以框架为基础的3种教学方式的比较
杨 银,张宇成
(1.中国医学科学院 基础医学研究所 北京协和医学院基础学院 病原学系;2.北京协和医学院 临床医学八年制2010级, 北京 100005)
医学教育
以框架为基础的3种教学方式的比较
杨 银1*,张宇成2
(1.中国医学科学院 基础医学研究所 北京协和医学院基础学院 病原学系;2.北京协和医学院 临床医学八年制2010级, 北京 100005)
目的探测以框架为基础的教学模式下3种不同教学方法的效果。方法在教学改革中,医学微生物教学和医学英语教学整合,采取多元化的全英文教学模式,其中包括以框架为基础的教学/自学模式。北京协和医学院73名学生参与该教学/自学模式的实践,在此模式下,通过客观测试评估和比较3种不同学习方式(教师讲解、同伴教育和学生自学)的效果。结果学生对所学知识的即时掌握程度和40 d后掌握程度得分从高至低依次为教师讲解(3.79±0.89 和 3.35±1.18)、学生自学(2.71±1.03 和2.86±0.88)和同伴教育(2.42±1.08 和 2.10±1.13)(P<0.01);不同学习方式下学生的即时掌握程度与40 d后掌握程度得分的差值各不相同,教师讲解部分和同伴教育部分得分明显降低,学生自学部分反而增高(P<0.05)。结论在以框架为基础的教学模式下,3种不同的教学方式各有其优缺点,这提示学生自学和教师讲解在教学中都应当有适当的比例。
以框架为基础的学习;教师讲解;同伴教育; 自学;评估
作为医学科学中的一部分,医学微生物所涵盖的内容非常多,而且变化和发展也非常迅速,这使得在医学微生物的教学实践中,在有限的时间内给学生灌输大量的知识比较困难,调查结果显示其可行性和教学效果也比较差[1- 2]。与此同时,近年来医学教育中出现了一些好的改革,如以问题为导向的教学方法(problem-based learning,PBL)、以团队为基础的教学方法(team-based learning, TBL)、基于案例和思想的学习(case and mind-based learning, CMBL)等,这些教学模式以PBL为代表,使得医学教育的模式逐渐从学究式的、以教师为中心的、讲述性教学逐渐向互动式问题为基础以学生为中心的教学模式转变, 尽管这些教学模式的具体形式各有不同,但其中都贯穿了一项首要理念即教会学生如何去学习并培养终生学习的习惯。有的医学院校甚至专门开设了‘learn to learn’作为一门课程[3]。另外,同伴教育作为一种独具特色的教学方法,也被逐渐应用于医学教育中[1,4- 5]。该研究旨在医学微生物教学中实施以框架为基础的教学/自学模式(frame-work based learning,FBL),同时在实践中评估和比较这种模式下教师讲解、同伴教育和学生自学3种不同学习方式的教学效果。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
研究对象为北京协和医学院临床医学八年制2010级学生。
1.2 研究方法
首先由教师介绍以框架为基础的学习模式, 以及如何利用这种框架模式进行学习:其中包括如何根据学习内容或职业目标设计相应的学习框架,再根据框架组织学习。在这种以框架为基础的模式下,分别采用3种不同方式进行学习:具体学习及评估过程详见图1, 其中即时测试(post-test)和40 d后测试(delayed retention test) 两次测试题目均为选择题,检测学生在这3种学习方式下对所学内容的掌握程度并进行比较,比较项目包括:1)3种学习方式下即时测试得分比较;2)3种学习方式下40 d后测试得分比较; 3)3种学习方式下即时测试得分与40 d后测试得分比较;4)3种学习方式下即时测试得分与40 d后测试得分变化情况比较。

图1 以框架为基础的学习过程及评估Fig 1 Process and evaluation of frame-work based learning
1.3 统计学分析
2 结果
2010级全体共73名学生参与该教学/自学模式的实践,前后两次测试结果分别见表1。
3 讨论
作为一种传统的教学方式,教师讲解在医学微生物教学中占有较大的比例。在医学教育改革中,是否该摒弃这种方式,或者保留一定的比例,不同教学环境中的具体细节是不能一概而论的。本研究的两次测试中,教师讲解显示了一定的优势(得分最高),能让学生在短时间内掌握较多基础知识,对于刚从预科教育阶段转至医学教育阶段的学生,他们对医学基础和临床知识了解甚少,因而教师的讲解和指导还是有一定必要性并应当占一定比例的。然而,从两次测试得分的变化情况来看,学生对于相关内容的遗忘也是最多的,这也符合爱德加·戴尔的现代学习方式理论[6]。
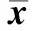
表1 三种教学方式测试结果比较Table 1 Comparison of learning results underlying three different teaching methods(±s,n=73)
#P<0.01即时测试或40 d后测试得分的组间比较;*P<0.05即时测试与40 d后测试得分的组内比较;△P<0.05即时测试与40 d后测试得分差值的组间比较.
相对而言,在知识的持久性方面,自学这种方式在本研究中展示了一定的优势。自我学习是医学教育改革中研究最多的课题之一,医学科学本身的特点也决定了无论学生将来从事医学领域中何种职业,对医学生自学能力的培养是不可或缺的,对于自学效果的评估,除了学生的主观感受和自我评估以外,对所学知识进行客观测试也是一个不可忽略的环节,其反馈结果能在较高程度上刺激学生调节其学习目的和内容[ 7 ]。在本研究中,学生自学效果的优势不如其他临床教学研究[8]显著, 但是前后两次测试结果的变化情况显示,自学部分内容得分随时间降低最少,甚至有增高倾向,这可能是因为:学生亲身参与度较高不容易遗忘,这是教师讲解主导的学习方法所不具备的优点[9- 10];另外,考试也可激发学生的主动学习行为。学生在考试中和考试后对自我把握程度不同的题目及相关内容的关注度不同,这不仅影响测试进行时的答题时间分配,也会影响考试后的自学行为,对自觉掌握不好的内容可能投入较多精力,因而第2次测试得分有改善的倾向[9,11]。
另外,同伴教育作为一种辅助教学手段,在教学实践中,有学生提出这种方式能使课堂环境轻松愉快。也有研究显示,这种教学方式具有其独特优势,尤其在临床医学教育阶段,对增强学生自信度和激发学习兴趣有一定的帮助[4- 5],且对将来的学术或职业生涯有益[12]。但本研究中同伴教育并没有显示出明显的优势,两次测试得分都比其他组低,只是学生随时间对这部分内容的遗忘也不明显。当然,学生对于这种学习方式的主观感受(包括其被认可程度以及这些不同的教学方式适合占多大比例)也是需要考虑的,这些都需要进一步的研究和调查。
本研究中,教师主导的学习和学生自学各有其优缺点,在基础医学教育阶段教师讲解及学生自学均应占一定比例;本研究结果与其他类似临床教学研究结果有一定差异,因此不宜套用其他研究或学校的教学模式,应在实践中探索并制定适合本院学生的教学模式。
志谢:衷心感谢管远志教授、江宇教授为本研究提供的技术指导和帮助。
[1] Mauksch L, Farber S, Greer HT. Design, dissemination, and evaluation of an advanced communication elective at seven U.S. Medical Schools [J]. Acad Med, 2013, 88:843- 851.
[2] Samarakoon L, Fernando T, Rodrigo C. Learning styles and approaches to learning among medical undergraduates and postgraduates [J]. BMC Med Educ,2013,13:42- 48.
[3] Sandars J, Homer M. Pause 2 Learn: a ‘learning to learn’ course to help undergraduate medical students to become more effective self-regulated learners [J]. Educ Prim Care, 2012, 23:437- 439.
[4] Sailer FC, Melvold RW, Hosford CC. Multiple benefits derived from a peer teacher program in two undergraduate microbiology lab courses [J]. J Microbiol Biol Educ,2010,11:102- 106.
[5] Mileder L, Wegscheider T, Dimai HP. Teaching first-year medical students in basic clinical and procedural skills—a novel course concept at a medicalschool in Austria [J]. GMS Z Med Ausbild, 2014, 31:1- 15.
[6] Masters K. Edgar Dale‘s pyramid of learning in medical education: a literature review[J].Med Teach, 2013,35:1584- 1593.
[7] Sagasser MH, Kramer AW, van der Vleuten CP. How do postgraduate GP trainees regulate their learning and what helps and hinders them? A qualitative study [J]. BMC Med Educ, 2012, 12:67- 78.
[8] Brydges R, Nair P, Ma I,etal. Directed self-regulated learning versus instructor-regulated learning in simulation training [J].Med Educ,2012,46:648- 656.
[9] Agrawal S, Norman GR, Eva KW. Influences on medical students’ self-regulated learning after test completion [J]. Med Educ,2012 46:326- 335.
[10] Van der Leeuw RM, Slootweg IA. Twelve tips for making the best use of feedback [J]. Med Teach, 2013,35:348- 351.
[11] Stegers-Jager KM, Cohen-Schotanus J, Themmen AP. Motivation, learning strategies, participation and medical school performance [J]. Med Educ,2012,46:678- 688.
[12] Yu TC, Wilson NC, Singh PP,etal. Medical students-as-teachers: a systematic review of peer-assisted teaching during medical school [J]. Adv Med Educ Pract, 2011,2:157- 172.
Frame-work based learning:comparison of learning results underlying three different teaching methods
YANG Yin1*, ZHANG Yu-cheng2
(1.Dept. of Medical Microbiology and Parasitology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences CAMS, School of Basic Medicine,PUMC;2.Grade 2010, Clinical Medicine, PUMC, Beijing 100005, China)
ObjectiveThis study is aiming for compareing the results of three methods of teaching/learning which are developed from frame-work based learning model.MethodsIn the reformaction of medical education, the teaching of Medical Microbiology was partly integrated with Medical English and the frame-work based learning model was involved. In the study, 73 students in Peking Union Medical College were enrolled in the practice of this reform of frame-work based learning and experience three methods of teaching/learning: instructor regulated learning, peer regulated learning and self regulated learning. Objective tests were taken to evaluation of learning out-comes both at the immediate time (post test) and after 40 days (delayed retention test).ResultsThe score of master degree of related knowledge ranking list are similar in the post test and delayed retention test: instructor regulated learning(3.79±0.89 and 3.35±1.18, self regulated learning(2.71±1.03 and 2.86±0.88)and peer regulated learning(2.42±1.08 and 2.10±1.13)(P<0.01).While the disparity between the two exams of the same student varies in three methods of teaching/learning, the scores in instructor regulated learning and peer regulated learning mode dropped significantly but exhibited a minor promotion in score in the self regulated learning mode(P<0.05).ConclusionsThe results demonstrates different advantages and disadvantages of the three modes of learning, showing that appropriate proportion of these three teaching/learning methods is needed to be detected and adjusted to get the best results.
frame-work based learning; instructor regulated learning; peer regulated learning; self regulated learning; evaluation
2014- 05- 03
2014- 06- 13
北京协和医学院基础学院教育教学改革立项(JG2011- 003)
*通信作者(correspondingauthor):yyboby@gmail.com
1001-6325(2014)08-1154-04
R 378
A

