Identification and Analysis of Symbolic Elements in the Mountain Tourism
Yingchun HU
1.School of Business and Administration,University of Science and Technology Liaoning,Anshan 114051,China;2.School of Tourism and Hotel Management,Dongbei University of Finance&Economics,Dalian 116023,China
1 Introduction
Mountain scenic area is a beautiful geographical complex in which mountain is the basic tourist resource carrier and component.After decades of development,China'smountain scenic area,especially famous scenic spot,has become an important tourist destination.It has played a crucial role in the development of China's tourism industry(Xie,2007).Behind the booming mountain tourism,there are a series of problems.For example,due to the lack of geographical features and regional culture,Chinamountain tourism developmentmodel is similar,and the important thing is scale but not quality,so the products are shoddy.Mountain scenic area should focus on innovation of tourism products in order tomeet the constantly changing needs of tourists(Liu et al.,2013).This shows that some kinds ofmountain tourism have not been able to effectively display the qualities of mountains,local characteristics,and their unique mountain tourism situation.In order to solve the above problems,with regard to the research about present situation ofmountain tourism,the development problems and developmentmodel,the practitioners and researchers have been going on.It ismeaningfulwhen the research conclusion can guide the practice.From the perspective of tourist experience,this article attempts to use themethod ofqualitative analysis to identify the symbolic elements of mountain tourism experience,extract the main elements,and provide reference and guidance formountain tourism developers.
2 Research methods
In order to find out the symbolic elements,this article is based on the perspective of tourist's experience,starting from themountainbased tourists to understand their awareness of mountain tourism area,grasp their symbolic recognition about themountain tourism,and summarize,classify these elements.Finally,we strip out the basic elements of mountain tourism landscape composition.Through this study,the researchers hope to provide some theoretical reference formountain tourism area in the developmentand operation.Based on these basic symbolic elements,themanager can produce themountain tourist products in accordancewith themarket demand and highlight the geographical and cultural aspects of the region's specialties.Themainmethod used in this study is the ZMET.For the traditional research methods,consumers are often unable to accurately express their intentions and expectations.That is to say,there aremany thoughts and feelings that are not expressed precisely in language.Maybe a lot of ideas are unaware because they are hidden in the consumer's subconscious.And a large part of expressions are based on non-literal language,while ZMET refers to the use of a kind of not easily be identified(such as pictures,paintings,stories,etc.)so that the respondents surveyed do the reaction in the absence of any restriction conditions(Zaltman et al.1995).ZMET assumptions:According to the potential needs,emotions and values,the tourists interpret the given information and put their own feelings,expectationsand intentions on object,third party,or the environment in theway ofanswer the questions.With questionnaires and interviews,respondents are easily affected by social expectations or intentions of the researchers.Using projection techniques with interviews and questionnaires in the study,itwill enable us to improve the accuracy of the study.This researchmethod isapplied inmountain tourism scenic areas to find the symbolic elements for the first time in China.
3 Research design
Technical problem needed to solve in this paper is to explore the tourists'expectations and feelings.The order of the design is sample selection,in-depth interviews,sorting,extracting constructs,analysis of constructs'intrinsic relationship,and eliciting final contracts,etc.
3.1 Samp le selectionThis study isqualitative research,and it needs to use in-depth interview method,so it takes a small sample of interviews(Zaichkowsky,1985).In order to ensure the validity of the findings,from more perspectives,the study explores the cognition of tourists'touristsituation,and focuseson sampling factors-gender,age,education,occupation and whether there was experience ofmountain tourist to finalize the 24 valid samples,of which 12 werewomen,12men,aged 17-60 years old in the distribution range.After selecting respondents,the researchers need to send the details and description of research topics to the respondents.Respondents are required to understand the research topics clearly.Then,the respondents select 8-10 pictures by themselves to represent their own feelings and ideas for research topics,and the interviewswill be conducted in 3-7 days later.
3.2 In-depth interviewsDuring the interview,respondents tell the story about the pictures one by one.They also need to describe the lost picture.The author should try to find out behind each picture represented constructs to guide the relationship between the constructs,to extract the constructs behind the thinking and behavior,so that there is a more accurate description of the respondents'experience and feeling.At this stage,the respondents describe a total of546 basic constructs,and express cognition and experience about symbolic elements ofmountain tourism.The author found thatmost respondents,either describinga landscape,building,or conducting activities,tended to think of a situation,atmosphere or feeling(Zaitman,2003).
3.3 Sorting and analysis of constructsIn this study,the constructs are means of expression that tourists'specific ideas which summarize ideas of otherswith simple and clearwords.The constructs are not real idea,justanote to capture and express ideas.During the interview process,the research willmake a further enquiry about the constructs the respondentsmentioned,ask origin and outspread feeling of the construct and relationship between constructs,and make the respondents express their ideas fully.After continuous discussing and organizing,24 respondentsmentioned 546 basic constructs,and then the researcher sorted them.Based on the principle of constructs'property,the same or similar constructsweremerged.Fig.1 is construct consistency trend diagram.As shown in Fig.1,although the number of respondents continues to increase,the new constructsare in decline.Respondent A puts forward 114 constructs,respondent F has 62 new constructs,while newly increased constructs decline to 5-0 from U to X.This shows that constructs provided by 24 respondents have internal consistency,and also proves that the 24 respondents can reveal the typical elements ofmountain tourism.Firstly,the researchers extract and merge the relevant constructsmentioned by all respondents,and then order them by frequency.We get84 key constructs,as shown in Table 1.Through the observation,we can find that there are two sorts:one is group of typical elements which include 58 elements(italics underlined);the other group includes26 elementswhich present the experience and feelings of respondents.Finally,the researchers elicit 3 types of constructs from the complicated relationship between constructs:basic constructs,link constructs,and ultimate constructs.Basic constructs are some basic landscapes,such as alpine,forest,sunrise,etc.They are the start point of all experience.Link constructs are the middle part which means a situation,a feeling,and an atmosphere.It is caused by basic constructs.The ultimate constructs are the final experience obtained by tourist through basic constructs,for example,"alpine"is basic construct,"magnificent"is link construct and achievement is ultimate construct.
3.4 Ultimate construct elicitationThrough the sorting of typical elements and experiential results,the researchers analyze the causality of constructs,and divide the experiential results of typical elements in mountain tourism into 3 types:relaxation,pleasure,and achievement.They are the ultimate constructs which represent the ultimate experience of tourists.
4 Identification and analysis of typical elements
Some main typical elements mentioned repeatedly are discarded because of the obscure relationship between the elementsand other constructs,especially ultimate constructs(pleasure,relaxation,and achievement).Finally,we select 19 valid typical elements:alpine,forest,mountain road,steps,pavilion,special plants,odd rocks,mountain spring,twitter,the sound ofwater,sunrise,sunset,porter,forest guard,allusions legends,celebrity ruins,squirrels,monkeys,welcoming pine.Here the typical elements are divided into two types:static elements and dynamic elements.According to the ZMET,the researchersextract the static elements(Alpine,Forest,Mountain road,Steps,Pavilion,etc).All these constitute the frame of mountain tourism which is dependent on material and space as a unique existence.The tourists'perception of the characteristicsof themountain tourism isnot the simple perception,but the deep emotion or experience caused by association,therefore,the dynamic factors such as Mountain spring,twitter,The sound of water,etc.must be integrated into the outline,the image ofmountain tourism will be completed,and the tourists can get relaxed,pleasurable and accomplished tourist experience.
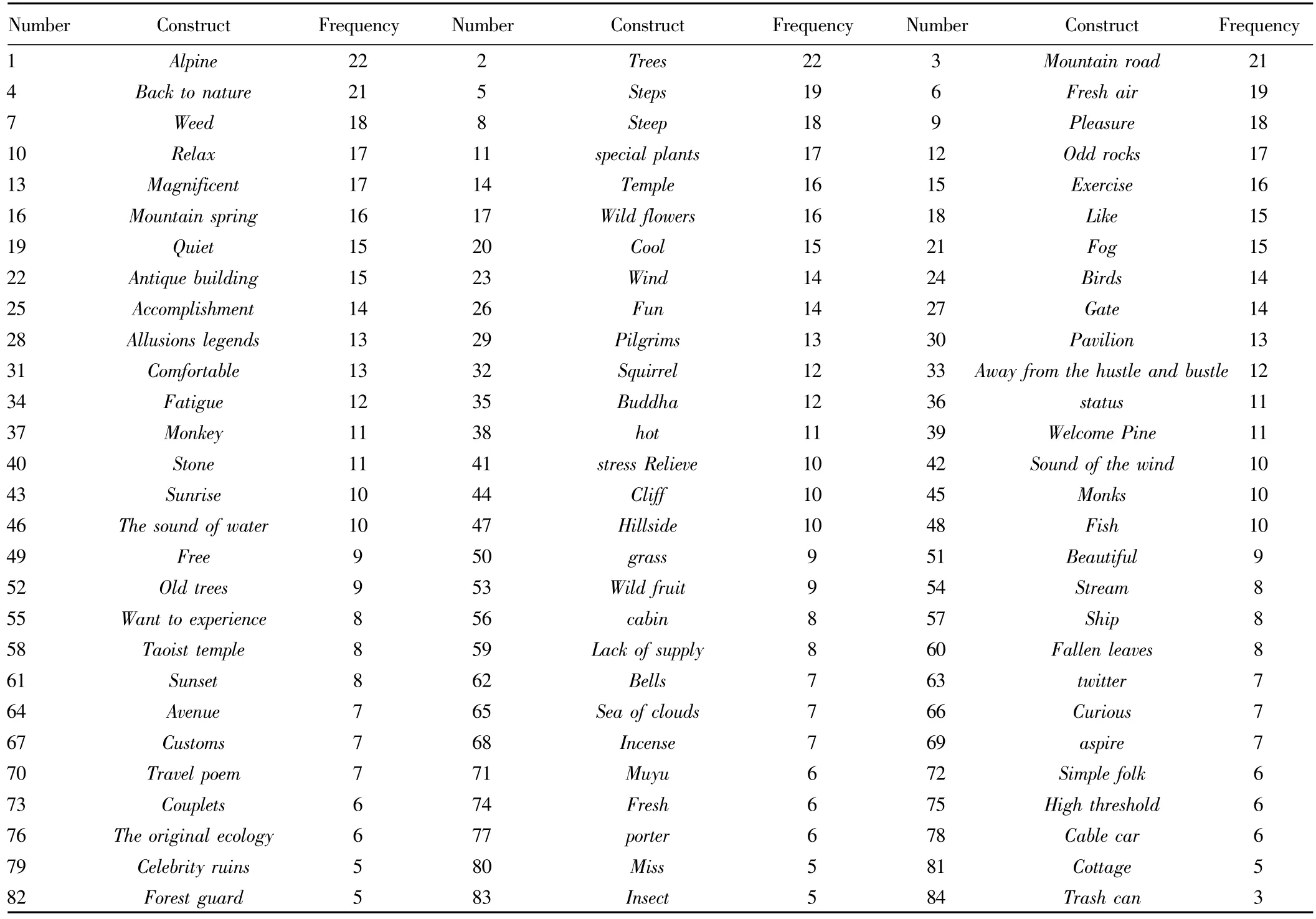
Table 1 The frequency of key constructs

Table2 Classification of typical elements
5 Conclusions
As a traditional tourist type,mountain tourism now is highly focused on and it has already accumulated a greatmany academic papers in different types of researches.However,there still exists improvement in positive and qualitative study.This paper uses Zaltman Metaphor Elicitation Technique(ZMET)as the study method to identify,sort and present all the typical elements in the mountain tourism context,aiming to find out the potential expectations and needshiding in the subconscious of themountain tourist.
[1]LIU ZX,etal.A research on tourism destination image perception ofmountain resorts-A case study ofmountain Wutai Scenery Area in China[J].Journal of Mountain Science,2013,31(3):370-376.
[2]XIE YH.A review of China’s tourism fundamental theoretical research in 2006-Take tourism tribune&tourism science for example.China's tourism yearbook newsroom.China tourism statistic annual[M].Beijing:China Travel&Tourism Press,2007:659-665.
[3]Zaltman G,Coulter RH.Seeing the voice of customer:metaphor-based advertising research[J].Journal of Advertising Research,1995:35-51.
[4]Zaichkowsky JL.Measuring the involvement construct[J].Journal of Consumer Research,1985.
[5]Zaitman G,Useem J.Theman can read yourmind[J].Fortune(Europe),2003,147(1):21.
[6]MA HM,ZHAOX,WU TY.Study on Tourism Spatial Distribution in Bortala[J].Agricultural Science&Technology,2015,16(2):369-372
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年9期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年9期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Risk Evaluation on Logistics Finance of Agricultural Products Based on Fuzzy-AHP Model
- An Analysis on Export Competitiveness of Vegetables from China to ASEAN
- The Influence of Agricultural Mechanization on the Development of Agricultural Economy in Chongqing City
- Forecasting and Analysis of Agricultural Product Logistics Demand in Tibet Based on Combination Forecasting Model
- Land Use Change and Driving Forces in Guangzhou City during 1996-2012
- Canonical Correlation between the Leaf Quality Indicators of"Moderate Aroma"Flue-cured Tobacco
