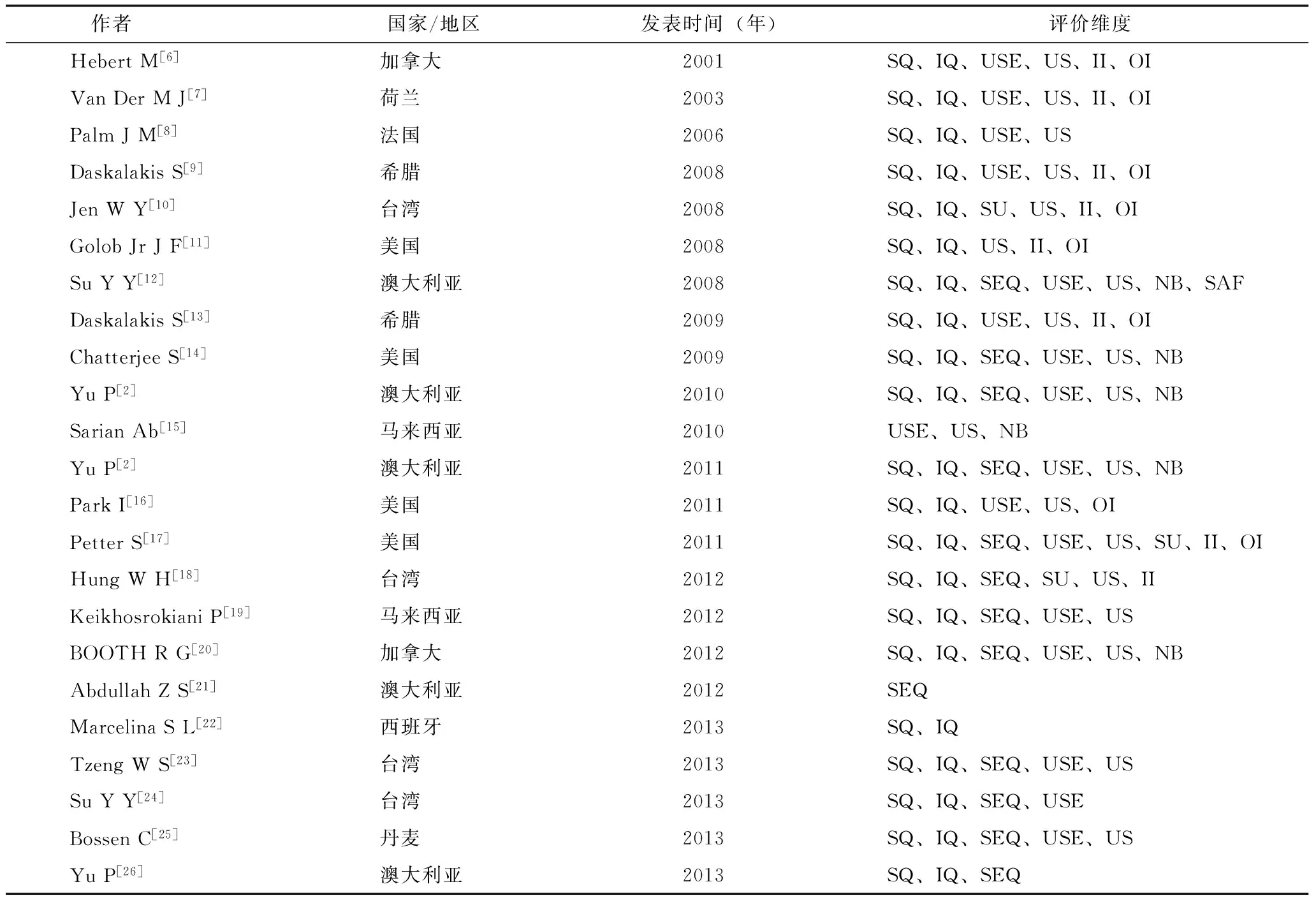
表1 最终统计23篇文献的基本信息
注:SQ:system quality,系统质量;IQ:information quality,信息质量;SEQ:service quality,服务质量;SAF: safe quality,安全质量; USE:使用; SU:system use,系统使用;US:user satisfaction,用户满意度;NB:net benefit,净收益;II:individual impact,个人影响;OI:organizational impact,组织影响。

表2 D&M模型评价维度的影响因素

表3 D&M模型维度频次分布情况(篇)
3 讨论
3.1 各个指标之间关系
从表2和表3可以看出,D&M模型对评价对象的系统质量、信息质量比较侧重。系统质量和信息质量的影响因素也明显多于其他评价指标。系统质量和信息质量作为系统的基本内容,直接影响着系统使用者的主观意愿,包括使用者对系统整体的满意度,对信息的及时性、完整性的感知等方面;同时系统质量和信息质量也反映出系统的服务质量,数据的处理能力、系统可操作性、数据标准等方面都可以体现出信息系统整合的能力,判定信息系统是否能够提供完整、及时、全面的服务;在信息系统实施后,系统和信息的质量同样也影响着实施效果,包括对个人和组织影响程度,是否产生了预期效益。在分析模型评价维度的影响因素时,各个维度中的影响因素处于相互作用之中,例如系统质量的稳定性与服务质量、用户满意度相关联,作为结果的个人和组织影响中,都直接或间接地对系统的性能产生作用等。各个因素之间的相互作用加大了评价指标之间的关联,使得相互独立的指标之间又有着相互联系、相互制约的关系,在评价之中加大对指标相关性的分析。
3.2 模型实际应用
对于具体研究来说,信息系统的评价需要根据研究背景、目的等因素来选择恰当的评价维度。Seddon等提出成功模式维度的选择及其评价需要考虑到具体的研究环境。Van der Meijden、Despont Gros等人在研究中发现,作为“独立的变量”的成功维度会给最终结果带来负面的影响。所以有学者提出应考虑信息系统成功模型评价对象的环境与指标之间的相关性,以提高成功模式在医疗环境里的应用能力[16,23,27-28]。本文通过对各个学者在研究中提出的问题进行整合,可以看出环境因素和指标之间的相关性影响着成功模型的评价功能,各个维度在不同环境中的具体定义以及相互联系等方面需要得到足够的重视,包括其评价维度的合理性、定义的范围、各个维度之间的具体联系都需要进行深入的研究。
4 结语
目前,我国的医疗卫生信息系统还处于探索和试验阶段,通过评价信息系统,不仅可以了解国内医疗卫生信息系统的发展方向,而且可以根据评价的结果指导信息系统的建设。本文对D&M模型在医疗卫生信息领域的应用做了较全面的评价,为我国对D&M模型的研究提供借鉴。
1 高晨光,马宝英,高照艳,等.医院信息系统评价分类及方法[J]. 医学信息学杂志,2011,32(4):52-63.
2 Yu P, Yu H, Soar J. Methods to Evaluate Health Information Systems[J]. Journal of Medical Informatics, 2011,32(2): 15-21.
3 韩志琰, 甄天民,谷景亮.社区卫生信息系统建设绩效评价指标体系研究[J].医学信息学杂志,2014,35(8):14-18.
4 郭小明,郭文秀,孔瑞珍,等.医院信息系统综合效益调查分析[J].医学信息学杂志,2013,34(7):38-59.
5 张会会,梁力凡,马敬东.国外卫生信息化评价视角的发展对我国的启示[J].医学信息学杂志,2014,35(8):2-6.
6 Hebert M. Telehealth success: evaluation framework development[J]. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 2001,(2): 1145-1149.
7 Van Der Meijden M J, Tange H J, Troost J, et al. Determinants of Success of Inpatient Clinical Information Systems: a literature review[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2003, 10(3): 235-243.
8 Palm J M, Colombet I, Sicotte C, et al. Determinants of User Satisfaction with a Clinical Information System[C].Philaodelphia: AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings, 2006: 614-618.
9 Daskalakis S, Mantas J. Evaluating the Impact of a Service-oriented Framework for Healthcare Interoperability[J]. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 2008, (136): 285-290.
10 Jen W Y, Chao C C. Measuring Mobile Patient Safety Information System Success: an empirical study[J]. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 2008, 77(10): 689-697.
11 Golob Jr J F, Fadlalla A, Kan J A, et al. Validation of Surgical Intensive Care-Infection Registry: a medical informatics system for intensive care unit research, quality of care improvement, and daily patient care[J]. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 2008, 207(2): 164-173.
12 Su Y Y, Fulcher J, Win K T, et al. Evaluating the Implementation of Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Systems from the perspective of Health Professional[C].Los Alamitos: IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology Workshops, 2008: 589-594.
13 Daskalakis S, Mantas J. The Impact of SOA for Achieving Healthcare Interoperability[J]. Methods Inf Med, 2009, 48(2): 190-195.
14 Chatterjee S, Chakraborty S, Sarker S, et al. Examining the Success Factors for Mobile Work in Healthcare: a deductive study[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2009, 46(3): 620-633.
15 Sarlan A, Ahmad W F W, Dominic P D D. Conceptual Information System Success Model for Small and Medium Enterprise Clinic Information System[C].Piscataway: 2010 International Symposium on Information Technology (ITSim), 2010, 3: 1142-1146.
16 Park I, Sharman R, Rao H R, et al. On the Two Factors Affecting Information Systems Success in the Extreme Event Context[M].Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 181-185.
17 Petter S, Fruhling A. Evaluating the Success of an Emergency Response Medical Information System[J]. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 2011, 80(7): 480-489.
18 Hung W H, Chang L M, Lee M H. Factors Influencing the Success of National Healthcare Services Information Systems: an empirical study in taiwan[J]. Journal of Global Information Management, 2012, 20(3): 84-108.
19 Zakaria N, Mustaffa N, Kianpisheh A, et al. A Proposal to Measure Success Factors for Location-Based Mobile Cardiac Telemedicine System (LMCTS)[J]. International Journal of Smart Home, 2012, 6(3):57-66.
20 Booth R G. Examining the Functionality of the DeLone and McLean Information System Success Model as a Framework for Synthesis in Nursing Information and Communication Technology Research[J]. Computers Informatics Nursing, 2012, 30(6): 330-345.
21 Abdullah Z S. Hospital Information Systems Implementation: Testing a structural model[C].Piscataway: Information Science and Digital Content Technology (ICIDT), 2012 8th International Conference on IEEE, 2012, 1: 74-81.
22 Solano-Lorente M, Martínez-Caro E, Cegarra-Navarro J G. Designing a Framework to Develop eLoyalty for Online Healthcare Services[J]. Electronic Journal of Knowledge Management, 2013, 11(1):107-115.
23 Tzeng W S, Kuo K M, Lin H W, et al. A Socio-technical Assessment of the Success of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems: the radiology technologist's perspective[J]. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 2013, 13(1): 109.
24 Su Y Y, Win K T, Chung T C. Identifying the Taiwanese Electronic Health Record Systems Evaluation Framework and Instrument by Implementing the Modified Delphi Method[M]. New York: Springer, 2013: 351-371.
25 Bossen C, Jensen L G, Udsen F W. Evaluation of a Comprehensive EHR based on the DeLone and McLean Model for IS Success: approach, results, and success factors[J]. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 2013, 82(10): 940-953.
26 Yu P, Qian S, Yu H, et al. Measuring the Performance of Electronic Health Records: a case study in residential aged care in Australia[J]. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 2013,(192):1035.
27 Lwoga E T. Measuring the Success of Library 2.0 Technologies in the African Context: the suitability of the DeLone and McLean's model[J]. Campus-Wide Information Systems, 2013, 30(4): 288-307.
28 Al-Debei M M, Jalal D, Al-Lozi E. Measuring Web Portals Success: a respecification and validation of the DeLone and McLean information systems success model[J]. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 2013,14(1):96-133.
Application Analysis of Delone and Mclean Information System Success Model in the Medical and Health Information Field
XUWen,LIUJia-lin,LIYong,EQi-min,
DepartmentofMedicalInformatics,WestChinaHospital/WestChinaSchoolofMedicine,SichuanUniversity,Chengdu610041,China
The paper retrieves the literatures about D&M model applying in medical and health information field from databases as CNKI, VIP, Wanfang data, Ovid-Medline, SCI, EI, EMBASE, SpringerLink, then retrieves the references of these literatures manually and carries out extraction analysis. The relations among various indexes and the actual application status of the model are discussed. The results show that D&M model is an effective tool for assessing the effects of medical and health information system, but its own evaluation dimensions have yet to be perfected.
D&M model (information system success model); Evaluation; Application
2014-11-05
徐雯,在读硕士研究生。
国家自然科学基金面上项目(项目编号:71273182)。
R-058
A 〔DOI〕10.3969/j.issn.1673-6036.2015.02.013

