Chinese Consumers' Awareness,Preferences and Purchasing Behavior on Korean Food
Yijun HAN,Suyun LIU,Nan JIANG
1.College of Economics and Management,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100083,China;2.Rural Economic Research Center of the Ministry of Agriculture,Beijing 100810,China
1 Introduction
China and South Korea are in close proximity to each other,and the international economic and trade exchanges between the two are close despite the different levels of economic development.Since China and South Korea established diplomatic relations in 1992,the economic and trade exchanges have been increasingly close,and the dependence has been gradually deepened.In terms of trade scale and status,the volume of trade was$5 billion in the early period,and it soared to$274.2 billion in 2013.Since 2003,China has become South Korea's largest trading partner,largest exporter and second largest source of import instead of the United States(Ding Kuangda,2013).In terms of the level of agricultural development and resource endowments in China and South Korea,the liberalization of agricultural trade will bring greater benefits to China,so the South Korean government has always been cautious about liberalization of agricultural trade,for fear that free trade may inflict brunt on its agricultural industry,endanger food security,and bring greater political risk(Cheng Wei,Wu Hao,2008).Since China's accession to World Trade Organization(WTO)in 2001,China and South Korea have carried out extensive exchanges and cooperation in agricultural trade,and Korean food and agricultural products have graced Chinese consumers' tables.In 2002,China's total volume of trade of agricultural products imported from South Korea was$127 million;in 2013,China's imports increased to$727 million,an average annual increase of17.2%.From the import category,the aquatic products have the largest proportion among the agricultural products imported from South Korea,followed by sugar which accounts for about half of total imported agricultural products,and beverages which account for about 12%.The food products,livestock,herbs,nuts and fruits account for less than 5%of the total imports.With the acceleration of pace of Sino-Korean FTA negotiations,the agricultural trade between China and South Korea will further increase.On the occasion of signing Sino-Korean FTA agreement,it is of important practical significance to analyze the Chinese consumers' purchasing awareness,preferences and purchasing behavior about Korean food and agricultural products.
2 Theory and literature review
In recent years,the Korean food has been widely favored by the Chinese consumers,but the consumer demand is often limited by awareness,consumption will and spending power,so the Chinese consumers' purchasing of Korean food and agricultural products is affected by multiple factors.The classic consumption theory tells us that consumers decide the purchase quantity according to maximization of utility,and consumers' purchasing amount of Korean food is determined by consumers' budget line and indifference curve.From the existing academic achievements,the income level is an important factor in determining consumer demand.Kuijs(2005)believes that the decline in income will lead to lack of consumer demand,and income is the most important factor affecting consumer demand.Chen Xiaoyan(2007)uses the Engel coefficient and ELES to study the factors that affect the consumer demand in Jiangsu Province,suggesting that interest rate,income disparity and consumer environment are important factors affecting consumer demand.Lou Feng and Li Xuesong(2009)use China's provincial data during 1991-2005 and employ Horowitz,Henderson semi-parametric panel estimation model and Hubler non-parametric GMM method to measure,indicating that the"ratchet effect"of urban residents' consumption is significant,and income and price are important factors affecting consumer demand.However,some scholars believe that the tradition and modern consumption function theory established by Western scholars is not entirely applicable to China's residents,and the existence of hidden income makes the spending power underestimated(ShiWen,2004).The consumer behavior researcher Katona(1953)believes that the consumer spending is not only the function of income,but also the function of"willingness to buy",and the consumer spending is affected by consumer motivation and consumer attitudes.Consumer psychology maintains that consumers have need in certain environmental stimuli,and then there is purchase motivation which stimulates people's buying behavior.For the study of consumer issues,domestic and foreign scholars mostly conduct discussions from purchase motivation,purchase intention and purchase behavior.Liu Zhichao and Bai Jing(1999)divide consumers' buying motivation into ten types,including physiological purchase motivation,psychological purchase motivation,and social purchase motivation.Liu Wenjun(2009)establishes the emotion-aroused purchase motivation model and the study suggests that white collar women have a rapid consumption habit,and along with increased education,consumers paymore attention to quality of service.Guan Weihua et al.(2012)study the regional distribution of consumption and believe that since the reform and opening up,the consumption differences between China's provinces have tended to expand;there were significant regional differences between north and south in 1978;there were not only differences between north and south but also differences between east and west;after 2008,consumption levels showed significant differences among three regions.According to the research results,the factors influencing consumers' purchase of Korean food include personal characteristics of consumers(gender,age,education,marital status and city),consumer awareness of Korean food,buying habits(purchase place and purchase options),price(Korean food prices and other food prices)and income(consumers' household income).
3 Chinese consumers' awareness,preferences and purchase concerning Korean food
We select five cities(Beijing,Shanghai,Qingdao,Chongqing and Shenyang)and use questionnaires and interviews to analyze Chinese consumers' awareness,preferences and purchase intention on the Korean agricultural products and food,and evaluate the export potential of Korean competitive agricultural products and food to China's market.500 questionnaires were distributed and 480 were returned.A total of 404 valid questionnaires were obtained after removing 76 invalid questionnaires.The survey data are cross-sectional data which can not reflect changes in Korean food prices,so we assume that the Korean food prices remain unchanged and focus on considering the awareness,preferences and purchasing behavior concerning the Korean food.
3.1 Basic characteristics of the respondentsAmong 404 consumers surveyed,177 are male(43.8%),and 227 are female(56.2%)(Table 1).In the survey,it is found that there are 18 respondents with income of less than 1000 yuan(4.5%);there are 80 respondents with income of 1000-3000 yuan(19.8%);there are 115 respondents with income of 3000-5000 yuan(28.5%),and they have high purchasing power;there are 168 respondents with income of more than 5000 yuan(41.6%),and these people have the strongest consumption capacity of Korean food;there are also 24 respondents refusing to disclose their income(5.9%).From the income distribution,it covers all levels of income,and can basically reflect different consumers' purchase of Korean food and agricultural products.
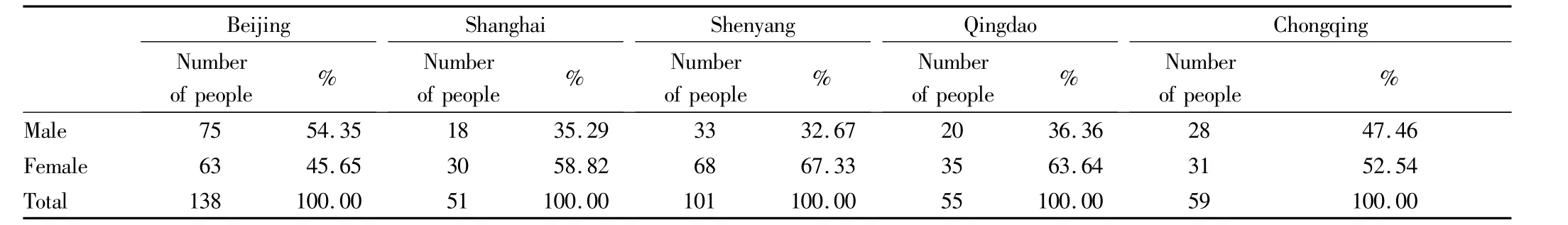
Table 1 Number of questionnaires and gender distribution
3.2 The basic situation of respondents' purchase
3.2.1 Respondents' awareness and purchase concerning Korean food and agricultural products.A total of 298 respondents(73.8%)know the Korean food and agricultural products exported to China(73.8%),while 106 respondents do not know about this(26.2%).A total of 33 respondents are very familiar with the Korean agricultural products and food(8.2%);159 respondents occasionally buy the Korean agricultural products and food(39.4%);175 respondents never purchase the Korean food(43.3%);37 respondents do not know whether they've bought the Korean food(9.2%).It can be found that most of people have high awareness of Korean food,and nearly half of consumers(47.5%)are sure that they've bought Korean food.For the Korean agricultural products and food purchased,105 people have bought drinks,especially bananamilk,juice and coffee;56 people have bought dairy;29 people prefer to buy dried fruit imported from South Korea;most consumers have bought South Korea's tea,and 70 people have bought tea drinks;South Korea's biscuits and bread are popular in China,and 102 consumers once purchased the biscuits and bread(25%);50 interviewees once purchased the Korean sour pickles;87 consumers once purchased Korean salty sauce.By contrast,noodles,red ginseng products,wine,seafood and fruits receive low recognition in China.In terms of price,82 respondents say they can not accept the difference in the price of Korean food and Chinese food(20.3%);208 respondents say they can accept that the price of Korean food is 20%or less higher than the price of Chinese food(51.5%);49 respondents say they can accept that the price of Korean food is 20%-50%higher than the price of Chinese food(12.1%);14 respondents say they can accept the price of Korean food is50%or above higher than the price of Chinese food(3.5%).In terms of the Purchase places,248 people usually buy Korean food in the supermarket(61.4%);77 people buy Korean food in shopping malls and stores(77.1%);79 people buy Korean food through online shopping,restaurants and overseas procurement(19.6%).In the respondents,89 of them think Korean food is safer than Chinese food(22%);104 of them think Korean food taste better(25.7%);29 of them think the Korea food is more nutritious than Chinese food(7.2%);148 of them think there is no difference between Korean food and Chinese food(36.6%);there are still some consumers preferring the package of Korean food.
3.2.2 Consumers' awareness and purchase about Korean food in different regions.As can be seen from Table2,Qingdao is the city with the highest awareness of Korean food,mainly because Qingdao is geographically close to South Korea,and the trade is frequent,and 85%of consumers know the Korean agricultural products and food exported to China;Shenyang has recognition of Korean food only after Qingdao,with awareness degree of 81.2%;Beijing and Shanghai also have high degree of awareness,and 71.7%and 72.6%of people know the Korean agricultural products and food exported to China,respectively;the degree of awareness is lowest in Chongqing,only 55.9%.
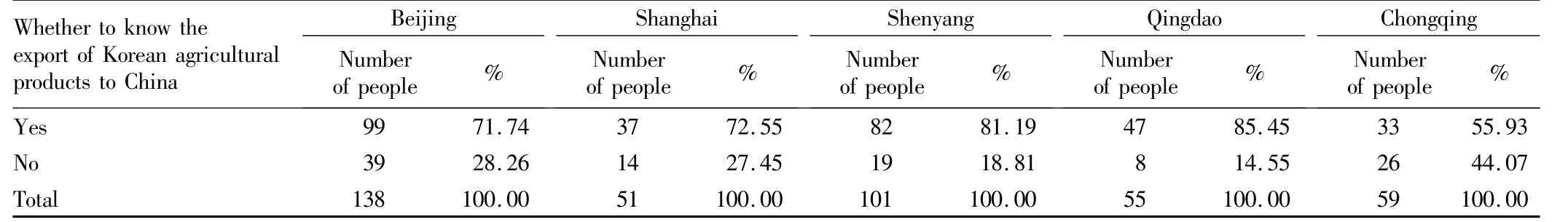
Table 2 Respondents' awareness of the Korean agricultural products exported to China
Table 3 shows the comparison of familiarity with the Korean agricultural products and food in different areas.The degree of familiarity is highest in Qingdao,where 12.73%of respondents are very familiar with the Korean agricultural products and food,and 43.64%of respondents know little about it,that is,56.3%of consumers have certain familiarity with the Korean food.The proportion of consumers who are very familiar with the Korean agricultural products and food in Beijing,Shanghai,Shenyang and Chongqing is11.59%,7.84%,5.94%and 0%,respectively.In addition,in the four cities,the proportion of consumers who only know the Korean agricultural products and food is 43.48%,37.25%,31.68%and 40.68%,respectively;the proportion of consumers who know little about the Korean agricultural products and food is 34.78%,49.02%,57.43%and 33.90%,respectively;the proportion of consumers who have never heard of the Korean agricultural products and food is 10.14%,5.88%,4.95%and 25.42%,respectively.In summary,Qingdao has the highest familiarity,followed by Beijing,Shanghai and Shenyang,and Chongqing has the lowest familiarity.
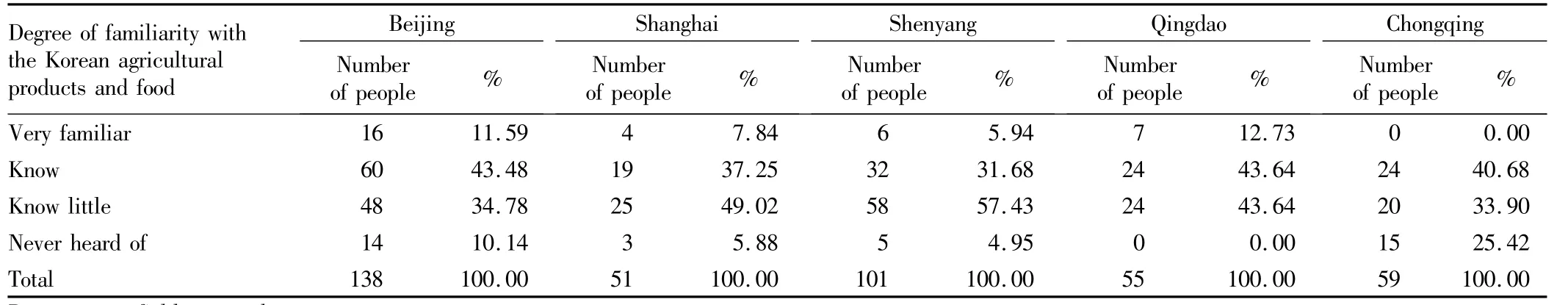
Table 3 Whether the respondents have purchased the Korean agricultural products and food
3.3 The factors that affect respondents' Korean food and agricultural products In the survey,62 respondents think the price is a factor that affect the purchase of Korean food;there are 127 respondents feeling that quality is a factor that affect the purchase;95 respondents believe that security is more important;159 respondents believe that unique taste is an important factor that affect the purchase;there are also40 respondents believing that nutrition is the main reason for the purchase and 21 respondents believing that convenience is the main reason for the purchase.In the 404 respondents,the purchase of247 people(61.1%)is affected by a single factor,and the remaining 38.9%of consumers will consider a number of reasons in purchasing.
3.4 Respondents' purchase expectation of Korean food in the futureTable 4 shows the survey about Chinese consumers' future purchase of Korean food and agricultural products.For most consumers at present,the purchasing amount of Korean food and agricultural products is stable.For beef(119 people,29.46%),milk(121 people,29.95%),pomelo tea(117 people,28.96%),hot pepper sauce(151 people,37.38%),rice wine(110 people,27.23%)and crackers(129 people,31.93%),many Chinese consumers will possibly increase the purchase of them in the future.There is a slight increase in the purchase of some products such as chestnuts,fruits,soy sauce and soybean oil.There is a decrease or no change in the purchase of some products such as red pepper(41 people,10.15%),soy sauce(50 people,12.38%),as well as beef,chestnuts,pomelo tea,ginseng,rice wine,sugar,coffee,etc.
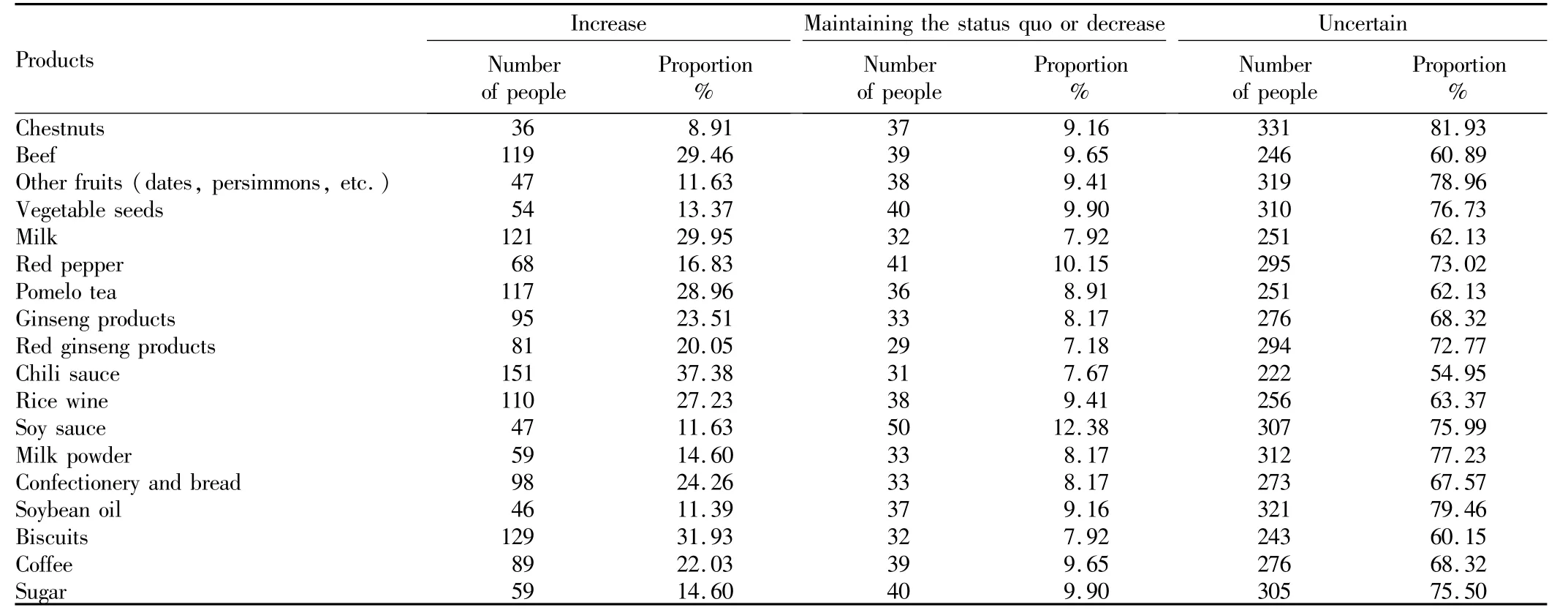
Table4 Chinese consumers' future purchase of Korean food and agricultural products
4 Empirical analysis of Chinese consumers' purchase of Korean food
4.1 Analysis frameworkAccording to research results,taking into account the feasibility of studies,we divide the consumers' personal characteristics into gender,age,education level,marital status and city;cognitive factors include consumers' understanding and awareness of Korean food;buying habits include purchase places and purchase options.
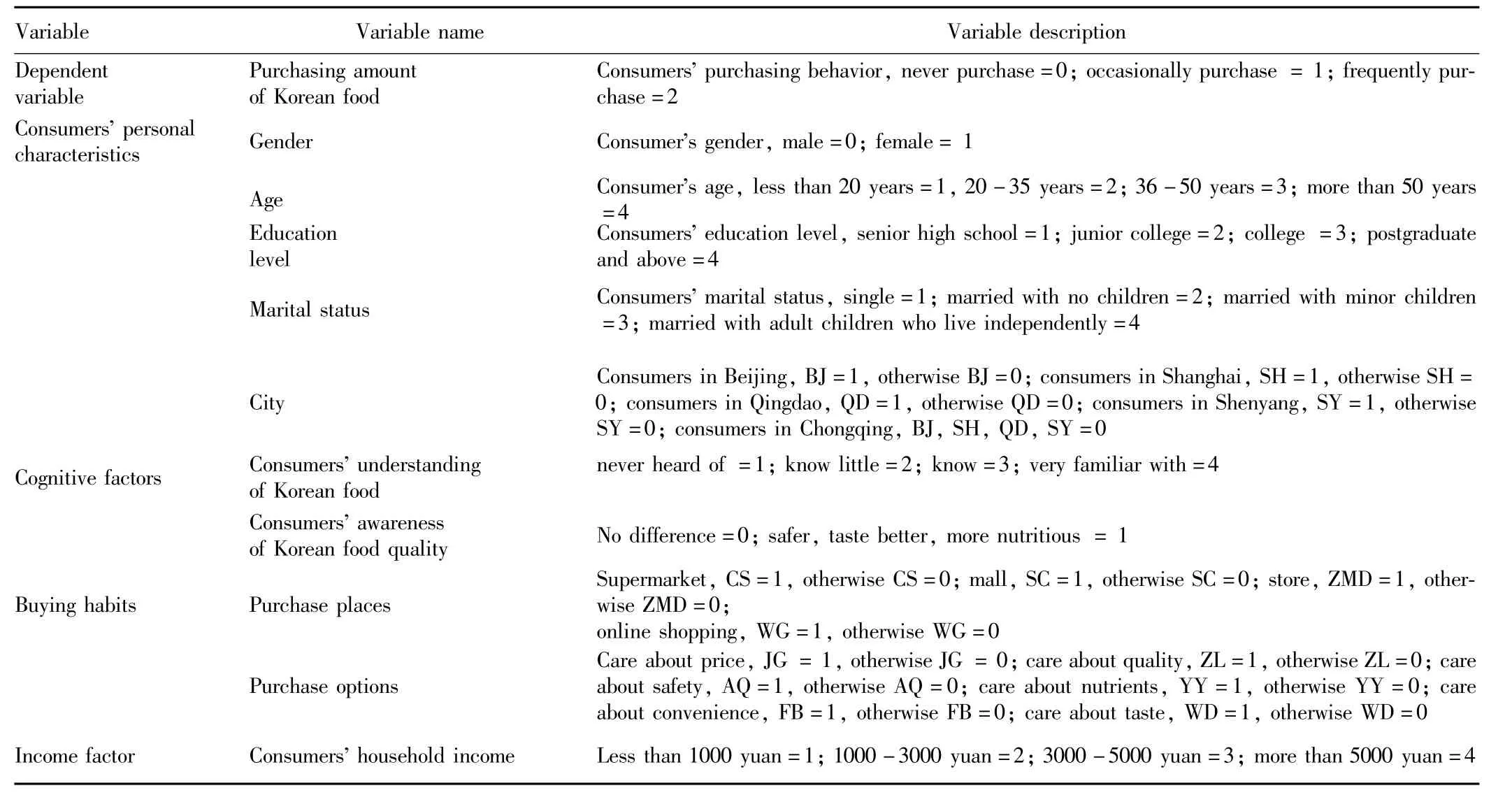
Table 5 The factors that affect consumers' purchase of Korean food and agricultural products
4.2 Hypotheses to be tested
(i)Hypothesis 1:Female consumers buy more Korean foods than male consumers.In general,female consumers are more affected by the Korean culture.(ii)Hypothesis 2:Younger consumers buy more Korean foods than older consumers.Typically,the younger consumers are greatly affected by the Korean culture.(iii)Hypothesis 3:High-income consumers buy more Korean foods than low-income consumers.It is generally believed that income has a significant positive effect on the purchasing amount of food.(iv)Hypothesis4:The consumers in high-income areas buy more Korean foods than the consumers in low-income areas.(v)Hypothesis 5:The consumers with higher level of understanding of Korean food will buy more Korean foods.The level of awareness also affects the consumers' purchasing behavior,and generally consumers will buy the products they are familiar with and recognize.(vi)Hypothesis 6:The consumers thinking the Korean foods are safer and more nutritious and taste better,are more than the consumers thinking there is no difference between Korean foods and Chinese foods.The direction of influence of education and marital status on the purchase of Korean food is uncertain,and this needs to be judged by the results of the model.Buying habit is one of the factors that influence consumers' purchasing behavior.Supermarkets,shopping malls,stores,and online shopping have an uncertain impact on consumers' purchasing amount.When buying the Korean food,consumers' focus on price,quality,safety,nutrition,convenience or taste has no certain impact on the purchasing amount,and this needs to be judged by the model.
4.3 Model selectionThe questionnaire survey data show that there iszero consumption among32.5%of consumers.In the economic sense,these sample values reflect a certain type of consumers' rational behavioral option following the utility maximization under certain constraints.Generally,the more serious the zero consumption problem,the greater the estimation error(Liu Hua,Zhong Funing,2009).Tobit model is often used to solve this problem.The Tobit model is a statistical model proposed by James Tobin(1958)to describe the relationship between a nonnegative dependent variable yiand an independent variable(or vector)xi.The term Tobit was derived from Tobin's name by truncating and adding-it by analogy with the probit model.In this paper,we use this method to solve zero consumption problems,and now we elaborate model setting and elasticity estimation.
Tobit model is as follows:
where Y is the amount of Korean food purchased by consumers;X is the factor that affects the purchasing amount of Korean food;β is the parameter to be estimated.
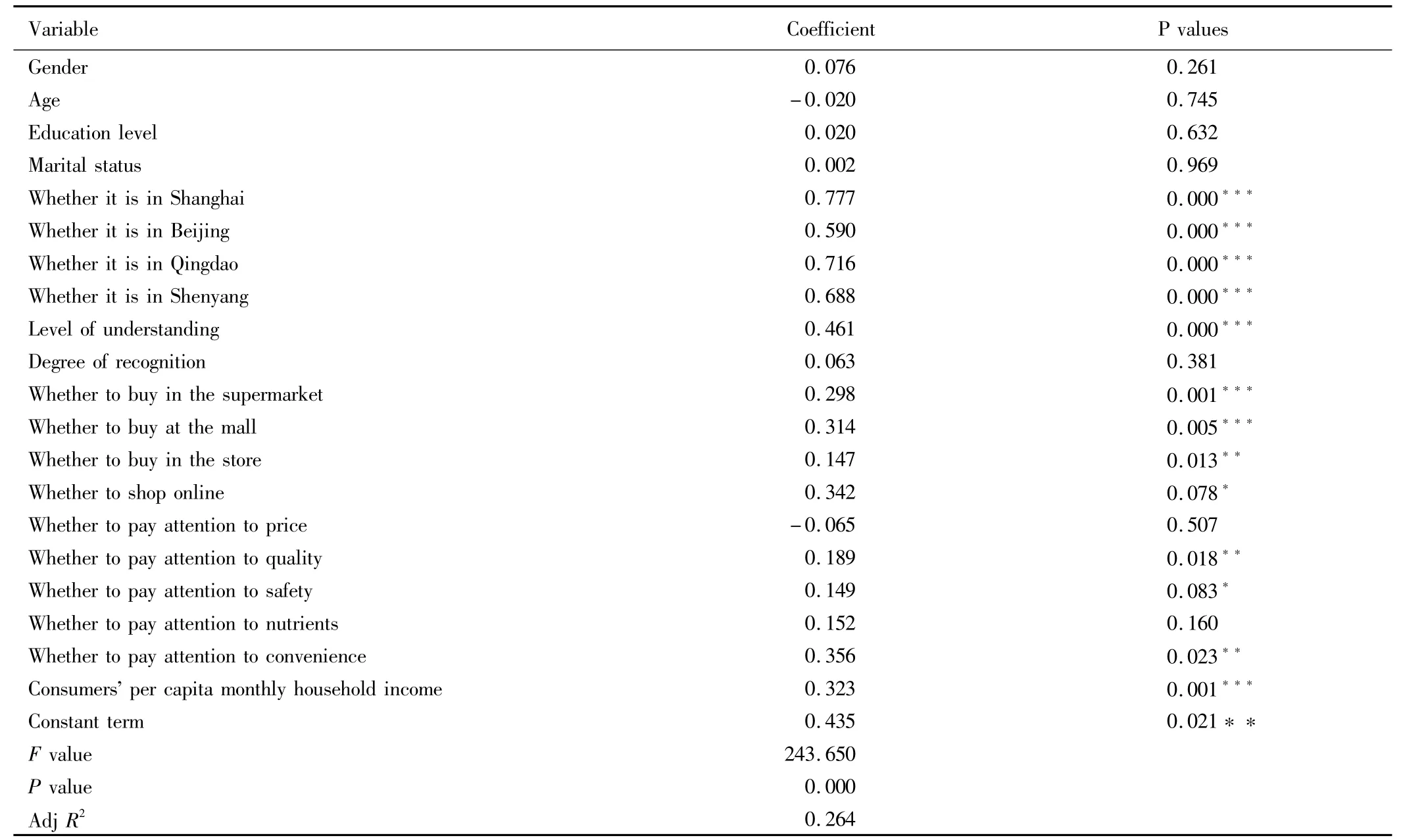
Table6 Regression results of model
4.4 Empirical resultsThe regression model results in Table6 show that the direction of influence of gender and age on the purchase of Korean food is consistent with hypothesis,but the results are not significant,so gender and age are not the key factors that affect the purchasing amount of Korean food.Education level and marital status have also no significant impact on the purchase of Korean food.Consumers' location has an important impact on consumers' purchase of Korean food,and it can be inferred that the purchasing amount of Korean food in Beijing,Shanghai,Qingdao and Shenyang is significantly larger than in Chongqing.On the one hand,the income of consumers in Beijing and Shanghai is higher than in Chongqing,and the model results show that consumers' per capitamonthly household income is a key factor affecting the purchasing amount of Korean food,so the consumers in Beijing and Shanghaibuy more Korean foods than in other cities.On the other hand,Qingdao and Shenyang are near the sea and easily exposed to Korean culture,while Chongqing is in themainl and,having less opportunities to know elements of Korean culture;Korean culture contact will have an impact on consumers' subjective utility when buying food,thus affecting consumers' purchasing behavior.Consumers' understanding of South Korea has a significant positive impact on the purchasing behavior,which is consistent with the foregoing hypothesis.The degree of consumers' recognition of Korean food has a positive effect on the purchasing amount,but the results are not significant.Through the model results,it can be found that the amount of Korean foods purchased by consumers in supermarkets,shopping malls and stores is significantly larger than the amount of Korean foods purchased using other shopping ways such as online shopping,possibly because consumers trust the real purchase and not completely identified with the online shopping.The consumers who lay great emphasis on quality and convenience are significantly more than other consumers when buying Korean food;the consumers who lay great emphasis on price,safety and nutrition are not significantly more than other consumers.
5 Conclusions
(i)Income has a significant positive effect on the purchasing amount of food.From the research results,the high-income consumers are more than low-income consumers in buying Korean food.Most researchers believe that the price of Korean food is generally higher than that of domestic food,so the consumption of Korean food is more significantly affected by income levels,and high-income people tend to pay more attention to nutrition and safety and trust the inspection and quarantine of Korean food.(ii)Geographical location is highly correlated with income levels,consumption habits,imported food awareness and purchase intention,so the city where respondents live is a key factor influencing the purchase of Korean food.Residents' income in Beijing and Shanghai is significantly higher than in Qingdao,Shenyang and Chongqing,so there are more consumers in Beijing and Shanghai buying Korean food.Qingdao and Shenyang are near the sea with convenient transportation,and the residents there have many opportunities to understand elements of Korean culture,while Chongqing is in the mainland,so the consumers buying Korean food in Qingdao and Shenyang are more than in Chongqing.(iii)Purchase place is an external factor having influence on potential customers, and changes with time. Supermarkets, shopping malls,stores and online shopping,as the main channels for consumers to purchase goods,have different effects on consumers' purchasing behavior.The advantage of supermarkets and shopping malls lies in the convenient purchase of goods and access to real products,and the disadvantage lies in the limited same type of merchandise for choice;the convenience of stores is not as good as supermarkets and shopping malls,but consumers can have more choices on the same type of merchandise,and the disadvantage is the high price;online shopping is featured by cheap price and many types,but consumers can not have access to real products and the convenience is not good.Thus,the type and number of Korean foods in the supermarkets directly affect consumers' purchase of Korean foods.(iv)Age,gender,education level and other factors do not significantly affect consumers' purchase of Korean food in model analysis,but it is found in the survey that the well-educated consumers with minor children are more willing to buy Korean food,and the appearance and unique taste of Korean food are more attractive to 20-35 year old female consumers and minors.For the older and less educated consumer groups,the willingness to buy Korean food is low.
[1]DING KD.On composition of trade between China and South Korea and its trend characteristics as well as its enlightenments to FTA negotiation[J].World Economy and Trade,2013(6):69-74.(in Chinese).
[2]KUIJS L.Investment and saving in China[R].The World Bank Office,China East Asia Pacific Poverty Reduction and Economic Management(EASPR),2005.
[3]CHEN XY.Main factors of the change of consumption in Jiangsu and main measures to expand consumption[D].Nanjing:Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2007.(in Chinese).
[4]LOU F,LIXS.Urban consumer demand in China:An empirical analysis using the dynamic semiparametric panel data model[J].Social Sciences in China,2009(3):109-115.(in Chinese).
[5]SHIW.Study on the change of China residents'consumption demand and propensity to consume[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2004.(in Chinese).
[6]Katona G.Rational behavior and economic behavior[J].Psychological Review,1953,60(5):307-318.
[7]LIU ZC,BAIJ.The types of purchasing motivations and its applications in marketing[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),1999,27(9):53-58.(in Chinese).
[8]LIUWJ.The research on the impact of emotional wake-up model on the white collar women workers consumer motivation[D].Changsha:Ji'nan University,2009.(in Chinese).
[9]GUANWH,ZHOU J,LU YL.Study on the regional pattern change of social consumption levels in China since the reform and opening up[J].Geographical Research,2012,31(2):234-244.(in Chinese).
[10]LIU H,ZHONG FN.Food consumption and demand elasticity:Evidence from household survey data[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University(Social Science Edition),2009,9(3):36-43.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Analysis on Factors Influencing Distribution of Vegetal Production
- Regional Differences in the Demand for Agricultural Socialized Service
- SWOT Analysis on Breeding R&D of Tropical Crops in China in the Context of Implementing UPOV Convention 1991 Act
- A Study of the Moderate Scale Operation of China's Agriculture
- Study on the Degree of Rural Empty Nesters' Satisfaction with Life Quality Based on Ordered Logit-ISM Model
- Current Situation and Development Trend of the Sugarcane Industry in Indonesia
