A Study of the Moderate Scale Operation of China's Agriculture
Ling XIN,Zhiquan HU
Institute of Agricultural Economics and Development,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100081,China
Supported by Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(ASTIP-IAED-2015-02);Fundamental Research Fund Project of Institute of Agricultural Economics and Development,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(0052015002-9).
1 Introduction
Since the reform and opening up,the basic operating system of agricultural production in China has always been the household contract responsibility system,which combines centralization with decentralization.At the initial stage of policy implementation,it greatly emancipated productivity of agricultural labor,and played an important role in protecting national food security,boosting agricultural production and increasing farmers' income[1-3].However,since joining the WTO,single household operating mode has not been unable to guarantee the basic living needs of farmers in many regions[4-6],causing a tremendous threat to China's agricultural development,so traditional agriculture urgently needs to shift to modern agriculture.Central Document No.1 in 2013 proposed encouraging and guiding the urban industrial and commercial capital to develop crop cultivation and aquaculture suitable for business-oriented operation in rural areas;guiding farmers to adopt advanced technology and modern factors of production according to scale,specialization and standardization requirements;accelerating the transformation of mode of agricultural production and operation,and focusing on supporting some new business entities such as family farms,farmer cooperatives,and"companies+cooperatives+farmers".This provides effective policy support for the transformation of agricultural production methods.Scale of operation will become a major business mode for China's agriculture to realize modernization in the future[7].With the improvement of industrialization and urbanization levels and rapid development of rural market economy,the competition for resources used in agricultural and non-agricultural production will be much fiercer[4].We measure the land inputscale realizing moderate scale operation to provide a scientific basis for realizing the reasonable allocation of finite agricultural resources,giving full play to the optimum production potential,and enhancing economic efficiency of agriculture.
2 Current situation of scale operation of China's agriculture
2.1 Current situation of scale operation of crop farm ing
According to the statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture,there were 8.874million large farming households with operating area of 2 ha or more in 2012,and the total operating scale of land was more than 33 million ha[8].However,the operating scale of the Chinese farming households is generally small.The rural households with arable land size of less than 0.33 ha account for50%,while the rural households with arable land size of less than 0.67 ha account for 75%[9].There are large differences in the arable land size for rural households between various regions of China.The rural households with arable land size of more than 1.3 ha account for more than25%in Northeast,while the operating scale of agriculture is small inmost southern regions[10-11].
2.2 Current situation of operating scale of animal husbandryChinese animal husbandry is dominated by scattering raisers and the scale is small.The main supplier of pork in China is scattering hog raisers.In 2013,30.1%of slaughtered hogs were provided by the scattering raisers with the scale of less than 50 slaughtered hogs per year[12].Sichuan is a major producer of hog in China,but the development of scale breeding is slow[13].The scattering raisers with the scale of less than 50 slaughtered hogs per year provide 75.45%of slaughtered hogs.China's main supplier of beef is also scattering cattle raiser,and the scattering raisers with the scale of1 to 9 head of slaughtered cattle per year provide 54.9%of slaughtered cattle.The scattering raisers with the scale of 1 to 29 slaughtered sheep per year provide 42.7%of slaughtered sheep.The scattering raisers with the scale of less than 2000 slaughtered laying hens per year provide 31.7%of slaughtered laying hens.The scattering raisers with the scale of less than 2000 slaughtered broilers per year provide 14.4%of slaughtered broilers[14].
3 Measurement and analysis of moderate scale operation of agriculture
The moderate scale operation of agriculture refers to the minimum scale of the agricultural industry under the premise of ensuring agricultural production and farmers' income,that's to say,the same income can be obtained either from agricultural production or from working outside the home[15-18].
3.1 Measurement modelDue to different net profit,there are differences in the operating area of land which achieves agricultural moderate scale between different industries,years or regions.The operating area of land which achieves agricultural moderate scale is calculated using the net profit of one product per unit area to divide the income from local work in the same year.It is shown in equation(1).
where S is the moderate scale land operation area;i is year;j is the product category;p is the area;IC represents wage income;RP is net profit.
The premise for equation(1)is to be engaged in the specialized operation,that is,the farmers are only engaged in the production and operation of a class of products,without considering by-business and multiple cropping.
3.2 Measurement of moderate scale of main crops
3.2.1 Moderate scale operation of food crops.The moderate operation scale of food crops is about 7.3 ha,and farmers lack enthusiasm for growing food crops,because the grain income is difficult to meet the needs of life,far less than the wage income[19].The fundamental starting point of measurement is that farmers' income from growing grain is basically equal tow age income.During 2009-2012,the annual per capita income of farmers was17004,20280,24588 and 27480 yuan,respectively,with an average income of 22338 yuan(Table 1).If the scale operation is realized,the grain planting area during 2009-2012 needs to reach 5.87,5.93,6.53 and 10.87 ha,respectively.In 2012,profit margins of food crops per hectare were low(only 319.35 yuan for wheat),resulting in too large moderate scale.Without considering the cropping of the same arable land,the average moderate scale of grain,rice,wheat and corn is 7.33,4.93,29.4 and 6.93 ha,respectively(Table 1).
3.2.2 Moderate scale of main cash crops.Vegetable,cotton and apple are selected as the representatives of cash crops,and research shows that the moderate scale operation area of vegetables in large and medium-sized cities averages0.61 ha;due to the impact of domestic and international markets,there are great fluctuations in moderate scale which averages 21.42 ha;the moderate scale area of apple is 0.37 ha.
3.2.3 Moderate scale of breeding industry.Due to data acquisition,the free-range hogs are selected as the representative of breeding industry.Due to great market impact,hog farming profits vary widely[20],and there was a loss in 2012;148 hogs in 2011 reached moderate operation scale;the average moderate scale during 2009-2012 was 388(Table 2).
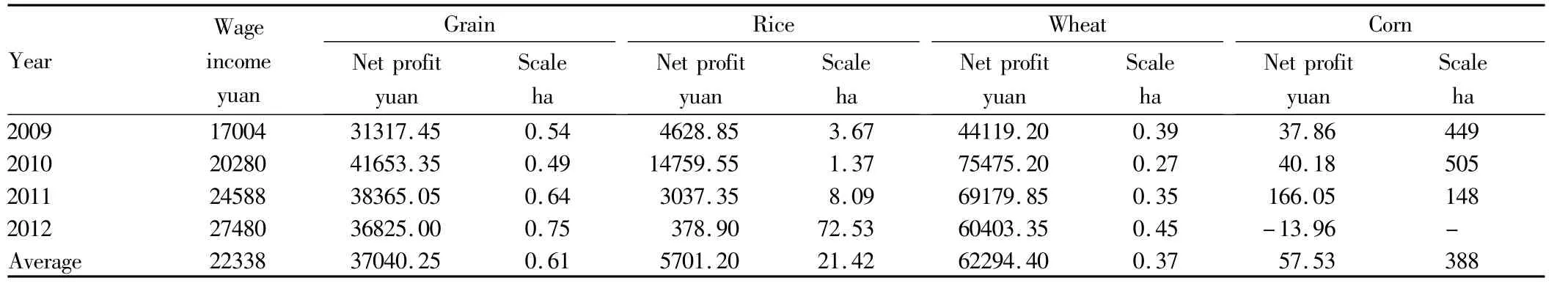
Table 2 The changes in the moderate scale area of main cash crops in recent years
3.3 Analysis of moderate scale operation in different regions
3.3.1 Regional distribution of moderate scale operation of food crops.The national average scale operation area of early indica rice is 14.61 ha,the largest scale operation area of early indica rice is 30.60 ha in Fujian Province,and the smallest scale operation area of early indica rice is 8.87 ha in Anhui Province(Table 3).The national average scale operation area of medium indica rice is5 ha,the largest scale operation area of medium indica rice is more than 69 ha in Guizhou Province,and the smallest scale operation area of medium indica rice is3.08 ha in Hubei Province(Table 4).The national average scale operation area of late indica rice is7.42 ha,the smallest scale operation area of late indica rice is 4.56 ha in Zhejiang Province,and the net profit in Hainan Province is negative(Table 5).The profit of japonica rice is significantly higher than that of indica rice.The national average scale operation area of japonica rice is4.53 ha,the smallestscale operation area of japonica rice is 2.77 ha in Inner Mongolia,and the largest scale operation area of japonica rice is10.39 ha in Hebei Province(Table 6).The profit of wheat is low,and negative in most provinces(Table 7).Corn is important grain and forage crop,and its profit is negative in Hubei,Guangxi,Chongqing,Guizhou and Yunnan(Table 8).The national average moderate scale operation area of soybean was14.24 ha in 2012(Table 9).
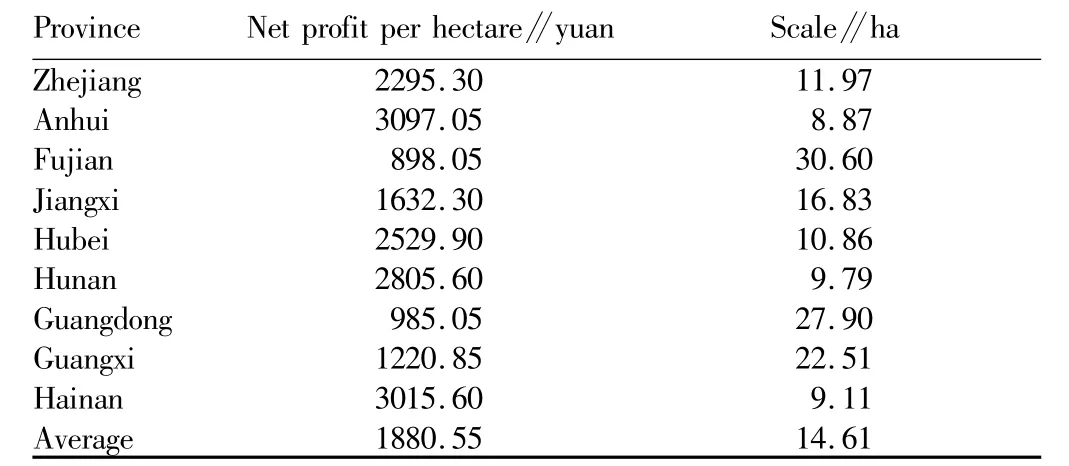
Table3 The moderate scale operation area of early indica rice
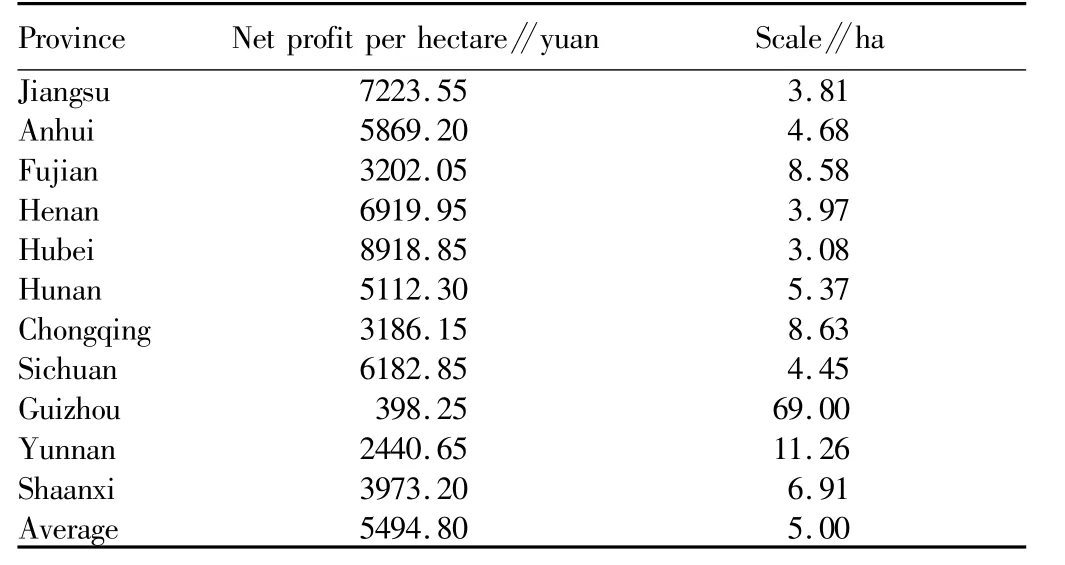
Table 4 The moderate scale operation area of medium indica rice

Table 5 The moderate scale operation area of late indica rice

Table 6 The moderate scale operation area of japonica rice
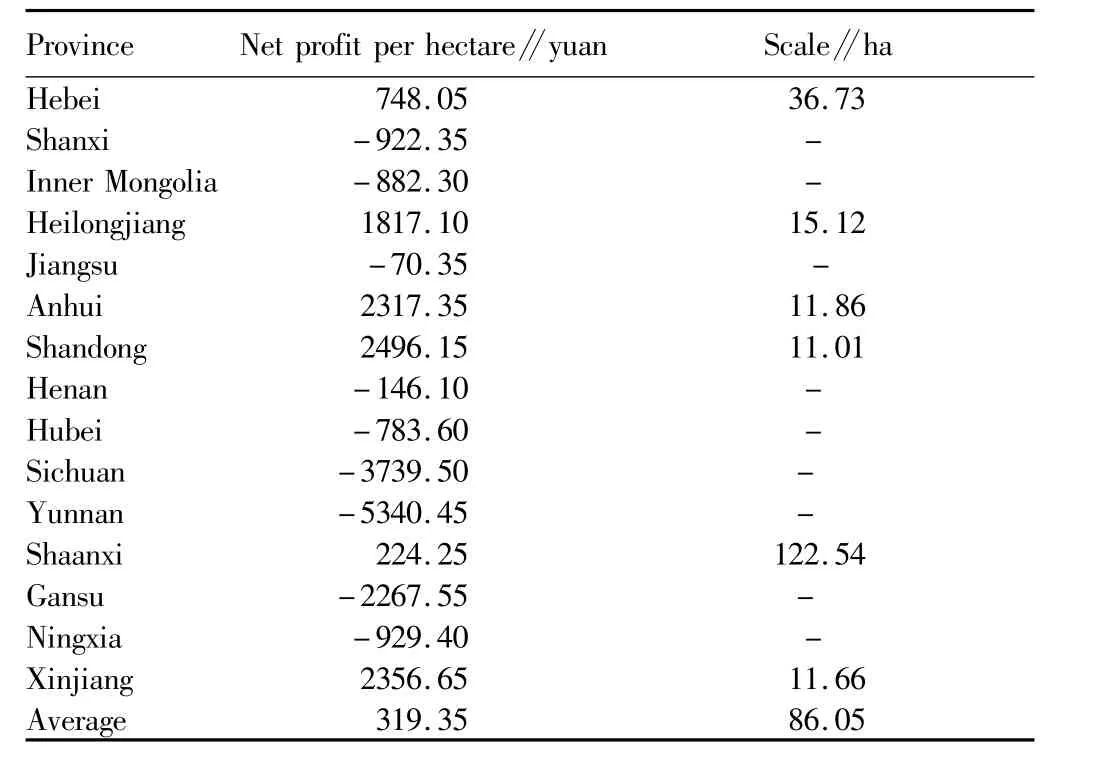
Table 7 The moderate scale operation area of wheat

Table 8 The moderate scale operation area of corn
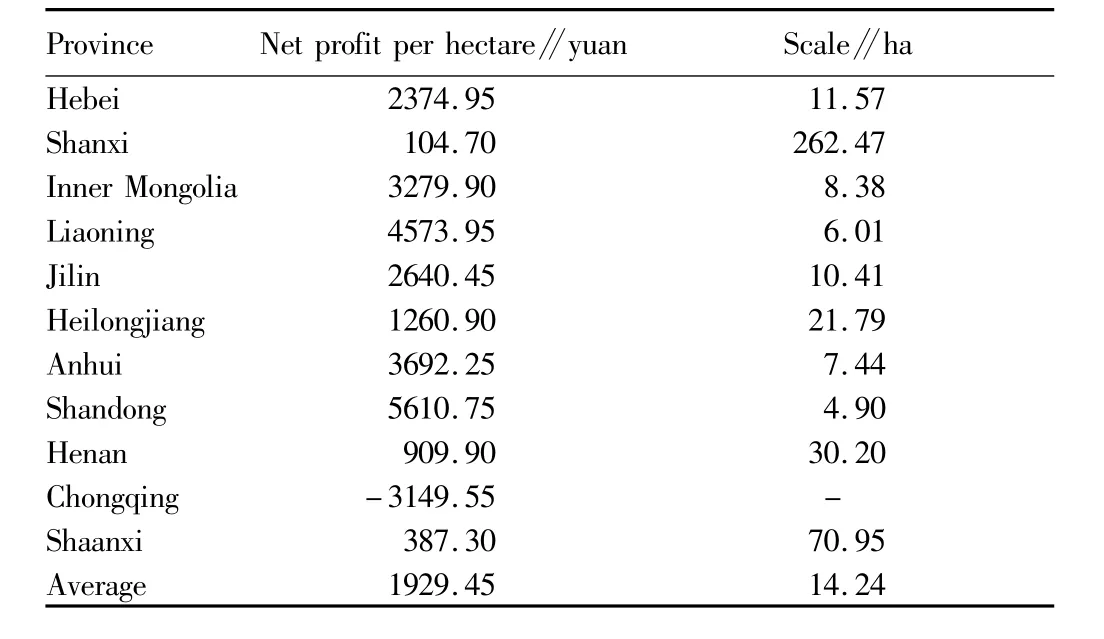
Table9 The moderate scale operation area of soybean
2.2.2 Regional distribution of moderate scale operation of cash crops.Cotton,apple and tomato are selected for the moderate scale operation analysis of regional cash crops.There are great fluctuations in cotton market.Most of regions suffered a loss in 2012,and only Gansu and Xinjiang had a great profit(Table 10).In 2012,the national average moderate scale operation area of apple was 0.45 ha;the smallest moderate scale operation area of apple was0.25 ha in Beijing;the largest moderate scale operation area of apple was 1.03 ha in Liaoning(Table 11).The national average moderate scale operation area of tomato was 0.47 ha,and the largest moderate scale operation area of tomato was 1.71 ha in Inner Mongolia(Table 12).

Table 10 Moderate scale operation area of cotton

Table11 Moderate scale operation area of apple
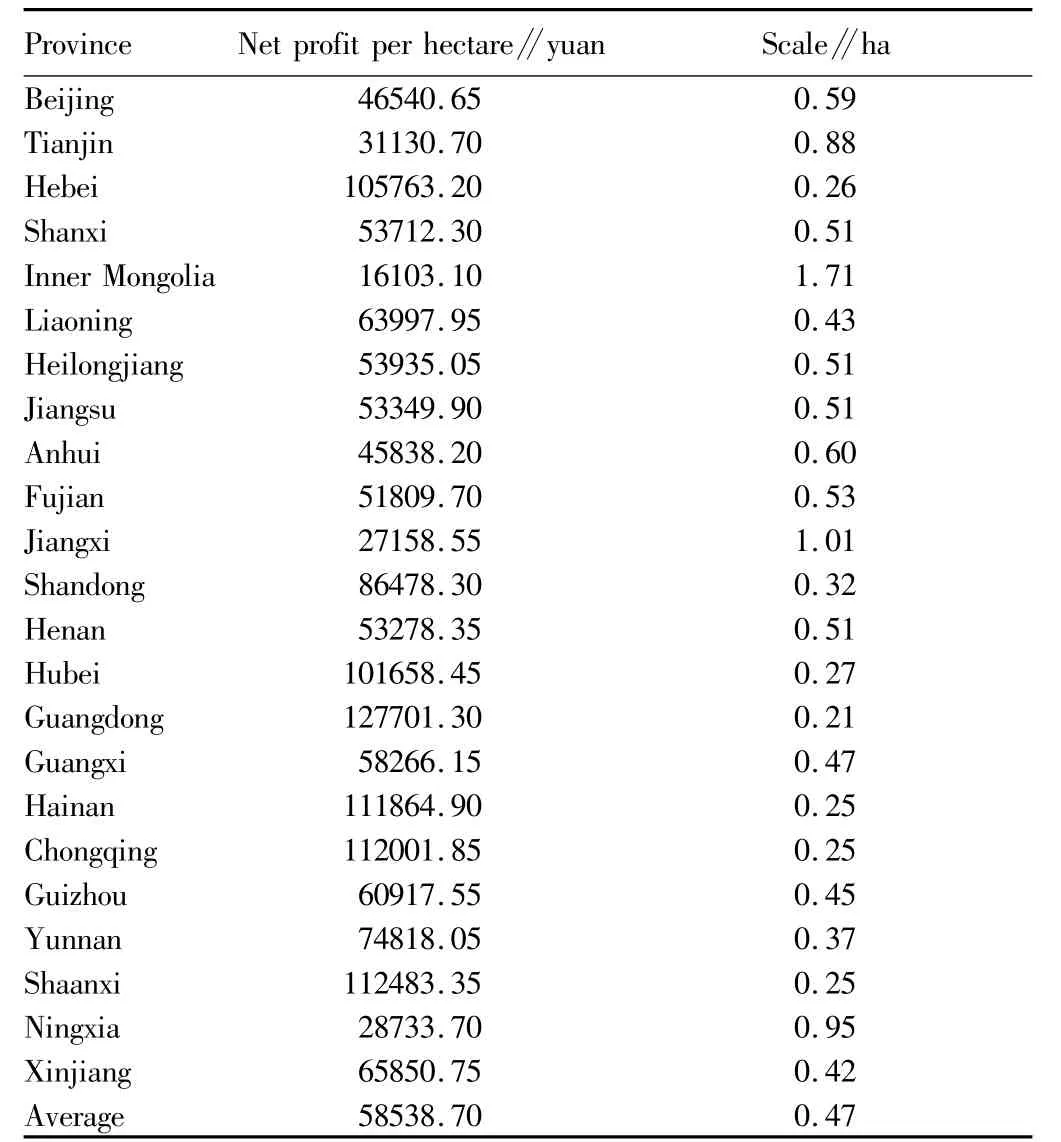
Table 12 Moderate scale operation area of tomato
2.2.3 Regional distribution of moderate scale operation of livestock products.Because of data availability,we select sheep as the livestock product.In 2012,the national net profit per 100 sheep was 11706 yuan,and the average moderate scale was 234.8;the smallest scale was 54.3 in Ningxia;the scale of demand was largest in Inner Mongolia(Table 13).

Table 13 Moderate scale operation area of sheep
4 Conclusions and policy recommendations
4.1 ConclusionsThe operating scale of Chinese rural households is generally small.Expanding farmers' arable land scale can help farmers to concentrate on agricultural production and increase agricultural productivity.The larger the arable land scale of farmers,the higher the enthusiasm for production input.The yields rise with the expansion of cultivated land,but the scale of cultivated land must be appropriate.Through measurement and analysis,it is found that the moderate operation scale of grain is around 7.3 ha;the average moderate scale operation area of vegetables is about0.6 ha in large and medium-sized cities;the moderate scale operation area of cotton is 21.4 ha;the moderate scale operation area of apple is 0.37 ha.From 2009 to 2012,the average moderate scale of free-range hogs was 388.In 2012,the national average moderate scale of sheep was234.8.
4.2 Policy recommendations
4.2.1 Encouraging farmers to transfer land and promoting the development of scale operation.It is necessary to focus on the construction of animal and plant disease control service system,agricultural product quality and safety service system,agricultural information-based service system,agricultural material service system,and farm machinery system[21-22].
4.2.2 Building a sound modern agricultural organization and management system.It is necessary to introduce the policies to support family farms,so that the production and management level of family farms is greatly enhanced[23];guide skilled agricultural technicians,entrepreneurial talents and farming and breeding experts to transfer land to form large farming and breeding households or family farms.
4.2.3 Innovating upon the cooperative mechanism and strengthening the organizing role of cooperatives in modern agricultural development.It is necessary to actively innovate upon the cooperative operation,expand service capabilities,and focus on cultivating a number of farmers' cooperative business entities with largescale operating scale,new operational mechanism and superior quality products to improve market competitiveness.
4.2.4 Enhancing the status of leading enterprises and playing the role of leading enterprises in modern agricultural development[24].It is necessary to innovate upon scientific and technological innovation capacity and improve core competitiveness of leading enterprises;enhance modern operation level of management personnel and increase the soft power of leading enterprises;increase training for various types of personnel to improve their quality;increase financial support to improve the scale operation level of leading enterprises[25].
4.2.5 Forming the modern agriculture industry consortium with family farms as main body,cooperatives as link and enterprises as leader.It is necessary to use cooperatives to promote the family farms and enhance organizational capacity of farmers to form organized production body;play the role of leading enterprises,change the previous disorder and chaos of myriad family farms and large farming households faced by enterprises,and establish a production and management community between cooperatives and farmers.
[1]GONG JX.The realization of proper scale management based on household contract system——The practice and thought of propelling agricultural moderate scale management in Haimen City[J].Shanghai Rural Economics,2009(7):39-43.(in Chinese).
[2]LICG.Research on appropriate scale for agricultural operation in Henan:Present situation,problems and countermeasures[J].Contemporary Economic Management,2013,35(10):37-42.(in Chinese).
[3]LIHY.A summary of the research into agriculture scale-management[J].Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology,2007,22(9):27-32.(in Chinese).
[4]LIXM,YINML.Large scale grain-production farmers' operation situation in the main grain-producing areas and development strategies:Analysis based on the survey of large scale grain producers in Anhui Province[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2008(10):21-25.(in Chinese).
[5]ZHANG YL.Current problems of appropriate scale operation of agricultural production[J].Journal of Jilin Province Economic Management Cadre College,2011(3):60-64.(in Chinese).
[6]YANG LR,CHENWK,MU PS.Analysis on agricultural economic efficiency of Shehong County based on DEA method[J].Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University,2009,27(2):243-247.(in Chinese).
[7]ZHANG SM.Advancing agricultural moderate mass production to change modernization agricultural development mode[J].Chinese Agricultural Mechanization,2008(2):10-13.(in Chinese).
[8]YANG GQ,HU L,WANGWX.Moderate scale of farmers'cultivated land management and its performance:An empirical analysis based on questionnaire survey of rural households in 6 counties in Hubei Province[J].Resources Science,2011,33(3):505-512.(in Chinese).
[9]LUOQ.Influencing factors of moderate agricultural operation[J].Economic Research Guide,2008(7):12-13.(in Chinese).
[10]QIAN GX,LINH.The analysis of optimized operating scale of farms in main cereal producing areas[J].Statistical Research,2004(10):40-43.(in Chinese).
[11]XUGS.A comparative analysis on agricultural business scale abroad and its economic benefit[J].Chinese Rural Economy,1990(10):46-51.(in Chinese).
[12]ZOU XY,XIAO GA.A game analysis on the management on agricultural small scale in China[J].China Rural Survey,2003(5):18-23.(in Chinese).
[13]QIC.An empirical analysis on the transfer of rural labor and moderate land scale management[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2008(4):40-43.(in Chinese).
[14]ZHANG ZM,ZHOU LJ,QIANWR.Study on the relationship between agricultural management scale and agricultural productivity——Based on the investigation and analysis of Zhejiang Province[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2011(12):23-29.(in Chinese).
[15]SHIYM.Analysis on the agricultural development[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2010(15):284-285.(in Chinese).
[16]FENG L.Main body of moderate scale management of agriculture in our country and route choosing[J].Chongqing Social Sciences,2013(9):84-88.(in Chinese).
[17]HUANG ZH,YU N.The current situation,constraint and development ideas of the new type of agricultural management subject——Based on the analysis of Zhejiang Province[J].Chinese Rural Economy,2010(10):16-26.(in Chinese).
[18]LIWA,MAWQ.Modes and efficiency analysis of agriculture lands'scale-management in Henan[J].Academic Forum of Nandu,2012,32(4):98-101.(in Chinese).
[19]CHEN YH.Speeding up the circulation of rural lands and promoting the agricultural scale management[J].South China Rural Area,2013,29(3):11-13.(in Chinese).
[20]XUE L.On the road of modern agricultural growth of Chinese specialty from the angle of agriculture scale management[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2008(6):4-9.(in Chinese).
[21]GONG LP,WANG YF.Inevitability and gradualness of scale management of agriculture in China[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2008,36(10):4289-4290.(in Chinese).
[22]YANGGY,HAOXY.The theoretical thinking on scale managementof agriculture[J].On Economic Problems,2006(12):42-45.(in Chinese).
[23]ZHAO XQ.The contradiction faced by agricultural scale operation and its outlet[J].On Economic Problems,2006(7):44-46.(in Chinese).
[24]XIN L,JIANGHP,LIU XY.The evaluation of county town’s agricultural modernization in China[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2014,30(20):87-94.(in Chinese).
[25]JIANG HP,XIN L.Effectively supporting main producing areas and ensuring food security[J].China Development Observation,2011(1):41-43.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年8期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Analysis on Factors Influencing Distribution of Vegetal Production
- Regional Differences in the Demand for Agricultural Socialized Service
- SWOT Analysis on Breeding R&D of Tropical Crops in China in the Context of Implementing UPOV Convention 1991 Act
- Chinese Consumers' Awareness,Preferences and Purchasing Behavior on Korean Food
- Study on the Degree of Rural Empty Nesters' Satisfaction with Life Quality Based on Ordered Logit-ISM Model
- Current Situation and Development Trend of the Sugarcane Industry in Indonesia
