内蒙古集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩变质作用及年代学研究*
蔡佳 刘福来 刘平华 施建荣
中国地质科学院地质研究所,北京 100037
1 引言
位于华北克拉通西北缘的孔兹岩带是一条古元古代碰撞构造带,是由西部陆块内北部的阴山陆块和南部的鄂尔多斯陆块碰撞形成的,该孔兹岩带出露大面积变质表壳岩系(Zhao et al.,1999,2003,2005,2012;Zhai et al.,2000),包括西段贺兰山-千里山变质杂岩、中段大青山-乌拉山变质杂岩以及东段集宁变质杂岩,近年来,许多研究者对上述杂岩中的泥质片麻岩的成因矿物学、矿物相转变、变质演化和同位素年代学等方面进行了深入研究(卢良兆等,1992,1996;Liu et al.,1993;Lu and Jin,1993;Liu et al.,1998;刘福来等,2002;Wan et al.,2006,2009,2013a;Santosh et al.,2006,2007a,b,2009;Xia et al.,2006a,b;Dong et al.,2007,2013;Yin et al.,2009,2011;Yin,2010;周喜文等,2010;Wang et al.,2011;Jiao and Guo,2011;Jiao et al.,2013a,b;Guo et al.,2012;Dan et al.,2012;Liu et al.,2012;Ma et al.,2012;刘平华等,2013;蔡佳等,2013a,b;Cai et al.,2014)。一些研究者(卢良兆等,1992;Lu and Jin,1993;Liu et al.,1993;Yin,2010;周喜文等,2010;Wang et al.,2011;Jiao et al.,2013a;蔡佳等,2013a;Cai et al.,2013)通过对孔兹岩带出露的变泥质岩变质作用研究,普遍得到了近等温减压的顺时针P-T轨迹。大量的锆石或独居石的年代学研究表明孔兹岩带的变泥质岩和变基性岩中的变质锆石记录了1950~1810Ma的变质年龄(Xia et al.,2006a,b;Wan et al.,2006,2009,2013a;Dong et al.,2007,2013;周喜文和耿元生,2009;Yin et al.,2009,2011;刘平华等,2013),其中~1950Ma可能代表了北部的阴山陆块和南部鄂尔多斯陆块碰撞拼合的时代(赵国春,2009;周喜文和耿元生,2009;Yin et al.,2009,2011;Zhao et al.,2010;Dong et al.,2013),1920~1890Ma则可能是碰撞后折返的时代(Yin et al.,2009;Jiao et al.,2013b)。然而 Wan et al.(2013a)研究得出大青山-乌拉山变基性岩记录了1970~1920Ma的岩浆年龄,反映古元古代陆内伸展事件,这对~1950Ma所代表的地质意义提出了质疑。最近,部分研究者(Hu et al.,2013;Wan et al.,2013b)还对孔兹岩带南部鄂尔多斯陆块新生代沉积盖层以下的变泥质岩进行了锆石UPb年代学研究,获得了两组锆石年龄,一组锆石显示>2.4Ga的核和>2.28Ga变质边年龄,另一组显示~2.08Ga的核和~1.9Ga变质边年龄,认为鄂尔多斯陆块并非太古代克拉通块体,其基底可能分布着大面积晚古元古代的变沉积岩,这表明鄂尔多斯陆块可能与孔兹岩带一样,也卷入了古元古代的构造-热事件。此外,一些研究者(Santosh et al.,2006,2007a,2009;Jiao et al.,2011;Guo et al.,2012;Liu et al.,2012)在孔兹岩带东段的土贵乌拉、和林格尔以及中段大青山-乌拉山的东坡地区识别出超高温变质岩,其变质温度可达950℃以上,变质时代为1930~1920Ma(Santosh et al.,2007a,b)。有研究者认为(赵国春,2009;Guo et al.,2012;Wan et al.,2013a)区域内的超高温变质事件与碰撞后伸展环境下的地幔岩浆底侵有关,而Peng et al.(2010,2011)报道的土贵乌拉附近的徐武家出露~1930Ma辉长苏长岩墙群也进一步佐证了这一观点。
有关孔兹岩带东段集宁地区的高级变质岩变质作用的研究已取得了大量的研究进展,早期研究者(Lu and Jin,1993)主要利用基于矿物端元反应的传统地质温压计进行研究,然而该方法有较多的局限性,例如易受晚期降温阶段的影响(Kohn and Spear,2000;Cesare et al.,2008)。近年来,基于内恰的热力学数据库的THERMOCALC程序被广泛应用于变质作用的研究,该方法利用某一特定的全岩化学成分以计算出该种岩石可能出现的矿物组合及相应的P-T条件(Powell and Holland,1988,2008;Powell et al.,1998;Holland and Powell,1998,2003),相平衡模拟手段较传统地质温压计而言可更精确的限定各变质阶段的温压条件且受到晚期降温影响较小(Powell and Holland,2008;Rigby,2009)。Wang et al.(2011)针对集宁-卓资一带的富铝片麻岩计算P-T视剖面图并建立了近等温减压型顺时针P-T轨迹。Jiao et al.(2013a)对东段卓资小什字地区的石榴石岩进行了详细的变质作用研究,利用相平衡模拟及金红石-Zr温度计方法也得到近等温减压的顺时针P-T轨迹。基于上述前人的研究,本文选取孔兹岩带东段集宁三岔口地区出露的典型变沉积岩,即夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩,该岩石保留多种退变质反应结构,是良好的变质演化研究对象。本文通过详细的野外地质观察,结合室内岩相学、成因矿物学、变质反应结构、传统地质温压计和相平衡模拟以及锆石U-Pb年代学等综合研究,建立该类岩石的P-T轨迹及其变质时代,为进一步揭示孔兹岩带东段集宁地区的变质演化和变质时代提供重要基础资料,并为建立华北克拉通西部孔兹岩带形成演化的动力学模式提供科学依据。
2 地质背景
华北克拉通西北缘孔兹岩带是西部陆块内的一条古元古代碰撞构造带,由北部的阴山陆块和南部的鄂尔多斯陆块于 ~1950Ma碰撞形成,西部陆块与东部陆块在~1850Ma碰撞形成中部造山带(Zhao et al.,1999,2003,2005;Zhai et al.,2000)。孔兹岩带由西向东沿千里山-贺兰山,大青山-乌拉山和集宁-卓资-丰镇一带展布,其北邻阴山陆块,南侧与鄂尔多斯陆块相接(图1a,b),东侧与中部造山带紧邻。孔兹岩带西段主要出露千里山变质杂岩和贺兰山变质杂岩,中段主要是乌拉山-大青山变质杂岩,东段主要出露集宁变质杂岩。
研究区位于孔兹岩带东段集宁地区,出露的岩石类型主要为古元古代集宁岩群变质表壳岩系(孔兹岩系),少量古元古代(石榴)基性麻粒岩和斜长角闪岩(卢良兆等,1992,1996;Lu and Jin,1993;Zhao et al.,1999),TTG 质片麻岩和紫苏花岗岩。其中孔兹岩系在区内出露广泛,主要分布于卓资县大榆树乡羊圈湾村、梨花镇大什字村、小什字村,集宁三岔口乡,凉城县东十号乡大羊报沟、永兴镇、新店子乡,以及和林格尔县老黑窑乡一带,岩石类型主要包括(石榴)黑云二长/斜长片麻岩、夕线石榴堇青黑云二长/斜长片麻岩和长英质粒状岩石,多以互层状产出,还出露大量钾质花岗质片麻岩、石榴黑云母花岗岩和少量(石墨)大理岩等。少量古元古代(石榴)基性麻粒岩零星分布于卓资县梨花镇里毫堑村、大什字村,集宁三岔口乡,丰镇市浑源窑乡一带,其岩石类型主要由角闪二辉麻粒岩、含榴角闪二辉麻粒岩、斜长角闪岩等组成,多成宽数十厘米到数米的似层状或团块状赋存于变质表壳岩系或(紫苏)花岗质片麻岩中。

图1 孔兹岩带在华北克拉通的分布和构造位置图(a,b,据Zhao et al.,2005)和集宁地区的地质简图及采样位置(c,据郭敬辉等,2001)Fig.1 Distribution of the Khondalite Belt in the North China Craton(a,b,after Zhao et al.,2005)and geological map of Jining area(c,after Guo et al.,2001)

图2 集宁三岔口地区变泥质岩野外露头照片(a)-石榴黑云二长片麻岩与夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1);(b)-石榴黑云二长片麻岩;(c)-石榴黑云二长片麻岩与夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1);(d)-夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)的矿物组合Spl+Sil+Crd+GrtFig.2 Outcrops of Sanchakou paragneisses in the Jining area(a)-Grt-Bt paragneiss and Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(BH53-1);(b)-Grt-Bt paragneiss;(c)-Grt-Bt paragneiss and Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(BH53-1);(d)-Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(BH53-1)with mineral assemblage of Spl+Sil+Crd+Grt
3 样品采集与分析方法
样品采样点位于内蒙古孔兹岩带东段集宁以西的三岔口乡白石头村(图1c)。该地区出露有典型的变泥质岩夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1),呈透镜状或夹层状产出于石榴黑云二长片麻岩中(图2)。夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中可见堇青石围绕石榴石边部形成特征的“黑眼圈”结构(图2d)。
矿物化学成分分析和显微结构特征的观察在中国地质科学院大陆动力学国家重点实验室进行。采用JSM-5610LV型扫描电镜(SEM)(日本电子公司JEOL生产)观察样品的显微结构特征,扫描电镜实验条件为:电子束的电压为20kV,焦距20mm,束斑大小为41nm。采用英国牛津公司生产的能谱仪(EDS)对样品中矿物化学成分进行半定量测试,同时运用英国牛津公司的INCA软件包进行数据处理(版本4.4)。在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室采用JXA-8100型电子探针仪对上述样品内各矿物的化学成分进行定量分析,仪器测试条件为:加速电压15kV,束流10nA,电子束斑为1μm,修正方法为PRZ,标样为美国SPI公司的53种标准矿物。主要矿物化学成分测试结果列入表1、表2、表3、表4。本文所有矿物代号均采用Whitney and Evans(2010)的资料。
全岩的主量和微量元素测试分析在国家地质实验测试中心3080E型荧光光谱仪XRF以及等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)上完成,具体测试条件和步骤可参阅靳新娣和朱和平(2000)的论述。样品破碎与锆石的分选在河北省区域地质调查所矿物分选实验室完成。首先,将样品(约5kg)进行破碎至适当粒级,经清洗、烘干和筛选后,采用磁选和重液分选出不同粒级的锆石晶体,然后在双目镜下挑选出颗粒相对完整的锆石晶体约200粒,制成符合阴极发光测试和LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年的标准锆石靶。锆石的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年测试在天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室Neptune型LA-ICP-MS上进行,该实验测试条件详见耿建珍等(2012)的论述。
4 岩相学特征及变质反应结构
夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)的主要组成矿物有石榴石(13% ~15%)、长石(27% ~40%)、石英(28% ~30%)、堇青石 (8% ~10%)、黑云母 (6% ~8%)和夕线石(3% ~6%)等,并含少量尖晶石(1% ~2%)、磁铁矿和钛铁矿(1% ~2%)。石榴石变斑晶多为浑圆粒状,粒径约0.5~1.5mm,核-幔部内包裹大量细长针状夕线石,偶见细粒黑云母、长石和石英等矿物包体(图3a),粒径5~45μm不等。基质中夕线石呈针-柱状集合体,黑云母沿其粒间分布(图3b)。石榴石的边部出现含堇青石的退变反应边结构(图3a,c-f、图4a,b),堇青石内常包含夕线石(图3a,d-f、图4a)、黑云母、石英(图3c、图4b)、细粒尖晶石(图3e,f、图 4a,b)和钛
铁矿-磁铁矿等。其中尖晶石粒径约10~70μm,可围绕残留的夕线石周围分布,亦可见局部尖晶石-钛铁矿-磁铁矿显微结构,颗粒间接触面平直,其中钛铁矿中含有近定向出溶的金红石(图3b,e,f、图4b)。石榴石边部分解形成细粒鳞片状黑云母和斜长石(图4c)。黑云母的产出包括:呈细小鳞片状包裹在石榴石内;位于基质中,与夕线石、长石和石英等矿物共同产出,粒径相对较大,近定向排列;晚期降温冷却阶段由石榴石分解形成,呈细长鳞片状分布在石榴石的边部(图4c),其形态明显不同于基质中的黑云母。浅色矿物包括斜长石、钾长石和石英,其中基质条纹长石内出溶的斜长石呈液滴状近定向排列(图4d)。

表1 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中石榴石的化学成分(wt%)Table 1 Representative compositions of garnets in the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(wt%)
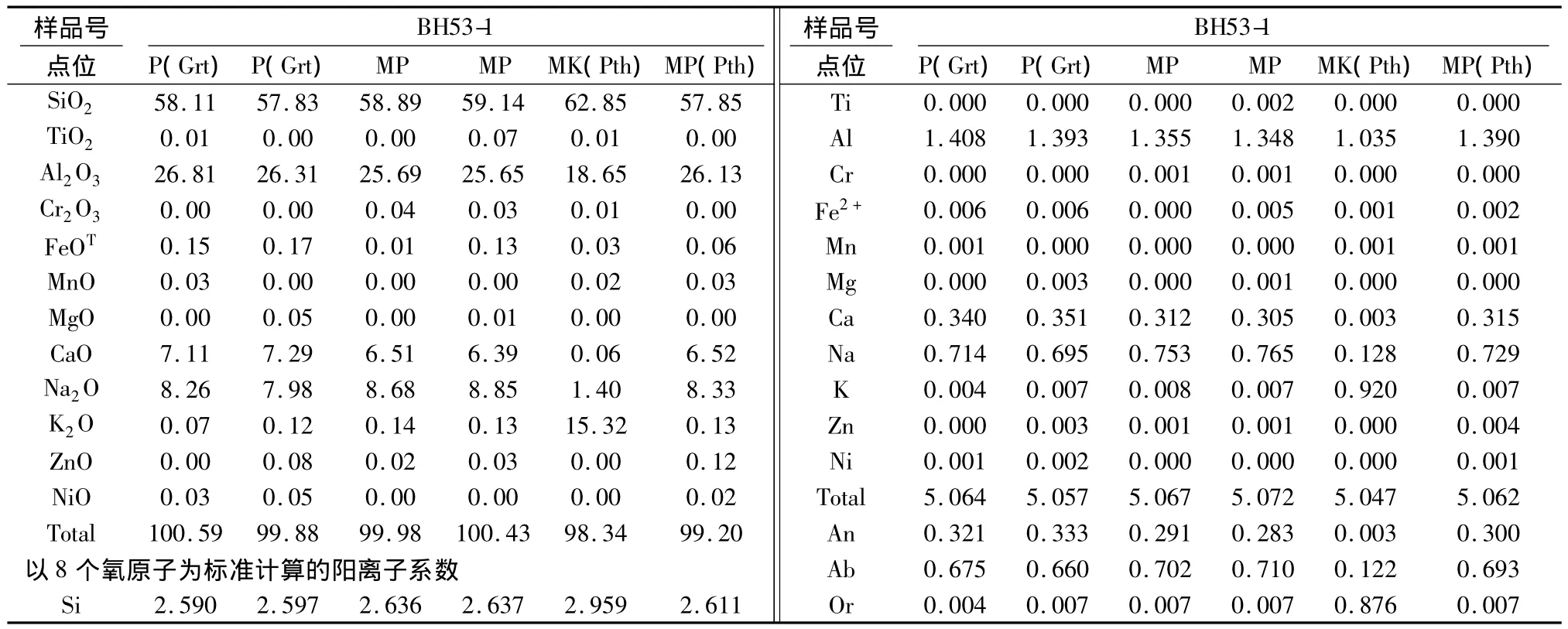
表2 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中长石的化学成分(wt%)Table 2 Representative compositions of feldspars in the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(wt%)

表3 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中黑云母的化学成分(wt%)Table 3 Representative compositions of biotites in the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(wt%)

表4 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中堇青石和尖晶石的化学成分(wt%)Table 4 Representative compositions of cordierites and spinels in the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(wt%)
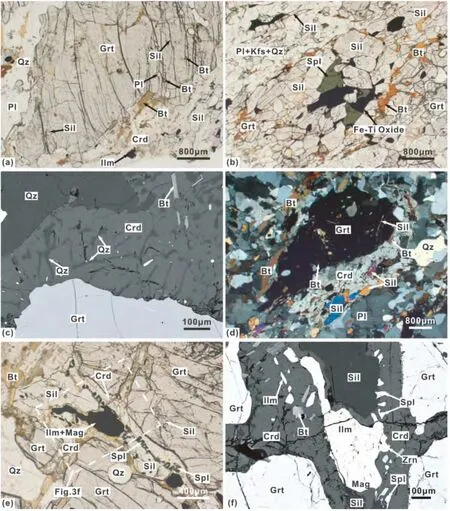

图3 集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩显微照片和背散射电子图像(a)-石榴石变斑晶内包裹针状夕线石,细粒黑云母和斜长石,石榴石边部围绕堇青石退变边(PL图像);(b)-柱状夕线石集合体的粒间分布黑云母、尖晶石和Fe-Ti氧化物(PL图像);(c)-石榴石变斑晶边部出现堇青石反应边,堇青石中含有残留的石英、黑云母和Fe-Ti氧化物(SEM图像);(d)-石榴石内部包裹细粒黑云母和细长针-柱状夕线石,石榴石边部分解成的堇青石内含有黑云母和残留夕线石(CPL图像);(e)-石榴石边部堇青石退变边内含夕线石、钛铁矿-磁铁矿、细粒尖晶石(PL图像);图框为图3f的区域;(f)-图3e中围绕夕线石和Fe-Ti氧化物周围分布的细粒尖晶石的放大照片(SEM图像)Fig.3 Representative photomicrographs and back-scattered electron(BSE)images of the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss from Sanchakou,Jining area(a)-fibrolitic sillimanite,minute biotite and plagioclase preserved within a garnet porphyroblast which is surrounded by a corona of cordierite(PL);(b)-intergranular biotite,spinel,and Fe-Ti oxides in contact with coarse-grained sillimanite(PL);(c)-garnet rimmed by cordierite corona with inclusions of vermicular quartz,biotite,and Fe-Ti oxides(SEM);(d)-fine-grained biotite and fibrolitic sillimanite included in garnet porphyroblast and the cordierite corona rimmed garnet containing biotite and relicts of sillimanite(CPL);(e)-relicts of sillimanite,Fe-Ti oxides,and fine-grained spinel in cordierite(PL).Box shows the area imaged in Fig.3f;(f)-higher magnification image of the rectangle shown in Fig.3e.Minute spinel surrounded sillimanite and ilmenite-magnetite composite grains within cordierite(SEM)

图4 集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)背散射电子图像(a)-石榴石内退变的堇青石中含有细粒尖晶石、磁铁矿、钛铁矿和残留的夕线石(SEM图像);(b)-石榴石边部微域可见尖晶石-磁铁矿-钛铁矿显微结构及粗粒夕线石(SEM图像);(c)-石榴石边部分解形成细粒斜长石和鳞片状黑云母(SEM图像);(d)-正条纹长石中的钾长石主晶和斜长石客晶(SEM图像)Fig.4 Back-scattered electron(BSE)images of the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss from Sanchakou,Jining area(a)-fine-grained spinel,magnetite,ilmenite,and sillimanite relicts in cordierite that partially replaced garnet(SEM);(b)-spinel-ilmenite-magnetite composite grains and coarse-grained sillimanite rimmed garnet(SEM);(c)-garnet fringed by biotite-plagioclase intergrowths(SEM);(d)-perthite in the matrix with K-feldspar host and plagioclase lamellae(SEM)
针柱状夕线石集合体和鳞片-片状黑云母分布在石榴石变斑晶周围(图3d),可能发生如下变质反应:

石榴石边部可出现堇青石的退变反应边结构,堇青石内含有残留的夕线石和蠕虫状石英、黑云母和不规则状的Fe-Ti氧化物(图3c,d),反映峰后减压的退变反应结构,可能的变质反应为:

在局部贫硅微域,石榴石边部的堇青石反应边内残留的不规则状夕线石周围可见细粒(<3μm)液滴状的暗绿色尖晶石(图3e,f、图4a,b),这是由于Al和Si元素的迁移能力较低(Sarkar et al.,2003;Tajcˇmanová et al.,2007),可能发生如下反应(Harris,1981):

部分石榴石边部亦被细小鳞片状黑云母和粒状斜长石和石英等环绕(图4c),可能的退变质反应为(Vielzeuf and Montel,1994):

局部微域亦可见尖晶石-钛铁矿-磁铁矿显微结构(图3b、图4b),尖晶石与钛铁矿、磁铁矿平直接触,可能是早期的钛尖晶石(ulvöspinel)组分在晚期降温过程中分解形成钛铁矿的出溶体,并残留富镁的尖晶石(Gnos and Kurz,1994;Bose et al.,2009),发生的反应为:
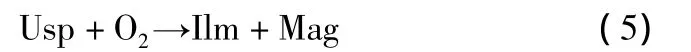
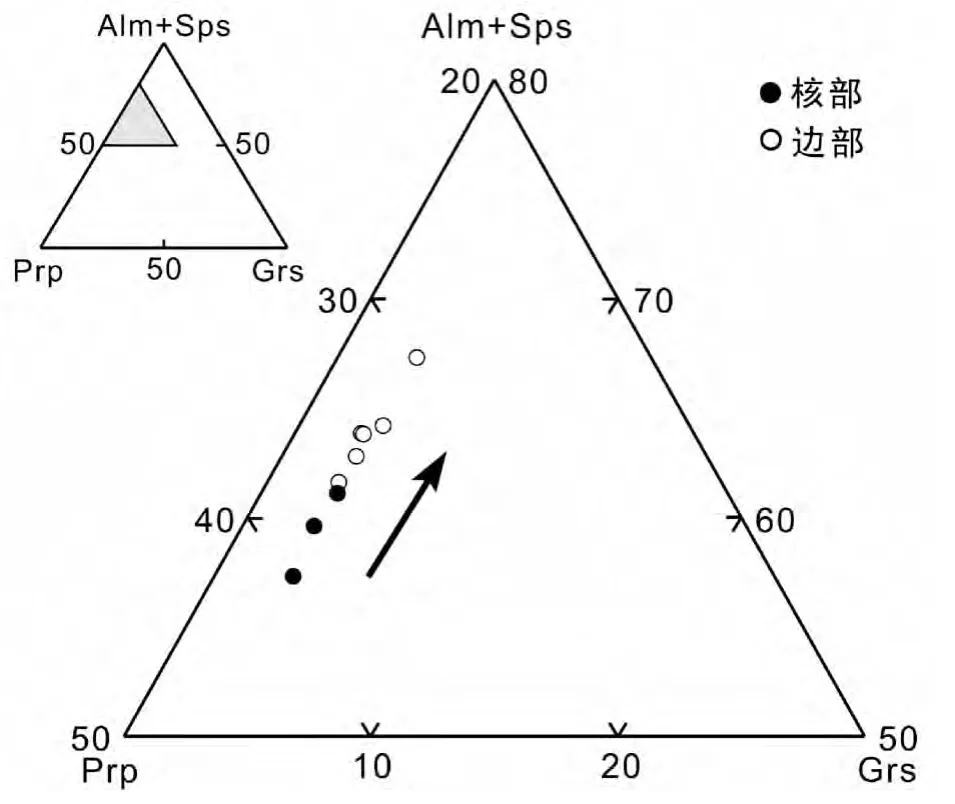
图5 集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中石榴石的Prp-(Alm+Sps)-Grs图解Fig.5 Prp-(Alm+Sps)-Grs diagram of garnet from Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss from Sanchakou,Jining area
5 矿物化学
5.1 石榴石
样品中石榴石变斑晶的化学成分测试结果如表1,所有石榴石均以富含FeO为特征,其中铁铝榴石端元组分变化于0.565~0.661之间,镁铝榴石端元组分为0.295~0.395,钙铝榴石端元组分为0.027~0.034,而锰铝榴石端元组分含量很低(<0.012)。石榴石的 XMg(Mg2+/(Fe+Mg2+))值在0.309~0.411。石榴石的核-边成分略有变化,核部相对富镁(0.372<XMg<0.411),而边部相对富铁(0.309<XMg<0.369)(图5)。
5.2 长石
斜长石属于奥长石-中长石组分(An端元含量为28~33;表2),其中石榴石边部分解而成的斜长石比基质斜长石更接近An端元,且Al2O3含量略高,说明石榴石边部分解过程中,钙从石榴石边部迁移进入后成合晶中的斜长石内。基质条纹长石中的钾长石主晶接近纯Or端元组分(Or为0.876)。
5.3 黑云母
黑云母的XMg值变化于0.682~0.769之间,而TiO2含量均较高,在4.49% ~5.52%(表3)。包裹于石榴石核部的黑云母较基质黑云母和位于石榴石边部黑云母的XMg值和TiO2含量高,而FeOT含量则较低。包裹在堇青石中的黑云母较基质黑云母的XMg值和Al2O3含量高,而FeOT和TiO2含量略低。基质黑云母则较石榴石边部黑云母的XMg值、TiO2和Al2O3含量略低,而FeOT含量较高。此外,Fe-Mg图解(图略)显示黑云母内Fe和Mg之间呈线性负相关关系,表明黑云母内发生了Mg-Fe间的相互替代(Aydin et al.,2003)。
5.4 堇青石
样品中的堇青石仅出现于石榴石边部,其 XMg值为0.792 ~0.848(表4),而 MnO、ZnO、Cr2O3、CaO、NaO 和 K2O等总含量很低(<0.3%),这与孔兹岩带中段的大青山-乌拉山地区典型变泥质岩中堇青石的成分特征(XMg值在0.806~0.829之间)相近(蔡佳等,2013a)。石榴石边部的堇青石内偶见细粒尖晶石,与尖晶石相接触的堇青石具有较低的FeOT含量(表4)。
5.5 尖晶石
样品中的尖晶石多出现在石榴石边部的堇青石内,化学成分总体变化不大(表4)。尖晶石主要是铁尖晶石和镁尖晶石的固溶体(0.315<XMg<0.370),ZnO的含量均较高(4.52% ~5.08%),并含少量 Cr2O3(<1.22%),而 TiO2和MnO等含量均很低。Fe3+/(Fe3++Fe2+)比值在0.057~0.112之间。与钛铁矿-磁铁矿固溶体相接触的尖晶石的XMg值和Cr2O3含量相对较高。
6 相平衡模拟
P-T视剖面图可以展示特定全岩成分下的变质矿物相平衡、模拟矿物成分和摩尔分数等值线(魏春景和周喜文,2003),可以采用该方法进行矿物相转变与变质反应关系、PT条件的系统研究。因此本文利用程序THERMOCALC 3.33(Powell and Holland,1988;2009年更新)及内部一致热力学数据库(tcds55,Holland and Powell,1998)对样品 BH53-1进行P-T视剖面图的计算。由于孔兹岩带经历了麻粒岩相变质(卢良兆等,1992)并伴随部分熔融,应考虑多种主量元素对平衡矿物组合的影响,故选择最接近实际岩石化学组分及矿物组合的体系Na2O-CaO-K2O-FeO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2OTiO2-Fe2O3(NCKFMASHTO),其中有关矿物固溶体的活度-成分关系引用的参考文献包括:石榴石(White et al.,2007),钾长石和斜长石(Holland and Powell,2003),黑云母和熔体(White et al.,2007),尖晶石-磁铁矿(White et al.,2002),石英和铝硅酸盐为纯端元组分。岩石中MnO含量很低(<0.1%),故在相平衡计算中未予考虑。
利用X荧光光谱仪(XRF)测得的样品全岩主量氧化物百分含量(%)分别为:SiO2=62.71,Al2O3=18.53,CaO=1.14,Fe2O3=1.00,FeO=6.65,K2O=3.65,MgO=2.80,MnO=0.1,Na2O=1.46,P2O5=0.08,TiO2=0.8 和 H2O=0.8。然而由于岩石的成分分布不均,尤其在高级变质岩中常出现变质反应微域,该全岩成分可能并非有效的全岩成分(Stüwe,1997;White et al.,2002;White and Powell,2002;Kelsey et al.,2003;Wei et al.,2007),可通过下列步骤获得岩石的有效全岩百分含量:首先选取样品的典型薄片中均匀且未蚀变的部分,然后估算矿物体积百分含量为:石榴石(14.6%)、钾 长 石 (17.2%)、斜 长 石 (13.7%)、石 英(29.52%)、堇青石 (8.8%)、黑云母 (7.6%)、夕线石(5.22%)、尖晶石(2.05%)、钛铁矿(0.73%)和磁铁矿(0.58%),最后将这些矿物的电子探针数据加权平均而得到其摩尔百分含量(mol%)为:H2O=3.66,SiO2=66.64,Al2O3=11.80,CaO=1.28,MgO=5.62,FeO=6.02,K2O=2.41,Na2O=1.52,TiO2=0.65,O=0.40。(如图6 所示)。全岩中H2O含量是通过给定矿物组合在~5kbar条件下的含H2O量确定的。
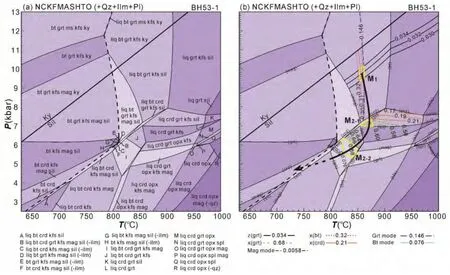
图6 三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)的相图计算(a)-P-T 视剖面图,全岩摩尔百分含量(mol%)为:H2O=3.66,SiO2=66.64,Al2O3=11.80,CaO=1.28,MgO=5.62,FeO=6.02,K2O=2.41,Na2O=1.52,TiO2=0.65,O=0.40;(b)-根据石榴石z(grt)(Ca/(Mg+Ca+Fe2+))和黑云母x(bt)(Fe/(Fe+Mg))成分等值线和石榴石摩尔分数等值线限定峰期(M1)阶段温压条件;根据堇青石x(crd)(Fe/(Fe+Mg))和石榴石x(grt)(Fe/(Fe+Mg))成分等值线,黑云母和磁铁矿摩尔分数等值线限定峰后减压阶段(M2-1和M2-2)的温压条件,各阶段均用实线框表示,得到近等温减压型顺时针P-T轨迹.所有图中黑色实线为蓝晶石-夕线石相变线Fig.6 Phase equilibria modeling for Sanchakou Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(BH53-1)(a)-P-T pseudosection with bulk composition in mol%of H2O=3.66,SiO2=66.64,Al2O3=11.80,CaO=1.28,MgO=5.62,FeO=6.02,K2O=2.41,Na2O=1.52,TiO2=0.65,O=0.40;(b)-z(grt)(=Ca/(Ca+Mg+Fe)isopleths for garnet,x(bt)(=Fe/(Fe+Mg))for biotite,and calculated garnet modal proportions are contoured in the predicted peak(M1)field,x(crd)(=Fe/(Fe+Mg))isopleths for cordierite,x(grt)(=Fe/(Fe+Mg))isopleths for garnet,and calculated biotite and magnetite modal proportions are contoured in the predicted post-peak(M2-1和M2-2)field.Thick solid lines delineate P-T conditions of predicted peak and post-peak assemblage,and a clockwise P-T path with near-isothermal decompression stage is inferred for the sample.The black bar corresponds to kyanite-sillimanite equilibria line
P-T视剖面图(图6)表明,固相线在6kbar以上出现在~800℃。石榴石的消失线整体近平行于T(温度)轴,表明石榴石的分解受压力影响较大,在>800℃的条件下石榴石的稳定域略向低压方向扩大。黑云母的消失线在>8kbar时出现在~910℃,且近平行于P(压力)轴,而<8kbar时黑云母的稳定域向低温方向缩小。钾长石在~870℃以上消失,而斜长石在整个P-T范围内稳定。斜方辉石可在>790℃和<7.3kbar的条件下出现,而岩相学观察中并未见斜方辉石。堇青石的稳定域随温度的升高向高压方向扩展,压力最高~8kbar。夕线石消失线的变化趋势与堇青石相似。钛铁矿在5.8~6.4kbar和793~812℃的狭窄域内消失。尖晶石则出现在>950℃和6~7kbar的窄域内。前人(Brown,2002;White et al.,2004;Wei and Wang,2007)认为高级变质条件下岩石产生熔体主要有三个阶段,包括~650℃水饱和条件下的部分熔融,700~750℃时白云母的脱水熔融和~800℃时黑云母的脱水熔融,由于该样品发生大量熔体迁移(丢失)使得麻粒岩相矿物组合得以保留(White and Powell,2002;White et al.,2004,2007)。
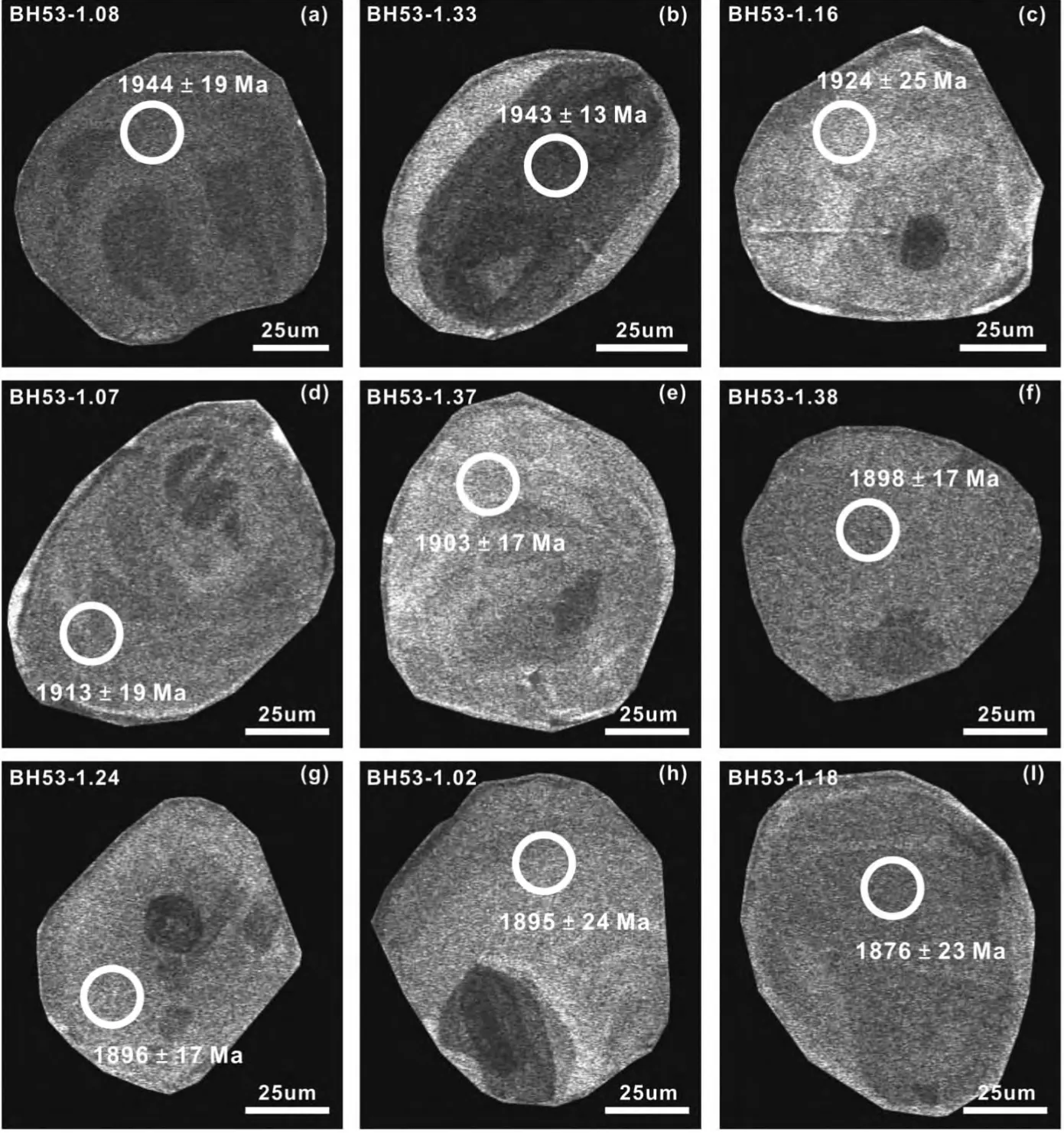
图7 三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)中变质锆石的阴极发光图像和LA-ICP-MS定年结果(a、b)-锆石具有相对均匀的弱发光效应(灰黑色);(c-f)-锆石具有相对均匀的强发光效应(灰色-灰白色);(g、h)-锆石具有核-边结构,核部呈灰黑色,边部具相对均匀的中等发光效应(灰色);(i)-锆石具有相对均匀的中等发光效应(灰色)Fig.7 Cathodoluminescent(CL)images and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of metamorphic zircons from the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(BH53-1)from Sanchakou,Jining area(a,b)-the zircon grain showing homogeneous low-luminescence(greyish black);(c-f)-the zircon grains showing homogeneous high-luminescence(grey-greyish white);(g,h)-the zircon grains showing low-luminescent(greyish black)core,middle-luminescent(grey)rim relationship;(i)-the zircon grain showing homogeneous middle-luminescence(grey)
7 锆石U-Pb年代学
7.1 锆石特征
夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(BH53-1)的锆石为暗紫红色,不透明-半透明,以不规则粒状和短柱状为主,少数为浑圆状。长宽比多为1∶1~1∶2。锆石颗粒较小,一般长轴为50~150μm,短轴为30~100μm。少数锆石含有包体。阴极发光(CL)图像表明该样品中多数锆石具有相对均匀的强发光效应(多呈灰色-灰白色),少数呈灰黑色-黑色,内部无分带特征,少数发育冷杉叶结构,显示变质锆石成因(图7)。部分锆石具有核-边结构,核部与边部之间的边界截然,核部多发育岩浆结晶环带,而部分锆石核部由于受到麻粒岩相变质作用的影响导致早期韵律环带被强烈改造而呈均匀的黑色,边部多呈灰色-灰白色,无分带特征,部分边部较窄。
对该样品的38颗锆石进行了系统的定年研究(表5),共计进行了38个点分析,多位于结构均匀的锆石和具核-边结构锆石的边部,其Th含量变化为10×10-6~250×10-6,U含量变化为122×10-6~1203×10-6,Th/U比值为0.02~1.66,其中,具有相对弱发光效应(灰黑色)的锆石微区与相对强发光效应的(灰色-灰白色)锆石相比,前者U含量高,而Th含量和Th/U比值普遍较低。

表5 集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(样品BH53-1)锆石LA-ICP-MS定年结果Table 5 LA-ICP-MS analyses of zircon from the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(sample BH53-1)from Sanchakou,Jining area
7.2 定年结果
对研究区样品的锆石系统的U-Pb定年结果列入表5中,如相应的207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U关系图解(图8)所示,该样品38个变质锆石微区的测试点均位于谐和线上,显示了比较集中的207Pb/206Pb表面年龄,变化于1944~1870Ma之间,其中两个锆石年龄分别为1944±19Ma和1943±13Ma(图8中的灰色椭圆),其CL图像(如图7a,b)表明该年龄可能是继承性的碎屑锆石受到变质热事件改造产生的混合年龄。其余的锆石年龄的加权平均年龄为1912±11Ma(MSWD=0.94,n=36;图8),它们代表了寄主岩石夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩的原岩所经历的中-高压麻粒岩相变质的时限。此锆石年龄纪录表明集宁三岔口地区变泥质岩在古元古代发生了一次大规模的变质事件。
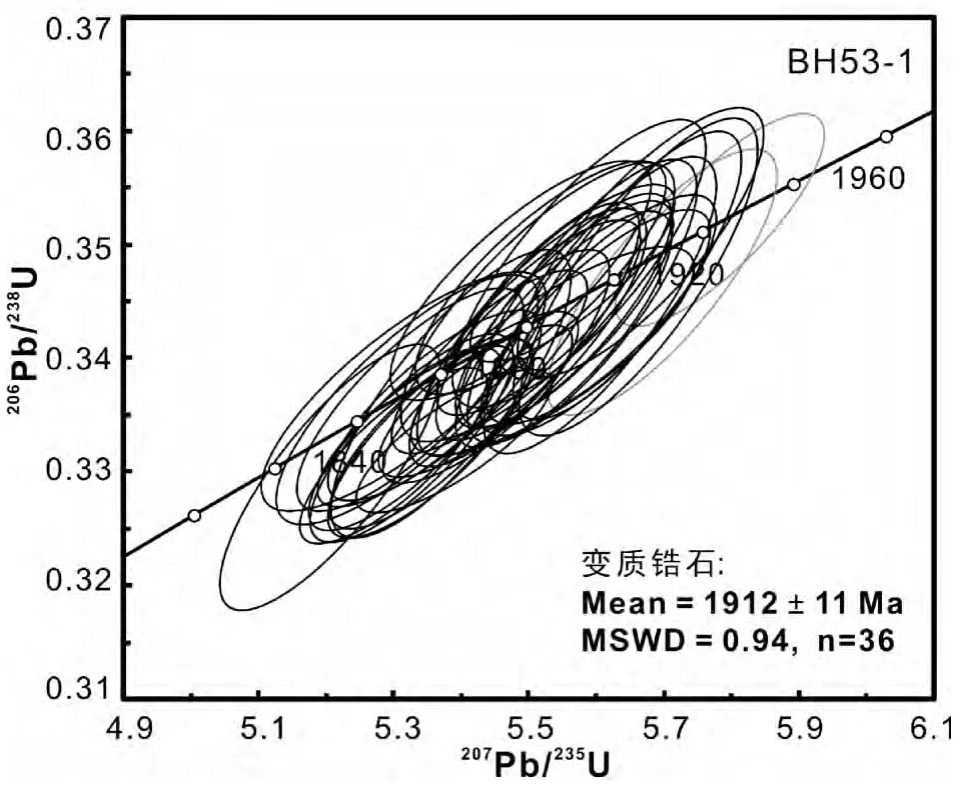
图8 集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩中锆石207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U年龄关系图Fig.8 207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U diagram showing U-Pb analyses for zircons of the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss from Sanchakou,Jining area
8 讨论
考虑到该岩石经历了麻粒岩相变质,能用于揭示早期进变质阶段信息的石榴石的生长环带已被均一化,因此对于石榴石核部包裹的黑云母、长石和石英等细粒包裹体,由于寄主矿物石榴石缺乏进变质生长环带,故难以确定上述矿物包体为进变质阶段产生的。此外,即使黑云母和长石等包体是在进变质阶段形成,在峰后及晚期冷却变质阶段会与寄主石榴石之间发生Fe-Mg或Ca的交换,导致这些包体矿物的成分遭受改造而不能反映早期进变质阶段的成分特征。此外,相平衡模拟结果表明(图6)样品经历了大量的熔体迁移和丢失,使得峰期麻粒岩相矿物组合得以保留,故该P-T视剖面图仅能用于讨论熔体丢失后麻粒岩相矿物组合的演化,而不能反映熔体丢失前的进变质矿物组合相关信息(White and Powell,2002;White et al.,2004,2007)。综合以上考虑,本文将着重讨论该岩石峰期和峰后两个变质阶段的温压条件。
8.1 峰期变质阶段(M1)温压条件
样品BH53-1的P-T视剖面图(图6a)结果表明峰期(M1)矿物组合为Grt+Sil+Bt+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm+Liq,稳定存在于800~900℃较窄的温度区间和较宽压力范围(6~12kbar),其中堇青石的消失线可作为其压力下限~7kbar,而压力的上限由蓝晶石和夕线石间的相变线限定,熔体的出现线为温度的下限~800℃,黑云母的消失线作为温度的上限~900℃。然而上述峰期矿物组合稳定域的温压范围总体较大,需通过主要矿物的成分等值线和摩尔分数等值线来进一步精确限定峰期的温压条件。本文利用石榴石z(grt)值(z(grt)=Ca/(Mg+Ca+Fe2+))和黑云母x(bt)(x(bt)=Fe/(Fe+Mg))的化学成分等值线以及石榴石的摩尔分数等值线(图6b),根据样品中石榴石核-幔部z(grt)值为0.030~0.034,基质黑云母的x(bt)值在0.31~0.32和石榴石摩尔百分含量为0.146,限定峰期矿物组合稳定的温压条件为T=852~862℃和P=9.3~10.2kbar,位于夕线石域。此外,石榴石的z(grt)值等值线变化趋势表明其内的Ca含量随压力的降低而减少。
利用传统地质温度计和压力计估算(采用Reche and Martinez(1996)的“GPT”Excel表格)各变质阶段温压条件,代表性结果如表6和表7。选择石榴石幔部、与基质夕线石共生的黑云母和斜长石的成分估算峰期变质阶段温压条件,利用石榴石-黑云母(GB)温度计(Thompson,1976;Holdaway and Lee,1977;Perchuk et al.,1985;Holdaway,2000)和石榴石-夕线石-石英-斜长石(GASP)压力计(Newton and Haselton,1981;Ganguly and Saxena,1984;Holdaway,2001)计算得到峰期P-T条件为660~855℃和6.32~7.23kbar(表6、表7)。以上估算的温压条件明显较低,可能由于用于计算的矿物化学成分受到晚期降温冷却阶段的改造,而相平衡模拟手段不受矿物端元反应的限制(Powell and Holland,1988,2008),故后者可反映岩石实际经历的峰期温压条件,即 T=852~862℃和 P=9.3~10.2kbar。
8.2 峰后减压变质阶段(M2)温压条件
峰后近等温减压阶段以石榴石边部转变为含堇青石的后成合晶(图3c-f、图4a,b)为特征,局部贫硅微域出现少量尖晶石,相平衡模拟得到峰后近等温减压阶段矿物组合为Grt+Crd+Pl+Kfs+Qz+Liq+Ilm ±Bt±Sil±Mag,其中斜方辉石的出现线可作为该矿物组合压力的下限~6kbar,而压力的上限为堇青石的消失线~8kbar,石榴石出现线为温度的下限 ~800℃,而钾长石的消失线作为温度的上限~940℃。如前所述,可利用堇青石的x(crd)值(x(crd)=Fe/(Fe+Mg)),石榴石 x(grt)值(x(grt)=Fe/(Fe+Mg))化学成分等值线和黑云母、磁铁矿的摩尔分数等值线(图6b)进一步精确限定峰后减压阶段的温压条件。其中M2-1阶段的矿物组合为Grt+Crd+Sil+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm+Liq,根据样品中堇青石的x(crd)值为0.15~0.21和石榴石的x(grt)值在0.59~0.69得到其温压条件为854~880℃,7.0~7.4kbar;M2-2阶段的矿物组合为Grt+Crd+Bt+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm+Mag+Liq,根据石榴石的 x(grt)值在0.59~0.69,黑云母和磁铁矿的摩尔百分含量分别为0.076和0.0058,得到其温压条件为820~848℃,5.3~6.4kbar。此外,P-T视剖面图显示含尖晶石的矿物组合出现在>950℃ (图6),这可能是由于体系中未考虑ZnO组分,而ZnO可将尖晶石的稳定域向低温和/或高压方向移动(Clarke et al.,1989;Sack and Ghiorso,1991;Nichols et al.,1992;Hand et al.,1994;Korhonen et al.,2011;Jiao et al.,2013a)。

表6 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(样品BH53-1)的温度条件计算Table 6 Geothermometry of the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(sample BH53-1)
针对石榴石边部堇青石的反应边结构,采用石榴石-堇青石(GC)温度计(Thompson,1976;Holdaway and Lee,1977;Perchuk et al.,1985;Bhattacharya et al.,1988)和石榴石-堇青石-夕线石-石英(GCAQ)压力计(Thompson,1976;Wells and Richardson,1979;Perchuk et al.,1985),选择样品中石榴石边部和相邻堇青石的成分,估算峰后减压阶段的温压条件为579~731℃和5.9~7.87kbar(表6、表7)。对于局部贫硅微域,即堇青石包含新生成的细粒尖晶石和残留的夕线石等,采用堇青石-尖晶石温度计(Vielzeuf,1983)和石榴石-尖晶石-堇青石-夕线石(GSCA)压力计(Perchuk,1991),利用堇青石和相邻尖晶石的成分计算得到T=610~667℃,P=7.01~7.05kbar(表6、表7)。此外,对于部分石榴石边部退变形成细小鳞片状黑云母和细粒斜长石、石英的局部晶域,采用石榴石-黑云母(GB)温度计(Thompson,1976;Holdaway and Lee,1977;Perchuk et al.,1985;Holdaway,2000)和石榴石-黑云母-斜长石-石英(GBPQ)压力计(Wu et al.,2004)计算得到T=626~712℃和P=4.1~4.7kbar。同样,上述石榴石-堇青石、堇青石-尖晶石矿物对可能受到晚期降温冷却阶段的影响而发生Fe-Mg离子间的再交换反应,会导致估算的温度较实际温度偏低,而估算的压力值变化不大且与相平衡模拟结果相近。而利用上述石榴石-黑云母-斜长石-石英(GBPQ)压力计估算的压力值明显较低,可能由于在晚期降温阶段石榴石-黑云母间的Fe-Mg离子的再平衡更为完全。因此,综合得到峰后减压的M2-1阶段的温压条件为854~880℃和7.0~7.4kbar;M2-2阶段的温压条件为820~848℃和5.3 ~6.4kbar。
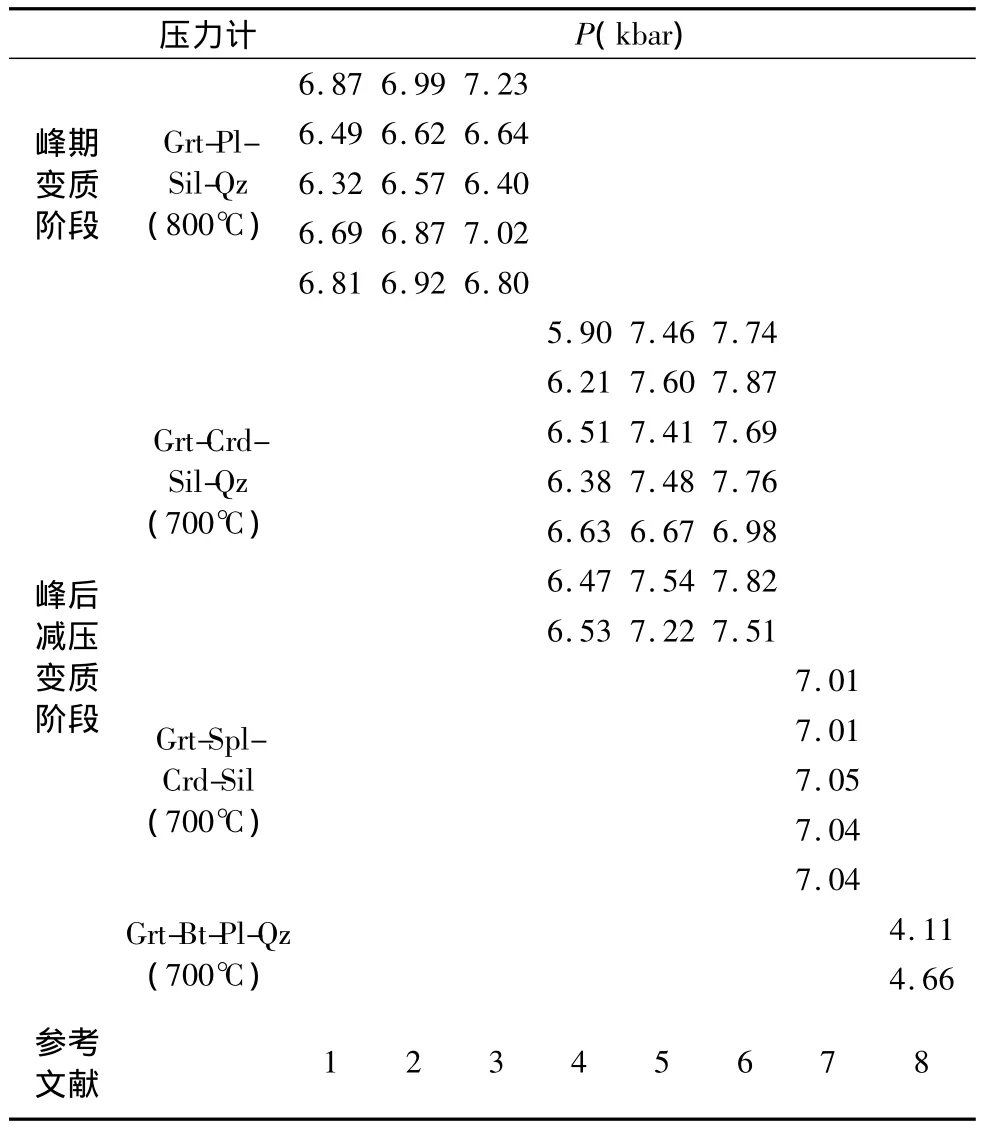
表7 夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(样品BH53-1)的压力条件计算Table 7 Geobarometry of the Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss(sample BH53-1)
8.3 变质演化P-T轨迹和变质时代
相平衡模拟结合传统地质温压计结果表明夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩样品在峰期麻粒岩相变质(M1,T=852~862℃和P=9.3~10.2kbar)之后又经历了峰期后近等温减压变质阶段(M2-1,854~880℃和 7.0~7.4kbar;M2-2,820~848℃和5.3~6.4kbar),得到了近等温减压型的顺时针P-T轨迹(图6b)。年代学研究表明该岩石的锆石年龄在1944~1870Ma之间,其变质时代为1912±11Ma。同样,前人(Lu and Jin 1993;Liu et al.,1993;周喜文等,2010;Yin,2010;Jiao et al.,2013a;蔡佳等,2013a;Cai et al.,2014)对内蒙孔兹岩带变泥质岩的变质作用研究也普遍得到顺时针的P-T演化轨迹(图9)。此外,大量的锆石或独居石的年代学研究表明孔兹岩带的变泥质岩和变基性岩中的变质锆石记录了变化于1950~1850Ma的变质年龄(Wan et al.,2006)。其中,对于孔兹岩带西段贺兰山-千里山地区,周喜文等(2010)和Yin(2010)在高压泥质麻粒岩中发现了Ky+Kfs矿物组合,并认为早期经历了高压变质作用,利用相平衡模拟得到了近等温减压的顺时针P-T轨迹,峰期变质温压条件为792~805℃和10.2~11.2kbar。锆石U-Pb年代学研究显示该地区变泥质岩的变质时代为~1950Ma(周喜文和耿元生,2009;Yin et al.,2009,2011)。在中段大青山-乌拉山地区,Liu et al.(1993)提出该区变泥质岩也经历了近等温减压的变质阶段,峰期温度达~800℃,压力最高达~8kbar,也得出顺时针P-T轨迹。另外,Cai et al.(2014)研究得到大青山富铝片麻岩经历了四个变质演化阶段,也显示近等温减压的顺时针P-T轨迹,通过P-T视剖面图限定出峰期变质温压条件为840~880℃和9~11kbar。锆石U-Pb年代学研究表明该地区变沉积岩记录的变质年龄为1840~1800Ma(Xia et al.,2006b),而变基性岩则记录了1933~1834Ma的变质年龄(刘平华等,2013)。值得注意的是,Wan et al.(2013a)提出大青山-乌拉山变基性岩记录了1970~1920Ma的岩浆年龄,反映古元古代陆内伸展事件,相反,部分研究者(赵国春,2009;周喜文和耿元生,2009;Yin et al.,2009,2011;Zhao et al.,2010;Dong et al.,2013)则认为孔兹岩带泥质麻粒岩的变质锆石记录的~1950Ma代表孔兹岩带碰撞拼合的时代,而~1920Ma为碰撞后的伸展事件。此外,对于东段集宁-卓资-凉城一带,卢良兆等(1992)指出集宁富铝片麻岩经历了两期变质作用,第一期变质作用的峰期温度条件为~850℃。刘福来等(2002)亦报道了凉城地区富铝片麻岩中的锆石含有代表进变质阶段的矿物组合的包裹体Ky+Grt+Kfs+Qz,并提出该区在早期经历了较高的变质压力条件。Wang et al.(2011)对集宁-卓资一带的富铝片麻岩利用相平衡模拟手段刻画出了近等温减压型的顺时针P-T轨迹,其中峰期温压条件可达825℃和13kbar。Jiao et al.(2013a)对小什字石榴花岗岩进行了详细的变质作用研究后进一步划分出M1,M2和M3三个变质阶段,金红石Zr温度计和P-T视剖面手段综合限定各变质阶段的温压条件分别为820~850℃(最高可达950℃)和8.5~9.5kbar,850 ~865℃和 7.4~7.6kbar,710~720℃和6.4~6.6kbar,同样得到了典型的近等温减压型的顺时针P-T轨迹。锆石U-Pb年代学研究表明集宁地区富铝片麻岩的变质年龄为1840~1870Ma(Wan et al.,2006),集宁-卓资的富铝片麻岩也记录了1810Ma的变质年龄(Xia et al.,2006a)。Jiao et al.(2013b)进一步研究获得了集宁小什字石榴石岩的变质年龄为~1890Ma,并认为是孔兹岩带开始折返的时代。对于孔兹岩带与中部造山带交界的地区如黄土窑-四方墩一带,刘福来和沈其韩(1999)研究认为该地富铝片麻岩也经历了近等温减压的顺时针P-T轨迹,峰期温度达750~850℃。此外,近年来,一些研究者在孔兹岩带中段大青山-乌拉山的东坡和东段土贵乌拉、和林格尔、土贵山等地区还报道了超高温变质岩的出露,超高温的标志性矿物组合包括假蓝宝石+石英,低Zn和Cr尖晶石+石英,斜方辉石+夕线石+石英等(Harley,2008;Kelsey,2008)。前人围绕这些超高温变质岩的变质演化和成因等进行了系统的研究,然而,对于该种岩石所经历的P-T轨迹样式仍有争议,其中Santosh et al.(2009)提出土贵乌拉超高温变质岩经历了逆时针的P-T轨迹(峰期变质温度 >950℃),Guo et al.(2012)则得出东坡超高温变质岩记录了顺时针的P-T轨迹(峰期温度为910~980℃),而二者的P-T轨迹均显示近等温减压的变质阶段(图9),并认为1930~1920Ma是超高温变质的时代。赵国春(2009)认为~1920Ma的超高温变质事件发生在阴山和鄂尔多斯陆块碰撞拼合之后,与碰撞后的伸展环境下的地幔岩浆底侵有关。

图9 孔兹岩带变泥质岩的P-T演化轨迹(1)集宁变质杂岩(第一期变质事件;卢良兆等,1992);(2)集宁变质杂岩(第二期变质事件;卢良兆等,1992);(3)集宁富铝片麻岩(Wang et al.,2011)(4)集宁小什字石榴石岩(Jiao et al.,2013a);(5)土贵乌拉超高温变质岩(Santosh et al.,2009);(6)东坡地区超高温变质岩(Guo et al.,2012);(7)大青山-乌拉山变质杂岩(Liu et al.,1993);(8)大青山地区富铝片麻岩(Cai et al.,2014);(9)贺兰山高压泥质麻粒岩(Yin,2010);(10)集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩(本文)Fig.9 Metamorphic P-T paths of the metapelites in the Khondalite Belt(1)Jining Complex(first metamorphic event;Lu et al.,1992);(2)Jining Complex(second metamorphic event;Lu et al.,1992);(3)Al-rich gneisses in Jining(Wang et al.,2011);(4)Xiaoshizi garnetite in Jining terrane(Jiao et al.,2013a);(5)ultrahightemperature granulites in Tuguiwula(Santosh et al.,2009);(6)ultrahigh-temperature granulites in Dongpo(Guo et al.,2012);(7)Daqingshan-Wulashan Complex(Liu et al.,1993);(8)pelitic granulites in Daqingshan area(Cai et al.,2014);(9)highpressure pelitic granulites in Helanshan(Yin,2010);(10)Sil-Crd-Grt paragneiss from Sanchakou,Jining area(this study)
本文通过对三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩的变质作用和锆石年代学研究得到近等温减压型顺时针P-T演化轨迹和变质时代均与上述前人研究结果一致,表明该岩石在古元古代(1912±11Ma)经历了麻粒岩相变质(峰期温压条件为852~862℃和9.3~10.2kbar),顺时针P-T轨迹可能与地壳挤压增厚有关,反映碰撞造山过程中,地壳挤压增厚并随后折返至地表的动力学过程(England and Thompson,1984;Thompson and England,1984;Condie,1992;Brown,1993),进一步支持了孔兹岩带的碰撞拼合模式(Zhao et al.,2005),表明华北克拉通西部的阴山陆块和鄂尔多斯陆块间的俯冲-碰撞作用造成陆壳加厚,加厚的陆壳物质经历了麻粒岩相变质作用,变质压力先达到最大值,在重力均衡效应的作用下,变质地壳发生快速折返导致变质压力迅速降低,而温度降低较慢,即经历了近等温减压的退变质过程,岩相学上表现为石榴石变斑晶边部产生含堇青石的退变边,指示该岩石形成于大陆碰撞的构造环境。
9 结论
对集宁三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩的岩相学、变质反应结构、矿物化学、相平衡模拟以及锆石U-Pb年代学等方面的综合分析研究,得出以下几点认识:
(1)三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩保留了典型的减压反应结构,研究结果表明该岩石明确记录了两个阶段变质作用的矿物组合:峰期变质阶段M1的矿物组合为Grt+Sil+Bt+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm±Mag;峰后减压变质阶段的M2-1阶段矿物组合为Grt+Crd+Sil+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm ±Spl,M2-2阶段的矿物组合为Grt+Crd+Bt+Qz+Pl+Kfs+Ilm+Mag±Spl。
(2)结合相平衡模拟和传统地质温压计获得研究区样品的峰期变质阶段M1的温压条件为T=852~862℃,P=9.3~10.2kbar;峰期后近等温减压的M2-1阶段的温压条件为854~880℃和7.0~7.4kbar,M2-2阶段的温压条件为820 ~848℃和5.3~6.4kbar。
(3)三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩经历的变质年龄在1912 ±11Ma。
(4)与孔兹岩带出露的其他变泥质岩类似,三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩记录了典型的近等温减压型的顺时针P-T轨迹,具造山带变质作用特点。
(5)三岔口夕线堇青石榴二长片麻岩可能卷入了华北克拉通西部古老陆块之间的碰撞造山作用,并经历了麻粒岩相变质作用后折返至地表。
致谢北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室电子探针室舒桂明老师在矿物成分测试过程中给予了指导和帮助;大陆动力学国家重点实验室扫描电镜和能谱实验室陈方远老师在实验中给予建议和指导;中国地质科学院地质研究所刘超辉博士和肖玲玲博士在野外提供了很大的帮助;北京大学魏春景教授对本文提出宝贵的修改意见和建议;两名匿名审稿人对本文提出建设性的评审意见;在此一并表示衷心感谢。
Aydin F,Karsli O and Sadiklar MB.2003.Mineralogy and chemistry of biotites from Eastern Pontide granitoid rocks,NE-Turkey:Some petrological implications for granitoid magmas.Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry,63(2):163-182
Bhattacharya A,Mazumdar AC and Sen SK.1988.Fe-Mg mixing in cordierite:Constraintsfrom naturaldata and implicationsfor cordierite-garnet geothermometry in granulites. American Mineralogist,73(3-4):338-344
Bose S,Das K,Ohnishi I,Torimoto J,Karmakar S,Shinoda K and Dasgupta S.2009.Characterization of oxide assemblages of a suite of granulites from Eastern Ghats Belt,India:Implication to the evolution of C-O-H-F fluids during retrogression.Lithos,113(3-4):483-497
Brown M.1993.P-T-t evolution of orogenic belts and the causes of regional metamorphism.Journal of the Geological Society of London,150:227-241
Brown M.2002.Retrograde processes in migmatites and granulites revisited.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,20(1):25-40
Cai J,Liu PH,Liu FL,Liu JH,Wang F and Shi JR.2013a.Genetic mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of Al-rich gneisses in the Shiguai area,Daqingshan-Wulashan metamorphic complex belt.Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(2):437-461(in Chinese with English abstract)
Cai J,Liu FL,Liu PH,Shi JR and Liu JH.2013b.Petrogenesis and metamorphic P-T conditions of garnet-spinel-biotite-bearing paragneiss in Danangou area,Daqingshan-Wulashan metamorphic complex belt.Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(7):2313-2328(in Chinese with English abstract)
Cai J,Liu FL,Liu PH,Liu CH,Wang F and Shi JR.2014.Metamorphic P-T path and tectonic implications of pelitic granulites from the Daqingshan complex,North China Craton.Precambrian Research,241:161-184
Cesare B,Satish-Kumar M,Cruciani G,Pocker S and Nodari L.2008.Mineral chemistry of Ti-rich biotite from pegmatite and metapelitic granulites of the Kerala Khondalite Belt(Southeast India):Petrology and further insight into titanium substitutions. American Mineralogist,93(2-3):327-338
Clarke GL,Powell R and Guiraud M.1989.Low-pressure granulite facies metapelitic assemblages and corona textures from MacRobertson Land,East Antarctica:The importance of Fe2O3and TiO2in accounting for spinel-bearing assemblages. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,7(3):323-335
Condie KC,Boryta MD,Liu JZ and Qian XL.1992.The origin of khondalites:Geochemical evidence from the Archean to Early Proterozoic granulite belt in the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,59(3-4):207-223
Dan W,Li XH,Guo JH,Liu Y and Wang XC.2012.Integrated in situ zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotopes for the Helanshan khondalites in North China Craton:Juvenile crustal materials deposited in active or passive continental margin?Precambrian Research,222-223:143-158
Dong CY,Liu DY,Li JJ,Wan YS,Zhou HY,Li CD,Yang YH and Xie LW.2007.Palaeoproterozoic Khondalite Belt in the western North China Craton:New evidence from SHRIMP dating and Hf isotope composition of zircons from metamorphic rocks in the Bayan Ul-Helan Mountains area.Chinese Science Bulletin,52(21):2984-2994
Dong CY,Wan YS,Xu ZY,Liu DY,Yang ZS,Ma MZ and Xie HQ.2013.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating ofLate Paleoproterozoic kondalites in the Daqing Mountains area on the North China Craton.Science China(Earth Sciences),56(1):115-125
England PC and Thompson AB.1984.Pressure-temperature-time paths of regional metamorphism I.Heat transfer during the evolution of regions of thickened continental crust.Journal of Petrology,25(4):894-928
Ganguly J and Saxena SK.1984.Mixing properties of aluminosilicate garnets:Constraints from natural and experimentaldata,and applications to geothermo-barometry.American Mineralogist,69(1-2):88-97
Geng JZ,Zhang J,Li HK,Li HM,Zhang YQ and Hao S.2012.Tenmicron-sized zircon U-Pb datingusingLA-MC-ICP-MS. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,33(6):877-884(in Chinese with English abstract)
Gnos E and Kurz D.1994.Sapphirine-quartz and sapphirine-corundum assemblages in metamorphicrocks associated with theSemail Ophiolite(United Arab Emirates).Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,116(4):398-410
Guo JH,Wang SS,Sang HQ and Zhai MG.2001.40Ar-39Ar age spectra of garnet porphyroblast:Implications for metamorphic age of highpressure granulite in the North China Craton.Acta Petrologica Sinica,17(3):436-442(in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo JH,Peng P,Chen Y,Jiao SJ and Windley BF.2012.UHT sapphirine granulite metamorphism at 1.93~1.92Ga caused by gabbronorite intrusions:Implications for tectonic evolution of the northern margin of the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,222-223:124-142
Hand M,Scrimgeour I,Powell R,Stüwe K and Wilson CJL.1994.Metapeliticgranulites from Jetty Peninsula,EastAntarctica:Formation during a single event or by polymetamorphism?Journal of Metamorphic Geology,12(4):557-573
Harley SL. 2008. Refining the P-T records of UHT crustal metamorphism.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,26(2):125-154
Harris N.1981.The application of spinel-bearing metapelites to P/T determinations:An example from South India.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,76(2):229-233
Holdaway MJ and Lee SM.1977.Fe-Mg cordierite stability in high-grade pelitic rocksbased on experimental, theoretical, and natural observations.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,63(2):175-198
Holdaway MJ.2000.Application of new experimental and garnet Margules data to the garnet-biotite geothermometer. American Mineralogist,85(7-8):881-892
Holdaway MJ.2001.Recalibration of the GASP geobarometer in light of recent garnet and plagioclase activity models and versions of the garnet-biotite geothermometer.American Mineralogist,86:1117-1129
Holland TJB and Powell R.1998.An internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for phases of petrological interest.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,16(3):309-343
Holland TJB and Powell R.2003.Activity-composition relations for phases in petrological calculations:An asymmetric multicomponent formulation.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,145(4):492-501
Hu JM,Liu XS,Li ZH,Zhao Y,Zhang SH,Liu XC,Qu HJ and Chen H.2013.SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Ordos Basin basement and its tectonic significance.Chinese Science Bulletin,58(1):118-127
Jiao SJ and Guo JH. 2011. Application of the two-feldspar geothermometer to ultrahigh-temperature(UHT)rocks inthe Khondalite belt,North China craton and its implications.American Mineralogist,96(2-3):250-260
Jiao SJ,Guo JH,Harley SL and Windley BF.2013a.New constraints from garnetite on the P-T path of the Khondalite Belt:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the North China Craton.Journal of Petrology,54:1725-1758
Jiao SJ,Guo JH,Harley SL and Peng P.2013b.Geochronology and trace element geochemistry of zircon,monazite and garnet from the garnetite and/or associated other high-grade rocks:Implications for Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal evolution of the Khondalite Belt,North China Craton.Precambrian Research,237:78-100
Jin XD and Zhu HP.2000.Determination of 43 trace elements in rock samples by double focusing high resolution inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry.Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,28(5):563-567(in Chinese with English abstract)
Kelsey DE,White RW,Powell R,Wilson CJL and Quinn CD.2003.New constraints on metamorphism in the Rauer Group,Prydz Bay,East Antarctica.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(8):739-759
Kelsey DE.2008.On ultrahigh-temperature crustal metamorphism.Gondwana Research,13(1):1-29
Kohn MJ and Spear FS.2000.Retrograde net transfer reaction insurance for pressure-temperature estimates.Geology,28(12):1127-1130
Korhonen FJ,Saw AK,Clark C,Brown M and Bhattacharya S.2011.New constraints on UHT metamorphism in the Eastern Ghats Province through the application of phase equilibria modelling and in situ geochronology.Gondwana Research,20(4):764-781
Liu FL,Shen QH,Geng YS,Xu XC and Ma R.1998.Genetic relationship ofmetamorphic reaction and dehydration-melting:Example from Al-rich gneiss of khondalite series on the border of Jin(Shanxi Province)-Inner Mongolia.Science in China(Series D),41(1):49-56
Liu FL and Shen QH.1999.Retrogressive textures and metamorphic reaction features of Al-rich gneisses in the granulite facies belt from northwestern Hebei Province.Acta Petrologica Sinica,15(4):505-517(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu FL,Shen QH and Zhao ZR.2002.Evolution of mineral assemblages of khondalite series in the process of prograde metamorphism,southeastern Inner Mongolia:Evidence from mineral inclusions in zircons.Geological Bulletin of China,21(2):75-78(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Cai J,Liu JH,Shi JR and Wang F.2013.Geochronological and geochemicalstudy ofthe Lijiazimafic granulites from the Daqingshan-Wulashan metamorphic complex,the central Khondalite Belt in the North China Craton.Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(2):462-484(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu SJ,Tsunogae T,Li WS,Shimizu H,Santosh M,Wan YS and Li JH.2012.Paleoproterozoic granulites from Heling’er:Implications for regional ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in the North China Craton.Lithos,148:54-70
Liu XS,Jin W,Li SX and Xu XC.1993.Two types of Precambrian high-grade metamorphism, InnerMongolia, China. Journalof Metamorphic Geology,11(4):499-510
Lu LZ,Jin SQ,Xu XC and Liu FL.1992.The Petrogenesis and Orebearing Potential of Precambrian Khondalite Series in Southeast Inner Mongolia.Changchun:Jilin Science and Technology Press,4-121(in Chinese)
Lu LZ and Jin SQ.1993.P-T-t paths and tectonic history of an Early Precambrian granulite facies terrane,Jining district,south-east Inner Mongolia,China.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,11(4):483-498
Lu LZ,Xu XC and Liu FL.1996.The Early Precambrian Khondalite Series in the North China.Changchun:Changchun Publishing House,16-118(in Chinese)
Ma MZ,Wan YS,Santosh M,Xu ZY,Xie HQ,Dong CY,Liu DY and Guo CL.2012.Decoding multiple tectonothermal events in zircons from single rock samples:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb data from the Late Neoarchean rocks of Daqingshan,North China Craton.Gondwana Research,22(3-4):810-827
Newton RC and Haselton HT.1981.Thermodynamics of the garnetplagioclase-Al2SiO5-quartz geobarometer. In: Newton RC,Navrotsky A and Wood BJ(eds.).Thermodynamics of Minerals and Melts.New York:Springer-Verlag,131-147
Nichols GT,Berry RF and Green DH.1992.Internally consistent gahnitic spinel-cordierite-garnet equilibria in the FMASHZn system:Geothermobarometry and applications.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,111(3):362-377
Peng P,Guo JH,Zhai MG and Bleeker W.2010.Paleoproterozoic gabbronoritic and granitic magmatism in the northern margin of the North China craton:Evidence of crust-mantle interaction.Precambrian Research,183(3):635-659
Peng P,Guo JH,Windley BF and Li XH.2011.Halaqin volcanosedimentary succession in the central-northern margin of the North China Craton:Products of Late Paleoproterozoic ridge subduction.Precambrian Research,187(1-2):165-180
Perchuk LL,Aranovich LY,Podlesskii KK,Lavrant’eva IV,Gerasimov VY,Fed’kin VV,Kitsul VI,Karsakov LP and Berdnikov NV.1985.Precambrian granulites of the Aldan shield,eastern Sibéria,USSR.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,3(3):265-310
Perchuk LL.1991.Derivation of a thermodynamically consistent set of geothermometers and geobarometers for metamorphic and magmatic rocks.In:Perchuk LL(ed.).Progress in Metamorphic and Magmatic Petrology:A Memorial Volume in Honor of D.S.Korzinskiy.London:Cambridge Univ.Press,93-111
Powell R and Holland TJB.1988.An internally consistent dataset with uncertainties and correlations:3.Applications to geobarometry,worked examples and a computer program.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,6(2):173-204
Powell R,Holland TJB and Worley B.1998.Calculating phase diagrams involving solid solutions via non-linear equations,with examples using THERMOCALC.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,16(4):577-588
Powell R and Holland TJB.2008.On thermobarometry.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,26(2):155-179
Reche J and Martinez FJ.1996.GPT:An excel spreadsheet for thermobarometric calculations in metapelitic rocks.Computers&Geosciences,22(7):775-784
Rigby MJ.2009.Conflicting P-T paths within the Central Zone of the Limpopo Belt:A consequence ofdifferentthermobarometric methods?Journal of African Earth Sciences,54(5):111-126
Sack RO and Ghiorso MS.1991.An internally consistent model for the thermodynamic properties of Fe-Mg-titanomagnetite-aluminate spinels.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,106(4):474-505
Santosh M,Sajeev K and Li JH.2006.Extreme crustal metamorphism during Columbia supercontinent assembly:Evidence from North China Craton.Gondwana Research,10(3-4):256-266
Santosh M,Tsunogae T,Li JH and Liu SJ.2007a.Discovery of sapphirine-bearing Mg-Al granulites in the North China Craton:Implications for Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh temperature metamorphism.Gondwana Research,11(3):263-285
Santosh M,Wilde SA and Li JH.2007b.Timing of Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in the North China Craton:Evidence from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology.Precambrian Research,159(3-4):178-196
SantoshM, Sajeev K, LiJH, Liu SJ and Itaya T. 2009.Counterclockwise exhumation of a hot orogen:The Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature granulites in the North China Craton.Lithos,110(1-4):140-152
Sarkar S,Dasgupta S and Fukuoka M.2003.Petrological evolution of a suite of spinel granulites from Vizianagram,Eastern Ghats Belt,India,and genesis of sapphirine-bearing assemblages.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(9):899-913
Stüwe K.1997.Effective bulk composition changes due to cooling:A model predicting complexities in retrograde reaction textures.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,129(1):43-52
Taj cˇmanová L,Konopásek J and Connolly JAD.2007.Diffusioncontrolled development of silica-undersaturated domains in felsic granulites of the Bohemian Massif(Variscan belt of Central Europe).Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,153(2):237-250
Thompson AB.1976.Mineral reactions in pelitic rocks II.Calculation of some P-T-X(Fe-Mg)phase relations.American Journal of Science,276(4):425-454
Thompson AB and England PC.1984.Pressure-temperature-time paths of regional metamorphism II.Their inference and interpretation using mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks.Journal of Petrology,25(4):929-955
Vielzeuf D.1983.The spinel and quartz associations in high-grade xenoliths from Tallante(S.E.Spain)and their potential use in geothermometry and barometry.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,82(4):301-311
Vielzeuf D and Montel JM.1994.Partial melting of metagreywackes Part I.Fluid-absent experiments and phase relationships.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,117(4):375-393
Wan YS,Song B,Liu DY,Wilde SA,Wu JS,Shi YR,Yin XY and Zhou HY. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton:Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event.Precambrian Research,149(3-4):249-271
Wan YS,Liu DY,Dong CY,Xu ZY,Wang ZJ,Wilde SA,Yang YH,Liu ZH and Zhou HY.2009.The Precambrian khondalite belt in the Daqingshan area,North China Craton:Evidence for multiple metamorphic events in the Palaeoproterozoic era.Geological Society,London,Special Publications,323(1):73-97
Wan YS,Xu ZY,Dong CY,Nutman A,Ma MZ,Xie HQ,Liu SJ,Liu DY,Wang HC and Cu H.2013a.Episodic Paleoproterozoic(~2.45,~1.95 and ~1.85Ga)mafic magmatism and associated high temperature metamorphism in the Daqingshan area,North China Craton:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and whole-rock geochemistry.Precambrian Research,224:71-93
Wan YS,Xie HQ,Yang H,Wang ZJ,Liu DY,Kröner A,Wilde SA,Geng YS,Sun LY,Ma MZ,Liu SJ,Dong CY and Du LL.2013b.Is the Ordos Block Archean or Paleoproterozoic in age?Implications for the Precambrian evolution of the North China Craton.American Journal of Science,313(7):683-711
Wang F, LiXP, ChuH andZhaoGC.2011.Petrologyand metamorphism of khondalites from the Jining complex,North China Craton.International Geology Review,53(2):212-229
Wei CJ and Zhou XW.2003.Progress in the study of metamorphic phase equilibrium.Geoscience Frontiers,10(4):341-351(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei CJ and Wang W.2007.Phase equilibria in the process of anatexis in high-grade metapelites.Earth Science Frontiers,14(1):125-134
Wei CJ,Clarke G,Tian W and Qiu L.2007.Transition of metamorphic series from the kyanite-to andalusite-types in the Altai orogen,Xinjiang,China:Evidence from petrography and calculated KMnFMASH and KFMASH phase relations.Lithos,96(3-4):353-374
Wells PRA and Richardson SW.1979.Thermal evolution of metamorphic rocks in the Central Highlands of Scotland.Geological Society,London,Special Publications,8(1):339-344
White RW and Powell R.2002.Melt loss and the preservation of granulite faciesmineralassemblages. JournalofMetamorphic Geology,20(7):621-632
White RW,Powell R and Clarke GL.2002.The interpretation of reaction textures in Fe-rich metapelitic granulites of the Musgrave Block,central Australia:Constraints from mineral equilibria calculations in the system K2O-FeO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O-TiO2-Fe2O3.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,20(1):41-55
White RW,Powell R and Halpin JA.2004.Spatially-focussed melt formation in aluminous metapelites from Broken Hill,Australia.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,22(9):825-845
White RW,Powell R and Holland TJB.2007.Progress relating to calculation of partial melting equilibria for metapelites.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,25(5):511-527
Whitney DL and Evans BW.2010.Abbreviations for names of rockforming minerals,American Mineralogist,95(1):185-187
Wu CM,Zhang J and Ren LD.2004.Empirical Garnet-Biotite-Plagioclase-Quartz(GBPQ)geobarometry in medium-to high-grade metapelites.Journal of Petrology,45(9):1907-1921
Xia XP,Sun M,Zhao GC and Luo Y.2006a.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons from the Jining Complex,North China Craton and its tectonic significance.Precambrian Research,144:199-212
Xia XP,Sun M,Zhao GC,Wu FY,Xu P,Zhang JH and Luo Y.2006b.U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of detrital zircons from the Wulashan khondalites:Constraints on the evolution of the Ordos Terrane,Western Block of the North China Craton.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,241(3-4):581-593
Yin CQ,Zhao GC,Sun M,Xia XP,Wei CJ,Zhou XW and Leung WH.2009.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of the Qianlishan Complex:Constrains on the evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the Western Block of the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,174(1-2):78-94
Yin CQ.2010.Metamorphism of the Helanshan-Qianlishan Complex and its implications for tectonic evolution of the khondalite belt in the western block,North China Craton.Ph.D.Dissertation.Hong Kong:The University of Hong Kong
Yin CQ,Zhao GC,Guo JH,Sun M,Xia XP,Zhou XW and Liu CH.2011.U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of zircons of the Helanshan Complex:Constrains on the evolution of the Khondalite Belt in the Western Block of the North China Craton.Lithos,122(1-2):25-38
Zhai MG,Bian AG and Zhao TP.2000.The amalgamation of the supercontinent of North China Craton at the end of Neo-Archaean and its breakup during Late Palaeoproterozoic and Meso-Proterozoic.Science in China(Series D),43(Suppl.):219-232
Zhao GC,Wilde SA,Cawood PA and Lu LZ.1999.Tectonothermal history of the basement rocks in the western zone of the North China Craton and its tectonic implications.Tectonophysics,310(1-4):37-53
Zhao GC,Sun M and Wilde SA.2003.Major tectonic units of the North China Craton and their Paleoproterozoic assembly.Science in China(Series D),46(1):23-38
Zhao GC,Sun M,Wilde SA and Li SZ.2005.Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited.Precambrian Research,136(2):177-202
Zhao GC.2009.Metamorphic evolution of major tectonic units in the basement of the North China Craton:Key issues and discussion.Acta Petrologica Sinica,25(8):1772-1792(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao GC,Wilde SA,Guo JH,Cawood PA,Sun M and Li XP.2010.Single zircon grains record two Paleoproterozoic collisional events in the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,177(3-4):266-276
Zhao GC,Cawood PA,Li SZ,Wilde SA,Sun M,Zhang J,He YH and Yin CQ.2012.Amalgamation of the North China Craton:Key issues and discussion.Precambrian Research,222-223:55-76
Zhou XW and Geng YS.2009.Metamorphic age of the khondalite series in the Helanshan region:Constraints on the evolution of the western block in the North China Craton.Acta Petrologica Sinica,25(8):1843-1852(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou XW,Zhao GC and Geng YS.2010.Helanshan high pressure pelitic granulite:Petrologic evidence for collision event in the western block of the North China Craton.Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(7):2113-2121(in Chinese with English abstract)
附中文参考文献
蔡佳,刘平华,刘福来,刘建辉,王舫,施建荣.2013a.大青山-乌拉山变质杂岩带石拐地区富铝片麻岩成因矿物学与变质演化.岩石学报,29(2):437-461
蔡佳,刘福来,刘平华,施建荣,刘建辉.2013b.大青山-乌拉山变质杂岩带大南沟地区含榴尖晶黑云钾长片麻岩成因及其形成的P-T条件.岩石学报,29(7):2313-2328
耿建珍,张健,李怀坤,李惠民,张永清,郝爽.2012.10μm尺度锆石U-Pb年龄的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定.地球学报,33(6):877-884
郭敬辉,王松山,桑海清,翟明国.2001.变斑晶石榴石40Ar-39Ar年龄谱的含义与华北高压麻粒岩变质时代.岩石学报,17(3):436-442
靳新娣,朱和平.2000.岩石样品中43种元素的高分辨等离子质谱测定.分析化学,28(5):563-567
刘福来,沈其韩.1999.冀西北麻粒岩相带富铝片麻岩的退变结构及其变质反应性质.岩石学报,15(4):505-517
刘福来,沈其韩,赵子然.2002.内蒙古东南部孔兹岩系进变质过程矿物组合演化——来自锆石中矿物包裹体的证据.地质通报.21(2):75-78
刘平华,刘福来,蔡佳,刘建辉,施建荣,王舫.2013.华北克拉通孔兹岩带中段大青山-乌拉山变质杂岩立甲子基性麻粒岩年代学及地球化学研究.岩石学报,29(2):462-484
卢良兆,靳是琴,徐学纯,刘福来.1992.内蒙古东南部早前寒武纪孔兹岩系成因及其含矿性.长春:吉林科学技术出版社,4-121
卢良兆,徐学纯,刘福来.1996.中国北方早前寒武纪孔兹岩系.长春:长春出版社,16-118
魏春景,周喜文.2003.变质相平衡的研究进展.地学前缘,10(4):341-351
赵国春.2009.华北克拉通基底主要构造单元变质作用演化及其若干问题讨论.岩石学报,25(8):1772-1792
周喜文,耿元生.2009.贺兰山孔兹岩系的变质时代及其对华北克拉通西部陆块演化的制约.岩石学报,25(8):1843-1852
周喜文,赵国春,耿元生.2010.贺兰山高压泥质麻粒岩——华北克拉通西部陆块拼合的岩石学证据.岩石学报,26(7):2113-2121