关节镜下经肌腱修补治疗关节侧肩袖部分损伤
汪滋民 李全 王一 沈锋 许国星 宋爽
·论著·
关节镜下经肌腱修补治疗关节侧肩袖部分损伤
汪滋民 李全 王一 沈锋 许国星 宋爽
目的探讨关节镜下经肌腱修补治疗关节侧肩袖部分撕裂(PASTA)损伤的方法和疗效。方法应用关节镜下经肌腱原位修补技术,探查清理关节侧肩袖部分撕裂后,穿刺损伤部位并用PDS线标记,关节镜转换至肩峰下,清理肩峰下滑囊并行肩峰成形术,评估滑囊侧肩袖完整性,关节镜转换至盂肱关节,保留滑囊侧的冈上肌腱足印,穿冈上肌腱置入铆钉,过线缝合关节侧部分撕裂,肩峰下间隙打结固定,解剖重建肩袖足印。2008年3月至2010年7月共治疗12例PASTA患者,年龄29~72岁,平均(52.9±13.3)岁。结果手术治疗后随访时间12~36个月,平均(22±7.3)个月。依据美国肩肘外科(ASES)评分:随访总分(89.7±5.6)分,与术前(49.8±9.8)分相比显著提高,差异有统计学意义(t=12.25,P <0.000 1);依据加利福尼亚大学洛杉矶分校(UCLA)评分:随访总分(30.4±3.2)分,与术前(17.3±3.3)分相比显著提高,差异有统计学意义(t=9.87,P <0.000 1),优良率为91.7%。结论应用经肌腱原位修补技术具有最大限度保留正常的肩袖组织,解剖重建肩袖足印,稳定的腱骨界面固定的优点,对于PASTA损伤是一种理想的修补技术。
关节镜; 肩袖部分损伤; 经肌腱修补
肩袖部分损伤可导致患者疼痛和功能受限。Ruotolo等[1]测量了17具尸体冈上肌腱的足印得到其平均厚度为12mm。Ellman[2]根据损伤部位将肩袖部分损伤分为关节侧撕裂、滑囊侧撕裂和肌腱内撕裂,并根据术中测得损伤所累积肩袖的厚度分为1度(≤3mm)、2度(3~6mm)和3度(≥6mm),其中3度损伤超过肩袖厚度的50%。Waibl等[3]提出了关节侧肩袖部分撕裂(partial articular surface tendon avulsions,PASTA)损伤一词,同时也提出了经肌腱修补该损伤的方法。关节侧部分肩袖损伤发病率高,Modi等[4]回顾性分析了100例35岁以上因肩袖病变行关节镜手术的患者,发现其中62例有关节侧的部分肩袖损伤。Yamanaka等[5]采用关节造影追踪了40例PASTA损伤的患者,平均随访412d,发现关节侧的部分肩袖损伤具有撕裂扩大(53%)以及进展为全层撕裂(28%)的倾向。鉴于此,多数学者倾向于对Ellman 3度以上损伤进行修补。修补技术包括转换成全层撕裂后常规修补的技术(切开外侧足印)和经肌腱修补技术(保留未损伤的外侧足印)。与前者相比,经肌腱修补技术保留了外侧残留的正常肩袖组织,修补后的肩袖长度-张力平衡更趋于正常解剖。目前国内尚缺少此类损伤治疗结果的报道。2008年3月至2010年7月,我们对12例肩袖PASTA损伤患者采用改良的Lo等[6]的经肌腱修补技术进行了关节镜下修补,所有病例随访12个月以上。
资料和方法
一、一般资料
本组12例患者,其中男性5例,女性7例;年龄29~72岁,平均(52.9±13.3)岁。右肩9例,左肩3例,涉及优势肩9例。6例有肩部外伤史,其中肩着地伤3例,手撑地伤3例。所有患者均有患侧肩部疼痛、夜间痛和肩关节活动受限,术前经功能锻炼、物理疗法、服用非甾体类抗炎药和封闭等保守治疗1~17个月(平均6个月)。体格检查:肩峰前外侧压痛11例,Neer撞击征阳性9例,Hawkins撞击征阳性9例,60°~120°疼痛弧征阳性7例,Jobe试验阳性9例。所有患者术前行MRI检查均显示肩袖撕裂。
二、手术方法
患者全身麻醉后,侧卧位患肢轻度外展前屈位牵引,消毒铺巾,在皮肤表面标记肩部诸骨性标志和工作入口的位置。首先建立后侧通道,对盂肱关节进行镜检,采用从外向内的技术建立前方通道并探查盂肱关节,用刨刀和射频对冈上肌止点损伤清理后,评估关节侧肩袖损伤程度,对损伤≥6mm宽度的肩袖足印,即Ellman 3度的PASTA损伤进行修补(图1A)。修补前首先要进行肩峰下间隙减压术,将关节镜经后侧同一切口插入肩峰下滑囊,通过前方通道和外侧通道将滑囊组织清除干净,直至清晰完整的显露滑囊侧肩袖足印,并对患者行肩峰成形术。然后探查是否伴有滑囊侧肩袖损伤,如清创后的外侧残留肩袖止点菲薄、明显退变或合并滑囊侧损伤,清理变成全层撕裂后修补;如外侧肩袖止点仍健康完整,同时又无滑囊侧损伤即可采用经肌腱修补术。关节镜再次经后方入口进入盂肱关节,调整视野并锁定PASTA损伤处,用磨钻对裸露的大结节肩袖内侧足印打磨新鲜化,用18号脊髓穿刺针紧贴肩峰外侧缘穿冈上肌腱刺入盂肱关节内定位铆钉置入点和方向。用小尖刀片平行定位针方向穿刺皮肤和肌腱,确定好方向和进针点,移除穿刺针,置入铆钉,根据肩袖损伤前后径大小置入1枚5.0mm或2枚3.5mm铆钉(图1B)。铆钉置入点紧贴肱骨头软骨与大结节骨面成45°角,置入两枚铆钉时,两枚铆钉呈前后方向,位于损伤的前缘和后缘。
采用鸟嘴样过线器穿过损伤的冈上肌腱内缘的健康组织逆行引出缝线,缝线间距离≥10mm以形成足够的组织桥固定肩袖足印;也可采用脊髓穿刺针,先经前侧入口将铆钉上两股不同颜色缝线中靠后的一股引出,穿刺针从冈上肌腱损伤残端内缘的健康组织中偏后穿刺,观察位置良好后引入PDS缝线,经前方入口引出,作为牵引线逆行引线将铆钉缝线后股穿过冈上肌腱,再由后向前穿刺冈上肌内缘引出其他几股缝线,如损伤的前后径不足2cm,也可一次过两股不同色的缝线(图1C)。如发现关节侧损伤肌腱残端回缩,需用抓线钳从外侧入口穿肌腱置入盂肱关节内抓持肌腱残端并协助复位,由一名助手持续握住抓线钳维持复位,再由术者进行上述缝合操作。如为两个铆钉可再重复上述操作后,准备打结固定(图1D)。关节镜再次置入肩峰下间隙,分别将同色的两股缝线用SMC结固定。关节镜置入盂肱关节内评估肩袖足印重建情况,此时重建后的肩袖足印紧贴肱骨头软骨(图1E),术后X线片示铆钉位置良好(图1F)。
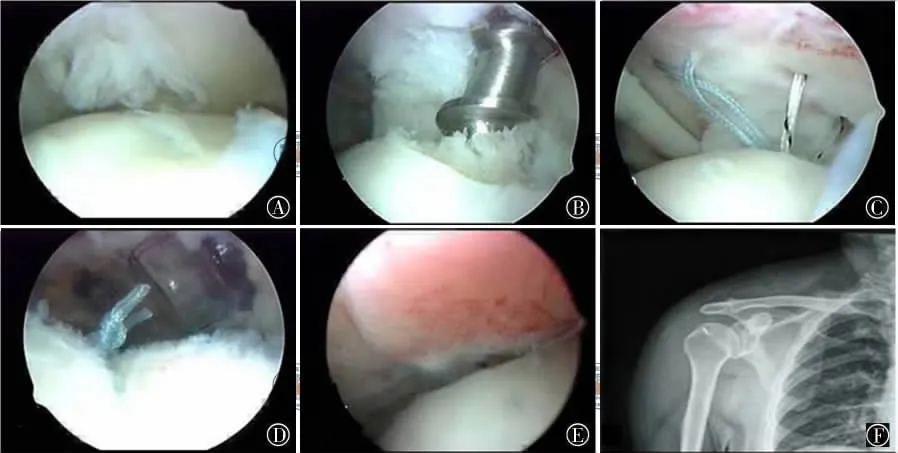
图1 Ellman 3度PASTA损伤的关节镜下修复手术方式 图A为镜下评估大于6mm宽度的关节侧肩袖足印损伤;图B为镜下置入1枚5.0mm铆钉(Smith&Nephew Twinfix screw);图C为肩袖组织间隔1cm引出缝线;图D为肩峰下间隙镜下用SMC结固定;图E为盂肱关节镜下见重建后的肩袖足印紧贴肱骨头软骨;图F为术后X线片示铆钉位置良好
三、术后康复
术后肩关节带枕吊带固定于轻度外展位4周,术后早期行钟摆运动、Godman运动,被动外旋练习、肘关节屈伸练习等,4周内避免肩过顶运动。4周后去除吊带,进行过顶拉伸练习和肩关节内旋拉伸练习。10周后开始等张肌力练习。
四、疗效评价
采用美国肩肘外科(american shoulder and elbow surgeons,ASES)评分标准和加利福尼亚大学洛杉矶分校(university of california at losAngeles,UCLA)评分标准。ASES评分的计算:从患者的调查表中得到视觉模拟评分(visual analogous scale,VAS)疼痛评分和累计日常生活能力评分(activity of daily living,ADL),用公式计算后使之各占50%的权重。即疼痛评分=(10-VAS评分)×5,功能评分=ADL评分÷3×5,得出疼痛和功能评分各占50分,两者相加即总分为100分[7]。UCLA评分总分为35分,包括疼痛评分10分、功能评分10分、关节前屈角度评分5分、前屈肌力评分5分、患者满意度5分。34~35分为优,28~33分为良,21~27分为可,0~20分为差[8]。
结 果
12例PASTA损伤患者,接受了经肌腱肩袖修补术。其中男性5例,女性7例;均为Ellman 3度撕裂。手术后随访时间12~36个月,平均(22±7.3)个月。ASES评分:随访总分(89.7±5.6)分,与术前(49.8±9.8)分 相 比 显 著 提 高 (t =12.25,P <0.0001);UCLA评分:随访总分(30.4±3.2)分,与术前(17.3±3.3)分相比显著提高(t=9.87,P <0.0001),优良率为91.7%。
讨 论
一、关节侧肩袖损伤的处理原则
关节镜术中对关节侧肩袖损伤的处理主要包括:(1)清理肩袖加或不加肩峰下减压;(2)步骤1加经肌腱修补;(3)步骤1加转变为全层撕裂后修补。尽管较早的报道显示仅清理肩袖和肩峰下减压也能够改善患者的疼痛和功能,但近年来的研究提示清理和减压并不能够阻止肩袖部分损伤进展为全层撕裂和症状的恶化。Kartus等[9]术后随访,B超检查发现清创和肩峰成形术后34.6%的患者部分撕裂进展为全层撕裂,而进展为全层撕裂的患者其疼痛和功能评分明显差于未进展者。相反,肩袖修补则能够取得更可靠的疗效,而且能够阻止肩袖撕裂的进展[1011]。询证医学的证据表明当撕裂≤50%时,单纯清创和肩峰下减压能够取得较满意的结果;但当撕裂≥50%时,修补才能够取得满意的结果[6,10-13]。传统的转变为全层撕裂修补的技术具有直接、方便的优势,并取得了良好的临床效果[6,12],但由于修补后的肩袖其骨-肌腱结合部仅形成瘢痕愈合,难以重塑纤维软骨性的连接,再撕裂率高[12]。因此,近年来很多学者开始探索穿肌腱修补技术以保留滑囊侧尚完整 的 足 印[6,11-12]。研 究 显 示,穿 肌 腱 修 补 技 术提高了肩袖修补后的愈合率[12]。
二、对Lo经肌腱修补技术的改良和体会
Lo等[6]所报道的技术中,采用1~2个5.0mm铆钉固定冈上肌内侧足印,采用两个铆钉时,采用双滑轮技术在冈上肌腱足印内侧表面形成一个水平的双股缝线桥有力的固定住内排足印。该技术的优点:(1)缝线桥对肩袖足印的固定具有生物力学上的优势;(2)双滑轮技术减少了穿线的次数,方便了手术操作,缩短了手术时间。该技术的缺点:(1)PASTA损伤大多数情况裸露出的肩袖足印只够打1个铆钉,如勉强打2个铆钉有超负荷的风险;(2)双滑轮技术推荐第六指推结器(国内并未引进),采用普通推结器有松结的风险;(3)对于一部分残端回缩较严重的PASTA损伤,Lo技术穿刺针的位置需要偏内置入,导致修补后肩袖张力过大,滑囊侧肩袖组织隆起,肌腱张力失平衡,术后疼痛加重[13]。我们的改良:(1)推荐置入1个带双线的5.0铆钉;(2)两股线可根据损伤宽度一次或分次过线,2股线用滑结固定。我们认为这样减少了大结节过负荷和松结的风险,也减轻了患者费用;(3)置入铆钉后,修补肩袖前,先用抓线钳穿肌腱抓持回缩的关节侧损伤肩袖残端并协助复位于大结节足印,维持复位同时,脊髓穿刺针穿肌腱过线修补,从而避免缝合后滑囊侧肩袖隆起和肌腱张力失平衡。
综上所述,对于≥50%的PASTA损伤治疗,经肌腱原位修补技术具有最大限度保留正常的肩袖组织,解剖重建肩袖足印,稳定的腱骨界面固定的优点。对Lo经肌腱原位修补操作技术进行适当改良,能够达到较为理想的治疗效果。
[1] Ruotolo C,Fow JE,Nottage WM.The supraspinatus footprint:an anatomic study of the supraspinatus insertion[J].Arthroscopy,2004,20(3):246-249.
[2] Ellman H.Diagnosis and treatment of incomplete rotator cuff tears[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1990,(254):64-74.
[3] Waibl B,Buess E.Partial-thickness articular surface supraspinatus tears:a new transtendon suture technique[J].Arthroscopy,2005,21(3):376-381.
[4] Modi CS,Smith CD,Drew SJ.Partial-thickness articular surface rotator cuff tears in patients over the age of 35:Etiology and intra-articular associations[J].Int J Shoulder Surg,2012,6(1):15-18.
[5] Yamanaka K,Matsumoto T.The joint side tear of the rotator cuff.A followup study by arthrography[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1994,(304):68-73.
[6] Lo IK,Burkhart SS.Transtendon arthroscopic repair of partial-thickness,articular surface tears of the rotator cuff[J].Arthroscopy,2004,20(2):214-220.
[7] Richards RR,An KN,Bigliani LU,et al.A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1994,3(4):347-352.
[8] Ellman H,Hanker G,Bayer M.Repair of the rotator cuff.End result study of factors in uencing reconstruction[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1986,68(8):1136-1144.
[9] Kartus J,Kartus C,Rostg rd-Christensen L,et al.Long-term clinical and ultrasound evaluation after arthroscopic acromioplasty in patients with partial rotator cuff tears[J].Arthroscopy,2006,22(1):44-49.
[10] Spencer EE.Partial-thickness articular surface rotator cuff tears:an all-inside repair technique[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2010,468(6):1514-1520.
[11] Duralde XA, McClelland WB Jr.The clinical results of arthroscopic transtendinous repair of gradeⅢpartial articular-sided supraspinatus tendon tears[J].Arthroscopy,2012,28(2):160-168.
[12] Shin SJ.A comparison of 2repair techniques for partialthickness articular-sided rotator cuff tears[J].Arthroscopy,2012,28(1):25-33.
[13] Eid AS,Dwyer AJ,Chambler AF.Mid-term results of arthroscopic subacromial decompression in patients with or without partial thickness rotator cuff tears[J].Int J Shoulder Surg,2012,6(3):86-89.
[14] Castagna A,Delle Rose G,Conti M,et al.Predictive factors of subtle residual shoulder symptoms after transtendinous arthroscopic cuff repair:A clinical study[J].Am J Sports Med,2009,37(1):103-108.
Arthroscopic treatment of articular side partial tear of supraspinatus tendon by the trans-tendon approach
Wang Zimin,Li Quan,Wang Yi,Shen Feng,Xu Guoxing,Song Shuang.Department of Orthopedics,Changhai Hospital,Second Military Medical University,Shanghai 200433,China
BackgroundPartial rotator cuff tears result in pain and disfunction in patients.An previous study,the researchers measured the supraspinatus tendon of 17corpses and came to a conclusion that the average thickness of the supraspinatus tendon was 12mm.Divides the rotator cuff tears into partial articular tears,partial bursa tears and intra-tendon tears according to the injury sites.Based on the thickness of injured rotator cuff measured during the operation,the tears are divided into 3degrees:Degree I(≤3mm),DegreeⅡ (3-6mm)and DegreeⅢ (≥ 6mm),and the injured thickness of the DegreeⅢis more than 50%.Waibl et al put forward the concept of partial articular surface tendon avulsions(PASTA)and the trans-tendon approach to repair the injury.The PASTA has a high morbidity.Modi et al reviewed 100cases who were all over 35years old.They recieved an arthroscopic surgery for rotator cuff lesions.Waibl then found 62cases had PASTA.Yamanaka et al followed 40PASTA patients using arthrography,the average follow-up was 412days.They found that the PASTA had a tendency to expand(53%)and to progress to full-thickness tears(28%).Take this into account,most scholars tend to endorse the decision that tears over degreeⅢ must be repaired.The methods include the conventional repair after the conversion of the full-thickness tear and the direct repair of the tears using the tendon approach.Compared with the former,the tendon repair can save the residual normal rotator cuff tissue,and the length-tension balance after rotator cuff repair is simmilar to normal anatomy.Up to now,China is still lack of treatment reports for such reported injuries.From March 2008to July 2010,we had 12cases of patients with PASTA who recieved the arthroscopictrans-tendon repair using the method improved by Lo.All patients were followed up for 12months or more,and the results are as follows.MethodsI.General Information:There are 12cases in the group,including 5males,7females,whose ages are from 29to 72years old with the average age of 52.9±13.3years old.9lesions were on the right shoulder,3on the left shoulder,and nine on the dominant shoulder.6patients had a history of trauma on their shoulders,of which 3patients hit their shoulders on the ground and 3hit their hands on the ground.All patients have a pain of the injured shoulder,night pain and most had a problem of shoulder mobility.The patients
the preoperative functional exercise,physical therapy,non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy and local steroid injection for 1to 17months (average 6months).Physical examination was as follows:11cases had front shoulder lateral tenderness,9cases had positive Neer impingement signs,9cases had positive Hawkins impingement signs,7cases had positive signs of painful arc from 60to 120°,and the Jobe tests of 9cases were positive.The preoperative MRIs of all the patients showed a rotator cuff tear.Surgical methods:After general anesthesia,the patient was placed in the lateral position with little abduction and anteflexion traction.After sterilization and drape,we marked the bony landmarks and the position of the surgery approach in the skin.Build a rear channel at the first step of surgery.Then we made a arthroscopic examination of the glenohumeral joint.Then build a front channel from outside to the front and examine the glenohumeral joint.Use the planer and radio frequency to repair and clear the damage at the end point of the supraspinatus muscle.Assess the extent of the damage of the joint side rotator cuff,and if the damage was up to 6mm in width which means Ellman degree Ⅲ PASTA lesion,the damage needed to be repaired(Figure 1A).Before the repair,we must take a subacromial decompression.Insert the arthroscope into the subacromial bursa using the same rear incision.Remove and clean the bursa tissue through the front and the lateral channel until the rotator cuff footprints besides the bursa could be exposed clearly and completely.Then the shoulder acromialplasty could be done.The next step was to examine if there is rotator cuff injuries by synovial side.If the residual end point of rotator cuff becomes thin or obvious degeneration or bursa side damage exists,clean up and make it become full-thickness tear,and then repair the damage.If the lateral rotator cuff end point was still healthy and there is no damage of the bursa side,we would do the trans-tendon repair.Insert the Arthroscope into the glenohumeral joint again through the rear entrance,adjust and lock the position of PASTA lesion,polish the greater tuberosity of the rotator cuff using the burr to make the inner side rotator cuff footprints fresh,and use a NO.18spinal needle to get close to the outer edge of the acromion to insert into the supraspinatus tendon till the glenohumeral joint.Then ensure the position and direction of the rivet.Puncture the skin and tendons with a small sharp knife parallel to the direction of the needle,make sure the direction and the needle insert position,remove the needle,and insert a 5.0mm rivet or 23.5mm rivets according to the anteroposterior dimension of rotator cuff injury(Figure 1B).The rivet should be close to the humeral head cartilage tightly and made a 45°angle with the major tubercle surface.The rivets should be placed in the anteroposterior direction and located in the front and posterior edges.Insert the healthy tissue in the inner rim of the injured supraspinatus tendon by a beak-like thread,and then haul the thread out retrograde.The distance of the threads must be at least 10mm to ensure that there was a bridge enough to fix the rotator cuff footprint.Spinal needle could also be used.First we should haul the latter thread of the two threads in the rivets with different colors through the front approach.Then puncture the healthy tissue of the inner rim of the injured supraspinatus tendon and haul the puncture needle out in the latter direction.If the position was good,the PDS thread was inserted out through the front approach.Using as the direct thread,the latter of the threads was inserted into the supraspinatus tendon retrograde.Then the thread punctured the inner rim of supraspinatus from the behind to the front with other threads.If the anteroposterior dimension of the injured tissue was less than 2cm,two threads with different colors could go through the channel at the same time(Figure 1C).If the residue injured tendon in the joint side was found retraction,grip pliers should be inserted into the glenohumeral joint through the latter approach to grip the residue tendon for the reduction during the surgery.The assistant hold the grippliers continuously to maintain the reduction,and then the surgeon accomplished the sutures.If there were two rivets used and when the sutures were accomplished,we should make a fixed knot(Figure 1D).Insert the arthroscope into the subacromial gap again and fix the threads with the same color using the SMC knot separately.Insert the arthroscope into the glenohumeral joint to assess the rebuilding of the rotator cuff footprint,and at this time the rotator cuff footprints was close to the humeral head cartilage(Figure 1E).Postoperative rehabilitation:The shoulder joint should be fixed in the little abduction position with a strap postoperatively for 4weeks.The pendulum motion,Godman movement,passive external rotation exercises,elbow flexion and extension exercises should proceed early after the surgery.Avoid the shoulder up over the head for 4weeks.After 4weeks,the strap could be removed and patients should do the stretching exercises over the head and stretching exercises in the shoulder rotation.Take isometric exercises 10weeks after the surgery.Efficacy evaluation:Here we use the american shoulder and elbow surgeons(ASES)scoring criteria and the university of california at los angeles(UCLA)scoring criteria.ASES score was calculated as follows:we got a visual analog scale(VAS)from a survey of patients in pain scores and cumulative activity of daily living score(ADL),after the calculation make each accounted for 50%of the weight.The pain score=(10-VAS score)×5,function score= ADL score÷3×5,which means that the pain and function scores account 50points each,and add the total score of 100points.UCLA score criteria total score is 35points,including the pain score of 10points,the function score of 10points,the joint flexion angle score of 5points,the flexion strength score of 5points and the patient satisfaction of 5points.34to 35points are considered as excellent,28to 33as good,21to 27as basically qualified,and 0to 20as poor.Results 12cases of patients had the PASTA receive rotator cuff trans-tendon repair.Among them,there are 5males and 7 females,and all of them had an Ellman degreeⅢ tear.The patients were followed up from 12to 36 months and the average follow-up period was (22±7.3)months.ASES score:follow-up score (89.7±5.6)points,significantly improved compared with the preoperative points(49.8±9.8)(t =12.25,P<0.0001).The follow-up UCLA score of (30.4±3.2)points improved significantly from the preoperative points of (17.3±3.3).The excellent rate was 91.7% .Discussion The principles of the joint side rotator cuff injury:The procedure for the joint lateral rotator cuff injury during the arthroscopic surgery includes:(1)clean up the rotator cuff with or without the subacromial decompression;(2)step 1with the intra-tendon repair;(3)step 1with the repair when the damage becomes into a complete tear.Despite earlier reports concluded that the simple clean of the rotator cuff with the subacromial decompression could relieve the pain and improve the function in patients,recent studies suggest cleaning and decompression cannot prevent the partial rotator cuff tear and damage to become a complete tear and symptoms to be worsen.Kartus et al found that 34.6%of the partial tear patients became a complete tear after a cleaning up of the rotator cuff with the subacromial decompression.And their pain and function scores were significantly less than the patients without a complete tear.By contrast,the rotator cuff repair obtains a more reliable effect,and prevents the progress of the rotator cuff tear.Evidence-based medicine shows that when tear is not more than 50%,the simply debridement of the rotator cuff with the subacromial decompression can achieve satisfactory results.But when the tear is not less than 50%,only the repair will be able to obtain satisfactory results.The traditional way which turns the damage into a complete tear has a direct and convenient advantage,and achieved good clinical results,but it is difficult to remodel the connection of fibrocartilage and has a high re-tear rate,for there is only scar healing in its bone-tendon junction.Thus,recently,many scholars have started to explore the trans-tendon approach to keep the bursa side with intact footprints.Studies have shown that the trans-tendon approach is able to improve the healing rates of the rotator cuff repair.Improvement and experience of the Lo intra-tendon repair technique:According to the technique reported by Lo et al,we can use one or two 5.0mm medial rivets to fix the medial supraspinatus footprint.When using two rivets,make the double pulley to form a horizontal double suture bridge on the surface of the medial supraspinatus footprint to fix the footprint strongly.The advantages of this technique are as follows:(1)the fixation of the suture bridge to the rotator cufffootprint has biomechanical advantages;(2)the double pulley technique reduces the frequency of threading,facilitating the surgical procedure and shortening the operation time.The disadvantages of this technique are as follows:(1)the bare footprints of PASTA only allow one rivet.If we use two rivets,there is a risk of overload;(2)the double pulley technique needs the sixth finger knot pusher which is not introduced to china,and there is a risk of loose knot using the ordinary knot pusher;(3)for some PASTA cases with serious retracting of the residual tissue,the puncture needle should be inserted bias the medial side using the Lo technology.It results in the high tension of the posterior repaired rotator cuff,the synovial tissue bulge and the tendon balance loss,which increase the postoperative pain.Our improvement is as follows:(1)a 5.0rivet with two strands is recommended;(2)two strands can be inserted at once or several times according to the injured width,and two strands are fixed with a slip knot.We think that it reduces the risk of overload of the major tubercle and loose knot,and reduces the cost of patients;(3)after implantation of rivets and before the rotator cuff repair,we can use a grasping grip pliers to grip the retraction residual rotator cuff on the joint side and help to reset the major tubercle footprint.At the same time,the spinal needle is inserted intra-tendon and repair with the strand,thus the synovial tissue bulge and tendon balance loss after the suture would be avoided.Conclusions In summary,for more than 50%PASTA patients,the trans-tendon repair in situ technique can maximumly preserve the normal tissue of the rotator cuff,reconstruct rotator cuff footprint anatomically and have a stable fixed tendon-bone interface.The Lo trans-tendon fixation in situ technology can also receive an ideal therapeutic effect when improved appropriately.
Arthroscopy; Partial rotator cuff tear; Trans-tendon repair
Wang Zimin,Email:ziminw@foxmail.com
2013-11-30)
(本文编辑:薛芳)
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2014.01.004
200433 上海,第二军医大学长海医院骨科
汪滋民,Email:ziminw@foxmail.com
汪滋民,李全,王一,等.关节镜下经肌腱修补治疗肩袖关节侧部分损伤[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2014,2(1):16-22.

