Determination and Evaluation of Heavy Met al Content of Freshwater Economic Fish in Northeast Guangdong
Yanmei ZHONG,Qingm ei ZHENG,Chunyan HAN,Rushu WEN,Hongli ZHANG
College of Life Science,Jiaying University,Meizhou 514015,China
The aquatic product is an important part of human food.With the improvement of living standards,people have placed increased demands on the quality of aquatic products,however,with the rapid development of industry and agriculture,the discharge of large amounts of sewage and waste often leads to heavy metal pollution[1].Heavy metal is a highly toxic pollutant with cumulative effect,which can directly or indirectly enter the body tissues through the food chain in water environments,resulting in a serious threat to human health[2].The fish is often at the top of food chain of aquatic ecosystems,so it is often regarded as a biological indicator to assess heavy metal pollution in the ecosystem[3].Meanwhile,excessive heavy metal in aquatic feed is also one of the important reasons for excessive heavy metal in aquatic products[4].In recent years,studies have indicated that the mass fraction of heavy metal in the body of freshwater economic fish is over the standard in some China's regions[5-8].Zeng Leyiet al.[9]study the mass fraction of heavy metal in eight kinds of fish,and the results show that the mass fraction of Pb and Cd in fish is over the Chinese food safety standards.Xie Wenpinget al.[9]analyze the mass fraction of heavy metal in fish in Pearl River Delta,and the results show that the residual heavy metals in fish are Cr,Pb and As,exceeding standard by 36.7%,27.1%and 6.3%,respectively.The fish muscle is an important part of human-ingested fish,so most studies only focus on the heavy metal pollution of edible parts of fish(such as muscle)[10].However,the fish muscle usually can not better reflect the heavy metal pollution in fish,and the study of other fish organs such as liver is becoming especially important[11].Some metals combined with proteins are usually distributed in a number of organs and tissues,for example,the metallothione in is distributed in the liver,and it has affinity for the metal,so the mass fraction of heavy metal in the liver is much higher than in muscle[12].It indicates that the determination of heavy metal content of fish liver is conducive to assessing the long-term exposure of fish to heavy metal environment[13-14].Northeast Guangdong is a traditional heavy industrial area in Guangdong Province,and a large number of new industrial transfer parks have been built here,increasing environmental pollution.This study takes 9 common economic fishes(Ctenopharyngodon idellu,Megalobrama amblycephala,Oreochromis niloticus×O.aureus,Colossoma brachypomum,Cyprinus carpio,Carassius auratus,Silurusasotus,MicropterussalmoidesandChanna argus)in Northeast Guangdong as the object of study to analyze the accumulation of heavy metals such as Pb,Cd,Cr,Zn,Mn and Cu in muscle and liver,so as to provide a scientific basis for the ecological protection of waters in Northeast Guangdong and safe fishery production.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Experimental materialsFrom March to July in 2012,we selected 9 kinds of fresh economic fishes with different feeding habits in Northeast Guangdong in three batches as the experimental fishes.The feeding habit,sample size,body length and body mass of each kind of fish are shown in Table 1.Using stainless steel dissecting scissors and scalpels,we dissected the experimental fishes,and obtained back muscles,liver,and gut,gill and other tissues ofC.idellus.After cleaning the surface blood,the samples were dried by filter paper,put into the plastic sealed bag,and stored in-20℃refrigerator for use.
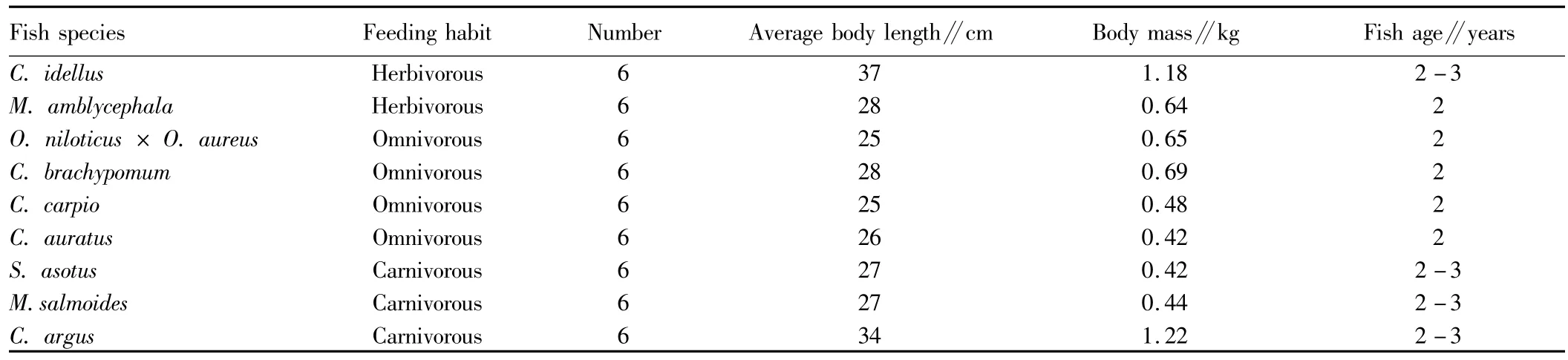
Table 1 The feeding habit,age,number,average body length and body mass of fish samples
1.2 Experimental methodsAfter the natural thawing of experimental fishes,the moisture was absorbed by absorbent paper and they were cut it into pieces with scissors.We accurately weighed muscles(about1.0 g),liver(about 0.5 g),and intestine and gills ofC.idellus(1.0 g).With ultra-pure water as the blank control,they were placed into the high pressure digestion tank,respectively.After being soaked with 3 mL concentrated HNO3and 3 mL H2O2overnight,the high pressure digestion tank was put into the oven for6 h digestion at150℃.After cooling to room temperature,they were transferred to a volumetric flask,and evenly mixed for use.The samples of two fishes were mixed into one sample,and three parallel samples were set for each kind of fish.Inductively-coupled plasma spectrometer(SP-127 ICPE-9000 Shimadzu)was used to measure the mass fraction of Zn,Cu,Pb,Cr,Mn and Cd in samples.The reagent blank solution and standard samples were also measured at the same time,and the relative deviation between standard substance measured values and standard values was less than 10%,in line with requirements.
1.3 Data processing and evaluation methods
1.3.1 Data processing.We use the following formula to calculate the mass fraction of measured samples:
whereXis the mass fraction of heavy metal in samples,mg/kg;A1is the measured mass fraction of samples,μg/mL;A2is the mass fraction of the control,μg/mL;Vis the total volume of samples processed,mL;Mis the actual mass of sample weighed,g.
Excel 2003 was used for data processing,and the average value was taken as the result.
1.3.2 Evaluation methods.The single factor pollution index method was used to evaluate the heavy metal contamination in fish,and the expression is as follows:
wherePiis the single factor pollution index;Ciis the actual mass fraction of factoriin the sample;Siis the standard evaluation value of factor i[15].
"S"evaluation standard values use Safety Qualification for Agriculture Product Safety Requirements for Non-environmental Pollution Products(GB 18406.4-2001).Since this standard does not involve Zn,the evaluation standard for Zn is in accordance with Limit Standard of Zinc in Food(GB 13106-1991).Mn has no limit standard.The evaluation standard can be shown in Table 2.If the pollution indexPi<0.2,it indicates that the mass ratio of heavy metals is within the normal background value range;if 0.2≤Pi<0.6,it is at the slight pollution-light pollution level;if0.6≤Pi<1.0,it is at the pollution level;if the pollution indexPi≥1.0,it is at the heavy pollution level.It shows that the heavy metal residues of this product exceed the requirements of Safety Qualification for Agriculture Product Safety Requirements for Non-environmental Pollution Products[15].
2 Results and analysis
2.1 The mass fraction of six kinds of heavy metal in muscle and liver of fish The measured mass fraction of Cd,Cr,Cu,Mn,Pb and Zn in muscle and liver of nine kinds of fish is shown in Table 2.From Table 2,it is found that the enrichment levels of heavy metal in different fishes and tissues are not consistent.In terms of the average mass fraction of heavy metals in of nine kinds of fish,it is sequenced in descending order as follows:Zn>Cu>Pb>Cr>Mn>Cd.In terms of the average mass fraction of heavy metals in muscles of nine kinds of fish,it is sequenced in descending order as follows:Zn>Cr>Pb>Mn>Cu>Cd.The average mass fraction of heavy metal in liver of fish is higher than that of heavy metal in muscles.
2.2 Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in different tissues of fishThe single factor pollution index of heavy metal pollution in fish is shown in Table3.From Table3,it can be found that Pb pollution is most serious for the nine kinds of fish,followed by Cd and Cr;the Cu and Zn pollution is light;Mn has no limit standards.The mass fraction of Pb in liver of the nine kinds of fish reached"heavy pollution level",and the mass fraction of Pb in muscle is at"pollution level".ExceptC.brachypomumandC.auratus,the mass fraction of Cd in liver of seven other kinds of fish and muscle and intestine ofC.idellus,is at"heavy pollution level";the mass fraction of Cd in muscle of the nine kinds of fish is mostly at"slight pollution-light pollution level"or"pollution level".The mass fraction of Cr in muscle and gill ofC.idellusis at"heavy pollution level",and"pollution level",respectively;the mass fraction of Cr in the tissues of other kinds of fish is at"slight pollution-light pollution level"or"pollution level".The mass fraction of Cu and Zn in liver of most fishes is at"slight pol-lution-light pollution level".The mass fraction of Cu and Zn in muscle of the nine kinds of fish is at the normal background value level.
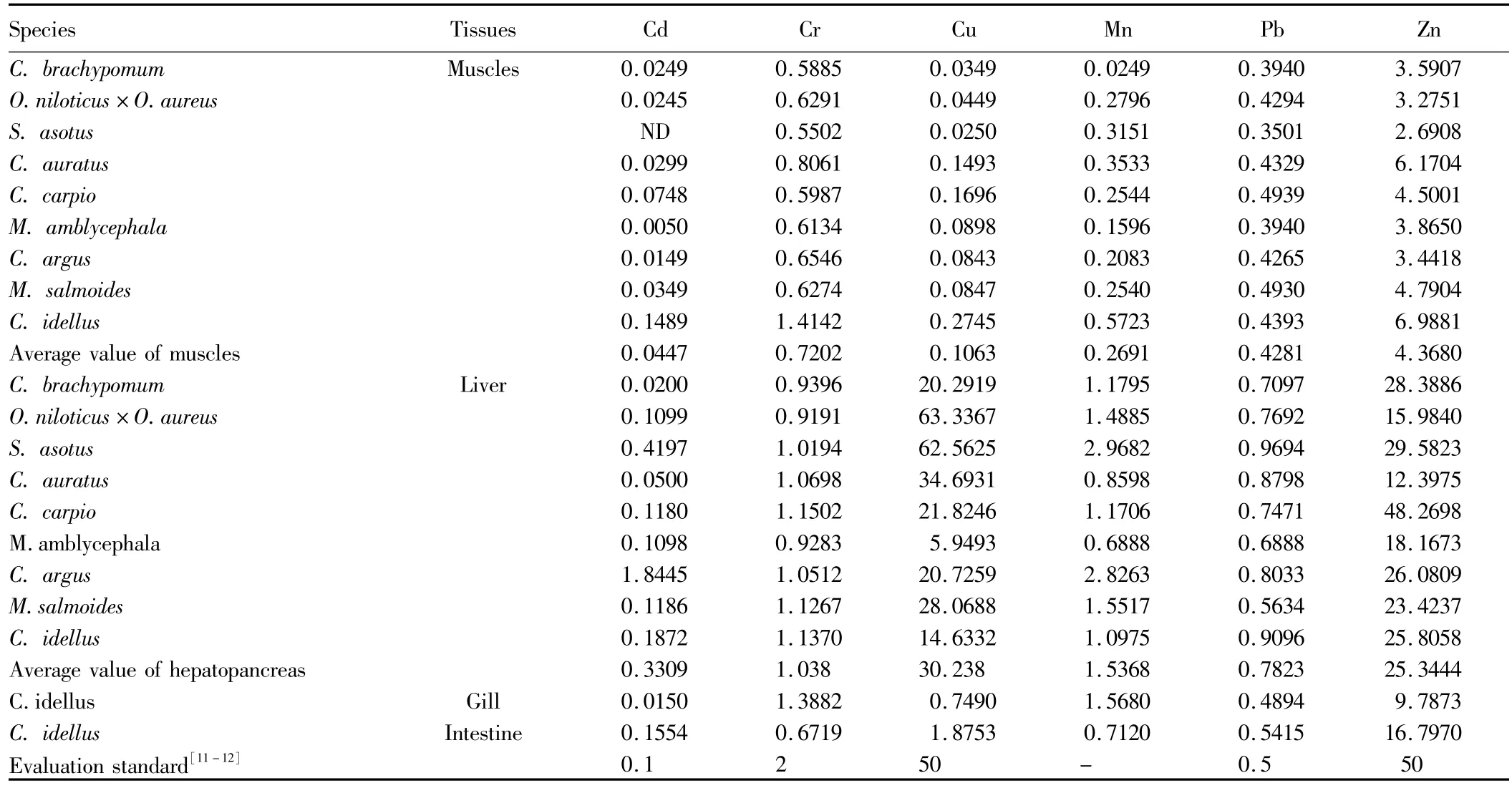
Table 2 Themass fraction of heavy metal in muscle and liver of nine kinds of fish(wet weight,mg/kg)
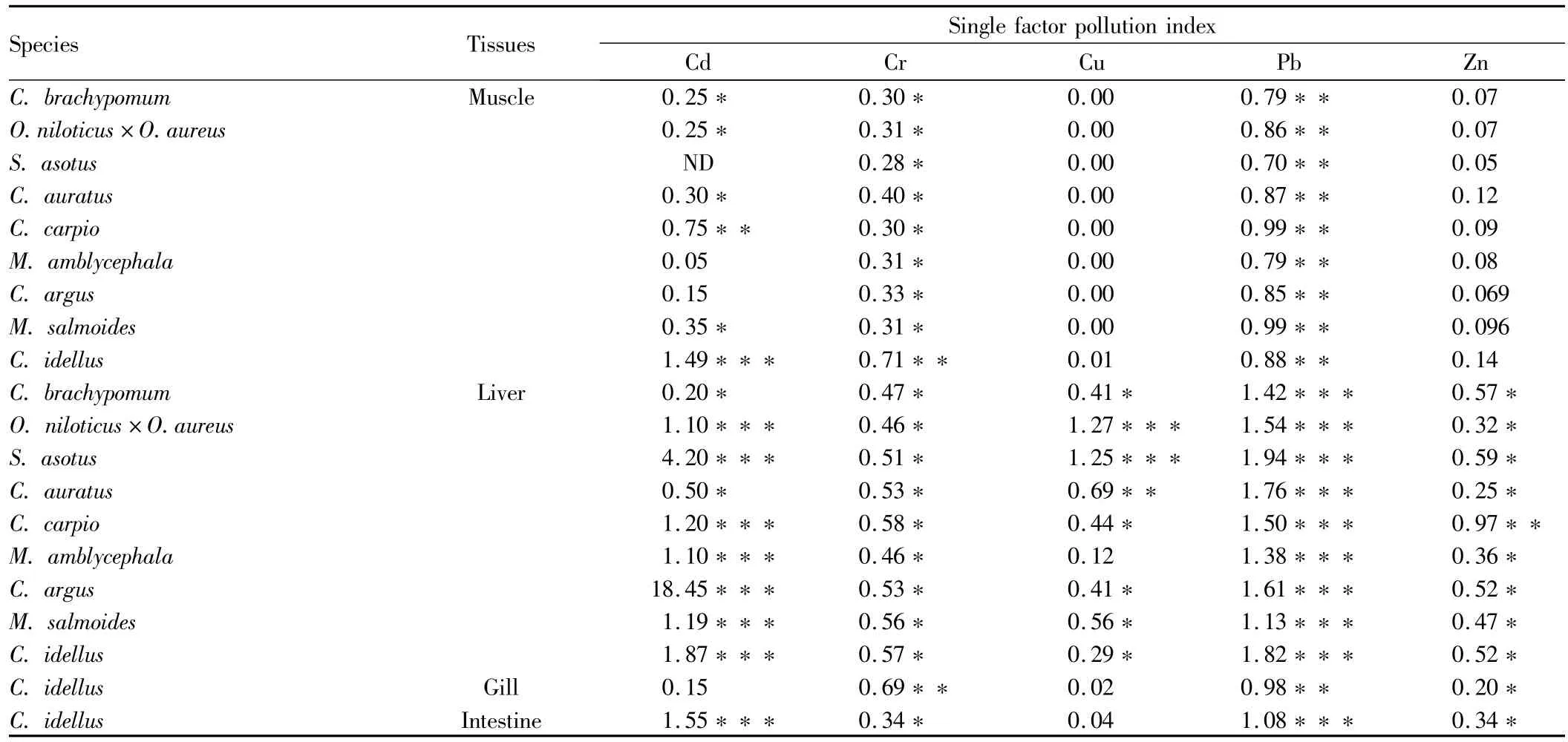
Table 3 The heavy metal pollution index of muscles and liver of nine kinds of fish
2.3 The differences in the mass fraction of heavy metal in fishThe mass fraction of Cd,Cr,Mn,Pb,Zn and Cu in muscle,liver of different kinds of fish is shown in Fig.1.From Fig.1,it is found that there is a great difference in the mass fraction of Cd between different kinds of fish and their tissues.In terms of the mass fraction of Cd in liver of the nine kinds of fish,it is sequenced in descending order as follows:C.argus>S.asotus>C.idellus>C.carpio>M.salmoides>O.niloticus×O.aureus>M.amblycephala>C.auratus>C.brachypomum.And the mass fraction of Cd in liver ofC.argusis much higher than that of other kinds of fish.Meanwhile,the enrichment level of Cd in different tissues of the same fish is also inconsistent.The mass fraction of Cd in liver ofC.argusis1.8mg/kg,and the mass fraction of Cd in its muscles is about0.1mg/kg.The enrichment level of Cd in muscle,liver ofC.auratusorC.carpiois similar.However,the mass fraction of Cr in liver of the nine kinds of fish is similar(Fig.1),approximately 1 mg/kg.The mass fraction of Cr in muscle ofC.idellusis very high,reaching the heavy pollution level.ExceptC.idellus,the mass fraction of Cr in muscle of eight other kinds of fish is similar,about0.6mg/kg.Fig.1 shows that there is a great difference in the mass fraction of Mn in muscle,liver between different kinds of fish.The measured mass fraction of Mn in liver of fish is much higher than in muscle.However,there is a slight difference in the mass fraction of Pb in muscle,liver between different kinds of fish(Fig.1),but the mass fraction is all high.The mass fraction of Pb in liver of the nine kinds of fish reaches"heavy pollution level",while the mass fraction of Pb in muscle reaches"pollution level".The mass fraction of Cu in liver of the nine kinds of fish is tens to hundreds of times as much as that in muscle(Fig.1),indicating that Cu is more easily accumulated in liver of fish.In terms of the mass fraction of Cu in muscle of the nine kinds of fish,it is sequenced as follows:C.idellus>C.carpio>C.auratus>M.amblycephala>C.argus>M.salmoides>O.niloticus×O.aureus>C.brachypomum>S.asotus.In terms of the mass fraction of Cd in liver of the nine kinds of fish,it is sequenced as follows:O.niloticus×O.aureus>S.asotus>C.auratus>M.salmoides>C.carpio>C.argus>C.brachypomum>C.idellus>M.amblycephala.
3 Conclusions and discussions
Different tissues and organs of fish have different ability to accumulate a variety of heavy metals,and the measured mass fraction of heavy metal in liver of nine kinds of fish is higher than in muscle of nine kinds of fish accordingly.The study is consistent with most studies[16-19].The enrichment level of heavy metal in fish tissues depends on exposure time,exposure concentration,and heavy metal types.It is also affected by chemical properties of water,fish species,characteristics of fish tissues and organs,physiological metabolic activity of fish and other factors[8].Dai Ziru[20]measures the heavy metal in Trachinotus ovatus,and the results show that gill and liver have stronger ability to accumulate a variety of heavy metals than other tissues and organs.The studies of Liu Fangfanget al.also show that during the growth ofC.carpio,the liver is the major accumulation site of Pb,Cd and Cu,gill is the main accumulation site of Zn,and muscle is the weakest part to accumulate heavy metal[21].Thus,it can be found that the mass fraction of heavy metal is associated with tissue and organ function.The liver of fish are the biochemical conversion centers,and a lot of metallothionein can be produced within the tissue to limit heavy metal,so that the liver have higher affinity for heavy metal.Meanwhile,the same organ of fish may have different affinities for different heavy metals.Studies have shown that the mass fraction of essential elements Cu and Zn in the fish is high,and mainly accumulated in the liver and gut,while the mass fraction of non-essential elements Pb and Cd in the fish is low[22-23].The study results of Liu Danchiet al.indicate that the basic trend of mass fraction of heavy metal in the same tissues or organs is Zn>Cu>Pb>Ni,Cr>Cd[24].This results in this experiment are similar to the above findings.According to Safety Qualification for Agriculture Product Safety Requirements for Non-environmental Pollution Products(GB18406.4-2001),the collected fish samples cultivated in Northeast Guangdong have been contaminated by Pb,Cd,Cr,Cu and Zn.The Pb pollution to the nine kinds of fish is most serious,followed by Cd and Cr,and the Cu and Zn are light.On the one hand,the accumulation of heavy metal in fish is related to the content of heavy metal in water body or sediment,and the higher the mass fraction of heavy metal in water body or sediment,the higher the mass fraction of heavy metal in fish[25];on the other hand,the accumulation of heavy metal in fish is related to the mass fraction of heavy metal in the food of fish,and the higher the mass fraction of heavy metal in feed,the higher the mass fraction of heavy metal in fish[1].Thus it can be inferred that the nine kinds of fish are artificially cultivated fishes,and the aquaculture water or feed is contaminated by Pb and Cd,so the cumulative amount of the two kinds of heavy metals in the body of fish is higher.It is generally believed that in the food web of natural environment,with the increase in organism trophic levels,the accumulation of heavy metal in organism increases,resulting in progressively amplified effect[27].The study results of Zhu Huiet al.indicate that except Zn,the mass fraction of the other four kinds of heavy metals(Pb,Cu,Hg,Cd)in carnivorous fish is higher than in omnivorous and herbivorous fish[6].Zeng Lingyiet al.investigate the heavy metal contamination in fish in Changsha section of the Xiangjiang River valley,and the results also show that the heavy metal contamination in the fish living at river bottom is greater than in the fish living in the upper layer[25].But there are also contrary findings[28].The study results of Zeng Leyiet al.show that the mass fraction of Pb and Cd inS.as otuswith higher trophic levels is lower than in several other kinds of fishes with lower trophic levels[9].The study of Liu Fangfanget al.also shows that the mass fraction of heavy metal is high in the aquaculture feed bran cake,which may be the main source of accumulated heavy metals inC.carpio[21].The nine kinds of fish investigated in this study have different trophic levels(Table 1),but there is no phenomenon that the mass fraction of heavy metal in fish increases along with the increase in trophic levels(Fig.1).In terms of the mass fraction of Cd in liver and pancreas,the nine kinds of fish are sequenced in descending order as follows:C.argus>S.asotus>C.idellus>C.carpio>M.salmoides>O.niloticus×O.aureus>M.amblycephala>C.auratus>C.brachypomum.In terms of the mass fraction of Zn in liver and pancreas,the nine kinds of fish are sequenced in descending order as follows:C.carpio>S.asotus>C.brachypomum>C.argus>C.idellus>M.salmoides>M.amblycephala>O.niloticus×O.aureus>C.auratus.It is inferred that the nine kinds of fish in this experiment are artificially cultivated fishes,and the mass fraction of heavy metal in feed or aquaculture water is an important factor affecting the heavy metal residues in fish.In summary,the nine kinds of freshwater economic fish in Northeast Guangdong are subject to different degrees of Pb,Cd,Cr,Cu and Zn contamination,respectively,indicating that there has been heavy metal pollution hazard in the water environ mentor safe fishery production in this region,so it is necessary to carry out the monitoring of heavy metal residues in the feed and water during the breeding process.
[1]XIEWP,CHEN KC,ZHU XP,et al.Evaluation on heavy metal contents in water and fishes collected from the waterway in the Pearl River Delta,South China[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2010,29(10):1917-1923.(in Chinese).
[2]Kaplan O,Yildirim NC,Yildirim N,et al.Toxic elements in animal products and environmental health[J].Asian JAnim Vet Adv,2011,6(3):228-232.
[3]Rashed MN.Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser lake[J].Environ Int,2001,27(1):27-33.
[4]Sivaperumal P,Sankar TV,Nair PGV.Heavy metal concentrations in fish,shellfish and fish products from internal markets of India vis-a-vis international standards[J].Food Chem,2007,102(3):612-620.
[5]SHIKJ,LIU J,MA LJ.Investigation and evaluation of lead,cadmium,arsenic,mercury in aquatic products of Nansihu[J].Food and Drug,2006,8(07A):59-61.(in Chinese).
[6]ZHU H,YAN BX,ZHANG FY.Enrichment of heavy metals in fishes of Songhua River and its pollution assessment[J].Rural Eco-Environment,2010,26(5):492-496.(in Chinese).
[7]LIUP,ZHOUYQ,ZANG LJ.Investigation of heavy metal contamination in four kinds of fishes from the different farmer markets in Beijing[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science,2011,32(7):2062-2068.(in Chinese).
[8]XIA ZH,WANG XM,LOU QT,et al.Distribution and consumption risk assessment of Cu,Pb and Cd in six freshwater fishes from the main market in Hefei[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2012,25(3):311-315.(in Chinese).
[9]ZENG LY,YAN YL,XIE XJ.The concentrations of lead,cadmium and chromium in the fishes from the Zhuyang section of the Yangtze River[J].Freshwater Fisheries,2012,42(2):61-65.(in Chinese).
[10]Keskin Y,Baskaya R,Ozyaral O,et al.Cadmium,lead,mercury and copper in fish from the Marmara Sea,Turkey[J].Bull Environ Contam Toxicol,2007,78(3-4):258-261.
[11]Has-Schon E,Bogut I,Strelec I.Heavy metal profile in five fish species included in human diet,domiciled in the end flow of river Neretva(Croatia)[J].Arch Environ Contam Toxicol,2006,50(4):545-551.
[12]Uysal K,Kose E,Bulbul M,et al.The comparison of heavymetal accumulation ratios of some fish species in Enne Dame Lake(Kutahya/Turkey)[J].Environ Monit Assess,2008,157(1-4):355-362.
[13]Usero J,Izquierdo C,Morillo J,etal.Heavy metals in fish(Solea vulgaris,Anguilla anguilla and Liza aurata)from salt marshes on the Southern Atlantic coast of Spain[J].Environ Int,2003,29(7):949-956.
[14]Abdulali KA Taweel,Shuhaimi-Othman M,Ahmad A K.Analysis of heavy metal concentrations in tilapia fish(Oreochromisniloticus)from four selected markets in selangor,Peninsular Malaysia[J].Journal of Biological Sciences,2012,12(3):138-145.
[15]QIN CY,FANG ZQ,TANG YJ,et al.Contents and evaluation of heavy metals in common aquatic from Lingdingyang in Peal River Estuary,South China Ocean[J].Journal of South China Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2010(3):104-109,114.(in Chinese).
[16]YANGXY,WEN Y,CHEN XY,etal.Heavy metalenrichment in aquatic organisms of Beijiang River:Its characteristics and pollution evaluation[J].Environmental Science and Technology,2010,33(6):194-198.(in Chinese).
[17]HE L,FAN BW.Study on the law of accumulation of copper in fish[J].Trace Elements Science,2007,14(4):15-19.(in Chinese).
[18]YANGML,JIA XP.Heavymetal in main economic fish in the Beibuwan Basin[J].Marine Science Bulletin,1990,9(5):39-45.(in Chinese).
[19]LU CH.Heavy metal contamination of commercial aquatic products and its evaluation in in northern South China Sea[J].Marine Environmental Science,1995,14(2):12-18.(in Chinese).
[20]DAIZR.Assessment of contents of heavy metals in the body of Pampano trachinotus ovatus derbio and its regular distributed pattern[J].Food Science and Technology,2012,37(12):298-300.(in Chinese).
[21]LIU FF,LIZH,FU XJ,et al.Enrichment of heavy metals in growth period of cage cultured carp(Cyprinus carpio)from the East Dongting Lake[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2013,26(2):166-172.(in Chinese).
[22]SHANG XD,HE ZQ.Advances in heavy metal accumulation in fish[J].Hebei Fisheries,2009(5):44-45.(in Chinese).
[23]LIUWP,LIU XY,PAN JM,et al.Levels of heavy metals in commercial fish species from the near-shore of Zhejiang Province[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Sciences Edition),2012,39(3):338-344.(in Chinese).
[24]LIU DC,SHAO CM.Assessment of contents of heavy metals in fish body and its regular distributed patter[J].China Measurement&Testing Technology,2007,33(4):121-122,132.(in Chinese).
[25]ZENG LY,LIWL,LIY.Analysis and evaluation on heavymetals pollution of fish in Xiangjiang River Changsha[J].Guangxi Journalof Light Industry,2012(9):94-95.(in Chinese).
[26]Meador JP,Ernest DW,Kagley AN.A comparison of the non-essential elements cadmium,mercury and lead found in fish and sediment from Alaska and California[J].Sci Total Environ,2005,339(1-3):189-205.
[27]Bowles KC,Apte SC,MaherWA,etal.Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of mercury in Lake Murray,Papua New Guinea[J].Can J Fish Aquat Sci,2001,58(5):888-897.
[28]Prahalad AK,Seenayya G.In situ compartmentation and biomagnifications of copper and cadmium in industrially polluted Husainsagar Lake,Hyderbad,India[J].Arch Environ Contam Toxicol,1986,15(4):417-425.
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年1期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年1期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Integration of Medical Care and Endowment:A New Exploration of Endowment Mode in the Context of Population Aging
- The Distribution of Benefits for Players in Agricultural Industrial Chain
- Price Conduction Mechanism of China's W heat Industry Chain Based on VECM
- On the Development and Maintenance of Cigarettes Exported to North Korea
- Study of the Factors Influencing Entrepreneurial Farmers' Formal Financial Credit Demand and Credit Constraints in Sichuan and Chongqing
- The Research on the Construction of Monitoring and Evaluation System for the Operation of Marine Economy in Liaoning Province
