On Modern Fruit Production in Japan
Lanhua ZHAO,Yilong PIAO
Agriculture College of Yanbian University,Yanji133000,China
1 Introduction
Japan's fruit tree cultivation technology has been at a leading level in theworld.Theworld'smajor fruit varieties cultivated at present aremostly from Japan,for example,"Fuji"apple has become the world'smain cultivar of apple,accounting for a large proportion;"Kyoho"grape has become popular in theworld since the 1970s,and theworld's cultivarsofgrape atpresentare still"Kyoho"varieties;"Niitaka","Kosui"and other varieties of pear have become the major cultivars of pear in Asia.Since the reform and opening up,China's fruit industry has developed by leaps and bounds,but compared with developed countries,the level of cultivation techniques is lower,and the yield or quality is also lower.In order to allow more farmers to understand the fruit tree cultivation in developed countries,we analyze the dynamic situation of Japan's fruit tree cultivation to provide a reference for the development of China's fruit industry.
2 Changes in the fruit tree cultivation area
According to the statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries of Japan in 2012[1],citrushas the largest cultivation area currently,followed by apple,persimmon,chestnut,grape,plum,Japanese pear and peach.The fruit tree cultivation area in Japan experienced large fluctuations from the 1980s to the 1990s,and then became gradually stabilized,as shown in(Fig.1-3).The cultivation area of kiwi fruitwent through the largest fluctuations,soaring from 516 ha in 1980 to 5210 ha in 1990,and then decreased rapidly and stabilized at 2400 ha.The cultivation area of pineapple underwent the sharpest decrease,from 3190 ha in 1980 to537 ha in 2012,a decrease of83.2%;the cultivation area of citrus,chestnut,grape,peach,Japanese pear and applewas also greatly reduced,a decrease of 58.2%,50.0%,37.4%,33.9%,27.6%and 20.9%,respectively.The fruitwith a great increase in cultivation area was European pear,from 851 ha in 1980 to 1760 ha in 2012,an increase of 106.8%;there was a large increase in the cultivation area of cherries,from 2780 ha in 1980 to 4880 ha in 2012,an increase of75.5%.In short,in the past 30 years,the cultivation area of kiwi fruit in Japan experienced great fluctuations;the cultivation area of pineapple,citrus,chestnut,grapes,peaches,Japanese pears and appleswas significantly reduced;therewas a significant increase in the cultivation area of European pear and cherries.The cultivation area of principal fruits decreased while the cultivation area of new fruits and characteristic fruits increased.
3 Fruit distribution
3.1 Themain fruit distributionAccording to the statisticsof the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries of Japan in 2012[1],the proportion of Japan'smain deciduous fruit trees in various countries can be shown in Table 1.The area producing the largest amount of apples is Aomori County,followed by Nagano County,accounting for53.6%and 20.2%of apple cultivation area,respectively;the main grape producing areas are Yamanashi County and Nagano County,accounting for 22.4%and 12.8%of grape cultivation area,respectively;themain Japanese pear producing areas are Chiba County and IbarakiCounty,accounting for 11.9%and 9.4%of Japanese pear cultivation area,respectively;themain European pear producing areasare Yamagata County and Aomori County,accounting for 58.5%and 8.4%of European pear cultivation area,respectively;themain peach producing areas are Yamanashi County and Fukushima County,accounting for 32.4%and 16.3%of peach cultivation area,respectively;the main plum producing areas are Yamanashi County and Nagano County,accounting for 29.6%and 13.0%of plum cultivation area,respectively;the main cherry producing areas are Yamagata County and Hokkaido,accounting for65.2%and 11.9%of cherry cultivation area,respectively;Japanese apricot and persimmon aremainly concentrated in Wakayama,accounting for 31.3%and 12.2%of cultivation area,respectively.In terms of the distribution of Japan's fruit trees in different regions,apple ismainly in Aomoriwhile European pear and cherry are concentrated in Yamagata,with themost prominent regional characteristics;the regional characteristics of grape,peach,plum and Japanese apricot are also obvious.In short,Aomori is apple's main producing area;Yamagatamainly produces European pear and cherry;Wakayama mainly produces Japanese apricot and persimmon;Yamanashi mainly produces grape,peach and plum.There aremany kinds of fruit trees cultivated in Nagano,but there is nomain variety.O-verall,the cultivation of Japan's fruit trees shows prominent regional characteristics.
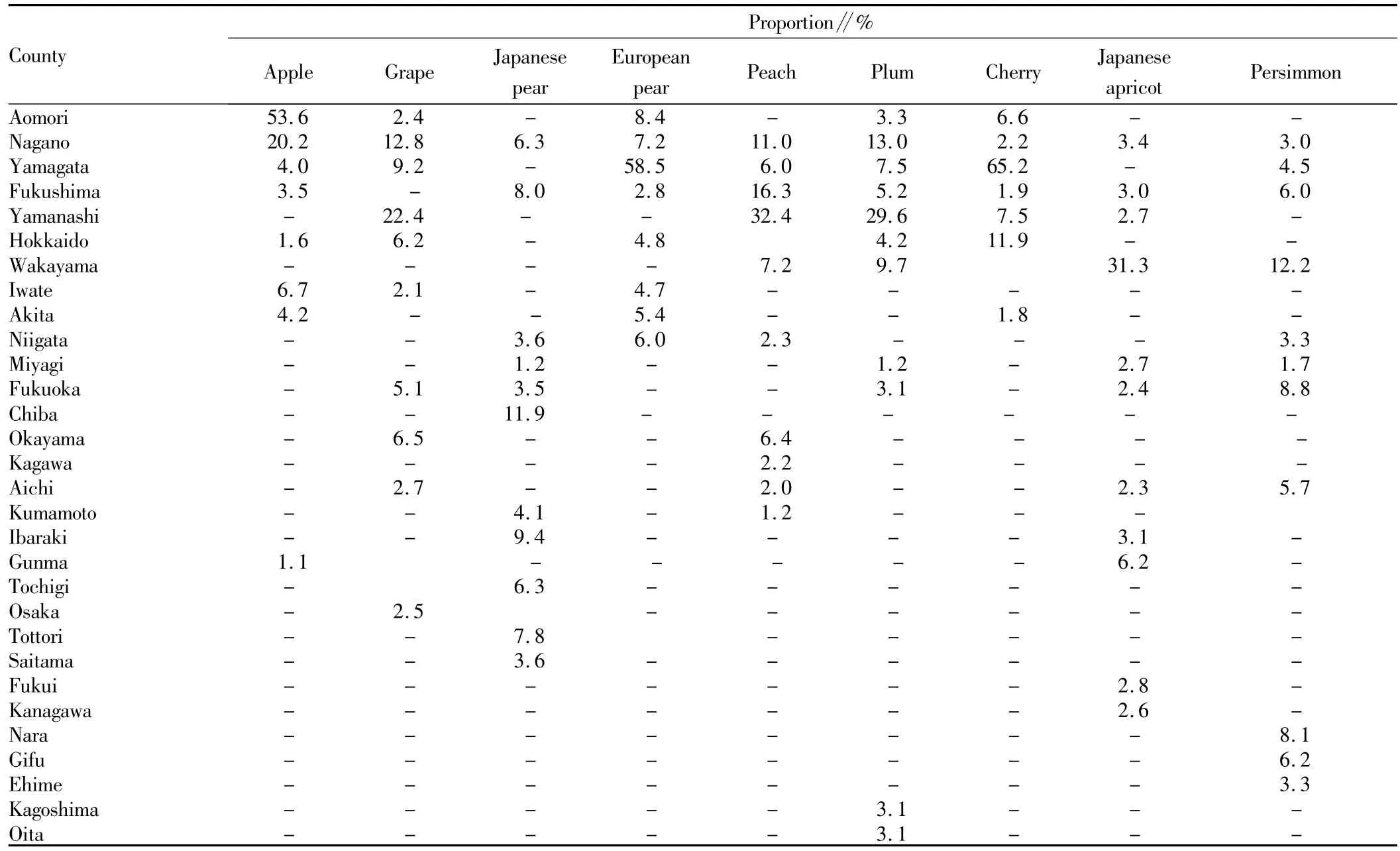
Table 1 The proportion of Japan'smain deciduous fruit trees in various countries
3.2 Rare fruit treesThe dynamic survey on specialty fruit production in 2012 by the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries in Miyagi County[2]shows that in addition to principal fruit trees,there are also some rare fruit trees to be cultivated in Japan.The rare fruits in Miyagi include grapefruit,fig,ginkgo,blueberry,Amur grape,West Indies cherry,passion fruit and raspberry.The cultivation area of the first four fruits ismore than 10 ha each.
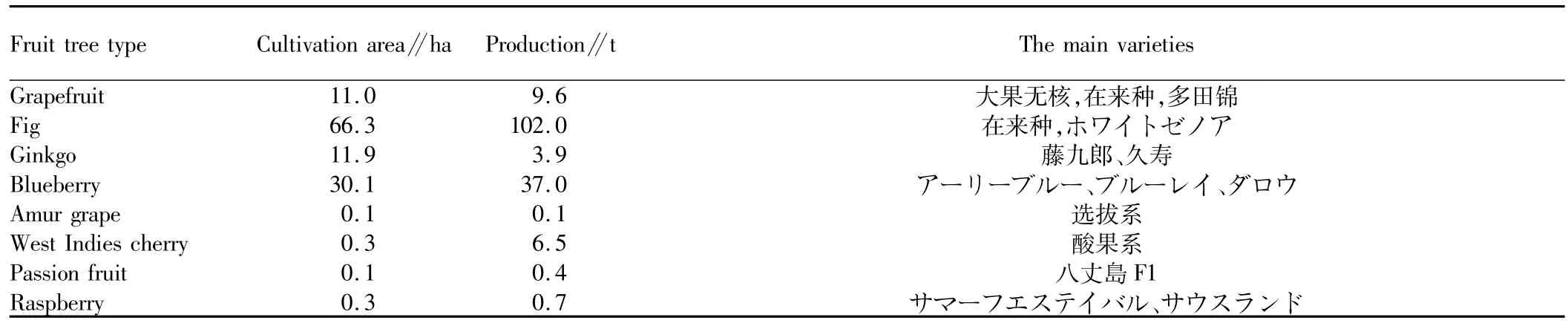
Table 2 The cultivation fruit trees not posted on the statistical table of the M inistry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries of Japan(M iyagi)
4 Themain cultivars
According to the statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries of Japan in 2012[1],the main cultivars of Japan's fruit trees are particularly clear(Table 3).The variety of70.4%of Japan's apples is"富士";37.4%and 30.7%of Japan's pear varieties are"丰水"and"幸水",respectively;16.7%,15.2%and 14.7%of grape varieties are"藤稔","康拜尔"and"巨峰";the variety of 68.36%of peaches is"あかつき(拂晓)";the variety of66.8%of plums is"ビューテイー";the variety of 75.8%of European pears is"ラ·フランス";the variety of56.5%of Japanese apricots is"白加贺";the variety of 64.4%of persimmons is"甲州百目".Except Japanese pear and grape varieties(dispersed),amain cultivar accounts formore than 50%,and the highest proportion reaches 75.8% (European pear).

Table 3 Themain cultivars of fruit trees
5 Fruit circulation
The change in the prices of fruits in wholesale agricultural product market in Sendai City in 2012 is shown in Fig.4[3].The prices of cherry underwent the greatest fluctuations in mid-2002.The price was up to 4031 yen/kg in April,while it dropped to less than 900 yen/kg in July and August.Therewere also great fluctuations in the prices of peaches.The price was up to 2356 yen/kg in April,while it dropped to 192 yen/kg in October.There was some volatility in the price of other fruits in the off-season,but the price was relatively stable.
[1]Statistics Department of Agriculture,Forestry and Aquatic Products Provinces.Statistics on cultivated area[Z].2012.(in Chinese).
[2]Investigation on production performance of special?fruit trees in 2012[Z].2012.(in Chinese).
[3]Annual report of Zhongyang wholesale market in Xiantai City,2012[Z].2012.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年7期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年7期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Em pirical Study on Online Political Participation of Young Migrant Workers
- Strategic Analysis on Objectives of National Grain Security
- Further Understanding of the Food Safety Problem
- Land Circulation and Increase of Farmers'Income:A Case Study of Dazhou City
- Reform of Rural Land System from the Perspective of New Urbanization
- How to Develop the Tea Industry in Leiyang City?
