Adaptive Modulation and Coding Based on Fuzzy Logic Cognitive Engine
ZHANG Chuang (张 闯), ZHAO Hong-lin (赵洪林), JIA Min (贾 敏)
Communication Research Center, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Adaptive Modulation and Coding Based on Fuzzy Logic Cognitive Engine
ZHANG Chuang (张 闯)*, ZHAO Hong-lin (赵洪林), JIA Min (贾 敏)
CommunicationResearchCenter,HarbinInstituteofTechnology,Harbin150001,China
Adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) which depends on channel state information (CSI) can make the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) for the sender changed, and make the spectrum efficiency enhanced. The traditional method of AMC establishes a lookup table of MCSs at first, and then the sender chooses the proper MCS according to the CSI from feedback channel. However, this method is not suitable for frequency selective and fast fading channel. Thus, a method based on fuzzy logic cognitive engine is proposed in this paper. The type of channel is recognized by the fuzzy logic cognitive engine, then the MCSs are modified to suit for the channel type. The simulation results show that the proposed method is more suitable for frequency selective and fast fading channel. And it is more reliability under the condition of meeting the bit error rate (BER).
adaptivemodulationandcoding(AMC);channelstateinformation(CSI);modulationandcodingscheme(MCS);fuzzylogic
Introduction
As the resource of frequency becoming more and more scarcer in wireless communication, adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) was investigated in the sixties of last century to improve the frequency utilization rate[1-2]. The core idea of AMC is that the sender adjusts the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) when the channel characteristic changed, namely the sender chooses the high order modulation and high code rate to transmit signals under the channel condition is good, and vice versa. But due to hardware constraints and lack of good channel estimation, the interest in this field didn’t last for long. As the technology developed and the need of bandwidth improvement, the interest in AMC is revived in the nineties of last century[3-7].
By now, the main cellular systems including CDMA (IS-95), wideband CDMA (CDMA2000 and UMTS WCDMA), TDMA (IS-136) and GSM (GPRS and EDGE) already adopted AMC, and the next generation wireless systems like long term evolution (LTE), worldwide interoperability for microwave access (WIMAX) regarded AMC as a major technical means to improve the spectral efficiency[6]. In Ref. [8], the author considered three adaptive modulation schemes and studied low-density parity-check code (LDPC). It showed that the adaptive modulation with LDPC can tolerate strong turbulence. In Ref. [9], the authors proposed a new scheduling scheme exploiting multiuser diversity, and they considered not only channel information but queue information as well. And they analyzed the performance of the proposed scheduler. In Ref. [10], aiming at the single-carrier frequency-domain-equalization (SC-FDE) system, an adaptive SC-FDE (ASC-FDE) scheme was proposed. It showed the proposed scheme had much better BER performance than traditional SC-FDE. In Ref. [11], to solve the problem of high data rate and improving coverage in future mobile broadband networks, the authors proved that choosing MCS was non-deterministic polynomial hard (NP-hard) problem, and then they proposed an optimal, two-step dynamic programming solution with pseudo-polynomial time complexity. In Ref. [12], the authors proposed a cross-layer design which combined a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) protocol at the data link layer and AMC at the physical layer. Further they derived the packet error rate and average spectral efficiency in closed-form for transmission over Nakagami fading channels. In Ref. [13], AMC was incorporated into WIMAX system to achieve higher throughput and improve spectral efficiency. The proposed schemes maximized the throughput, while maintaining a target bit error rate (BER).
Most previous researches either applied adaptive modulation and coding to special channel condition or special systems. Different from their works, we consider when channel is fast fading or frequency selective, how to choose modulation and coding scheme. Without loss of generality, we apply the proposed method to a very common system, and prove that our method is more reliable.
1 Traditional AMC Method
The traditional method of modulation and coding establishes a lookup table of MCSs according to the average channel signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and the sender chooses an appropriate MCS based on the channel state information (CSI) from channel estimation. The major steps of this method are as follows.
(1) Determine the target BERR0.
(2) Establish the relationship between MCS and average channel SNR, as shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 The relationship between SNR and BER

where Mndenotes the MCS, corresponding to the different order modulation and different code rate.γndenotes the SNR threshold of each MCS,γn<γn+1.
(4) By the channel estimation, the receiver receives the channel SNR and sends it to the sender through the feedback channel. According to the feedback information, the sender chooses MCS in the lookup table, and changes the MCS in next frame.
The essence of traditional AMC is a lookup table method, which is based on an established static MCSs table. The advance of this method is simple and short time decision-making. But in Fig.2, even under the same SNR, BERs are very different in frequency selective channel and non-frequency selective channel. So the traditional AMC method is not suitable for frequency selective channel, and similarly it is not suitable for fast fading channel. It is necessary to establish a channel cognitive method to cognize the channel type and modify the MCSs depending on the different channel types. Furthermore under the condition of improving the frequency utilization rate, the reliability of communication system is guaranteed.
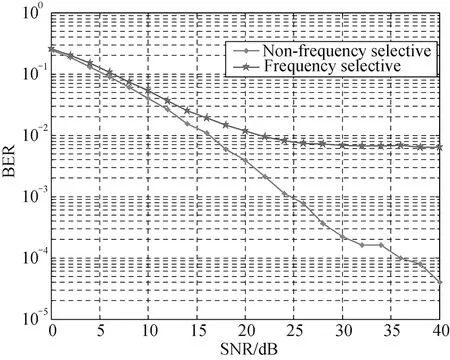
Fig.2 The relationship between BER and SNR under the conditions of frequency and non-frequency selective channels
2 Fuzzy Logic Cognitive Engine
Fuzzy set theory was proposed by Zadeh in 1965, and this theory was to solve the problem that the research object was too complex to accurately describe[14].
The fuzzy set theory uses fuzzy membership to express the degree that the objectXbelongs to the setω, and usually membership value is denoted byμω(X). The membership value is between 0 and 1, namely 0≤μω(X)≤1. The membership valueμω(X)=1 denotes the objectXbelongs to the set with 100% membership, and it is equivalent to the traditional concepts of sets thatX∈ω.Oppositely,μω(X)=0 denotes the object does not belong to the set, and it is equivalent to the traditional concepts of sets thatX∉ω. The membership value is closer to 1 that the degree of objectXbelongs to setωis higher; the membership value is closer to 0 that the degree of objectXbelongs to setωis lower. Fuzzy sets are generalization of the common sets, and the common sets are the special fuzzy sets. A fuzzy set is only determined by the membershipμω(X).
Fuzzy set theory provides a method to judge the type of channel under the condition of mobile communication environment. It is hard to descript the channel accurately, so it is necessary to establish a cognitive engine which is based on fuzzy logic to cognize the channel type.
Usually, channel can be distinguished as flat channel and frequency selective channel, fast fading channel and slow fading channel. There are four parameters to determine the channel type, which are: symbol durationTb, delay spreadτ, signal bandwidthBs, doppler frequencyBd.
The type of channel can be determined through fuzzy logic cognitive engine by using these parameters. The main set of rules used in the fuzzy logic cognitive engine as the followed rules.


The fuzzy logic cognitive engine cognizes the channel type through those rules by using four parameters.


The crux of the matter is how to determine the membership function. It is not easy to determine the membership function, until now there are no general methods to determine the membership function[15]. Commonly, the methods to determine the membership function including: expert system, according to the objective measure, statistical method, contrast-sequence method, comprehensive weighted method and so on[16].
An easy way to determine membership function is to choose some common functions. And by using these functions, the membership function can be represented approximately. The common expression ways of membership function are trapezium distribution, rectangular distribution, triangle distribution and Gaussian distribution.
Based on the analysis of membership values of input parameters before, trapezium distribution is chosen as the membership function to determine fuzzy variables. The function forms are as follows.
(1) Minor type membership function pattern:
(2) Middle type membership function pattern:
(3) Major type membership function pattern:
And the shapes of functions are shown in Fig.3.
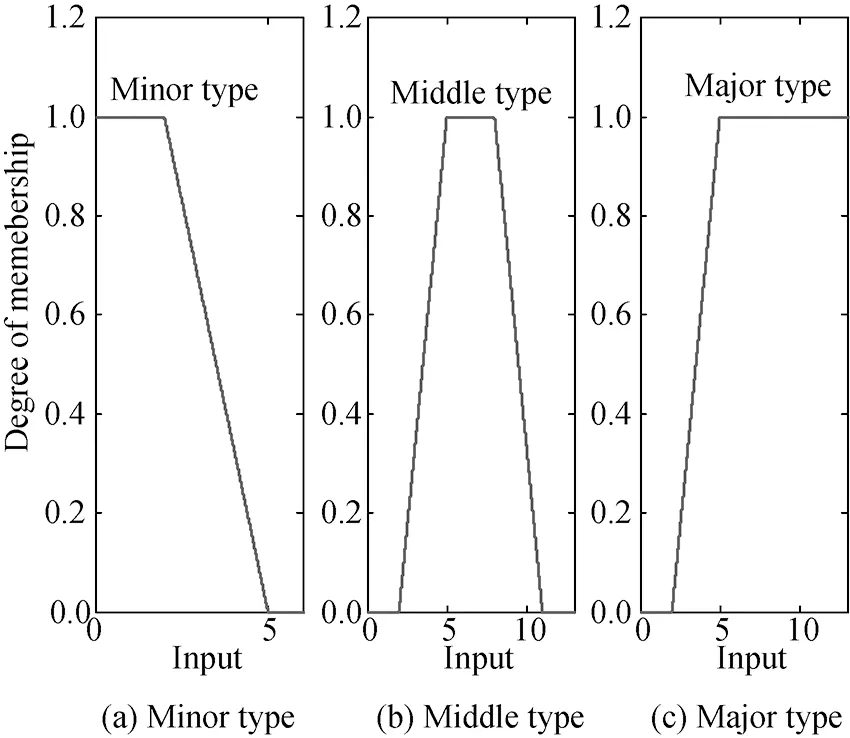
Fig.3 Trapezium distribution
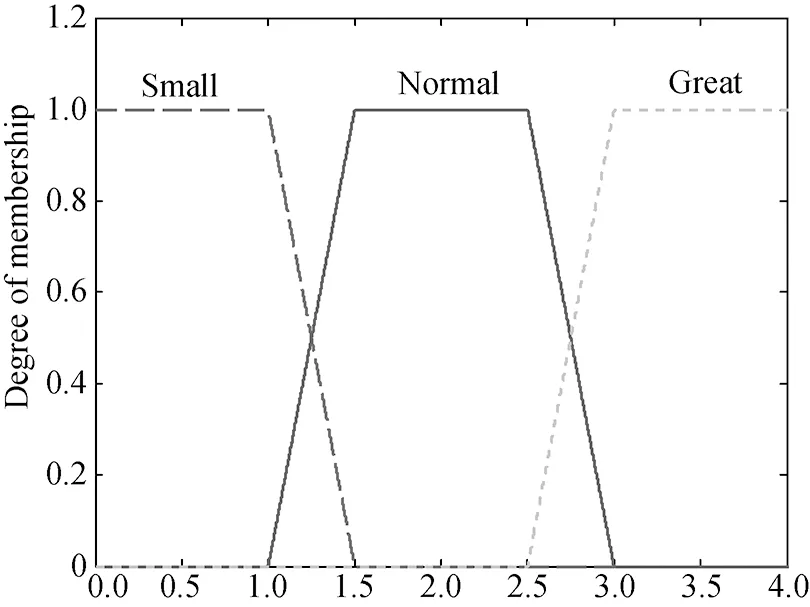
After determined the forms of membership functions, through the analysis before, the membership functions of fuzzy logic cognitive engine can be established. By using it, the channel types can be cognized, and the forms of these channel types are shown in Fig.4.
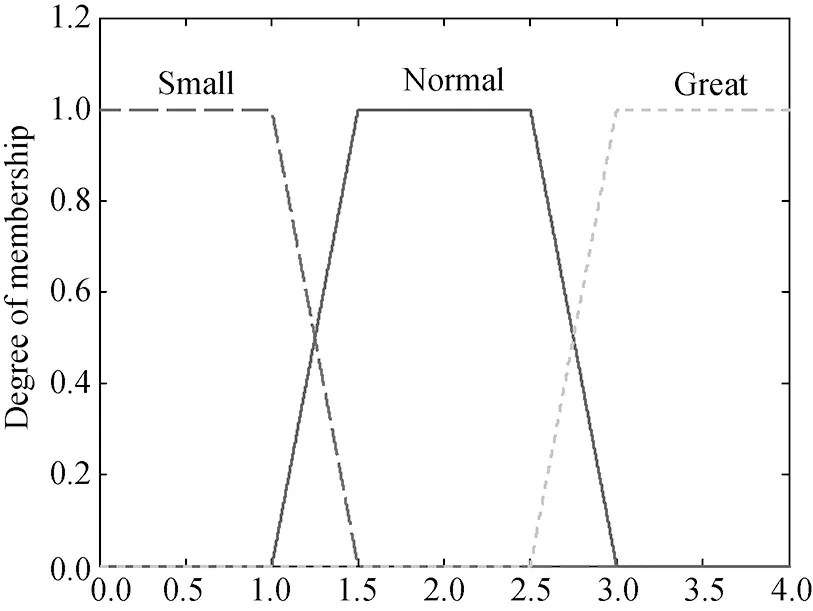

O1(c) The membership of O1 to determine the degree of frequency selective

O2(d) The membership of O2 to determine the degree of fast fading
3 System Model
The adaptive transmission system is mainly composed of sender, receiver and feedback channel. The whole system is shown in Fig.5. The sender uses variable bitrate coding and variable order modulation. The research interest is focused on the AMC, so the transmit power keeps constant. The receiver is composed of demodulation, decoding and channel estimation. Channel estimation can use least square (LS) estimator or minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator. The estimated parameters are used as fuzzy logic cognitive engine input, and then the types of channel are cognized by this cognitive engine. At last, the MCSs are modified to suit for the channel change.
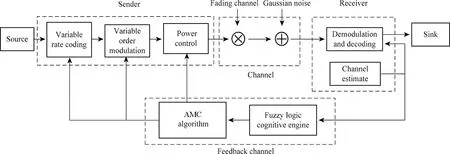
Fig.5 System model
4 Simulation and Results
It is assumed that the feedback channel has no delay. The sender uses four code rates LDPC code to transmit. The code rates are 1/2, 2/3, 3/4 and 5/6. The variable order modulation uses binary phase shift keying (BPSK) and quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK). Channel estimation uses LS estimator.
SUI-6 is adopted as the simulation channel, the relative delay of each path is (0, 14, 20) (μs), and the fading of each path is (0, -10, -14) (dB).
Under the condition of meeting targetR0=10-3, Fig.6 gives the adaptive MCSs, in which the source rate is 5M sym/s, and the maximum doppler frequency is 5 Hz. In Fig.6,ri(i∈(1, 2, …, 5)) represents the threshold. According to the maximizing the throughput, MCS is determined in each interval.
When the situation of channel is changed, MCSs cannot meet the target BER in Fig.7 with doppler frequency 5 Hz.
To meet the target BER, we depend on the channel type to modify the thresholds to transmit. The modified schemes are shown in Fig.8.
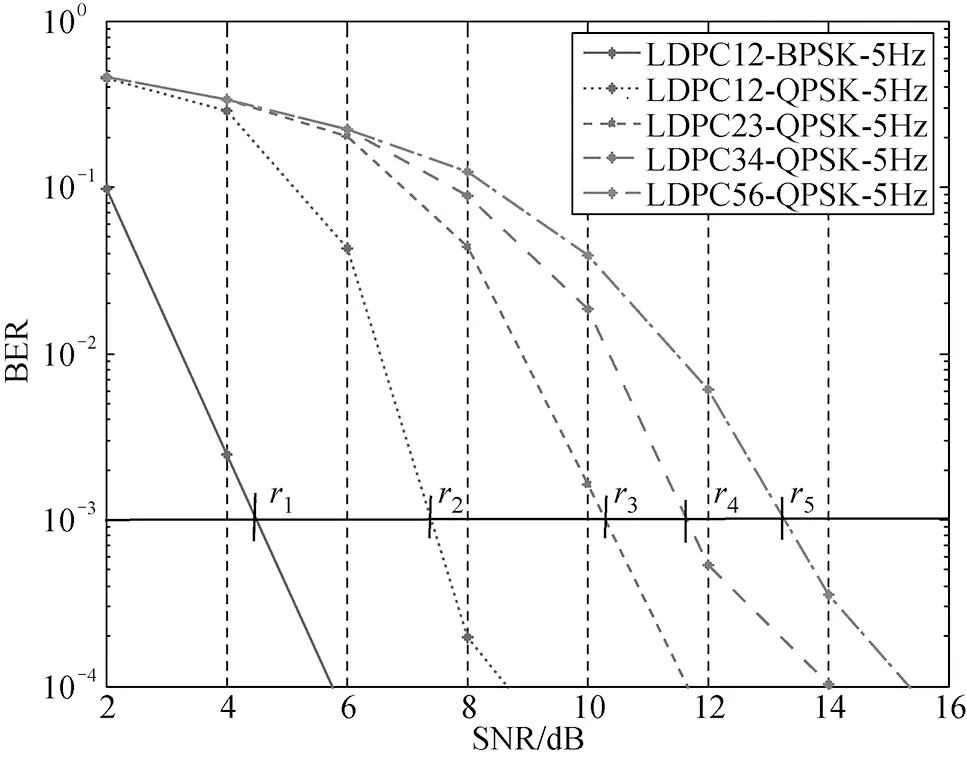
Fig.6 MCSs of 5 Hz
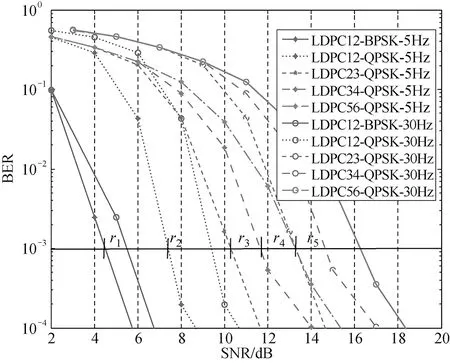
Fig.7 Comparison schemes maximum with Doppler frequency 5 Hz and 30 Hz
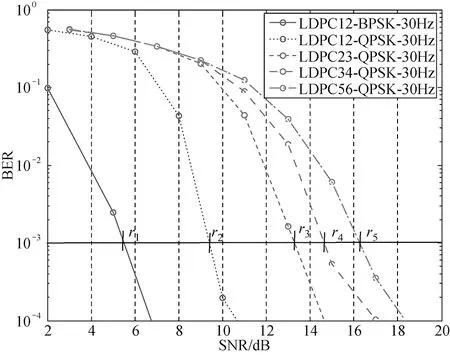
Fig.8 The modified schemes
5 Conclusions
In this work, by analyzing the process of the MCSs through traditional AMC, we found that the traditional method is not suitable for frequency selective and fast fading channel. By investigating the fuzzy sets theory, we created rules for cognitive engine to determine the type of channel in AMC system. Moreover, the use of fuzzy logic cognitive engine is crucial as the sender can modify the transmission MCSs based on the information of the cognitive channel. The simulation results show that the traditional method is suitable when channel is non-frequency selective and slow fading, but the MCSs cannot suit the channel when the channel becomes frequency selective and fast fading. The proposed method modifies the schemes based on the cognitive channel information. The simulation results prove that the proposed method is availability and can guarantee the reliability of communication system. An algorithm to modify the transmission schemes can be developed for the future work.
[1] Hayes J F. Adaptive Feedback Communications [J].IEEETransactionsonCommunicationTechnology, 1968, 16(1): 29-34.
[2] Cavers J K. Variable-Rate Transmission for Rayleigh Fading Channels [J].IEEETransactionsonCommunication, 1972, 20(1): 15-22.
[3] Chung S T, Goldsmith A J. Degrees of Freedom in Adaptive Modulation: a Unified View [J].IEEETransactionsonCommunication, 2001, 49(9): 1561-1571.
[4] Furuskar A, Mazur S, Olofsson H. EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM and TDMA/136 Evolution [J].IEEEPersonalCommunications, 1999, 6(3): 56-66.
[5] Ghosh A, Jalloul L, Love B,etal. Air-Interface for 1XTREME/1xEV-DV [C]. IEEE VTS 53rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Rhodes, 2001: 2474-2478.
[6] Nanda S, Balachandran K, Kumar S. Adaptation Techniques in Wireless Packet Data Services [J].IEEECommunicationsMagazine, 2000, 38(1): 54-64.
[7] Sari H.Rends and Challenges in Broadband Wireless Access [C]. Symposium on Communications and Vehicular Technology, Leuven, 2000: 210-214.
[8] Djordjevic I B. Adaptive Modulation and Coding for Free-Space Optical Channels [J].IEEE/OSAJournalofOpticalCommunicationandNetworking, 2010, 2(5): 221-229.
[9] Kim T, Lim J T.Queuing Analysis in a Multiuser Diversity System with Adaptive Modulation and Coding Scheme [J].IEEETransactionsonVehicularTechnology, 2011, 60(1): 338-342.
[10] Wang W J, Jiang W, Dong M K,etal. A Constant Sending Symbol Rate Adaptive SC-FDE Scheme [J].ActaScientiarumNaturaliumUniversitatisPekinensis, 2011, 47(3): 411-417.
[11] Li P L, Zhang H H, Zhao B H,etal. Scalable Video Multicast with Adaptive Modulation and Coding in Broadband Wireless Data Systems [J].IEEE/ACMTransactionsonNetworking, 2012, 30(12): 1818-1828.
[12] Dai C Q, Yu R, Li J,etal. Cross-Layer Design of Combining HARQ with Adaptive Modulation and Coding for Nakagami-m Fading Channels [J].JournalofCommunications, 2012, 7(6): 458-463.
[13] Zadeh L. Fuzzy Sets [J].InformationandControl, 1965, 8(3): 338-353.
[14] Boppana L, Amanchi C N, Kodali R K. Coding Rates and MCS Using Adaptive Modulation for WiMAX in OFDM Systems Using GNU Radio [C]. IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems, Trivandrum, 2013: 53-58.
[15] Pawlak Z, Peters J, Skowron A.Approximating Functions Using Rough Sets [C]. IEEE Annual Meeting of the Fuzzy Information, Banff, 2004: 785-790.
[16] Baldo N, Zorzi M. Cognitive Network Access Using Fuzzy Decision Making [J].IEEETransactionsonWirelessCommunications, 2009, 8(7): 3523-3535.
Foundation items: National Natural Science Foundations of China (Nos.61071104, 61201143); Innovation Foundation of China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) (ITS) (No. F-W-YY-2013-016)
TP393. 01 Document code: A
1672-5220(2015)01-0030-05
Received date: 2013-11-11
* Correspondence should be addressed to ZHANG Chuang, E-mail: cangshanerhai@126.com
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年1期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2015年1期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Joint Optimization Strategy for Video Transmission over Distributed Cognitive Radio Networks
- Asymptotic Behavior of the Drift Coefficient Estimator of Stochastic Differential Equations Driven by Small Noises
- Modeling and Simulation of P-Aloha, CSMA/CA and MACAW Protocols for Underwater Acoustic Channel
- Design and Analysis of Axial Thrust Roller-Exciting Vibrating Table and Its Motor-Control System Based on Co-simulation
- Effects of Compression Garments on Lower Limb Muscle Activation via Electromyography Analysis during Running
- Analysis on Nipper Balance Shaft Movement with Transmission Drive of Comber
