Study of the Factors Influencing Entrepreneurial Farmers' Formal Financial Credit Demand and Credit Constraints in Sichuan and Chongqing
Yingliang ZHANG,Jianfeng ZHANG,Guangying LIU
College of Economics and Management,Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China
1 Introduction
Entrepreneurship is the main engine of economic activity(Peter Drucker,1989),and entrepreneurial economy promotes social progress,leads the direction of industrial development and boosts economic development by creating jobs(Jiao Xiaobo,Guan Pu,2012).Farmers start up an undertaking by relying on families and friends and relatives to form loose informal organization or create a new organization to seek development opportunities,and increase investment to expand the existing scale or engage in new productive activities to create value and seek development opportunities(Guo Junying,2006).The entrepreneurial farmers use diversified means to mainly engage in moderate scale farming,breeding,processing and sales of agricultural products and non-agricultural production and business activities,showing a strong sense of the market,and they have the strong market adaptation and self-adjustment capability(Jiang Heping,Cui Kai,2012).At present,the development of agriculture and rural areas in China is entering a new phase characterized by rising costs of agricultural production,prominent structural contradiction of agricultural supply and demand,rapid transformation of rural social structure and accelerated integration of urban and rural development,vigorously cultivating entrepreneurial farmers and promoting orderly farmers' entrepreneurship is conducive to promoting the transformation of traditional agriculture,enhancing the development of non-agricultural industries,accelerating the transfer of rural surplus labor force,and promoting agricultural modernization,rural industrialization and rural urbanization(Zhang Yingliang,2012).Due to the financial constraints in the developing countries,farmers are often in a weak position in the lending market,and find it difficult to obtain sufficient funds from the formal financial departments(Edward·S·Shaw,1973;Ronald·I·McKinnon,1973).There is a small proportion of farmers who can get loans from formal finance,and the borrowers are mainly concentrated in the hands of a few wealthy people(Pischet al,1987).Only 27%of farmers in China can have access to formal credit channels,and more than 40%of farmers who have financial demand can not get formal credit support(Zhang Xiaoshan,2010).The loans of formal financial institutions mainly flow to those relatively affluent farmers with higher social capital(Ye Jingzhonget al,2004;Zhang Qingfang,2010),or well-educated farmers(Zhang Qingfang,2010).Funding constraints become a major obstacle to individuals' entrepreneurship(Peter Drucker,1989),and a shortage of funds has become a key factor restricting farmers' entrepreneurship(Zheng Fengtian,Sun Jin,2006).The perfect credit markets and ade-quate credit support will be conducive to entrepreneurship generation and business growth(Black&Strahan,2002;Klappera&Laevena&Rajan,2006),and the loan has a significant positive impact on farmers' entrepreneurial behavior(Wei Jifeiet al.,2008).Rural financial constraint has always been a hot research issue for scholars.Overall,domestic recent studies are based on macroeconomic and microeconomic perspectives.The macroeconomic perspective is based on Stiglitz's incomplete market theory,which believes that the rural financial development strategy can be supplied to promote reform of China's rural financial system,and eliminate financial constraints;the microeconomic perspective is based on Menger's adaptive evolution and Hayek's spontaneous extended market order theory(1967),which believes that the ideal financial system must meet the financial needs of the micro body,and it is necessary to design rational institutional arrangement to eliminate rural financial repression(Xu Zhangyong,Wang Hongli,2009).Currently,based on microscopic investigation of farmers,the scholars mainly carry out empirical analysis from farmers' credit demand and its influencing factors.The explanatory variables include farmers' household characteristics variables,rural householder's characteristic variables,production and management features,loan characteristics,financial ecological variables and so on.The dependent variables mainly include the amount of loans,the substitution variables indicating whether there is lending or whether the lending is successful,and the substitution variables indicating credit degree or whether the bank lends or not.The research methods mainly include polynomial regression (Pal,2002),Probit regression model(Li Rui,Zhu Xi,2007;Zhang Qingfang,2010;Qin Jianqunet al.,2011;Tang,2009;Huang Zuhuiet al.,2009;Wang Dingxianget al.,2011;Xiao Huafang,Bao Xiaolan,2011),Logistic regression model(LiCuimei,Chen Qiaoling,2007;Xu Zhangyong,2009;Zeng Xuewen,Zhang Shuai,2009;BaiYongxiu,Ma Xiaoyong,2010;Wang Xiuhua,Tan Kaitong,2012;Shi Zhiping,Zhang Wenqi,2012;Tong Xinyueet al.,2011),Tobit regression model(Gong Jianqiang,Zhang Bing,2008;Han Jun,etal.,2007),simultaneous equation model(Zhu Xi,Li Zinai,2006),and other models(SEM structural equation model,Wang Jining,Zhao Shunlong,2007;multinomial choice and stereotype Logistic,Chen Peng,Liu Xiliang).The conclusions of the study vary due to the difference in the sample size,study farmer selection,sample time span and sample space span.Income level,education level and use of the loans are the main factors influencing farmers' credit demand(Yazdani and Gunjal influence,1998;Zhou Xiaobinet al.,2004;Xiong Xueping,et al.,2007;Chaudhary and Ishfaq,2008;He Mingsheng,Shuai Xu,2008;Cheng Yuet al.,2009;Wang Dingxianget al.,2011).In terms of formal financial demand and credit constraints,He Guangwen(1999),Wen Tiejun(2001),Zhu Shouyinet al.(2003),Wang Yuzhou(2004),Xiong Jieet al.(2004),Guo Xiaominget al.(2005),and Liu Linglinget al.(2007)believe that the Chinese farmers are prone to formal financial credit constraints.The proportion of relatively affluent farmers borrowing money from rural credit cooperatives and other formal financial institutions is higher than the proportion of farmers with low income level(Zhu Shouyin,2003).The formal channel loans have a significant positive correlation with the investment(Zhang Xinminet al.,2001).The scholars at home and abroad gradually change the research focus from qualitative study to econometric model study,and lay equal emphasis on macroeconomic research and microeconomic research.However,there is little literature on farmers' credit behavior and credit constraints from the perspective of agricultural ecology,and there are few studies on entrepreneurial farmers' credit demand,credit supply,credit choice and influencing factors.This paper selects entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit constraints as the research object,to analyze entrepreneurial farmers' credit demand,formal financial credit wishes and influencing factors,and analyze the formal financial credit constraints from the perspective of entrepreneurial farmers' credit demand.
2 Study theory and methods
2.1 Analytical frameworkThe theory of financial constraints believes that the credit constraints mainly include supply-based constraints and demand-based constraints.The former maintains that the credit constraints arise from inadequate supply of formal financial institutions or credit exclusion,while the latter believes that the credit constraints arise from insufficient effective credit demand of farmers.Under information symmetry,farmers can better understand the credit procedures and conditions of formal financial institutions,and reduce the cognitive biases and opportunity cost.In the context of urban and rural dual financial system,the external constraints of rural formal financial institutions such as withdrawal from rural areas and absence of rural financial services,increase the formal financial credit acquisition costs.Farmers' economic characteristics,householder's personal characteristics and the characteristics of industries that farmers are engaged in,by a certain degree determine the availability of financial resources and financial credit repayment capacity.Entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial demand preferences and choices also follow the cost-benefit principle,and the factors influencing net income and repayment ability of entrepreneurs include business owners' characteristic variables,industry variables and firm characteristic variables.The formal financial institutions are faced with a serious problem of information asymmetry,and in the process of making credit decision,the financial institutions judge borrowers' risk type to address the adverse selection problem caused by information asymmetry based on the characteristics of rural households.Under given loan interest rate,the higher the financing costs of financial institutions,the lower the willingness to grant loans to farmers;the better the level of financial development in the areas where rural loan applicants live,the better the individual characteristics of the loan application farmers,and the richer the rural household's resource endowments and social capital,then the lower the likelihood of formal financial constraints;the farmers with better collateral are less likely to be vulnerable to credit exclusion.
2.2 Theoretical modelThe farmers' credit behavior is jointly determined by demand willingness and credit constraints.Based on the theoretical model analysis of Xiao Huafang and Bao Xiaolan(2011),it is assumed that the entrepreneurial farmers apply for loans from formal financial institutions in accordance with the cost benefit principle.The net income function is as follows:
whererepresents entrepreneurial farmers' net income;X1irepresents the vector of factor influencing entrepreneurial farmers' net income;β1represents the coefficient vector;μ1irepresents the residual term.Then the probability of entrepreneurial farmers applying for loans from formal financial institutions is as follows:
After entrepreneurial farmers apply for loans,the formal financial institutions make assessment and make decisions.It is assumed that the formal financial institutions make lending decisions based on the borrower's repayment ability,then the entrepreneurial farmers' repayment ability is expressed as follows:
whereis entrepreneurial farmers' repayment ability;X2iis the vector of factor influencing entrepreneurial farmers' repayment ability;α2is the coefficient vector;υ2iis the residual term.Then the probability of formal financial institutions lending loans to entrepreneurial farmers is as follows:
If the residuals follow the standard normal distribution,then we can perform the Probit model analysis.The factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' net income and repayment ability also include entrepreneurial householder characteristics,entrepreneurial farmer characteristics,entrepreneurship situation,and financial ecology in the place where entrepreneurial farmers live.
2.3 VariablesBoth supply and demand contribute to the low level of participation of farmers in formal credit markets(Huang Zuhui,Liu Xichuan,2009).The interest rate of rural financial market is exogenous,and the interest rate is not a major consideration for the borrowing farmers;farmers' household income,production and operation characteristics,and household characteristics are the determinants of farmers' credit demand behavior(Han Jun,et al.,2007).In this study,we consider the factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand mainly from the characteristics of entrepreneurial rural householder,family characteristics,formal financial ecology,and farmers' entrepreneurial characteristics.(i)Characteristics of entrepreneurial rural householder.The characteristics of entrepreneurial rural householder mainly include householder's gender,age and education level.Theoretically,householder's gender affects the entrepreneurship format choices,thereby affecting the expected benefits of entrepreneurship.In terms of age,the entrepreneurial success is related to the maturity of entrepreneurs.The householder's education level is closely related to householder's identification of business opportunities,credit procedures,knowledge and social capital.There are existing research results agreeing that education level is one of the main factors affecting the credit needs of farmers,and has a certain impact on farmers' formal credit constraints(Wang Dingxianget al.,2011).(ii)Entrepreneurial farmers' household characteristics.Farmer is the basic subject of agricultural entrepreneurship,and the average annual household income reflects the farmers' ability to repay loans,and is the fundamental factor determining the farmers' loan demand(Han Jun,et al.,2007).There may be a substitutional relation between high household income and financial lending.Meanwhile,the rural household size theoretically has a positive impact on entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand.(iii)Formal financial ecology.Farmers' formal financial credit participation is not only affected by farmers' demand,but also affected by formal financial credit supply.The availability of formal financing for farmers' entrepreneurship hinges on whether the formal finance can provide appropriate credit products for entrepreneurial farmers.Meanwhile,the farmers' cognition of formal financial credit difficulty,and their mastery of lending procedures and loan knowledge to a certain extent determines the farmers' formal financing needs.(iv)The scale of demand for loans and entrepreneurship format features.Foreign scholars generally believe that in the developing countries,farmers' formal credit demand is mainly focused on production,while the non-formal credit demand is mainly focused on non-production(Kochar,A.,1997;Manfred Zeller,1994;F.N.Okurut,A.Schoombee,S.Van Der Berg.,2005;Pham BaoDuong and Yoichi Izumida,2002).Wang Sangui(2001),He Guangwen,Li Lili(2005)find that the loans of China's formal financial institutions are mostly used for production,while the non formal loans are mostly used for consumption;the production loans are far greater than consumption loans.The entrepreneurial farmers' loans are mainly for production investment,the scale is large,and the repayment period is long.The entrepreneurial format features to a certain extent reflect the entrepreneurial profitability,and is an important factor for the formal financial institutions' credit check.In this study,we choose 9 factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand and credit success.The definition of variables is shown in Table 1.
3 Sample selection and variable features
3.1 Sample selection and data sourcesThere are three principles for the sample selection:(i)The entrepreneurs are rural residents;(ii)The entrepreneurship location is village or township;(iii)The entrepreneurship industries are divided into traditional large-scale operation,establishing new industries,specialized production,develop new business,and building new organizations.The data sources are mainly based on questionnaire survey.In May 2011,the research group first conducted a pilot survey in Chongqing and finally decided to hand out questionnaires and carry out case interviews in Shuangliu County,Suining County of Sichuan Province,and Hechuan District,Kaixian County,Tongliang County and Rongchang County of Chongqing City.The survey used the stratified random sampling method,involving five industries.A total of 960 questionnaires were recovered,and 939 valid questionnaires,were obtained after excluding 21 questionnaires with untrue information and incomplete information.The valid response rate was97.8%.
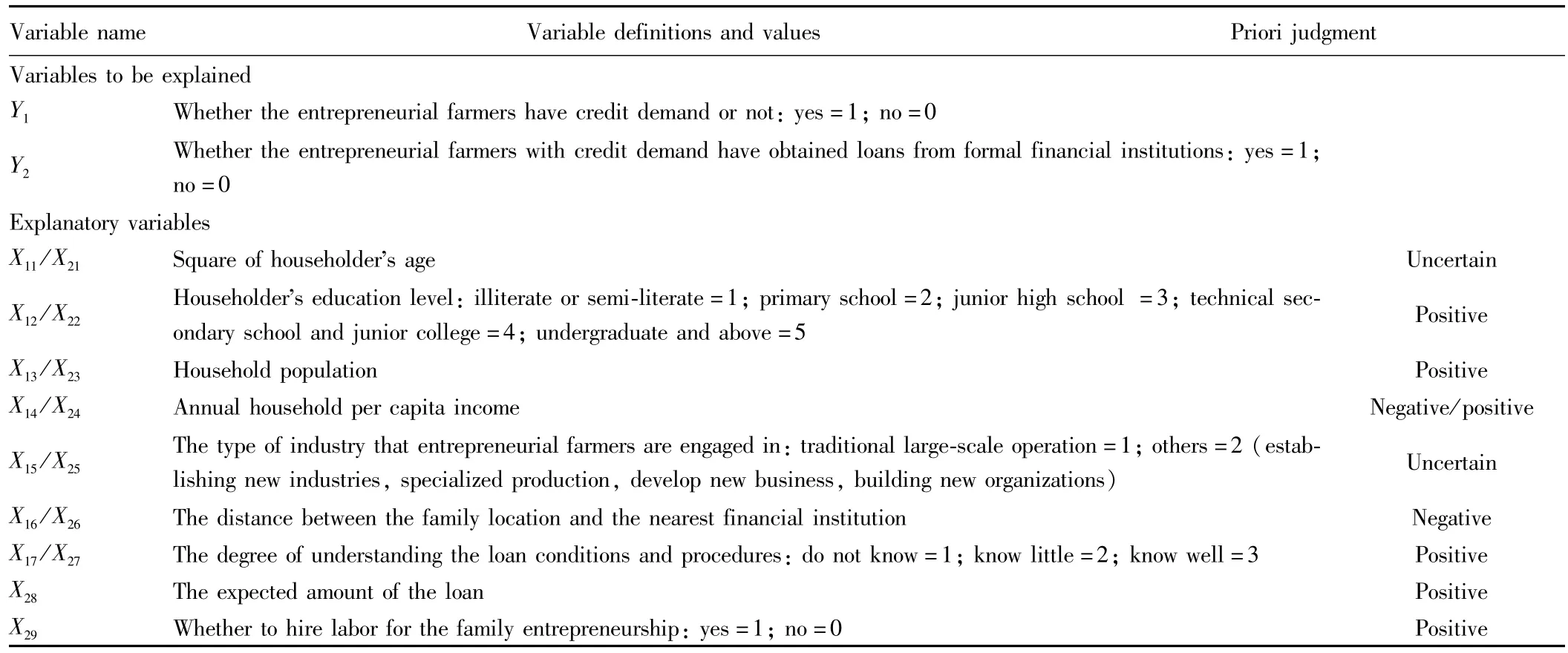
Table 1 The definition of model variables
3.2 Basic features of sample variables
3.2.1 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand.(i)Formal financial credit willingness.Different from ordinary farmers and poor farmers,the entrepreneurial farmers have a growing demand for money with the expansion of business scale and their credit demand is also constantly enhanced.From Table 2,it can be found that the entrepreneurial farmers have a strong formal financial demand,and the entrepreneurial farmers willing to get loans from formal financial institutions account for 79.54%of respondents.
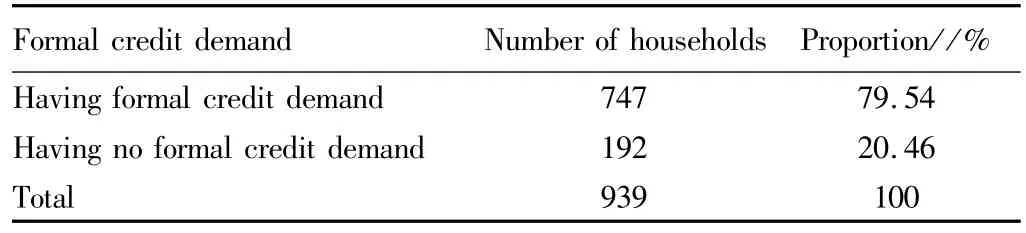
Table 2 The sample entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand
(ii)Formal financial credit channel selection.The entrepreneurial farmers have a tendency when selecting the formal financial credit channel.From Table 3,it shows that 35.12%of the sample farmers tend to get loans from the rural credit cooperatives;29.76%of the sample farmers tend to get loans from ABC;28.05%of the sample farmers tend to get loans from RCC;7.07%of entrepreneurial farmers tend to get loans from other institutions(ICBC,CBC,BOC,etc.).For most of the farmers who have formal credit demand,rural credit cooperative is the primary source of funding for the entrepreneurial farmers,followed by ABC and RCC.
3.2.2 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit purposes.The survey finds that the sample farmers' formal credit is mainly used for productive investment,rather than life consumption.Fig.1 shows that96.18%of the sample farmers use the formal credit for production,including33.7%of farmers purchasing means of production,31.1%of farmers purchasing agricultural machinery,17.7%of farmers expanding the scale of production and 17.5%of farmers using the formal credit for production and management funds.Only 3.82%of sample farmers use the formal credit for life purposes.

Table 3 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit channel selection
3.2.3 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand scale.To investigate the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand scale,we divide the demand scale into nine levels:A≤10000,10000<A≤20000,20000<A≤30000,30000<A≤4000,40000<A≤50000,50000<A≤60000≤,60000<A≤70000,70000<A≤80000.From Fig.2,it is found that entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand scale presents left-skewed distribution.14.6%of entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand scale is less than 10000 yuan;15.49%of sample farmers' loan size is between 10000 to 20000 yuan;40.12%of sample farmers' credit demand scale is between 20000 yuan and 30000 yuan;the credit scale of 30000-40000 yuan drops by 13.42%.The credit demand during farmers' entrepreneurship has exceeded the scope of micro-credit support.In particular,the incidence of micro-credit of less than 5000 yuan is very low,and the incidence of super large credit is also low.The scale of loans is concentrated in 20000 to 30000 yuan.
3.2.4 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit pattern.From Table 4,it is found that35.18%of sample entrepreneurial farmers choose the credit pattern of mortgage loans;19.44%of farmers choose secured loans;24.25%of farmers choose microcredit loans;21.11%of farmers choose multi-household joint guarantee.The mortgage loans occupy the highest proportion.As to the choice of collateral,42.47%of sample farmers choose housing as collateral;26.34%of sample farmers choose farm machinery and household appliances as collateral;17.2%of sample farmers choose arable land as collateral;13.98%of sample farmers choose to use the agricultural products harvested in the future as collateral.
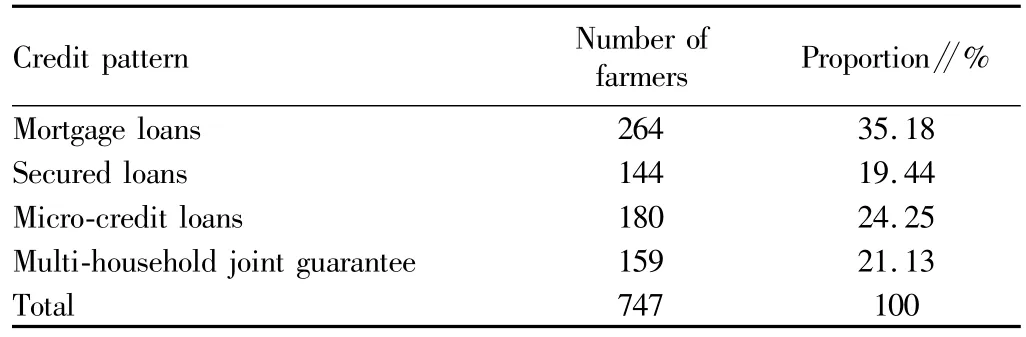
Table 4 Sample entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit pattern
3.2.5 Entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit constraints.The survey finds that the probability of farmers getting loans from formal financial institutions is small.From Table5,we see that there are 747 sample farmers having formal financial demand;441 farmers never get loans from formal financial institutions due to various reasons,accounting for 59.03%;306 farmers have received the formal financial credit,and some of them have only received a portion of expected loans.
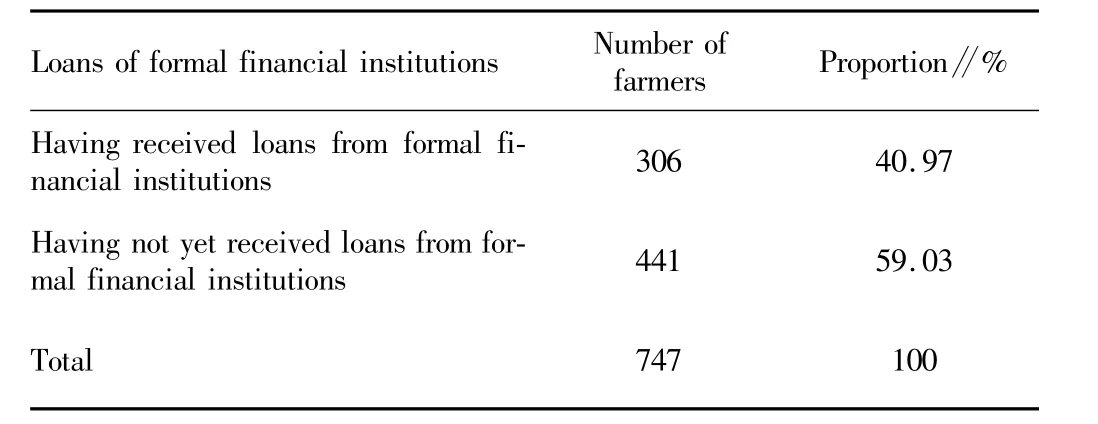
Table5 Whether the entrepreneurial farmers get loans from formal financial institutions
3.2.6 The entrepreneurial rural householder with formal financial demand and household characteristics.(i)Rural householder characteristics.(a)Gender.The male entrepreneurial farmers have stronger credit demand than female entrepreneurial farmers.The female rural householders with formal financial demand account for 13.74%,while their male counterparts account for 86.26% (see Table 6).

Table 6 Male and female householders' formal credit demand

Table 7 The formal credit demand of entrepreneurial rural householders of different ages
(b)Age.The incidence of entrepreneurial rural householder aged between 36 and 45 having credit demand is highest.Leighton(1989)believes that for the 40-year-old householders,they have accumulated a certain amount of skills and funds.For the age groups of18-25,26-30,31-35,36-40,41-45,46-50,51-55,56 and above,the incidence of formal credit demand is 69.18%,70.23%,72.10%,83.62%,80.20%,75.98%,65.41%,and 64.17%,respectively.Meanwhile,it is found that the entrepreneurial farmers are getting younger,and some college students return home to start their own undertaking,becoming an emerging group of agricultural entrepreneurship.
(c)Education level.The survey divides the education level of entrepreneurial rural householders into five levels:illiterate or semi-literate,primary school,junior high school,technical secondary school(senior high school),junior college,undergraduate and above.It can be found from Table 7 that the incidence of formal credit demand of householders with different education levels is89.49%,82.17%,80.72%,79.06%and 68.93%,respectively.The proportion of entrepreneurial farmers with different education levels is 1.59%,21.73%,42.17%,25.24%and 9.27%,respectively.On the one hand,from the incidence of formal credit demand,the incidence of formal credit demand of entrepreneurial farmers with low education level is high,and they have a strong credit demand and are eager to change the existing production and living conditions through entrepreneurship.On the other hand,from the proportion of number of farmers,the education level of entrepreneurial rural householders is concentrated in junior high school,technical secondary school and junior college,constituting the main education level of entrepreneurial farmers.

Table 8 The formal credit demand of entrepreneurial farmers with different education levels
(ii)Entrepreneurial farmers' household characteristics.For the sample farmers,the average household size is four.There are three labor forces aged more than 16 in the household on the average,and there is one schoolchild on the average for each household.The proportion of farmers with 3-5 labor forces in the household is highest,reaching 78.31%.Table 9 shows that with the expansion of family size,the incidence of formal credit demand is gradually increased,and the sample farmers with formal financial demand are mainly concentrated in 3-5 person households.

Table 9 The formal credit demand of sample farmers with different household size
3.2.7 Entrepreneurship characteristics of entrepreneurial farmers with formal financial demand and entrepreneurial farmers successfully getting loans.
(i)Entrepreneurship characteristics of entrepreneurial farmers with formal financial demand.The survey finds that for the sample entrepreneurial farmers with formal credit demand,the proportion of farmerseng aged in traditional large-scale agricultural operation is highest(75.90%),and entrepreneurial farmers are highly dependent on traditional agriculture.The proportion of entrepreneurial farmers establishing new industries and engaging in specialized production is small(5.22%and 4.41%,respectively);the proportion of entrepreneurial farmers launching a new business and establishing new organizations is 7.23%(see Table 10).
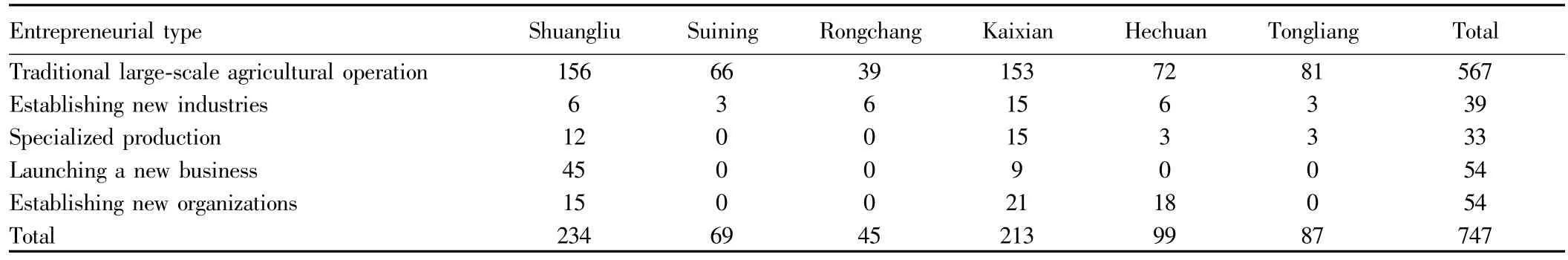
Table 10 The regional distribution of sample entrepreneurial farmers and industry
From the incidence of formal credit demand,the incidence of formal credit demand of entrepreneurial farmers engaged in traditional large-scale agricultural operation and establishing new industries is more than 70%;the incidence of formal credit demand of entrepreneurial farmers choosing the other three industries is significantly increased,more than 80%.
(ii)Entrepreneurship characteristics of entrepreneurial farmers successfully getting loans.The survey finds that the entrepreneurial farmers choosing the business type of traditional largescale agricultural operation have the highest success rate of formal financial credit(48.13%),significantly higher than the incidence of formal credit behavior of overall samples(40.97%).The incidence of formal credit behavior of entrepreneurial farmers engaged in specialized production and establishing new industries declines slightly,while the incidence of formal credit behavior of entrepreneurial farmers launching a new business and establishing new organizations becomes very low,down to about33%.

Table 11 Formal credit demand of entrepreneurial farmers engaged in different industries
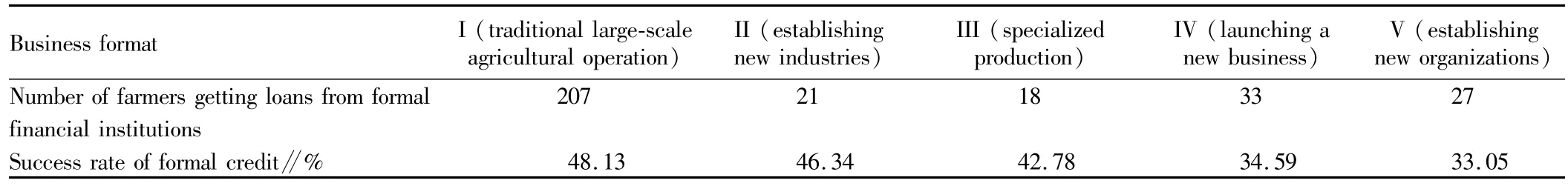
Table 12 Different business formats and success rate of formal credit
4 Model estimation results and discussions
Model estimatioThis paper selects binomial Probit model,to analyze entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand and the factors influencing formal financial credit.The model is as follows:
whereYtakes the value of 1(having the formal credit demand;having the formal credit demand and having obtained loans from formal financial institutions)and 0(having no formal credit demand;having the formal credit demand but never obtaining loans from formal financial institutions);Xjiis the factor influencing the entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand and formal financial credit success;jtakes the value of 1(whether there is formal credit demand)and 2(whether having obtained loans from formal financial institutions);n1is the number of explanatory variables concerning"whether there is formal credit demand";n2is the number of explanatory variables concerning"whether having obtained loans from formal financial institutions".To avoid the heteroscedasticity by linear model and non-normality problem of random disturbance term,the latent variablesis introduced.Assuming that when>0,Yj=1;whenYj<0,Yj=0.Meanwhile,letfollow N(0,1)distribution,the following is obtained:
In this paper,we use Eviews 6.0 software to estimate model(6),and the estimation results are shown in Table 13.From the model fitting results in Table 13,the estimation results of model likelihood ratio function and goodness of fit indicate that the overall fitting effect of model is good.
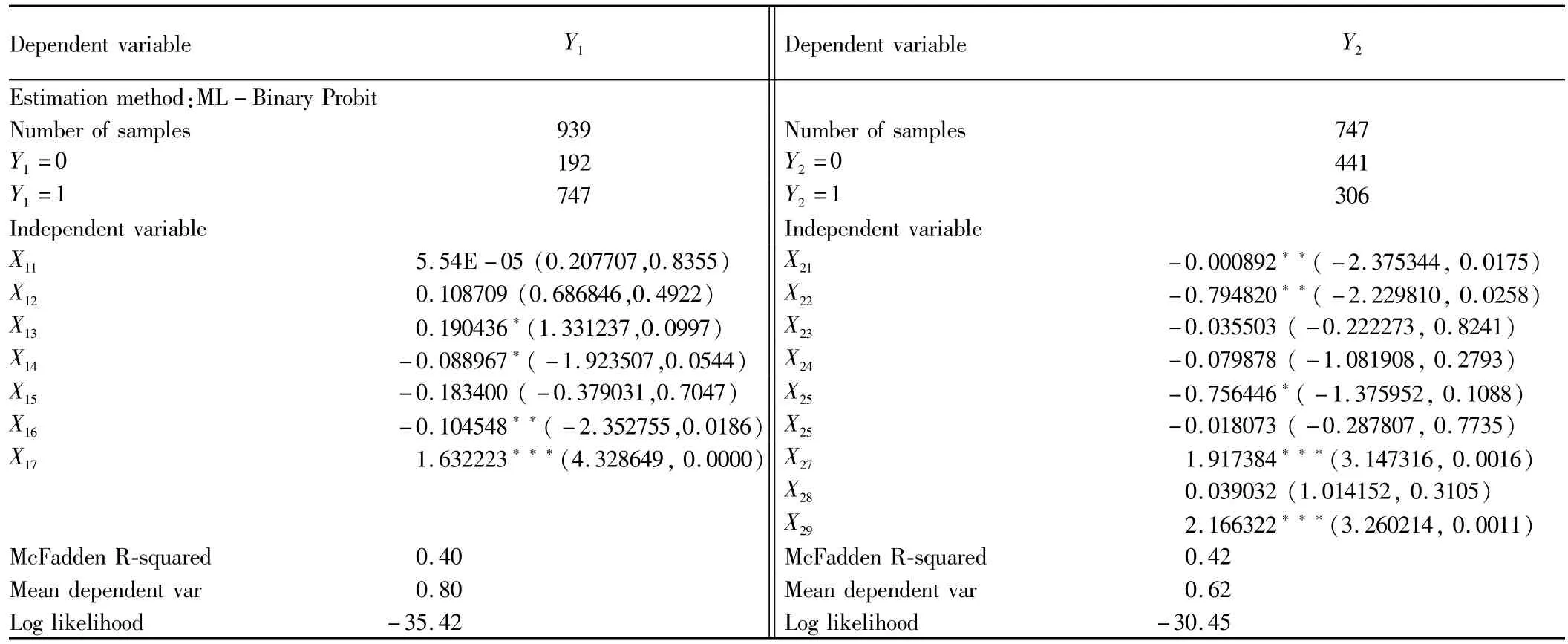
Table 13 Econometric model regression results
4.2 Results(i)At the 5%significance level,square of householder's age(X11/X21)does not pass the test in the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand model,but pass the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success.The householder's age has no significant impact on farmers' formal credit demand,and there is an inverted U-shaped relationship between householder's age and credit success.There is an inverted U-shaped relationship between householder's age and"whether having obtained loans from the formal financial institutions",consistent with China's reality.Age is an important factor in the assessment of bank lending,and bank favors the middle-aged entrepreneurial farmers,who have high human capital accumulation,strong entrepreneurial opportunity recognition ability and stronger ability to repay.(ii)At the 5%significance level,householder's education level(X12/X22)does not pass the test in the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand model,and householder's education level has no significant impact on the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand.However,it passes the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success,and there is a negative correlation.The entrepreneurial rural householders with lower education level more easily obtain loans from formal financial institutions,because the size of loans of entrepreneurial farmers with lower education level is often small,and it is easier to get credit support.Meanwhile,the entrepreneurial rural householders' education level is concentrated in junior high school and technical secondary school,mainly responsible for the negative correlation between farmers' entrepreneurial credit success and education level.(iii)At the 10%significance level,household population(X13/X23)passes the test in the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand model,but does not pass the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success.There is a positive correlation between household population and entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand.In the case of large-scale agricultural operation and slow agricultural scientific and technological progress in the western region,the more the labor force,the greater the demand for venture capital,and the greater the formal financial needs.But in the current situation,the family size is not the main reference variable for lending decisions of formal financial institutions,and large-scale labor forces may not mean the easier access to loans from formal financial institutions.(iv)At the 10%significance level,annual household per capita income(X14/X24)has a negative impact on entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand,and it has no significant impact on farmers' formal financial credit success.The annual household per capita net income has a substitution effect on entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial demand,so they are negatively correlated,but the annual household per capita net income is not positively correlated with the formal financial lending as expected.(v)At the 5%significance level,the type of industry that entrepreneurial farmers are engaged in(X15/X25)does not pass the test in the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand model,and it is not a major factor influencing the formal financial demand.At the 10%significance level,it passes the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success.The entrepreneurial farmers engaged in traditional largescale operation are easier to get loans from formal financial institutions.The technical requirements,risks and benefits of traditional large-scale operation are in line with the majority of farmers' mental capacity and mental expectations,so they are still dependent on traditional large-scale operation.Few farmers choose other types of entrepreneurial industry and the proportion of loans obtained is relatively small,which reflects the defects of other types of entrepreneurial industry and entrepreneurial farmers' credit market potential.(vi)At the 5%significance level,the distance between the family location and the nearest financial institution(X16/X26)passes the test in the entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand model,but fails to pass the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success.The distance between the family location and the nearest financial institution has a negative impact on the entrepreneurial farmers'formal credit demand,indicating that the stronger the formal financial availability,the greater the entrepreneurial farmers' credit demand.The distance between the family location and the nearest financial institution has no significant impact on entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit success.The short distance from the financial institutions can facilitate bank's understanding of borrowing farmers,but it is not the main factor affecting the bank's lending decisions.(vii)At the 1%and 5%significance levels,the degree of understanding the loan conditions and procedures(X17/X27)passes the test,and it has a positive impact on the formal financial demand and formal financial credit success.Entrepreneurial farmers' understanding of the loan conditions and procedures can help entrepreneurial farmers to make decisions based on their own needs and socio-economic conditions and reduce the wrong cognition of formal financial credit.The withdrawal of formal financial institutions and financial services from agriculture and rural areas,combined with the complex credit procedures and high lending conditions,has exacerbated the information asymmetry between farmers and formal financial institutions,and strengthened the formal financial credit exclusion.(viii)The expected amount of the loan(X28)does not pass the test in the model of factors influencing entrepreneurial farmers' borrowing success.The entrepreneurial farmers' credit is mainly the productive investment loan,with a large sum,to a certain extent reflecting the investment scale and profitability of entrepreneurial agriculture.(i)At the 5%significance level,whether to hire labor for the family entrepreneurship(X29)passes the test,showing a positive correlation.The entrepreneurial farmers who hire labor for the family entrepreneurship are easier to get loans from formal financial institutions.Farmers 'entrepreneurship is a special economic behavior in the rural economy,and whether to hire labor for the family entrepreneurship to some extent reflects the entrepreneurial scale,operating earnings and revenue expectations,which can serve as an important indicator of banks' entrepreneurial project evaluation.
5 Conclusions and recommendations
5.1 ConclusionsThe entrepreneurial farmers have a strong formal financial demand,and most of the demand is productive investment demand,but there are constraints on entrepreneurial farmers' loans from formal financial institutions.Based on an survey of 939 farmers in Sichuan and Chongqing,this paper analyzes the influencing factors of entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand and credit constraints with Probit model.It is found that the household size has a positive impact on entrepreneurial farmers' formal credit demand;per capita household income has a negative impact on the formal financial credit and household income has a substitution effect on formal financial credit;the distance between the family location and the nearest financial institution has a negative impact on entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial demand,and the improvement of financial ecology is conducive to enhancing entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand;entrepreneurial farmers' understanding of lending procedures and conditions helps to improve the entrepreneurial farmers' formal financial credit demand,and the withdrawal of formal financial institutions and financial services from agriculture and rural areas has strengthened the formal financial credit exclusion;the constraints of lending procedures and conditions inhibit the farmers' credit demand;there is an inverted U-shaped relationship between householder's age and credit success;householder's education level is negatively correlated with credit success;compared with the traditional large-scale agricultural operation,other types of entrepreneurial industry is developed insufficiently,having exacerbated the information asymmetry between farmers and formal financial institutions,and increased the credit risks;lending procedures and conditions have played a good"filter"role,and entrepreneurial farmers' understanding of the loan conditions and procedures is positively correlated with the creditsuccess,and can help entrepreneurial farmers to make decisions based on their own needs and socio-economic conditions and reduce the wrong cognition of formal financial credit;the entrepreneurial farmers who hire labor for the family entrepreneurship are easier to get loans from formal financial institutions;statistically,household size,per capita household income,the distance between the family location and the nearest financial institution and the expected size of loans,have no significant impact on the formal financial credit success.
5.2 Recommendations(i)In the places where conditions permit,it is necessary to promote the development of township banks and rural community banks to make up for the credit supply shortage of RCC,ABC and other commercial banks.In the development of township banks and rural community banks,it is necessary to strengthen supervision and expand farmers' agricultural entrepreneurial loans while ensuring the interests of depositors to foster the new body of agriculture.(ii)It is necessary to promote the rural and agricultural credit service innovation,increase support to entrepreneurial farmers in the case of risk control.When conditions permit,there is a need to build the rural credit system to reduce the information asymmetry between formal finance and farmers,and establish the interest rate system to meet entrepreneurial farmers' credit demand.Meanwhile,in the loan review process,it is necessary to set up"rural community-loan officer-bank"review system,gradually increase the project loans according to farmer's credit situation in the case of controlling credit risk,gradually reduce lending procedures,and actively use a variety of channels to make farmers understand the lending procedures and conditions and reduce the credit constraints arising from information asymmetry.(iii)When conditions permit,it is necessary to actively build agricultural development and agricultural entrepreneurship foundation,to support farmers' agricultural entrepreneurial behavior,draw on the foreign experience of cultivating new body of agriculture,and provide the venture start-up capital to the entrepreneurial farmers who lack collateral,guarantees and other formal financial credit conditions.
[1]Peter F.Drucker.Innovation and entrepreneurship[M].China Beijing:China Workers Publishing House,1989.(in Chinese).
[2]JIAO XB,GUAN P.Probe into research the development of entrepreneurial economy and Chinese farmers'entrepreneurship theory[J].Reform of Economic System,2012(1):29-33.(in Chinese).
[3]ZANG YL,CHEN HL,LU X.Multiple functions of peasant household entrepreneurship and its transmission mechanism——Taking Chongqing as an example[J].Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University Social Science Edition,2012,29(3):57-64.(in Chinese).
[4]Black SE,Strahan PE.Entrepreneurship and bank credit availability[J].Journal of Finance,2002,57(6):2807-2833.
[5]Klappera L,Laevena L,Rajan R.Entry regulation as a barrier to entrepreneurship[J].Journal of Financial Economics,2006,82(3):591-629.
[6]WEIJF,WANG JH,LILT.Factors affecting the entrepreneurship of farmers:Survey form five northwestern provinces[J].Finance and Trade Research,2008,19(5):16-22.(in Chinese).
[7]MA XQ,HUANG ZH.Comparison analysis on rural credit demand and financing preference in Jiangsu Province[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University(Social Science Edition),2010,10(1):57-63.(in Chinese).
[8]HUANG ZH,LIU XC,CHENG EJ.Explanations for the low participation rate in the formal credit market by rural households in the poor areas[J].Economic Research Journal,2009(4):116-128.(in Chinese).
[9]WANG DX,TIAN QG,LI LL,et al.Empirical study on poverty peasant households’credit demand and credit behavior[J].Journal of Financial Research,2011(5):124-138.(in Chinese).
[10]ZHUX,LIZN.Analysis of credit rationing by Chinese formal rural finance[J].The Journal of Quantitative&Technical Economics,2006,23(3):37-49.(in Chinese).
[11]HAN J,LUO D,CHENG Y.Empirical study on peasant households’credit demand behavior under the credit constraint[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2007(2):44-52.(in Chinese).
[12]ZHU SY,ZHANG ZX,et al.On supply and demand of financial market in rural China—Taking the case of traditional agricultural areas[J].Management World,2003(3):88-95.(in Chinese).
[13]ZHANG XM,et al.Rural finance and credit policy[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2001.(in Chinese).
[14]XIAO HF,BAO XL.The credit constraint of farmers'entrepreneurship—Based on the empirical study of 930 rural micro and small enterprises in Hubei Province[J].Journal of Agrotechnical Economics,2011(2):102-109.(in Chinese).
[15]CHENG Y,LUO D.The choice of entrepreneurship under the credit constraint—Based on the empirical analysis of household survey of rural China[J].Chinese Rural Economy,2009(11):25-38.(in Chinese).
[16]WANG JN,ZHAO SL.Exterior restrictions,congnitive bias,behavior bias,and the farmer's loan dilemma[J].Management World,2007(9):69-75.(in Chinese).
[17]SHIZP,ZHANGWQ.Empirical study on the influencing factors of peasant households’credit demand and credit behavior—Based on the survey of Fujian households[J].Southeast Academic Research,2012(3):105-112.(in Chinese).
[18]MA XY,BAIYX.Influence of farmers'individual characters upon credit constraint:An experiential evidence from Shaanxi[J].China Soft Science,2010(9):148-155.(in Chinese).
[19]WANG XH,TAN KT.Inherent mechanism for formation of rural households credit exclusion and its empirical test based on micro survey data in China[J].China Soft Science,2012(6):139-150.(in Chinese).
[20]MA XY,BAIYX.Farmers'individual characters and credit constraints:Comparative analysis of formal and informal credit market[J].Soft Science,2011,25(2):94-98.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2015年1期
Asian Agricultural Research2015年1期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Integration of Medical Care and Endowment:A New Exploration of Endowment Mode in the Context of Population Aging
- The Distribution of Benefits for Players in Agricultural Industrial Chain
- Price Conduction Mechanism of China's W heat Industry Chain Based on VECM
- On the Development and Maintenance of Cigarettes Exported to North Korea
- The Research on the Construction of Monitoring and Evaluation System for the Operation of Marine Economy in Liaoning Province
- Wetland Purification Pattern for Surface Runoff Pollution of Coastal Highway in Liaoning Province
