Dynamic Land Use/Cover Change and Analysis of Landscape Pattern in the Hilly and Gully Region of Loess Plateau:A Case Study of Pengyang County in Southern Ningxia
Jia HANG,Yun SHI,Dahan HE,3,Sha GENG
1.School of Agriculture,Ningxia University,Yinchuan 750021,China;2.College of Resources and Environment,Ningxia University,Yinchuan750021,China;3.State Key Laboratory for Restoration and Reconstruction of Degraded Ecosystem in Northwestern China,Ningxia University,Yinchuan 750021,China
Land use/cover change(LUCC)is one of the most important indicators to understand the relationship between human activity and the environment[1].Although the land use/cover change is the result of natural and man-made factors working together,the land use/cover change caused by human factors has intensified,strongly affecting the global ecosystem[2].It is particularly prevalent in the developing countries where urban sprawl,population migration,agricultural mechanization,regional development and other social and economic development issues have resulted in a wide range of land use/cover change,especially the landscape pattern change[3-5].The monitoring of land use/cover change is an important tool for identifying the dynamic regional change and the relationship between it and human activities,but the statistical description of landscape attributes is still not detailed,such as the landscape composition and landscape configuration[6].Thus,the quantitative description of landscape characteristic index of land use change at the level of patches,types or landscape comes into being[7].In recent years,the domestic and foreign researches begin to use the land use/cover change data based on landscape characteristic index to assess landscape structure and pattern[8-11],but there are few studies on the ecologically fragile loess hilly areas in the context of returning farmland to forests.The mountainous areas of southern Ningxia are located in the hilly and gully region of Loess Plateau with severe soil erosion and extremely fragile ecological environment[12].This paper selects Pengyang County as the study area to explore the relationship between land use/cover change and landscape pattern change in the context of returning farmland to forests,in order to provide a scientific basis for achieving the ecological redevelopment,and sustainable development of ecology,society and economy.
1 Overview of the study area and methods
1.1 Overview of the study areaPengyang County(106°32′-106°58′E,35°41′-36°17′N)is located in the southern part of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,with an altitude of 1248-2483 m.It features a semi-arid continental monsoon climate.The annual average temperature is 7.5℃;the annual rainfall is 442 mm;the accumulated temperature≥ 10℃ is 2746℃;the average frost-free period is148 d;the annual evaporation is1330mm.The soil is the loess soil,mainly distributed in the hilly slope,with low fertility and low production levels.It is one of the counties with the most serious soil erosion in Ningxia,and also the key national soil and water conservation area.Studies have shown that the project of returning farmland to forests is an important way to control the soil erosion and rebuild the ecological environment in mountainous areas of southern Ningxia[13].
1.2 Basic dataThe land use/cover data used in this study mainly come from the TM/ETM data(1991,2000,2005 and 2010)in Pengyang County.The spatial resolution is 30×30m,and the image phase is August-October.In Arc Map GIS environment,the near-infrared wavelength of remote sensing image,near-infrared short wavelength and blue wavelength undergo false color synthesis.
Based on the national land use classification system,the land use/cover types in the study area are divided into arable land,woodland and grassland,unused land,water area and construction land(Table 1).

Table 1 The classification system of land use/cover type in Pengyang County
The land use dynamic degree(K)[14]is used to describe the land use/cover change in the study area,and the expression is as follows:

where K is the land use dynamic degree;Uaand Ubare the area(hm2)of one land use type in the initial period and late period of study,respectively;T is the study period.
When T is set as the year,K is the annual rate of change in one land use type within the study period.
1.3 Landscape pattern analysisThe landscape characteristic index is used to quantitatively describe and monitor the change in landscape structure characteristic over time,and divide the complex landscape into the simple and recognizable landscape pattern[15].According to the purposes of this study,during the analysis of landscape pattern at the level of patch type,we only select the following 8 in dices:percentage of landscape(PLAND);number of patches(NP);patch density(PD);landscape shape index(LSI);the largest patch index(LPI);mean patch size(MPS); area-weighted mean patch fractal dimension(AWMPFD);interspersion juxtaposition index(IJI).During the analysis of landscape pattern at the level of landscape,we only select the following 8 in dices to characterize the landscape pattern characteristics and changes in Pengyang City from number characteristics,shape characteristics and structure characteristics[7]:number of patches(NP);mean patch size(MPS);the largest patch index(LPI);interspersion juxtaposition index(IJI);area weighted mean shape index(SHAPE-AM);contagion index(CONT);Shannon's diversity index(SHDI);Shannon's evenness index(SHEI).The above data are analyzed using ArcView 3.2,ArcGIS 10.0,Excel2003 and Fragstat3.3.
2 Results and analysis
2.1 Land use/cover change in Pengyang CountyFig.1 shows the spatial pattern of land use/cover change in the study area in 1991,2000,2005 and 2010.As shown in Fig.1,there was little change in the land use type in Pengyang County from 1991 to 2000,and it was mainly arable land and unused land.Since the implementation of the project of returning farmland to forests in 2000,the woodland and grassland have been substantially increased,while the arable land and unused land have been significantly reduced.The main land use type is woodland and grassland.Table 2 shows the change in the area of main land use types in Pengyang County from 1991 to 2010.In 1991,the land use types in Pengyang County were arable land(54.79%),unused land(29.79%),woodland and grassland(14.87%),water area(0.44%),and construction land(0.12%).In 2010,the major land use type in Pengyang County was shifted to woodland and grassland(62.97%),followed by arable land(30.46%)and unused land(5.85%),and the proportion of water area(0.47%)and construction land(0.20%)was the lowest.
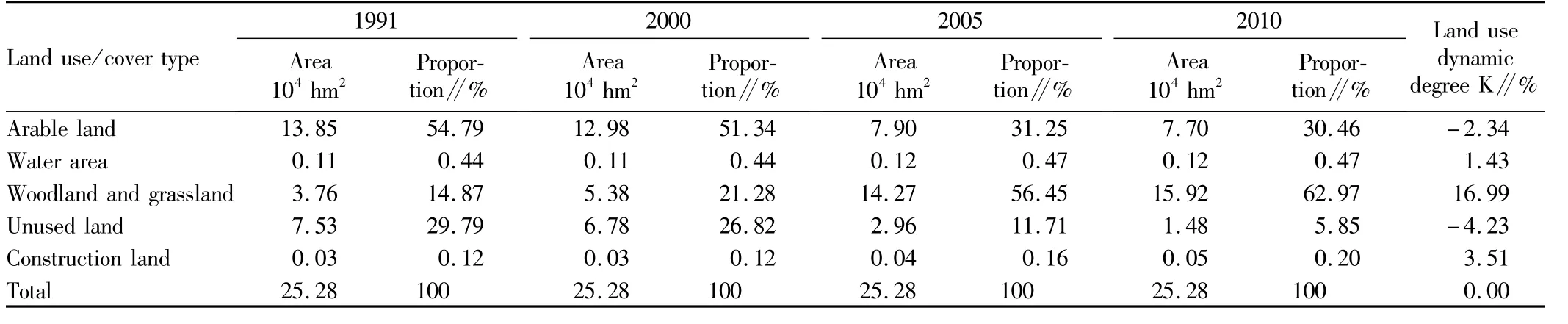
Table 2 The area of land use/cover type in Pengyang County from 1991 to 2010

Fig.1 The spatial distribution of land use/cover change in Pengyang County from 1991 to 2010
From 1991 to 2000,the area of woodland and grassland was increased by 16 198.78 hm2,an average annual increase of 1 799.86 hm2.From 2000 to 2010,woodland and grassland,water area and construction land showed an increasing trend,of which woodland and grassland experienced the highest growth rate(66%),with an average increase of 10 533.23 hm2,followed by construction land(40%),with an average annual increase of27.46 hm2;the water area first declined but then rose;the unused land and arable land showed a decreasing trend,a decrease of 78%and 41%,with an average annual reduction of5 295.13 hm2and 5 280.56 hm2.Based on Table 2,we calculate the land use transfer matrix in Pengyang County during this period(Table 3).From 1991 to 2000,the reduction of arable land and unused land in Pengyang County was accompanied by the increase of woodland and grassland.The land use transfer matrix shows that 12 261.3 hm2of arable land and 4945.72 hm2of unused land were converted to woodland and grassland,and the water area and construction land were not changed significantly.From 2000 to 2005,there was a great change in the land use/cover pattern in the study area.The area of woodland and grassland was increased significantly,reaching 142728.31 hm2(56.45%),occupying the majority of land use types in the study area;the area of arable land and unused land was decreased by 50839.11 hm2and 38241.98 hm2,accounting for 31.25%and 11.71%of the land area,respectively;the water area was decreased by 38.97 hm2,while the construction land area was increased by 91.63 hm2.The change in the pattern of land use/cover in the period 2005-2010 is similar to that in the period 2000-2005.
2.2 Landscape pattern change
2.2.1 The landscape pattern analysis based on the level of patch type.
(i)Number characteristics.From 1991 to 2000,the arable land and unused land were themain land use type in the region,and the percentage of landscape(PLAND)showed a slightly decreasing trend,decreased to51.34%and 26.82%,respectively;the woodland and grassland were slightly increased,and the water area and construction land accounted for less than 1%;the landscape types with the greatest number of patches(NP)and patch density(PD)were woodland and grassland,followed by unused land and arable land,and the water area and construction land had the smallest NP and PD;arable land had the highest largest patch index(LPI)and mean patch size(MPS),followed by unused land and woodland and grassland,and the construction land and water area had the lowest LPI and MPS.From 2000 to 2010,the area of woodland and grassland was rapidly increased,and the percentage of landscape was increased from 21.28%to 62.97%;the proportion of arable land and unused land was decreased to 30.46%and 5.85%,respectively;the proportion of water area and construction land was still small;the landscape type with the greatest number of patches and patch density was arable land;woodland and grassland had the highest LPI and MPS,followed by arable land and unused land,and the construction land and water area still had the lowest LPI and MPS.

Table 3 The transfer matrix of land use/cover type in Pengyang County from 1991 to 2010

Table 4 The change in the landscape characteristic index at the level of patch type in Pengyang County
(ii)Shape characteristics.From 1991 to 2000,the landscape shape index(LSI)of arable land,woodland and grassland was decreased,while the landscape shape index(LSI)of water area,unused land and construction land was increased;the area-weighted mean patch fractal dimension(AWMPFD)of arable land and unused land was decreased,while the area-weighted mean patch fractal dimension(AWMPFD)of woodland,grassland and water area was increased,indicating that the arable land and unused land were the landscape mainly based on complex patches while the woodland,grassland and unused land were the landscape mainly based on simple patches.From 2000 to2010,LSI of arable land and construction land was first increased but then decreased;LSI of woodland and grassland,unused land and water area showed a decreasing trend,and the overall landscape types tended to be simple;AWMPFD of arable land,unused land and water area showed a decreasing trend;AWMPFD of woodland,grassland and construction land showed an increasing trend;the arable land,unused land and water area were the landscape mainly based on simple patches while the woodland,grassland and construction land were the landscape mainly based on complex patches.
(iii)Structural characteristics.From 1991 to 2000,the interspersion juxtaposition index(IJI)of arable land,water area and unused land showed an increasing trend,while the interspersion juxtaposition index(IJI)of woodland,grassland and construction land showed a decreasing trend.In terms of IJI,the land use types were sequenced in descending order as follows:water area>arable land>construction land>woodland and grassland>unused land.It indicates that the water area and arable land were highly concentrated,while the unused land was relatively dispersed.From 2000 to 2010,IJI of arable land,water area,woodland and grassland showed a decreasing trend,while IJI of unused land and construction land was first increased but then decreased.In terms of IJI,the land use types are sequenced in descending order as follows:construction land>water area>unused land>woodland and grassland>arable land.It indicates that the arable land was vulnerable to human activities,with dispersed distribution while the construction land and water area were highly concentrated.
2.2.2 Analysis of pattern based on the level of landscape.In order to learn more about the landscape pattern at the level of landscape,we select 8 landscape in dices(NP,MPS,LPI,IJI,SHAPE-AM,CONT,SHDI and SHEI)for description,and the results are shown in Fig.2.From 1991 to2010,landscape number of patches(NP),interspersion juxtaposition index(IJI),landscape diversity index(SHDI)and landscape evenness index(SHEI)in Pengyang County showed a decreasing trend after the initial increase;mean patch size(MPS),the largest patch index(LPI),area-weighted mean shape index(SHAPE-AM)and contagion index(CONT)showed an increasing trend after the decline,indicating that from 1991 to 2000,the degree of landscape fragmentation and mixed distribution of patches in Pengyang County was enhanced,the patch shape tended to be simple,and the distribution of landscape area among various types tended to be even.From 2000 to 2010,the degree of landscape fragmentation was weakened in this region,the degree of mixed distribution of patches was decreased,and the patch connectivity was enhanced;only one or a few patch types dominated the landscape,and the distribution of landscape area among various types tended to be uneven.
These results confirm that with increasing human activities,there are significant changes in the natural landscape and the diversity index shows a downward trend,while the dominance index shows an increasing trend.
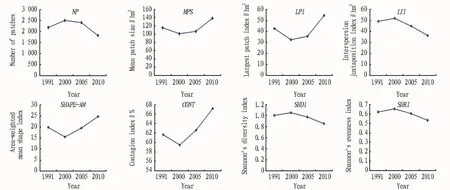
Fig.2 The changes in the landscape characteristic index at the level of landscape in Pengyang County
2.3 Analysis of the driving forces for land use/cover and landscape pattern change(i)From 1991 to 2000,the state and autonomous local government introduced a series of preferential policies,not only allowing but encouraging individual and collective to open up wasteland[16].The irrational cultivation and overgrazing caused soil erosion[17-18],and directly increased the area of arable land and unused land,but decreased the area of woodland and grassland.
Since the implementation of the project of returning farmland to forests,the area of arable land and unused land has shown a slight decreasing trend,while the area ofwoodland and grassland has been increased.The area of water body remained stable during this period,mainly because Honghe River,Ruhe River and Anjiachuan River flowing through Pengyang County was in a relatively stable period during this period.
(ii)The period 2000-2005 is a crucial period for the change in land use/cover and landscape pattern.The implementation of returning farmland to forests,controlled grazing and afforestation projectsmade the area of sloping land and unused land significantly decline,and the area of woodland and grassland surge.After years of practice and exploration,Pengyang County has fully used the"88542"soil preparation technique and some other soil and water conservation measures[17]to rationally use the only natural precipitation,making the water area increase during this period.In addition,the comprehensive control of Nanshan basin and Caomiao basin in Pengyang County is also another factor for the land use/cover change.
3 Conclusions and discussions
3.1 Conclusions(i)From 1991 to 2010,the overall trend of land use/cover change in Pengyang County was that the area of woodland and grassland was constantly increased while the area of arable land and unused land plummeted.Water conservation measures,small watershed control and dam construction were the main reason for the increase in water area;the increase in the area of construction land wasmainly caused by the county development and rural industrial development.From the point of view of the study period,the period 2000-2005 is the dominant period for the land use/cover change in Pengyang County.
(ii)The landscape pattern also underwent dramatic changes in various study periods.The change in number characteristics shows that the degree of landscape fragmentation in this region was increased from 1991 to 2000,but it was decreased from 2000 to 2010.The change in shape characteristics shows that the landscape shape experienced irregular to regular changes.The change in structure characteristics shows that from 1991 to 2000,the degree of mixed distribution of various patches in the landscape was increased,the patch connectivity was weakened;there were many patch types dominating the landscape,and the distribution of landscape area among various types tended to be even.From 2000 to 2010,the degree ofmixed distribution of various patches was weakened,and the patches connectivity was enhanced;only one or a few patch types dominated the landscape,and the distribution of landscape area among various types tended to be uneven.
(iii)The driving force analysis shows that from 1991 to 2000,the soil erosion caused by irrational human exploitation and excessive reclamation was the main reason for land use/cover change within this period.After 2000,the regional development planning(returning farmland to forests,controlled grazing and afforestation projects)was the main reason for land use and landscape pattern change in the study area.Based on the basic farmland construction,rural energy construction,ecological migration,follow-up industry development and other measures,Pengyang County has made the land use/cover and landscape pattern maintain the positive trends.
3.2 DiscussionsThe hilly and gully region of Loess Plateau is one of the regions with the most serious soil erosion in China.The biggest obstacle to the sustainable development of the region is the problem of soil erosion,so effectively controlling the soil erosion and restoring the basin ecological environment has always been an important issue concerning the sustainable development of land resources in the hilly and gully region of Loess Plateau.When conducting the studies on traditional land use and landscape pattern change,most scholars emphasize the land use pattern change at the overall landscape level,but ignore the impact of individual land use type or certain pattern characteristics under this type on the ecological process.Therefore,when researching the regional land use change and landscape pattern change,it is necessary to focus on considering the impact of individual land use type on the land use pattern optimization and the entire regional ecological process.The change in land use/cover type is closely related to the change in landscape pattern.The project of returning farmland to forests is a policy-driven factor for land use/cover change.Strengthening the study of the impact of land use change arising from the project of returning farmland to forests on landscape pattern,is of important guiding significance to sustainable use of land resources and ecological environment reconstruction in the study area.Based on the GIS and landscape ecology methods,this paper makes a preliminary analysis of20 years of landscape pattern characteristics and driving forces in Pengyang County as an ecologically fragile hilly and gully region of Loess Plateau,and in the future,this paper will continue to carry out the study of the impact of land use/cover and landscape pattern change on the ecosystem services,biodiversity conservation,small watershed management,soil conservation and soil erosion in Pengyang County.
[1]Ashraf MD,Yasushi Y,Md ZR.Dynamics of land use/cover changes and the analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dhaka Metropolitan,Bangladesh[J].Geology Journal,2012(77):315-330.
[2]Lambin EF,Turner BL,Geist HJ,et al.The causes of land-use and land cover change moving beyond the myths[J].Global Environmental Change,2001,11(4):261-269.
[3]Jongman RHG.Homo genisation and fragmentation of the European landscape:ecological consequences and solutions[J].Landscape and Urban Planning,2002,58:211-221.
[4]Van Eetvelde V,Antrop M.Analyzing structural and functional changes of traditional landscapes—two examples from southern France[J].Landscape and Urban Planning,2004,67:79-95.
[5]Grimm NB,Faeth SH,Golubie wskiNE,et al.Global change and the ecology of cities[J].Science,2008,319(5864):756-760.
[6]Narumalani S,Mishra DRM,Roth well RG.Change detection and landscape metrics for inferring anthropogenic processes in the greater EFMO area[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2004,91(3-4):478-489.
[7]McGarigal K,Cushman SA,NeelMC,et al.FRAGSTATS:Spatial pattern analysis program for categoricalmaps,2002,URL:www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html.
[8]Kamusoko C,Aniya M.Land use/cover change and landscape fragmentation analysis in the Bindura District,Zimbabwe[J].Land Degradation and Development,2007,18(2):221-233.
[9]Tzanopoulos J,Vogiatzakis IN.Processes and patterns of landscape change on a small Aegean Island:The case of Sifnos,Grecce[J].Landscape&Urban Planning,2010 ,99(1):58-64.
[10]WU X,SHEN ZY.Analysis of the changes of land use/cover and landscape pattern in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2007,23(10):86-93.(in Chinese).
[11]A RH,YANGC.Dynamic changes of landscape pattern during desertification in Duolun County of Inner Mongolia[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2007,18(11):2520-2525.(in Chinese).
[12]SHIY,MIWB.Design and implementation of returning grain plots to forestry(grass)in the southern region of Ningxia information system[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2007,14(2):155-157.(in Chinese).
[13]SHIY,JIAOCW,MIWB,et al.GIS-based decision analysis on conversion of cropland to forest(grass)in Pengyang County[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2009(9):26-28.(in Chinese).
[14]LAIYC,LIXW,FENGS,et al.Impact of grain for green project on ecosystem service values in the hilly region in Sichuan Basin:A case study of Hongya County[J].Journal of Natural Resources,2011,26(5):755-768.(in Chinese).
[15]Yeh CT,Huang SL.Investigating spatiotemporal patterns of landscape diversity in response to urbanization[J].Landscape and Urban Planning,2009(93):151-162.
[16]ZHANG F,TASHPOLAT· Tiyip,DING JL,et al.The change of land use/cover and characteristics of landscape pattern in arid areas oasis:A case study of Jinghe County,Xinjiang Province[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(3):1251-1263.(in Chinese).
[17]LIU K,XIE YZ,LIYB,et al.Ecological degradation and restoration in loess hilly area of South Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region—taking Pengyang County as an example[J].Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,26(2):54-56.(in Chinese).
[18]XIE YZ.Research and constructive practice of ecological agricultural system in the hilly area of South Ningxia[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2000,19(1):12-18.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2014年7期
Asian Agricultural Research2014年7期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Quantile Regression Analysis on Convergence of China's Regional Econom ic Grow th
- A Study on Antibacterial Activity and Chem ical Com position of the Petroleum Ether Extract from Aspergillu sniger Mycelia
- Current Situation of Information Demand of Farmers in Taihang Mountain Area:A Case Study of Pingshan County in Hebei Province
- Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Key Driving Force concerning the Efficiency of Green Supply Chain of Fruits and Vegetables
- Study of the Option Ordering Policy concerning Perishable Farm Produce Based on Revenue Sharing Contract
- Study on Rural Poverty Reduction Effect of Traffic Infrastructure
