跨伤椎置钉和经伤椎置钉治疗A型胸腰椎骨折效果比较
王方永,李建军,洪毅
跨伤椎置钉和经伤椎置钉治疗A型胸腰椎骨折效果比较
王方永,李建军,洪毅
[摘要]目的探讨跨伤椎置钉和经伤椎置钉治疗A型胸腰椎骨折的手术效果。方法胸腰椎骨折行后路椎弓根系统内固定术治疗患者23例,按手术方法分为A组(跨伤椎置钉组) 11例和B组(经伤椎置钉组) 12例。手术前后测量伤椎前缘高度、伤椎后缘高度、局部后凸角。结果所有椎弓根螺钉均顺利植入,螺钉位置及内固定稳定性良好。两组椎体高度和后凸角均改善(P<0.05),B组后凸角矫正程度优于A组(P<0.05)。结论后路椎弓根系统内固定结合经伤椎置钉,矫正后凸畸形的短期效果优于单纯内固定。
[关键词]胸腰椎骨折;伤椎置钉;手术;椎弓根系统
[本文著录格式]王方永,李建军,洪毅.跨伤椎置钉和经伤椎置钉治疗A型胸腰椎骨折效果比较[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2015, 21(11): 1308-1310.
CITED AS: Wang FY, Li JJ, Hong Y. Effect of Short-segment pediclescrewssystem with or without pediclescrewson fractured level ontypeA thoracicandlumbar spinefracture[J]. Zhongguo Kangfu LilunYu Shijian, 2015, 21(11): 1308-1310.
Roy-Camille等发明的经椎弓根镙钉固定技术已得到广泛应用[1]。后路椎弓根镙钉固定因其特有的生物力学优势,应用指征广泛,从外伤引起的脊柱不稳,到脊柱肿瘤、感染和退变性疾病均可应用[2-6]。但对胸腰椎骨折患者进行椎弓根固定过程中,伤椎是否需要置钉存在一定争议。本研究对胸腰椎骨折患者,分别进行伤椎置钉和伤椎不置钉处理,对手术效果进行比较分析。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选取本院2010年3月~2015年3月住院手术的胸腰椎骨折患者23例。
纳入标准:①创伤性胸腰椎骨折;②年龄20~60岁;③无明显骨质疏松等情况;④骨折AO分型为A型单椎体骨折;⑤无开放手术禁忌症。
排除标准:①伤椎椎弓根破坏严重,无法置钉;②术前术后资料不完整。
按伤椎是否置钉分为跨伤椎置钉组(A组)和经伤椎置钉组(B组)。A组11例,其中男性9例,女性2例;年龄19~45岁,平均23岁。B组12例,其中男性9例,女性3例;年龄21~52岁,平均26岁。
1.2手术方法
1.2.1跨伤椎置钉
以伤椎棘突为中心,沿各棘突连线纵行切开皮肤、皮下,钝性分离筋膜及肌肉层,暴露椎板;显露伤椎上下两个椎体的椎弓根后方解剖标志,定位椎弓根螺钉进入点。沿正确角度植入长度合适的椎弓根螺钉,共4枚。术中透视确认椎弓根螺钉位置良好,安装螺钉连接棒,行椎间撑开;锁紧螺帽,逐层缝合伤口。
1.2.2经伤椎置钉
在跨伤椎置钉的基础上,在伤椎额外植入2枚螺钉(共6枚)。根据伤椎骨折程度,这2枚螺钉长度可较其他4枚稍短。
1.3评定方法
分别于手术前1周内、术后1个月内摄X片,常规测量伤椎前缘高度、伤椎后缘高度、局部后凸角。
1.4统计学方法
使用SPSS13.0进行数据处理。数据符合正态分布,各指标用(xˉ±s)描述,采用独立样本t检验和配对t检验。显著性水平α=0.05。
2 结果
所有椎弓根螺钉均顺利植入,螺钉位置及内固定稳定性良好。1例患者因自身免疫状态不佳,出现伤口不愈合,反复清创无好转,于术后3个月取出内固定。其余患者均未出现严重手术相关并发症。无患者出现脊髓神经症状加重等情况。
A组术后椎体前缘高度和后凸畸形均有改善(P< 0.05),后缘高度改善不明显(P>0.05)。B组术后椎体前缘高度、后缘高度和后凸角度均有改善(P<0.05)。B组手术前后后凸角改善优于A组(P<0.05)。具体见表1、表2和表3。

表1 A组手术前后各指标变化(n=11)

表2 B组手术前后各指标变化(n=12)
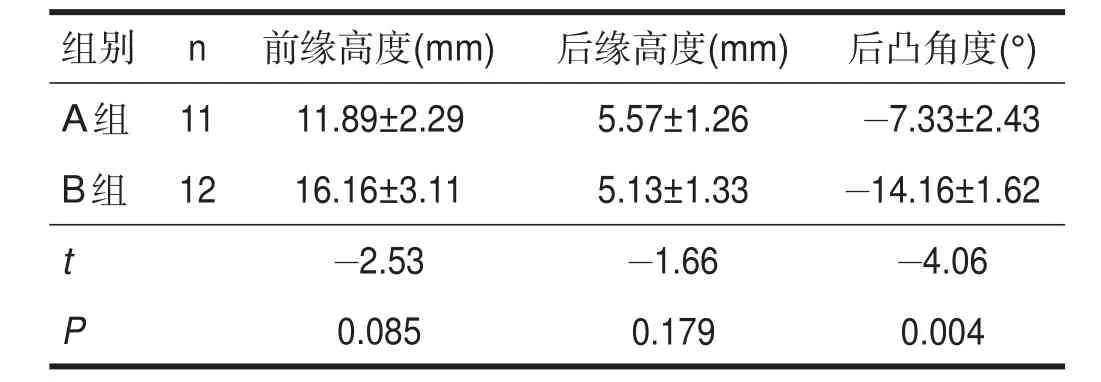
表3 两组各指标手术前后差值比较
3 讨论
不稳定性腰椎爆裂骨折的手术治疗包括前路手术、后路手术和前后联合入路手术。内固定术的主要目的是尽可能减少固定融合节段,尽量使用短节段固定[7-8]。
传统短节段固定主要涉及伤椎上下两椎体。尽管这一术式已经广为使用,但临床失败率较高。内固定失败潜在危险因素包括骨质疏松、固定及支撑点过少、前路支撑不足等。文献报道的机理还包括[9-10]:①悬挂效应,即上、下椎体前缘趋于靠近伤椎,伤椎自身趋于后移,易产生后凸,增加内固定松动或断裂的风险;②平行四边形效应,进而产生侧向不稳,且抗旋转性差,不利于骨组织、韧带、纤维环及椎间盘的修复;③内固定承受的负荷大。
伤椎置钉固定可增加内固定框架的稳定性,并间接增加前路支撑力量。临床中发现,多数爆裂性胸腰椎骨折表现为脊柱前中柱爆裂,而椎弓根,特别是椎弓根体部保持完整。大部分爆裂骨折患者,伤椎后方的韧带复合体保持完整。椎体皮质骨的应力主要集中于椎弓根基底。对于椎弓根基本完整的胸腰椎骨折,采用经伤椎置钉在技术上可行。
后路短节段固定是治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的常用方法。与跨伤椎固定相比,经伤椎置钉可增加椎弓根系统稳定性。生物力学研究表明,经伤椎置钉可将扭转稳定性提高1倍。
临床经伤椎固定后凸畸形矫正优于传统的跨伤椎固定。Carl等报道,跨伤椎固定后凸矫正为7°[11],Cho等报道的矫正角度为6°[12]。在这两个研究中,矫正的后凸畸形均在随访过程中丢失。McNamara等报道,使用跨伤椎固定,角度丢失达9°[13]。McLain等研究表明,因前路不稳导致的角度丢失主要发生在术后半年内[14]。
本研究中,经伤椎固定术后凸矫正14°,而跨伤椎固定后凸矫正仅为7°左右。
与跨伤椎四钉两椎体固定的两椎间撑开相比,六钉三椎体固定可根据伤椎终板损伤位置,选择终板损伤侧的椎间进行撑开,即单椎间撑开,避免正常椎间盘的过度撑开。六钉三椎体固定仅仅是脊柱固定方式的改变,未改变伤椎及脊柱的骨性结构,故不能增加脊柱的载荷能力;但因其分散了内固定负荷,并使螺钉的负荷均匀,相应增加内固定的载荷能力及脊柱稳定性;同时通过伤椎螺钉向前顶压作用,及伤椎两侧螺钉向中部的钳夹作用(爆裂性骨折椎弓根间距增宽),可很好恢复伤椎高度及脊柱生理弧度。
有作者通过对四钉和六钉固定的生物力学对比研究认为,六钉三椎固定较四钉两椎固定减少螺钉应力,增加内固定的轴向负载能力、抗屈曲和抗旋转能力[9-10]。我们在使用过程中发现,六钉三椎体固定后,椎管也获得较好的间接减压效果,可能是由于单椎间撑开,撑开间距短,韧带与纤维环的轴向牵张力量大,使椎管骨块获得较好回纳;另外,由于在伤椎上建立了一个额外支撑点,可通过提拉而将脱位的椎体复位。故当存在骨折脱位时,六钉三椎体固定也有明显优势。
总之,经伤椎固定增加整体内固定框架稳定性,同时减轻前中柱骨折椎体所承受的应力。另外,伤椎置钉所提供的额外支撑点,使后路固定术可以使用长节段三点复位技术。本研究所使用的跨伤椎固定方法增加了前路支撑,避免前路手术带来的风险。对于不适合前路手术的胸腰椎骨折患者,如并发胸腹腔创伤患者,可以考虑使用传统后路椎弓根系统内固定结合经伤椎置钉技术。
[参考文献]
[1] Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating [J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986, (203): 7-17.
[2] Park JH, Roh SW, Rhim SC. A single-stage posterior approach with open reduction and pediclescrew fixation in subaxial cervical facet dislocations [J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2015, 23(1): 35-41.
[3] Bunmaprasert T, Roobsoong A, Pongmanee S, et al. Safety entry point, size and direction for placement of thoracic pedicle screw-acadaveric study [J]. JMed Assoc Thai, 2014, 97(12): 1344-1351.
[4] Liu HF, Won HS, Chung IH, et al. Morphological characteristics of the cranial root of the accessory nerve [J]. Clin Anat, 2014, 27(8): 1167-1173.
[5] Kwan MK, Chiu CK, Lee CK, et al. Comparison between percutaneous fluoroscopic-guided and conventional open pedicle screw placement techniques for the thoracic spine: a safety evaluation in human cadavers [J]. Bone Joint J, 2015, 97(11): 1555-1561.
[6] Bajwa NS, Toy JO, Ahn NU. Establishment of parameters for congenital thoracic stenosis: a study of 700 postmortem specimens[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2012, 470(11): 3195-3201.
[7] Korovessis P, BaikonsisA, Zacharatos S, et al. Combined anterior plus posterior stabilization ventral posterior short-segment instrumentation and fusion for mid-lumbar burst fractures [J]. Spine, 2006, 31(8): 859-868.
[8] Verlaan JJ, Diekerhof CH, Buskens E, et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a systematic review of the literature on techniques, complications, andout-come[J]. Spine, 2004, 29(7): 803-814.
[9] Isaacs RE, Perez CM, Fessler RG, et al. Complications in the treatment of L1 burst fractures. Techniques in Neurosurgery [J]. Thoracol Trauma, 2003, 8(2): 130-139.
[10] Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Nonoperative treatment versus posterior fixation for thoracolumbar junction burst fractures without neurologicdeficit [J]. Spine, 2001, 26(9): 1038-1045.
[11] Carl AL, Tromanhauser SG, Roger DJ. Pedicle screw instrumentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures and fracture-dislocations[J]. Spine, 1992, 17(suppl 8): 317-324.
[12] Cho DY, LeeWY, Sheu PC. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with polymethyl methacrylate vertebroplasty and short-segment pedicle screw fixation [J]. Neurosurgery, 2003, 53(6): 1354-1361.
[13] McNamara MJ, Stephens GC, Spengler DM. Transpedicular short- segment fusions for treatment of lumbar burst fractures[J]. JSpinal Disord, 1992, 5(2): 183-187.
[14] McLain RF, Sparling E, Benson DR. Early failure of short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar fractures. A preliminary report [J]. JBone Joint Surg Am, 1993, 75 (2): 162-167.
·临床观察·
作者单位:1.首都医科大学康复医学院,首都医科大学骨外科学系,北京市100068;2.中国康复研究中心北京博爱医院,北京市100068。作者简介:王方永(1978-),男,汉族,江苏宿迁市人,博士,副主任医师,主要研究方向:脊柱外科、脊柱微创、脊髓损伤。通讯作者:李建军、洪毅。E-mail: crrc100@163.com(李建军)、hongyihhyy@163.com(洪毅)。
Effect of Short-segment PedicleScrewsSystemwithor without PedicleScrewson Fractured Level on TypeAThoracicand Lumbar SpineFracture
WANGFang-yong, LI Jian-jun, HONGYi
1. Capital Medical University School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beijing 100068, China; 2. Department of Spine and Spinal Cord Surgery, Beijing Bo'ai Hospital, ChinaRehabilitation Research Center, Beijing100068, China
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of short-segment pedicle screws system on type A thoracic and lumbar spine fracture with or without pediclescrewson thefractured level. Methods23 patientswith typeA thoracic and lumbar spinefracturewereincluded, in which 11 casesreceived traditional short-segment pediclescrewssystem without pediclescrewson thefractured level (group A), and other 12 caseswith pediclescrewson thefractured level (group B). Theanterior vertebral height, posterior vertebral height and local kyphosisangleweremeasured beforeand after operation. ResultsAll pediclescrewsweresuccessfully implanted with good location and stability. The vertebral height and kyphosisanglesignificantly improved after operation in both groups(P<0.05), and theimprovement of kyphosisangle wasmorein group B than in group A (P<0.05). Conclusion Short-segment pediclescrewssystem with pediclescrewson thefractured level may finecorrect thekyphosisangleinshort term.
Keywords:thoracicandlumbar spinefractures; pediclescrew onfracturedvetebral; surgery; short-segment pediclescrewssystem
(收稿日期:2015-08-02修回日期:2015-10-10)
基金项目:首都卫生科研专项基金项目(No.2014-4-4144)。
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2015.11.016
[中图分类号]R681.5
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1006-9771(2015)11-1308-03

