Study of the Option Ordering Policy concerning Perishable Farm Produce Based on Revenue Sharing Contract
Xiaojing LIU
1.School of Economics and Management,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 611731,China;2.Aba Teachers College,Wenchuan 623002,China
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of economic globalization,the enterprise competition becomes more and more obvious,making the procurement of raw materials,marketing and other aspects run faster.Therefore,when the supply chain members make decisions in order to maximize their own profits,it can easily lead to the conflict with the whole supply chain profits.We use the revenue sharing contract to avoid this conflict.There are many studies on revenue sharing.
With the revenue sharing policy implemented by the famous Blockbuster video rental company and its suppliers as the object of study,Cachon et al.establish the two-stage supply chain model,and find that the revenue-sharing mechanisms can improve the operational efficiency of the entire supply chain system[1].Ilaria revenue sharing contract further extends it to the three-stage supply chain model[2].Dana Spier studies the revenue sharing contract under price competition[3].
Koulamas uses the revenue sharing contract under the newsboy model to study the supply chainmem bers'profit problems[4].Ye Fei researches the revenue sharing contract problems of supply chain technology innovation cooperation projects under uncertain demand[5].Song Huaming et al.study the revenue sharing contract issues in the case of ordering time influencing the market demand and channel costs,and prove that the revenue sharing contract can coordinate the supply chain[6].
However,due to the long process of agricultural production,there are many uncertainties.The insufficient production,weather and other uncertainties may cause price rise,and if the price is too high,the purchase will not be completed,and the entire agricultural supply chain will be broken,causing chain reaction and the collapse of agricultural markets,thereby threatening the fundamental interests of the majority of farmers.Therefore,studying the retailer ordering policy issues under the revenue sharing option contract will be of more practical significance.We mainly focuson the impact of revenue sharing ratio on the ordering quantity of perishable farm produce and supply chain profits.
2 Symbols and hypotheses
We consider the two-echelon supply chain system which consists of single agricultural producers and single retailers.Due to the great loss in the circulation of farm produce,perish ability and other features,we assume that the retailers can only purchase farm produce in the futures market.The producers of farm produce are the labor leaders,and the retailers of farm produce are the followers.When there is Stackel berg game between the two,the option contract parameter first given by the producers is(c0,ce),the unit cost of production for farm produce is c,and the option contract parameter observed by the retailers is(c0,ce).In the futures markets,q agricultural products are ordered at the price of c0,and according to market demand,the option number of qeis executed at the price of ceduring the selling.
And a certain proportion of shared revenue(1-θ)is given to producers.the market demand is D,and the probability density function and distribution function are f(x)and F(x),respectively.F(x)is continuous and differentiable,and F(0)=0.
The members participating in the supply chain are risk neutral,and it is assumed that,that is,the production cost of agricultural producers is lower than the option ordering and execution cost to ensure the producers'limited profits,and the option ordering and execution cost is lower than the sales price to make retail-ers can obtain profit.
3 Model analysis
In this case,the retailers'profit is as follows:

The retailers'expected profit is as follows:
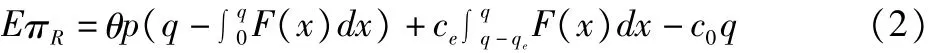
The producers'profit is as follows:

The producers'expected profit is as follows:
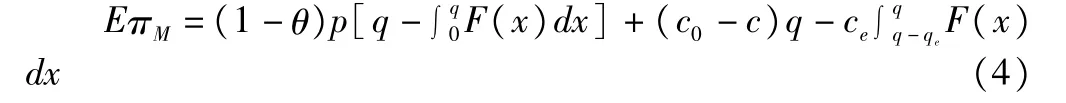
The expected profit of supply chain is as follows:


Proof:Seek the firs torder and second order derivative of and in formula(2),respectively:
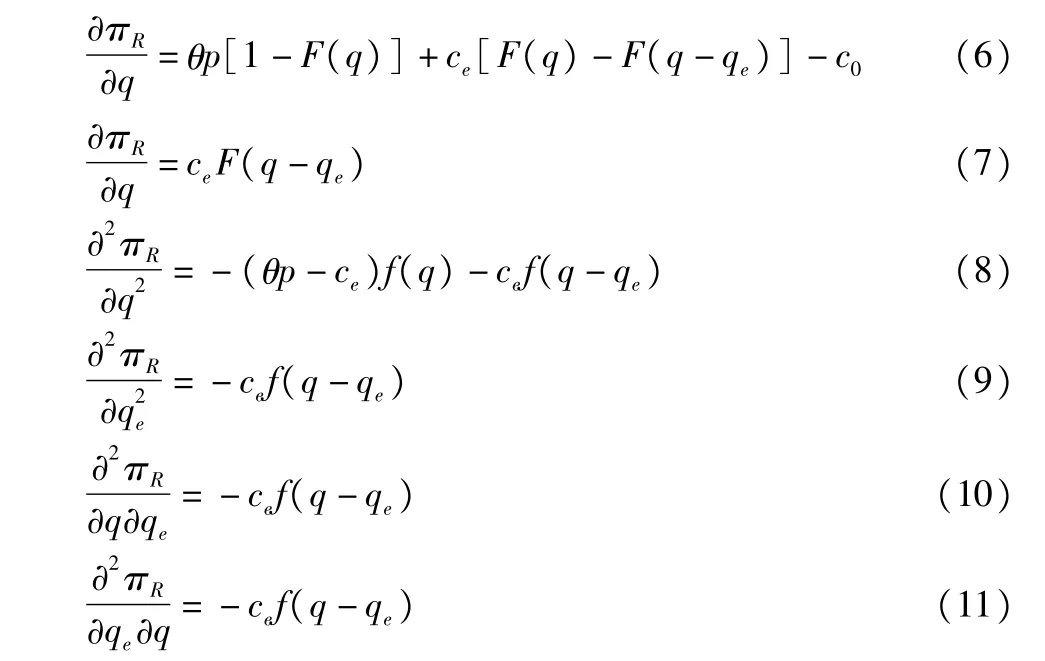
From the Hessian matrix,it is found that:

Substitute formula(8),(9),(10)and(11)into(12),we get:

Thus it can be found that the retailers'expected profit is the concave function of q and qe,and there are optimal q*and.
Let formula(6),(7)be 0,we can get the optimal q*and

Proposition 1 shows that in the case of decentralization,the farm produce retailers only consider their own interests maximization but without concern for the interests of supply chain system,so in this case,the retailers will execute all options ordered.
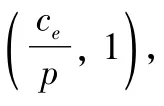
Proof:According to the nature of the implicit function,seek the derivative of the revenue sharing ratioθon both sides of formula(13):

It is transformed as follows:

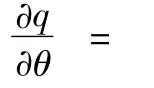
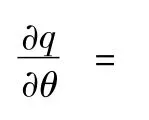
Theorem 1 is proved.
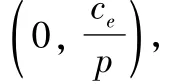
At this point,the retailers'expected profit is as follows:
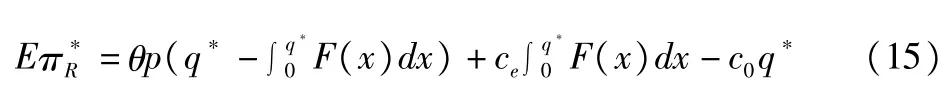
The producers'expected profit is as follows:

The expected profit of supply chain system is as follows:
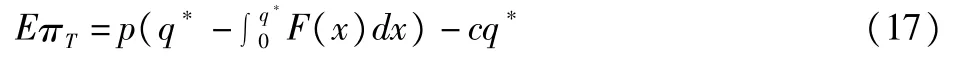
Proposition 2:In the case of centralization,there is the optimal option ordering quantityin the supply chain system,andnothing to do with the revenue sharing ratio.
Proof:Seek the first order and second order derivative of option ordering quantity in formula(5):
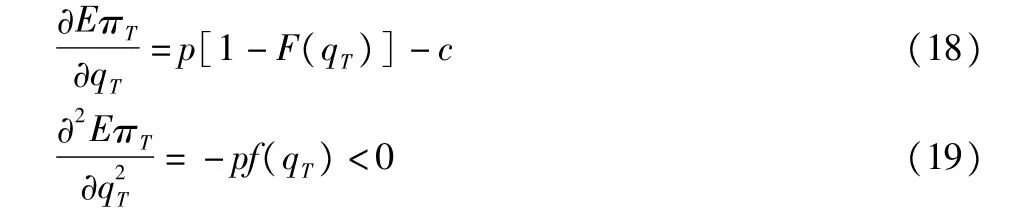
The expected profit of supply chain is the concave function of the option ordering quantity q,thus there is optimal option ordering quantity,making the supply chain system having a maximum value.Let formula(18)be equal to 0,the optimal option ordering quantity is as follows:

Proposition 2 is proved.
Proposition 2 shows that in the case of centralization,there is optimal option ordering quantity in the supply chain system,nothing to do with the revenue sharing ratio and option contract parameter combination,and the ordering quantity is only related to production prices of farm produce and sales price on the market.
4 Example
Assuming the production cost of one perishable agricultural product c=2,the option ordering price c0=1,the option execution price ce=3,and the market sales price p=10.The market demand x of this product follows uniform distribution of[0,1 000],and the corresponding distribution function and density function are as follows:

Fig.1 shows that in the case of decentralization,the option ordering quantity of farm produce is the decreasing function of revenue sharing ratio,that is,the higher the revenue sharing ratio,the smaller the retailers'option ordering quantity,but it is always greater than the option ordering quantity of supply chain system in the case of centralization;the option ordering quantity of supply chain system has nothing to do with the revenue sharing ratio in the case of centralization,and it is only related to the production costs and selling prices of farm produce.
Fig.2 shows that in the case of decentralization,agricultural producers and retailers'expected profit is related to revenue sharing ratio.The producers'expected profit first decreases and then increaseswith the increasing revenue sharing ratio,that is,when the revenue sharing ratio is in(0,0.217),producers'expected profit is the decreasing function of revenue sharing ratio;when the revenue sharing ratio is in(0.421,1),producers'expected profit is the increasing function of revenue sharing ratio.

Fig.1 The relationship between option ordering quantity and revenue sharing ratio under decentralization and centralization decisions of farm produce
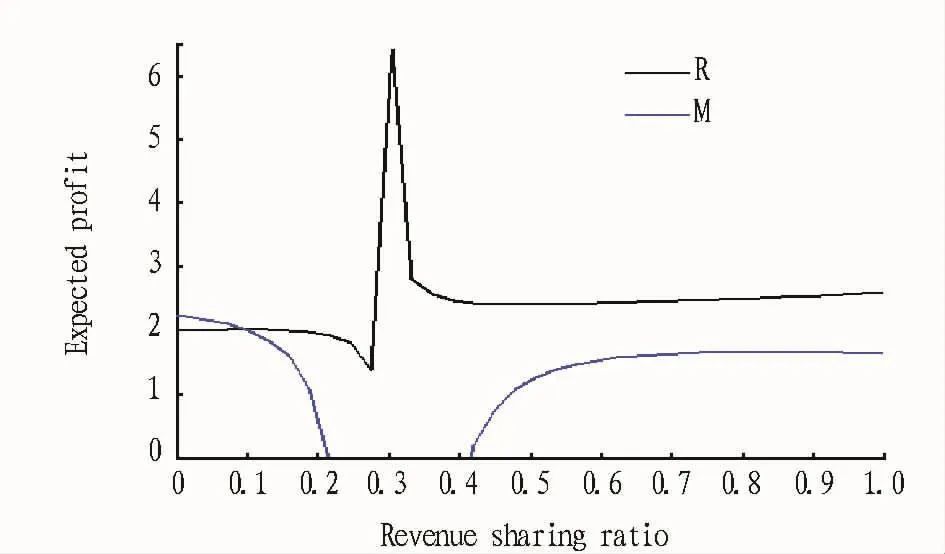
Fig.2 The relationship between farm produce retailers and producers'expected profit and sharing ratio in the case of decentralization
When the revenue sharing ratio is 0.316,the retailers'expected profit is the highestwhile the producers'expected profit is negative.To ensure that producers are also involved in the supply chain system,only when the revenue sharing ratio is in(0.421,1)can it make sense.
Consequently,when the revenue sharing ratio is in(0.421,1),the agricultural producers and retailers'expected profit is the increasing function of sharing ratio,that is,the expected profit will increase with the increasing sharing ratio.
Therefore,the revenue sharing option contract is conducive to increasing supply chainmembers'expected profit in the case of decentralization.
5 Conclusions
This paper considers the two-echelon supply chain system which consists of single agricultural producersand retailers,and analyzes the impactof sharing ratio on the option ordering quantity,and retailers and producers'expected profits.
Studies have shown that in the case of decentralization,when the revenue sharing ratio is between 0 and 0.3,the option ordering quantity of farm produce is a decreasing function of the sharing ratio;when the revenue sharing ratio is between 0.3 and 1,the option ordering quantity of farm produce is an increasing function of sharing ratio;when the revenue sharing ratio is between 0.421 and 1,the agricultural producers and retailers'expected profits are an increasing function of sharing ratio.
Therefore,the revenue sharing contract is conducive to increasing supply chainmembers'expected profit in the case of decentralization.Finally,through the numerical calculation,the applicability of the conclusions is verified,to provide a reference for the supply chain management practices.
[1]Cachon,GP,Lariviere,AM.Capacity choice and allocation:Strategy behavior and supply chain performance[J].Management Science,1999,45(8):1091-1100.
[2]Ilaria Giannoeearo,Pierpao loPontrandolfo.Supply chain coordination by revenue sharing contracts[J].Production Economies,2004(89):131-139.
[3]Dana Spier.Revenue sharing and vertical control in the video rental industry[J].The Journal of Industrial Economies,2001(3):223-245.
[4]Christos Koulamas.A newsvendor problem with revenue sharing and channel coordination[J].Decision Sciences,2006,37(1):91-98.
[5]YE F,LIYN,HU XL.Research on the revenue sharing contract of supply chain technology innovation under uncertainty market demand[J].Science and Technology Management Research,2005,25(3):81-83.(in Chinese).
[6]SONG HM,MA SH.An extended supply chain revenue-sharing contract with consideration of influence of order time[J].Systems Engineering,2005,23(9):59-63.(in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2014年7期
Asian Agricultural Research2014年7期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- A Study on Antibacterial Activity and Chem ical Com position of the Petroleum Ether Extract from Aspergillu sniger Mycelia
- On the Relationship between Duration of Vegetative Grow th Stage of W heat and the Average Daily Temperature
- The Design and Implementation of Black Tea Traceability System Based on UHF RFID
- Innovation of Supervision System for Quality and Safety of Edible Agricultural Products
- Com position,Property Characterization and Application of Agricultural and Forest Biomass Carbon
- The Survey of Ermia mangshanensis Resource in South China Tiger Nature Reserve
