Current Situation and Development Trend of the Sugarcane Industry in Indonesia
W enhui PU
Scientific and Technical Information Institute,Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences,Danzhou 571737,China
1 Sugarcane production
Indonesia is the world's leading sugarcane producer,and its sugarcane production ranked 12th in 2008,followed by Thailand and the Philippines in Southeast Asia.Sugarcane cultivation in Indonesia datesback to the17th century,mainly distributed in Java Island,Sumatra Island,Kalimantan Island,Sulawesi Island and other islands,and the harvested area of Java Island accounts for almost 75 percent of national harvested area.Indonesia's sugarcane plantations are divided into three types(small farmers,state owned companies and private companies);small farmers are the main growers of sugarcane,and there are660000 rural households depending on it to live on[1].In Java Island and several other major sugarcane islands,plantation operation is dominant.The growing area of sugarcane in Indonesia experienced the average annual growth rate of 7.5 percent from the mid-1970s,and it peaked in 1994(423000 ha)but then declined slightly.From 2000,the harvested area of sugarcane fluctuated around 330000 to400000 ha inmost of the years,and it rebounded to more than 400000 ha in 2007.In 2008,the sugarcane harvest area was 415600 ha,accounting for 1.7%of the world's total harvest area.In the early 1990s,the sugarcane production was 28 million t,and peaked in 1994(33 million t),but then fell slightly to 30 million t.In 2008,the sugarcane production was 26 million t,accounting for 1.49%of the world's total production.At the end of the last century,the fluctuations in sugar production were basically consistent with the fluctuations in sugarcane production over the same period in Indonesia,increasing from 2.1 million t in 1990 to nearly 2.5 million t in 1993 and 1994,but decreasing to 2.1 million t in 1996.At the end of2009,the officials of the Ministry of Agriculture once expected the sugarcane harvest area in 2010 to be 450000 ha,and it was436000 ha in 2009[2].The sugarcane production in Indonesia from 2000 to 2008 can be shown in Table 1.

Table 1 The sugarcane production in Indonesia from 2000 to 2008[3]
2 The development of sugar industry
Indonesia has a long history of sugar making.In 1931,there were 179 sugar enterprises in the country,and the total sugar output reached a record high at nearly 3 million t[4].But later with the fall in sugar prices and due to the impact of war,sugar industry underwent a huge recession from 1931 to the early 1970s.It was not restored until a"sugar development plan"was developed in the 1970s.There are 9 provinces producing sugar in Indonesia,mainly in Java Island,Sumatra Island and Sulawesi Island.There are a total of 58 sugar processing plants in Indonesia,46 in Java,8 in Sumatra and 4 in Sulawesi[1].The sugar yield in Java accounts for about60 percent of total sugar yield in Indonesia[4].At the end of2009,the officials of the Indonesian Ministry of Agriculture expected that sugar production in 2010 would increase by 8.6%to 2.9 million t.However,the continued rainfall in Java Island in 2010 postponed the grinding time from May to June,and reduced the sugar content of sugarcane,so that the Ministry of Agriculture lowered the expected sugar production in 2010[2].At present,the sugar industry in Indonesia has been restored,but the domestic sugar does not realize self-sufficiency.Since the 1980s,with the increase in land and labor costs and the rapid increase in domestic demand,the sugar demand gap has continued to widen.The government planned to double sugar production to 5.7million t in 2014,to end the dependence on import[5].But the development of the sugar industry in Indonesia is relatively backward,and the sugar making equipment is outdated,leading to low productivity of sugar plants.Currently,the daily processing capacity of most sugar plants is less than 4000 t,and the total production and processing capacity of all sugar plants is only 0.19 million t/day,lower than 0.21 million t/day in the 1990s[1].Now sugarcane is facing the challenges from other crops,especially rice,the enthusiasm of farmers for planting is declining,and some sugar production enterprises are facing inadequate raw material supply.
3 Sugar consumption
In recent years,population growth and economic development in Indonesia have increased the pastry and beverage consumption,leading to an increase in the sugar consumption.Since 1970,the economy has developed by leaps and bounds.The annual growth rate of GDP is maintained at7%and the annual growth rate of per capita GDP is 5%.According to FAO statistics,during 1976-1996,the consumption of sugar in Indonesia increased from 1.8 million t to 2.75 million t,with average annual consumption growth rate of 2.0%.The per capita consumption increased from 12.9 kg in 1976 to 14.4 kg in 1994.From the beginning of the 1960s,Indonesia became a sugar importer;from the mid-1980s,the annual imports of sugar fluctuated between 50000 to 350000 t,and exceeded 570000 t in 1995.In 1997,Indonesia mainly imported refined sugar or directly consumed sugar.
4 Sugar imports
Indonesia implements strict management on sugar imports,and approves only five state-owned sugar companies as the registered sugar importers(the Ninth Agricultural and Horticultural Company;the Tenth Agricultural and Horticultural Company;the Eleventh Agricultural and Horticultural Company;Rajawali Nusantara;Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia).These importers must be approval by BULOG to get import quota and import sugar from abroad.BULOG is the country's only legitimate sugar importing agency,exempt from import tariffs.The sugar produced in Indonesia must be sold to BULOG.As domestic sugar supplier,BULOG has played an important role in the formation of sugar prices.Since 2000,there have been great fluctuations in Indonesia's imports of refined sugar.During 2002-2004,there were less few imports(540000 to 670000 t).In 2007,it imported 2.2628 million t of refined sugar,and the imports amounted to$76.772 million.In the joint conference attended by the representatives of sugar traders,sugar refining providers and business community convened in September 2008,Indonesia curtailed the importing amount of sugar previously agreed during 2008-2009 by 214000 t,and reduced the amount of raw sugar that can be imported by sugar plant by300000 t.The Government of Indonesia(GOI)also shortened the period of validity of imported sugar for the food and beverage industry from six months to two months.In order to avoid the lack of raw materials for the production of sugar plant,the government issued the import license of 115000 t of raw sugar to four domestic companies in June2010.The import of refined sugar in Indonesia from 2000 to 2007 is shown in Table 2.
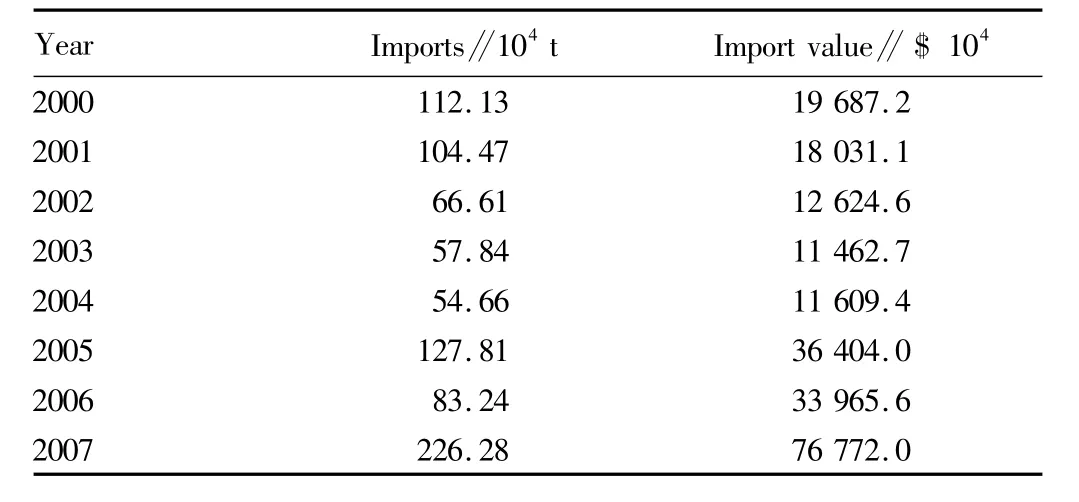
Table 2 The import of refined sugar in Indonesia from 2000 to 2007[3]
5 Industrial management and policies
Indonesia has special sugarcane research institutions.Sugar Industry Research Institute,located in Pasuruan City,East Java,founded in 1887,is a comprehensive research institute specialized in the study of sugarcane planting and sugar production technology equipment as well as related economic and social issues.The main research areas include sugarcane planting,soil,and plant protection;socio-economic issues,factories and distribution of interests for sugarcane growers.Indonesian Sugar Industry Commission,as the country's governing body of sugar industry,is responsible for sugarcane planting,sugar industry planning and guidance,sugar industry investment affairs,and sugar production,processing,import and export.In order to increase sugar production,expand the bioethanol production capacity and reduce dependence on fossil fuels,Indonesia hasbegun to implement the sugar revitalization plan since 2003.In order to achieve self-sufficiency in sugar,the Ministry of Agriculture,the Ministry of Industry,and the Ministry of Trade cooperate to revise and improve the sugarcane planting,sugar production,processing and trade system.The main measures include:(i)expanding sugarcane acreage;(ii)improving the performance of sugarcane varieties;(iii)stabilizing sugar prices(the Ministry of Agriculture is considering the establishment of price information system in national agricultural production centers to realize sugar price monitoring and management);(iv)improving the production efficiency of the sugar industry(the Ministry of Industry is preparing to provide special funds for the sugar industry to update outdated equipment;(v)improving the sugar business laws;(vi)improving the distribution and supply system of sugar dominated by mayor.The use and import of sugar in Indonesia remain in the hands of the government.Government issues import licenses annually to some designated companies to control sugar import.
6 Industry trends
(i)The sugar demand is expected to continue to grow.With population growth and economic development in Indonesia,the sugar demand will gradually increase.Due to the current growth in potential demand,the country is faced with the challenge of whether the domestic sugar production can meet the demand.Although sugarcane production showed a strong growth trend in the early 1980s to 1990s,the stable sugar production in recent years has precisely reflected the bottlenecks facing sugarcane planting and sugar production.So it is necessary to meet domestic sugar demand through import.(ii)The sugarcane land will face competition on many factors.When some crops have higher benefits than sugarcane,farmers will abandon the cultivation of sugarcane in the soils with good conditions for planting.In Java and other densely populated areas,sugarcane land is also facing the occupation and expropriation for urbanization,so sugarcane can only be transferred to the land without irrigation conditions or barren land for planting.(iii)The sugar production and technical departments still have a large room to improve production efficiency,and improvement of efficiency will bring more returns to sugarcane processing industry and sugar industry.(iv)As the areas out of Java Island reclaim new sugar plantations and establish large sugar companies,the national sugar production capacity increases,and the domestic sugar demand gap will be reduced accordingly.(v)In view of the current difficulty in achieving self-sufficiency in sugar,the government is considering providing incentives to attract domestic and foreign investors to invest in Indonesia's sugar industry.The competent sugar enterprises in China can consider using the opportunity of sugar revitalization in Indonesia,to seek cooperation with the country in terms of sugarcane planting technology,sugar production and processing mechanic equipments.
[1]The Website of ASEAN.The current situation of productive consumption of Indonesian sugar industry[DB/OL].http://www.asean35.com/News/2901.html,2008-04-30.(in Chinese).
[2]China Light Industry Network.The expected yield of sugar was lowered by the Government of Indonesia[DB/OL].http://www.clii.com.cn/news/content-312111.aspx,2010-07-21.(in Chinese).
[3]Database of Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations[DB/OL].http://faostat.fao.org.(in Chinese).
[4]PEISP.Investigation report on Indonesian sugar industry[J].Guangxi Sugarcane&Canesugar,1996(3):58-60.(in Chinese).
[5]The food industry network[DB/OL].http://www.foodqs.cn/news/gjspzs01/2009112716326706.htm,2009-11-27.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Analysis on Factors Influencing Distribution of Vegetal Production
- Regional Differences in the Demand for Agricultural Socialized Service
- SWOT Analysis on Breeding R&D of Tropical Crops in China in the Context of Implementing UPOV Convention 1991 Act
- Chinese Consumers' Awareness,Preferences and Purchasing Behavior on Korean Food
- A Study of the Moderate Scale Operation of China's Agriculture
- Study on the Degree of Rural Empty Nesters' Satisfaction with Life Quality Based on Ordered Logit-ISM Model
