共形阵列幅相误差校正快速算法
张学敬 杨志伟 廖桂生
共形阵列幅相误差校正快速算法
张学敬*杨志伟 廖桂生
(西安电子科技大学雷达信号处理国家重点实验室 西安 710071)
基于子空间的联合迭代算法可以实现对空间信源方位和阵列幅相误差参数的联合估计。当对共形阵列进行幅相误差校正时,由于其空域导向矢量不具有Vander monde结构,导致快速高分辨空间谱估计方法无法直接应用,而利用2维谱峰搜索实现空间方位估计的运算量较大,限制了算法在共形阵列上的应用。针对此问题,该文提出一种借助虚拟阵列实现共形阵列幅相误差校正的新方法。该方法利用虚拟阵列的特殊结构快速实现对信源的DOA估计,省去了谱峰搜索过程,因而运算复杂度低,便于工程实现。理论分析和仿真结果验证了所提算法的有效性,可为共形阵列的工程应用提供参考。
DOA估计;幅相误差校正;共形阵列;虚拟内插
1 引言


本文通过深入分析WF算法,将虚拟内插变换法[14]引入到共形阵列的幅相误差校正中。算法通过调整虚拟阵列变换矩阵,对虚拟子空间进行修正,利用修正后的虚拟子空间之间的正交关系实现对信源方位的DOA估计,并由此得到原共形阵列的幅相误差参数。该算法无需谱峰搜索,具有较低的运算复杂度,可以快速高效地完成共形阵列幅相误差和信源方位的联合估计。文中对算法进行了理论分析和仿真验证,可为共形阵列的应用提供参考。
2 共形阵列信号模型
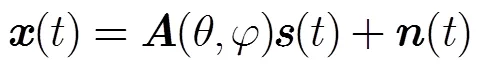
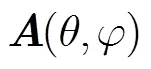



图1 任意几何结构阵列模型

阵列输出模型式(1)可修正为

阵列误差的存在使得实际噪声子空间与理想信号子空间不完全正交,需要进行误差校正。
3 幅相误差对虚拟内插变换的影响


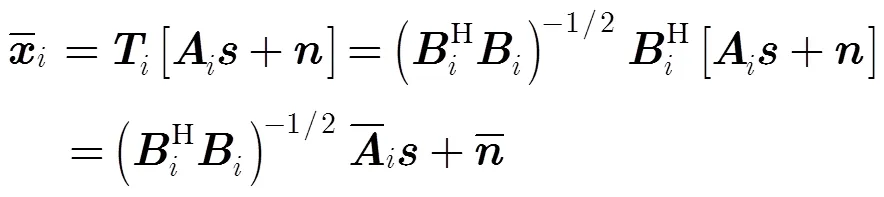




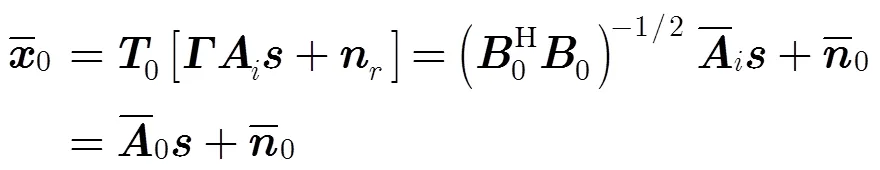

4 联合迭代自校正算法
为了论文的完整性,下面首先简要介绍文献[10]基于子空间的正交原理提出的经典联合迭代自校正算法(WF算法),该算法通过对式(13)的优化问题进行迭代求解来实现阵列误差的自校正。


WF算法通常采用谱峰搜索方法来获得信源方位估计,对于共形阵列,进行两维谱峰搜索的运算量大,难以实时快速完成,从而限制了WF算法在共形阵列上的应用。为解决WF算法在共形阵列上运算量大的问题,同时考虑到误差校正的复杂性,本文利用虚拟阵列进行快速DOA估计,同时结合原阵列进行误差估计,具体流程如下:
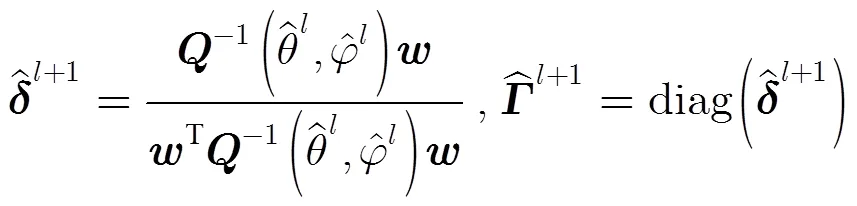


5 运算复杂度分析
下面以图2所示的阵列模型为例进行分析,原共形阵列采用图2(a)所示的半球阵列结构,利用图2(b)所示结构的虚拟十字阵列对其进行内插变换。

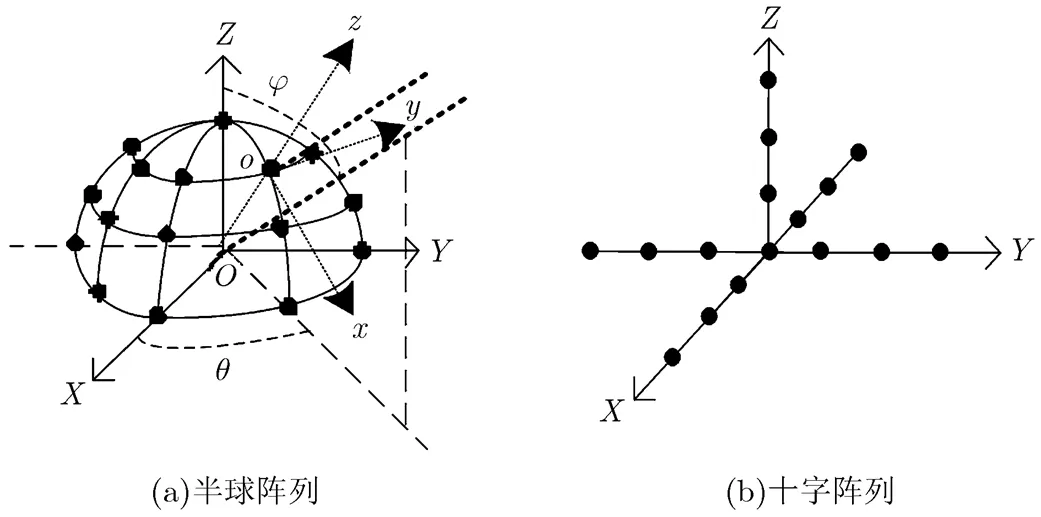
图2 阵列模型
6 仿真实验

实验1 半球共形阵列含有0.1 dB的幅度误差和5°的相位误差,信噪比为10 dB,得到不同快拍数下WF算法和本文算法在线实现幅相误差校正所需的CPU时间,如表1所示。
表1在线实现幅相误差校正的CPU时间对比(s)

快拍数WF算法本文算法 100224.44430.3702 200224.20720.3584 500225.91540.3723
可以看出,相比于WF算法,本文算法在线完成1次幅相误差校正所用时间缩短了两个数量级,证实了本文算法运算量低、实现快速的优点。
实验2 半球共形阵列含有0.1 dB的幅度误差和5°的相位误差,快拍数为500,当信噪比由0 dB变化至20 dB时,经过1000次独立的蒙特卡洛实验,得到WF算法和本文算法进行DOA估计以及幅相误差校正的性能对比曲线,如图3所示。
由仿真结果可知,两种算法的幅相误差校正性能受信噪比影响较大,信噪比越大两种算法的校正性能越优。在幅度误差校正方面,两种算法性能接近;相位误差校正方面,信噪比较低时,本文算法性能明显低于原算法,随着信噪比的增大,二者校正性能接近。
实验3 信噪比取10 dB,相位误差由0°变化至8°,其它条件同实验2,得到WF算法和本文算法进行DOA估计和幅相误差校正的性能对比曲线,如图4所示。
由仿真结果可知,两种算法对幅度误差的校正性能受相位误差影响较小,WF算法性能略优于本文算法。在DOA估计和相位误差校正方面,两种算法的的校正性能均随相位误差的增大而变差,相位误差较小时,文中算法与WF算法性能接近,随着相位误差的增大,文中算法性能逐渐变差。简言之,文中算法对幅度误差的校正性能受相位误差影响较小,而在DOA估计和相位误差校正方面对相位误差更敏感。
实验4 相位误差取5°,幅度误差由0 dB增至0.5 dB,其它条件同实验3,得到两种算法进行DOA估计和幅相误差校正的性能对比曲线,如图5所示。
由仿真结果可知,在DOA估计和幅相误差校正方面,文中算法略差于WF算法,其性能不随幅度误差的增大而变化,即文中算法DOA估计和幅相误差校正性能独立于幅度误差。

图3 均方根误差随信噪比变化对比曲线
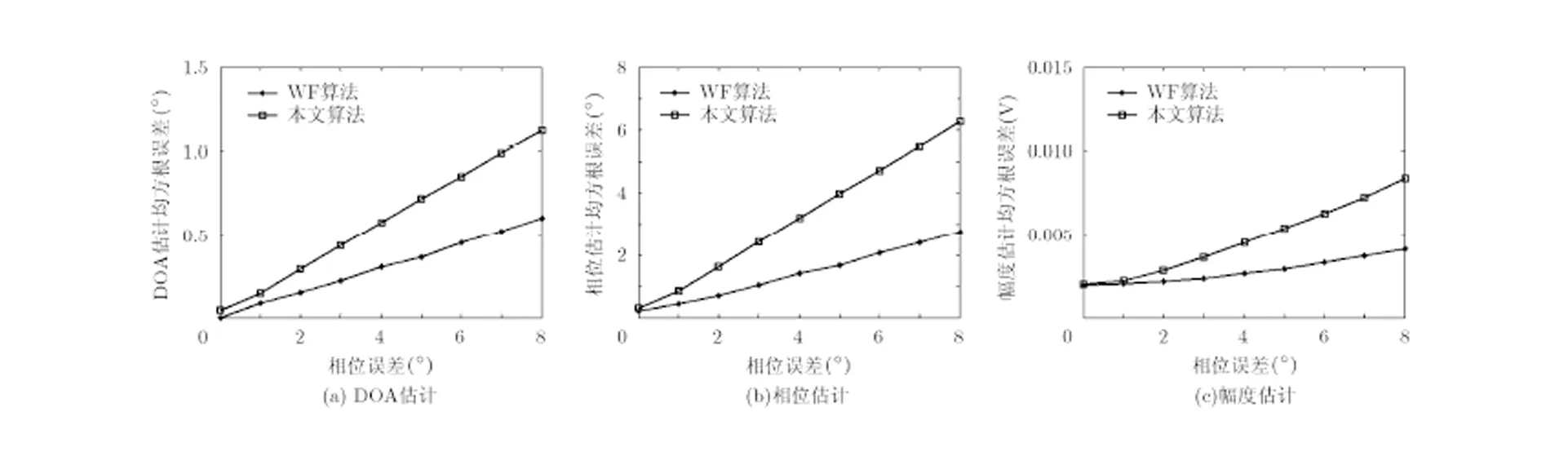
图4均方根误差随相位误差变化对比曲线
图5均方根误差随幅度误差变化对比曲线
7 结束语
本文将虚拟内插变换引入到共形阵列的幅相误差校正中,利用虚拟阵列快速高效地实现对信源方位的DOA估计,并利用DOA估计值得到原阵列的误差参数。所提算法具有运算复杂度低、实现快速的优点,可为共形阵列工程应用提供参考。本文方法仅适合对幅相误差进行校正,当阵列存在方位依赖误差时如何进行误差校正,还需进一步探讨和研究。
[1] Mailloux R J. Conformal array antenna theory and design[J]., 2007, 49(5): 126-127.
[2] Belloni F, Richter A, and Koivunen V. DoA estimation via manifold separation for arbitrary array structures[J]., 2007, 55(10): 4800-4810.
[3] Blomberg A E A, Austeng A, and Hansen R E. Adaptive beamforming applied to a cylindrical sonar array using an interpolated array transformation[J]., 2012, 37(1): 25-34.
[4] Zou L, Lasenby J, and He Z. Direction and polarisation estimation using polarised cylindrical conformal arrays[J]., 2012, 6(5): 395-403.
[5] 王布宏, 郭英, 王永良, 等. 共形天线阵列流形的建模方法[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(3): 481-484.
Wang Bu-hong, Guo Ying, Wang Yong-liang,.. Array manifold modeling for conformal array antenna[J]., 2009, 37(3): 481-484.
[6] Costa M, Richter A, and Koivunen V. DoA and polarization estimation for arbitrary array configurations[J]., 2012, 60(5): 2330-2343.
[7] Boon C N and See C S. Sensor-array calibration using a maximum-likelihood approach[J]., 1996, 44(6): 827-835.
[8] See C M S. Sensor array calibration in the presence of mutualcoupling and unknown sensor gains and phases[J]., 1994, 30(5): 373-374.
[9] See C M S. Method for array calibration in high-resolution sensor array processing[J].,, 1995, 142(3): 90-96.
[10] Friedlander B and Weiss A J. Eigenstructure methods for direction finding with sensor gain and phase uncertainties[C]. Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, New York, 1988: 2681-2684.
[11] Liu Ai-fei, Liao Gui-sheng, Zeng Cao,.. An eigenstructure method for estimating DOA and sensor gain-phase errors[J]., 2011, 59(12): 5944-5956.
[12] Cao Sheng-hong, Ye Zhong-fu,.. DOA estimation based on fourth-order cumulants in the presence of sensor gain-phase errors[J]., 2013, 93(9): 2581-2585.
[13] Cao Sheng-hong, Ye Zhong-fu, Xu Dong-yang,.. A Hadamard product based method for DOA estimation and gain-phase error calibration[J]., 2013, 49(2): 1224-1233.
[14] Friedlander B. The root-MUSIC algorithm for direction finding with interpolated arrays[J]., 1993, 30(1): 15-29.
[15] Weiss A J and Gavish M. Direction finding using ESPRIT with interpolated arrays[J]., 1991, 39(6): 1473-1478.
张学敬: 男,1988年生,硕士生,研究方向为共形阵列信号处理.
杨志伟: 男,1980年生,副教授,研究方向为阵列信号处理、地面运动目标检测、极化处理.
廖桂生: 男,1963年生,教授,研究方向为自适应信号处理、信号检测与估计.
A Fast Method for Gain-phase Error Calibration in Conformal Array
Zhang Xue-jing Yang Zhi-wei Liao Gui-sheng
(,,710071,)
The joint estimation of the Direction of Arrival (DOA) and gain-phase errors can be implemented by the joint iteration method based on the eigen structure subspaces. However, when applying the method to correct the amplitude and phase error of the conformal array, the fast high-resolution spatial spectrum estimation methods can not be applied directly, because of that the space-domain steering vectors of the conformal array does not possess the Vander monde structure. On the other side, the computation of DOA estimation implemented by searching peak of spatial spectrum in 2-dimension is very large, which limits the application of joint iteration method in conformal array. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a new method for gain-phase error calibration in conformal array by virtual interpolation. The DOA estimation can be implemented rapidly by utilizing the special structure of virtual array, and the searching process of the spatial spectrum peak is eliminated, thus the computational complexity of the proposed method is low and the engineering realization of the proposed method is easy. Theoretical analysis and extensive simulations verify the effectiveness of the proposed methods, and provide a reference for the engineering applications of conformal arrays.
DOA estimation; Gain-phase error calibration; Conformal array; Virtual interpolation
TN911.7
A
1009-5896(2014)05-1100-06
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01025
张学敬xjzhang7@163.com
2013-07-11收到,2013-11-07改回
长江学者和创新团队发展计划(IRT-0954),国家自然科学基金(60901066),中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(K5051302007)和陕西省教育厅科研计划项目(2013JK1051)资助课题
——以鲁甸地震相关新浪微博为例

