Maximum Likelihood Grid Search Based Weighted Cost Function Localization of TDOA and FDOA*
TONG Juanjuan,CHEN Xiaohui,SHU Feng,2,3* ,LI Jun,WANG Jianxin,LU Jinhui
(1.School of Electronic and Optical Engineering,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China;2.National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China;3.Ministerial Key Laboratory of JGMT,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China)
Passive source localization plays an extremely important role in many applications such as radar,sensor networks,navigation,microphone arrays,wireless communications,and tracking of acoustic sources[1-10].In the past decades,various methods were developed for localization as follows:least squares(LS)[2-3],spherical intersection[4],plane intersection[5],particle filtering[6]and Hough Transform[7].Recently,the received signal strength measured at different sensors is also used to estimate a source position[8-9].In Ref.[10 -11],semidefinite programming based on time difference of arrival(TDOA)is used to estimate sensor location in wireless sensor networks.In Ref.[12],authors considered recursive tracking of one mobile emitter using a sequence of TDOA and frequency difference of arrival(FDOA)measurement pairs obtained by one pair of sensors.However,TDOA or FDOA usually involves several remote sensors,which require precise timesynchronization and frequency-locking among them.In Ref.[13],authors proposed a maximum likelihood(ML)estimation approach using only two sensors,without any synchronization or locking.In Ref.[14],authors derived a“conditional”(or a“signal-specific”)Cramer-Rao bound,modeling the signal as a deterministicunknown. Furthermore,a cooperation method is proposed to track the position of a moving target with high accuracy,and to reduce the energy consumption and signaling overhead via node selection[15]. In Ref.[1 ],maximum ratiocombining(MRC)was used to combine two independent passive source solutions from the TDOA maximum likelihood grid search(MLGS)and the frequency difference of arrival(FDOA)MLGS,resulting in better performance than TDOA MLGS or FDOA MLGS alone.Unfortunately,its complexity is high for practical applications.Thus,a lower-complexity approach achieving the joint Cramer-Rao Lower Bound(CRLB)is highly desirable.
1 System Model and CRLB

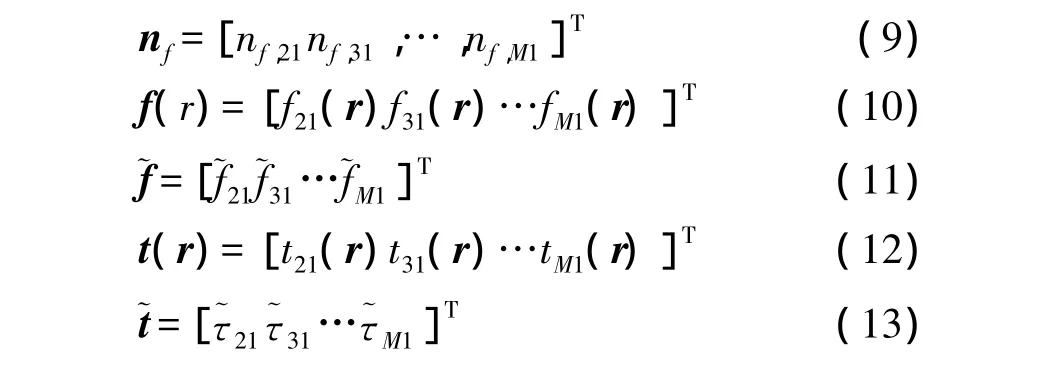
CRLB can be used to evaluate the error bound that optimal unbiased estimator can achieve.The covariance matrix of CRLB with the parameter vector of constrained unbiased estimation is as follows:
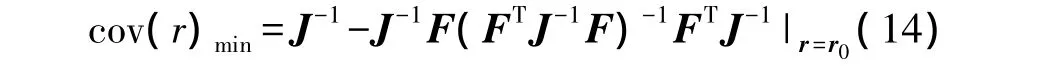
where Jis Fisher information matrix,Fis the gradient matrix of unknown parameters for constraints
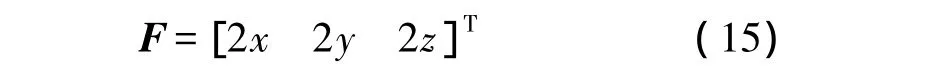
In the unconstrained case,the CRLB covariance matrix is equal to J-1.The Fisher information matrix is as follows:

2 Proposed Weighted ML Grid Search
To reduce computational complexity of MRC,a weighted joint localization of TDOA and FDOA,called weighted ML Grid Search(WMLGS),is proposed.
2.1 Determining Local Search Space(LSS)

To observe the property of error function,we define the following localization errorsurface of TDOA as wherer0=[x0,y0,z0]is the exact position of passive source andr=[x,y,z]is the estimated position.The above error function is helpful to determine the local search space in which the error function is convex.In the same manner,the FDOA error function is given by

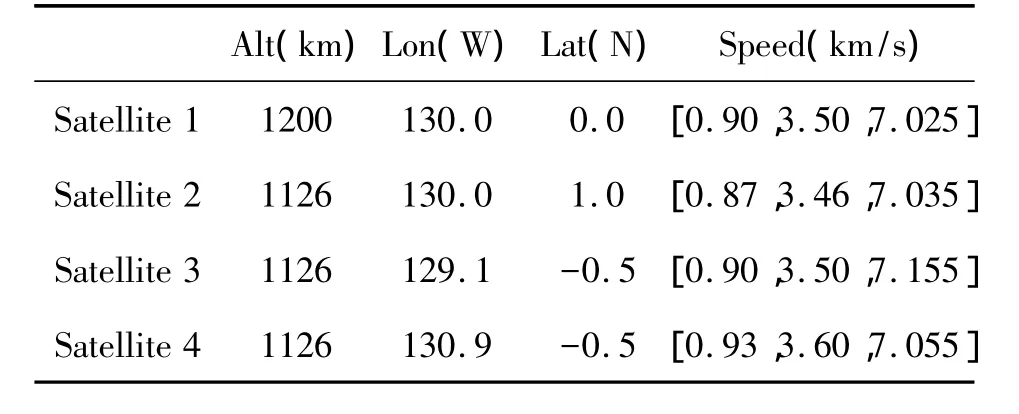
Table 1 Satellite Parameters
Fig.1 plots the 3D error surface for TDOA with satellite parameters as listed in Table 1.In the figures,the errorfunction from TDOA is convex within[(-0.5°,0.5°)(129.5°,130.5°)].
This means the LSS of TDOA below will be chosen to lie in this region.
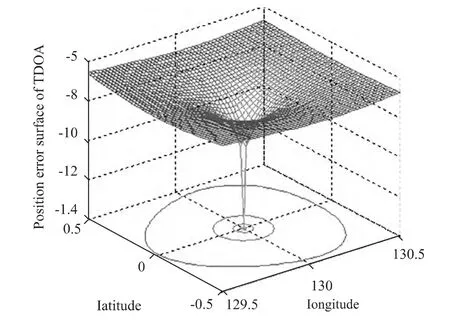
Fig.1 Position error surface from TDOA
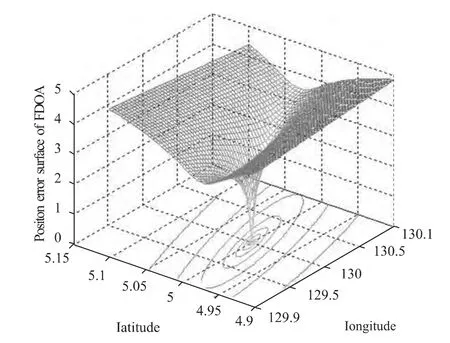
Fig.2 Position error surface from FDOA
Fig.2 plots the 3D error surface for FDOA with satellite parameters as listed in Table 1.In the figures,the error function from FDOA is convex within[(-4.9°,5.1°)(129.9°,130.1°)].
This means the LSS of FDOA will also be chosen to lie in this region in the following.
2.2Proposed WMLGS
To achieve the joint CRLB of TDOA and FDOA,a five-step localization is devised as follows:(1)One algorithm in Ref.[2-6]is first adopted to make a coarse estimation of the passive source position as ras;(2)A small LSS around rasis constructed with each dimension divided to N equally-spaced intervals per dimension;(3)The proposed WMLGS is given as
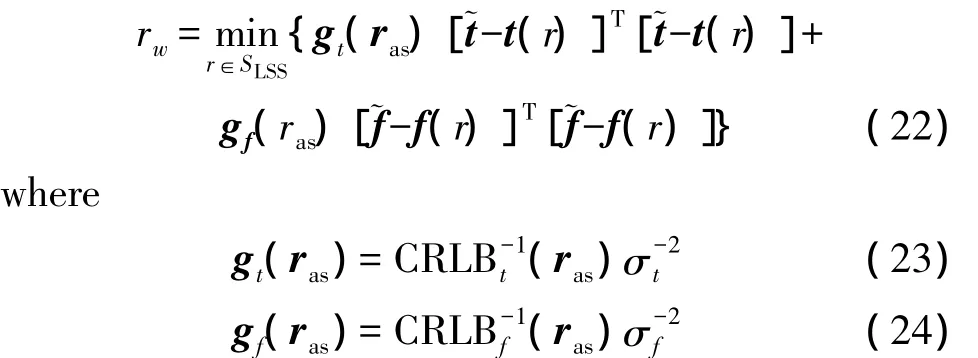
(4)Setras=rwand construct a smaller LSS as in(2)with each dimension search interval being half that of the previous LSS and being equally divided into N intervals.(5)Repeat step(3)and step(4)until convergence.The process above becomes TDOA MLGS forgf(ras)=0 in Eq.(22)whereas it degenerates towards FDOA MLGS forgt(ras)=0 in Eq.(22).From Eq.(23)and Eq.(24),the smaller position estimation error of TDOA and FDOA will be heavily weighted in Eq.(22).Essentially,the MRC of the objective functions of TDOA and FDOA is replaced by the MRC of the TDOA and FDOA position solutions in Ref.[1].That is,it needs one MLGS not two ones in Ref.[11].Its complexity isO{(N+1)dlog2[R/(Δr(N+1)d)]}float point operations where Δris the predefined position precision andRis the diameter of initial LSS.Thus,its search complexity is almost half that of this method in Ref.[1].
3 Simulation Results
In our simulation,Mwas chosen to be 4.The passive source has a longitude 132 °W and latitude 2 °N with zero altitude.Earth radius is 6 378 km.The relative speeds,longitudes,latitudes,and altitudes of satellites to Earth are listed Table 1.
In Fig.3,the root mean squared error(RMSE)of source position estimation is plotted versus the TDOA measurementerror(TDOAME)fortheproposed WMLGS,MRC in Ref.[1],and the TDOA and FDOA MLGS with FDOA measurement error(FDOAME)being 1 Hz.Like MRC,the proposed WMLGS achieves the joint CRLB of TDOA and FDOA for all TDOAMEs.The proposed WMLGS performs slightly better than the MRC,TDOA and FDOA MLGS methods.
Fig.3 RMSE of estimation versus TDOA measurement error
Fig.4 plots the RMSE of the source position estimation versus FDOAME with TDOAME=50 ns.The same trends are seen as in Fig.3 and Fig.4.
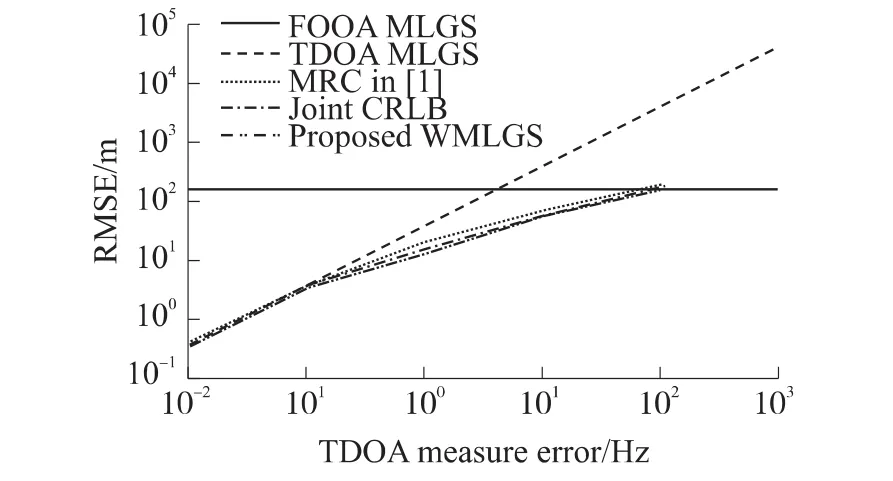
Fig.4 RMSE of estimation versus FDOA measurement error
Fig.5 illustrates the running times of the TDOA algorithm,MRC and proposed WMLGS roughly measured by the cputime function in MATLAB.Obviously,the running time of the proposed WMLGS is only half of that of MRC in Ref.[1].

Fig.5 Running Time
4 Conclusions
A weighted MLGS localization method has been proposed to reduce the high computational complexity of existing MRC[1].Simulations show that its performance is very close to the joint CRLB of TDOA and FDOA by using only half of the complexity of the MRC method in Ref.[1].
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the open research fund of National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory,Southeast University(2013D02),the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(30920130122004),and the National Natural Science Foundation of China(61271230,61472190).
[1]Shu F,Zhu W Q,Lu J H,et al.Maximum Ratio Combining Based Maximum Likelihood TDOA/FDOA Joint Localization[J].Journal of Astronautics,2010,31(4):1143-1148.
[2]Chan Y T,Ho K C.A Simple and Efficient Estimator for Hyperbolic Location[J].IEEE Trans Signal Processing,1994,42(8):1905-1915.
[3]Smiht J O,Abel J S.Closed-Form Least-Square Source Location Estimation from Range-Difference Measurements[J].IEEE Trans on ASSP,1987,35(12):1661-1669.
[4]Shau H C,Robinson A Z.Passive Source Localization Employing Intersecting Spherical Surfaces from Time-of-Arrival Differences[J].IEEE Trans.on ASSP.,1987,35(8):1223-1225.
[5]Schmidt R O.A New Approach to Geometry of Range Difference[J].IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron,1972,8(6):821-835.
[6]Gustafsson F,Gunnarsson F.Positioning Using Time Difference of Arrival Measurements[C]//Proc IEEE Int Conf Acoust,Speech,Signal Process,Hong Kong,China,Apr.2003,6:553-556.
[7]Mikhalev A,Ormondroyd R F.Comparison of Hough Transform and Particle Flter Methods of Emitter Geolocation Using Fusion of TDOA Data[C]//4th Workshop on Positioning,Navigation and Communication 2007(WPNC’07),Hannover,Germany,Mar.2007:121-127.
[8]Sheng X,Hu Y,Hu H.Maximum Likelihood Multiple Source Localization Using Acoustic Energy Measurements with Wireless Sensor Networks[J].IEEE Trans Signal Process,2005,53(1):44-53.
[9]Birchfield S T,Gangishetty R.Acoustic Localization by Interaural Level Difference[C]//Proc IEEE Int Conf Acoust,Speech,Signal Process,Phiadeiphia,Pennsylvania,USA,Mar.2005,4:1109-1112.
[10]Yang K,Wang G,Luo Z.Efficient Convex Relaxation Methods for Robust Target Localization by a Sensor Network Using Time Differences of Arrivals[J].IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2009,57(7):2775-2784.
[11]Xu E,Zhi D,Dasgupta S.Robust and Low Complexity Source Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Time Differ ence of Arrival Measurement[C]//IEEE WCNC 2010,Sydney,Australia,Apr.2010:1-5.
[12]Musicki D,Kaune R,Koch W.Mobile Emitter Geolocation and Tracking Using TDOA and FDOA Measurements[J].Signal Processing,IEEE Transactions on,2010,58(3):1863-1874.
[13]Yeredor A.On Passive TDOA and FDOA Localization Using Two Sensors with no Time or Frequency Synchronization[C]//Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP),2013 IEEE International Conference on IEEE,2013:4066-4070.
[14]Yeredor A,Angel E.Joint TDOA and FDOA Estimation:A Conditional Bound and Its Use for Optimally Weighted Localization[J].Signal Processing,IEEE Transactions on,2011,59(4):1612-1623.
[15]Hadzic S,Yang D,Viola M,et al.Energy Efficient Mobile Tracking in Heterogeneous Networks Using Node Selection[J].EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking,2014,2014(1):2.

童娟娟(1989-),女,研究生,研究方向为无线通信(协作多蜂窝无线通信系统预编码技术)。2012年本科毕业于南京理工大学,硕士期间获得校优秀研究生和特等奖学金等诸多荣誉称号;

束 锋(1973-),男,南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院,研究员,博士生导师,主要研究方向为无线通信、雷达信号处理、无线定位技术。发表期刊和会议论文100余篇,其中 SCI/SCIE收录22篇,EI已收录60多篇,论文被国内外学者引用291次,申请国家发明专利15项,已和正在主持国家层次项目三项。
