A Study on the Driving Factors of Food Production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain Based on Path Analysis
Yaqi LIU,Jiazhen LIU,Jinping ZHANG,Yongjin CHEN,Mengchen XU,Chengxiang WANG
School of Environment and Planning,Liaocheng University,Liaocheng 252000,China
1 Introduction
The food is the basis for human survival,and also an important part of the national security strategy[1].Ensuring the stable supply of food is of important significance tomeeting the social needsand maintaining national security and social stability[2].In terms of food production,the influencing factors are very complex,including climate,rainfall,geology,soil and socio-economic factors[3].In recent decades,with the rapid development of the economy,accelerated urbanization and population growth,the per capita arable land has been undergoing increasing pressure.Studies have shown that when China's population reaches its peak,Huang-Huai-HaiPlainmay shift from the currentmajor food transfer-out area to China's largest food transfer-in area,which will bring a huge crisis to China's food security[4-5].The current researches related to the driving factors of China's food production aremostly based on the provincial and municipal levels,and it lacks regionalexploration on plain zone.There isa need to further study the driving factors of food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.Therefore,based on years of statistical data,using path analysis method,this paper analyzes the driving factors of food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain to identify the key factors in food production,and propose effective measures to solve the regional food problems,which isof practical significance to food security in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.
2 Overview of the study area
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain(32°-40°N,114°-121°E)is the largest plain in China,across379 counties(cities)in Beijing,Tianjin,Hebei,Shandong,Henan,Anhui and Jiangsu,with a total area of 300000 km2.The plain is flat and there are numerous rivers and lakes,with convenient transportation and developed economy.The area is rich in land resources and has good light and heat conditions,so it becomes an important agricultural economic zone and amajor grain producing area in China.There are about 350million people in this plain,accounting for about26%of the total population in China.This region now has32925800 ha of arable land,accounting for about40%of the total arable land area in China(China Statistical Yearbook 2013).Huang-Huai-Hai Plain features awarm temperatemonsoon climatewith four distinct seasons.The average annual temperature in the southern Huaihe River Basin is 8-15℃,with cold and dry winters.Itmostly yields three crops two years in the northern plain but two crops a year in the southern plain[6].It has dry and cold winters,hot and rainy summers,and dry springs with serious drought and strong evaporation[7].The yellow soil is the major soil for farming in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.The total amount of radiation is 4605-5860 mj/(m·a),and the annual sunshine hours are 2 800 h in the north and 2300 h in the south.The annual precipitation is500-900 mm,and the precipitation in the south of the Yellow River is700-900 mm,with relative variability of 20-30%and even more than 30%in Beijing and Tianjin[8].
3 Data sources and research methods
3.1 Data sourcesDifferent levels of economic development in different regions cause differences in the factors influencing food production,and a dominant factor for one region's food production may become a secondary factor in another region.The study is based on China Statistical Yearbook 1996-2013,and the selected variables are shown in Table 1.
3.2 Research methodsThe stepwise regression analysismethod is first used to screen out themain factors affecting food production[9-10],and then the path analysismethod isused to analyze the influence of the main factors.In statistics,path analysis is used to describe the directed dependencies among a set of variables.This includesmodels equivalent to any form ofmultiple re-gression analysis,factor analysis,canonical correlation analysis,discriminant analysis,as well asmore general families ofmodels in the multivariate analysis of variance and covariance analyses.The specific calculation steps are as follows[11-12]:

Table 1 Classification of the factors influencing food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
(i)According to the principle of least squares,the linear regression equation y=β0+β1x1+β2x2+…+βnxnis transformed into the normalmatrix equation:
where y is the dependent variable;xi(i=1,2,…,n)are n independent variables;rxixjis the simple correlation coefficient between xiand xj;rxiyis the simple correlation coefficientbetween xiand y;Pyxiis the direct path coefficient of xito y.
(ii)The abovematrix equation is converted into linear equations,and the path coefficient Pyxiis calculated as follows:
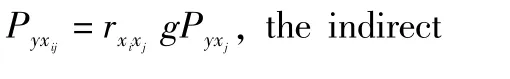
4 Analysis and discussions
4.1 Food production situationIn 2012,the total food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain topped 2×108t for the first time,an increase of 2.3%compared with 2011.The production in various provinces and cities is as follows:Beijing(113.8×104t);Tianjin(161.8×104t);Hebei(3246.6×104t);Henan(5638.6×104t);Shandong(4511.4×104t);Anhui(3289.1×104);Jiangsu(3372.5×104t).The changes in the per capita food production from 2002 to 2012 are shown in Fig.1.Except 2003 when more rainfall affected food production,the per capita food production in other years basically showed a rising trend,and itwas 380.43 kg in 2012.
Judging from the development trend(Fig.2),the province's total food production trend was similar to China's total food production trend during 1995-2012,and the food production trend can be divided into the following three stages:(i)Fluctuating growth period(1995-1999).The total food production increased from 16786.2×104t to 17974.7×104t,but affected by natural disasters,agricultural infrastructure and other factors,the food production declined in some years.(ii)Continuous decline period(1999-2003).Itwasmainly affected by natural disasters,and relevant studies show that agricultural natural disasters is strongly correlated with food production,but the area affected is negatively correlated with food production[11].The area was affected by the monsoon climate,and the droughts and floods often occurred,seriously affecting food production.
(iii)Continuous growth period(2003-2012).The food production soared from 14256.8×104t to20333.8×104t,mainly due to food subsidy support,large-scale construction of irrigation infrastructure,and improvement of overall grain production capacity and growing area[12].
4.2 Analysis of the driving factorsThe test of normality is performed on the dependent variable Y(food production)(Table 2),and the output results of Shapiro-Wilk Test are used.The Shapiro-Wilk statistic is0.981,and the significance level Sig.=0.955>0.05,so Y follows the normal distribution,that is,regression analysis can be performed on Y as dependent variable.According to the stepwise regression analysis,we get five input variables:X8(growing area of crops);X6(rural electricity consumption);X3(affected area);X10(annual average temperature);X14(arable land area at the end of the year).

Table 2 Normality test
According to the path analysis(Table3),it is found that X3and X14are negatively correlated with Y,while other indicatorsare positively correlated with Y.X6is the primary factor affecting Y.Among five independent variables,X8has the greatest direct impact on Y,followed by X6.By analyzing various indirect path coefficients,it is found that the growing area of crops has the greatest direct impact,but the total indirect impact of growing area of crops on food production through other factors is negative(-0.253),so the simple correlation coefficient of growing area of crops reaches 0.521,and it is not themost important influencing factor,but has a great impact on food production Y.

Table 3 Decomposition of path correlation coefficient
Based on X8,X6,X3,X10and X14,we get the optimalmultiple stepwise regressionmodel:
By substituting the number in column"B"under"nonstandardized regression coefficients"in Table 4 into the multiple stepwise regression model,we get the forecast equation for the food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain under the impactof various factors:

Table 4 Regression coefficient of food production
5 Conclusions and recommendations
5.1 ConclusionsThe effects of 14 factors on food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain are analyzed by path analysis in this paper,and then the linear regressionmodels of them are established by SPSSsoftware.The results show thatelectricity consumption for agriculture,growing area of crops,the affected area,annual average temperature and arable land area at the end of the year have great effects on food production.Therefore,in order to improve food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain,there is a need to ensure the power supply,improve the level ofmechanization,maintain a certain level of arable land,and reduce the affected area.
5.2 Recommendations
5.2.1Maintaining the electricity consumption for agriculture and improving the level of agriculturalmechanization.The electricity consumption foragriculture indirectly reflects the levelofmechanization in the study area,and the electricity consumption is the primary factor affecting food production,reflecting the high degree of mechanization in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain.To continue to play advantage,it is necessary to take themodern agriculture demonstration zone and village demonstration plots as the carrier,and strengthen scientific and technological innovation,to achieve a major breakthrough in themain crop cultivation technology.
5.2.2Protecting the arable land and stabilizing food production.In the context of a large population in a small area,strengthening the protection,managementand effective use ofarable land resources,and implementing the most stringent farmland protection system,has become an inevitable choice to achieve food security.It is necessary to strictly control the encroachment of various types of construction land on arable land,strictly protect arable land,especially basic farmland,and enhance reclamation to increase arable land resources,to ensure the supply capacity of the region's food production.
5.2.3Strengthening the natural disaster prevention and reducing the agricultural disaster area.Research shows that the food production in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is negatively correlated with the area affected by natural disasters,so it is necessary to strengthen the monitoring and prevention,establish the defense engineeringmeasures,and strengthen the rescue and reliefwork.
[1]GU LL,GUO QH.Study on fluctuation of food output in Northeast China Region[J].China Statistics,2009(9):17-19.(in Chinese).
[2]LIU S,HUANGGQ.Study on fluctuation of food output in Anhui Province[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(21):125-130.(in Chinese).
[3]CAO ZH,HAO JM,LIANG LT.Gray comprehensive correlation analysis onmajor grain output and inputelements of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain[J].Research of Agricultural Modernization,2008,29(3):310-313.(in Chinese).
[4]YAO HM.Study on Grain Productivity of Arable Land in Yellow River-Huaihe River-Haihe River Plain[D].Beijing:China Agricultural University,2004.(in Chinese).
[5]MAO ZQ.Study on sustainable landmanagementbased on field experiment and crop growth simulationmodel[D].Beijing:China Agricultural University,2003.(in Chinese).
[6]Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,CAS.Characteristics of climatic resources of North China Plain[M].China resources science encyclopedia.(in Chinese).
[7]GU TM.Climate of North China Plain[M].University ofMichigan:China Meteorological Press,1991.(in Chinese).
[8]Chinese Academy of Sciences.Soilof North China Plain[M].Beijing:Science Press,1961.(in Chinese).
[9]ZAISH,GUO SL,WEN J,et al.Analysis on influencing factors of grain output of Henan Province[J].Yellow River,2011,33(12):94-95.(in Chinese).
[10]ZHANGC.Foundation of Quantitative Geography[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2010:117.(in Chinese).
[11]DU JJ,CHEN ZW.Method of path analysis with SPSS linear regression[J].Bulletion of Biology,2010,45(2):4-6.(in Chinese).
[12]NIC,LEIGP.Dynamic change and driving force of grain production in Heilongjiang Province[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2013,27(5):14-19.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年7期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年7期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Forecasting of the Egg Price Based on EEMD
- On Modern Fruit Production in Japan
- Study on the Improvement of Performance of Global Supply Chain Based on Quantity Flexibility Revenue Sharing Contract
- Supply Chain Optimized Strategies in the Mode of External Financing
- Financial Support for Rural Cooperative Economy in China Based on Grey Correlation Analysis
- An Analysis of the Consumer Demand Structure of Rural Residents in Chongqing City in the Context of New Urbanization
