髌股关节发育不良对髌骨脱位磁共振成像表现的影响
魏民刘玉杰 李众利 王志刚 蔡谞
(中国人民解放军总医院骨科,北京 100853)
髌股关节发育不良对髌骨脱位磁共振成像表现的影响
魏民*刘玉杰 李众利 王志刚 蔡谞
(中国人民解放军总医院骨科,北京 100853)
背景:当存在髌股关节发育不良时,髌骨脱位的损伤程度较轻,因此更加依赖影像学诊断。
目的:比较髌股关节发育不良患者和髌股关节发育正常患者髌骨脱位时磁共振成像(MRI)表现的异同。
方法:回顾性分析54例经临床证实的髌骨脱位患者的MRI影像学资料。髌股关节发育不良患者32例,髌股关节发育正常患者22例。记录患者MRI中髌骨内侧骨挫伤或撕脱骨折、髌骨关节面骨软骨骨折、股骨外侧髁外侧部骨挫伤、髌股内侧支持带撕裂等情况。
结果:髌股关节发育不良组的32例患者中,髌骨内缘骨折12例,内侧支持带损伤10例,髌骨软骨损伤7例,股骨外髁骨挫伤18例;髌股关节发育正常组的22例患者中,髌骨内缘骨折8例,内侧支持带损伤14例,髌骨软骨损伤14例,股骨外髁骨挫伤14例。两组在内侧支持带损伤和髌骨内缘骨折上有显著统计学差异(P<0.05)。
结论:MRI可以较好地诊断髌骨脱位。当髌股关节发育不良时,内侧支持带损伤和髌骨内缘骨折的发生率降低。
髌骨脱位;髌股关节发育不良;磁共振
Background:When patellofemoral joint is dysplastic,the injury caused by patellar dislocation is slighter than that of normal patellofemoral joint.Therefore,magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)is very important for dignosis of dysplasia of patellofemoral joint after patellar dislocation.
Objective:To explore MRI features of dysplasia of patellofemoral joint after patellar dislocation.
Methods:A retrospective study was conducted in 54 patients with patellar dislocation.There were 32 patients with dysplasia of patellofemoral joint,and 22 patients with normal patellofemoral joint.MRI features were investigated,including medial patellar fracture,medial patellar retinaculum injury,osteochondral injury of patellar,bone contusion of lateral femoral condyle.
Results:In the group of dysplasia of patellofemoral joint,there were 12 cases of medial patellar fracture,10 cases of medial patellar retinaculum injury,7 cases of osteochondral injury of patellar,and 18 cases of bone contusion of laterl femoral condyle.In the group of normal patellofemoral joint,there were 8 cases of medial patellar fracture,14 cases of medial patellar retinaculum injury,14 cases of osteochondral injury of patellar,and 14 cases of bone contusion of laterl femoral condyle. There were significant differences in medial patellar retinaculum injury and medial patellar fracture between two groups(P< 0.05).
Conclusions:Patellar dislocation is diagnosed effectively by MRI.The incidence of medial patellar retinaculum injury and medial patellar fracture presented by MRI will lower when patellofemoral joint is dysplastic.
急性髌骨脱位多发生于运动过程中,患者感觉腿打软而摔倒。髌骨脱位属于复合性损伤,包括髌骨内侧骨挫伤或撕脱骨折、髌骨关节面骨软骨骨折、股骨外侧髁外侧部骨挫伤、髌股内侧支持带撕裂、关节积液等一系列膝关节损伤。除非发生髌骨内侧撕脱骨折或关节面骨软骨骨折,常规X线片中没有特异性表现。由于多数髌骨脱位可自行复位,因此常遗漏诊断。在评价骨软骨和软组织损伤方面,磁共振成 像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)检 查 具 有 常规影像检查无法比拟的优势,能清楚显示骨软骨损伤的部位、大小、程度,尤其能清楚显示骨挫伤,因此有助于临床诊断和治疗决策。
当存在髌股关节发育不良时,髌骨更容易发生脱位和复位,损伤程度较轻。本研究通过回顾性分析54例经临床证实的髌骨脱位的MRI资料,探讨髌股关节发育不良患者和髌股关节发育正常患者髌骨脱位时MRI表现的异同。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
本研究患者54例,男30例,女24例;右膝25例,左膝29例;年龄14~33岁,平均21岁;均经临床证实为髌骨脱位。从外伤到MRI检查的时间间隔为2~45 d,平均 12 d。48 例主诉髌骨有向外侧错位感,髌骨自行复位;6例髌骨不能自行回复,经医生手法复位。临床检查显示54例均有膝关节肿胀,关节屈伸活动受限,髌骨内侧缘压痛,髌骨恐惧实验阳性。
1.2 MRI 检查
百 胜 0.3TMRI扫 描 仪 ,使 用 膝 关 节 专 用 线 圈 。T1WI 采 用 SE 序 列 ,扫 描 参 数 为 TR/TE=680 mm/ 20 mm;T2WI 采 用 TSE 序 列 ,扫 描 参 数 为 TR/TE= 2540 mm/90 mm。 FOV=20 cm×20 cm,矩 阵 =(224~288)×(192~200),层厚 3.5~5 mm,间距 0.0~0.5 mm,1次采集。
1.3 分组标准
髌 股 关 节 发 育 不 良 :① 髌 骨 高 位 Insall-Salvati T/P>1.2;②矢状位股骨滑车角>140°。A 组:32 例,均存在髌股关节发育不良的情况;B组:22例,不存在髌股关节发育不良。
1.4 观察指标
记录患者MRI中髌骨内侧骨挫伤或撕脱骨折、髌骨关节面骨软骨骨折、股骨外侧髁外侧部骨挫伤、髌股内侧支持带撕裂等情况。
1.5 统计学分析
采用Stata10.0 软件,计数资料采用χ2检验。
2 结果
髌股关节发育不良组的32例患者中,髌骨内缘骨折12例,内侧支持带损伤10例,髌骨软骨损伤7例,股骨外髁骨挫伤18例;髌股关节发育正常组的22例 患者 中,髌骨 内 缘 骨 折 8例 ,内 侧支 持带 损 伤 14例,髌骨软骨损伤14例,股骨外髁骨挫伤14例。两组在内侧支持带损伤和髌骨内缘骨折的差别有显著统计学意义(P<0.05)。

表1 髌骨脱位的MRI表现
3 讨论
髌骨脱位多发生于胫骨固定而股骨强力内旋时,也有直接剪切暴力造成脱位的情况。脱位如果不能得到有效的治疗,再脱位的发生率 高达 44%[1]。股四头肌肌力是促进髌骨向外移位的因素,而髌股内侧支持带和股骨外侧髁高度是限制髌骨向外移位的因素。当二者之间的平衡被打破时,髌骨脱位就会发生。髌骨脱位属于复合性损伤,包括髌骨内侧骨挫伤或撕脱骨折、髌骨关节面骨软骨骨折、股骨外侧髁外侧部骨挫伤、髌骨内侧支持带撕裂、关节积液等一系列膝关节损伤[2-4](图 1)。
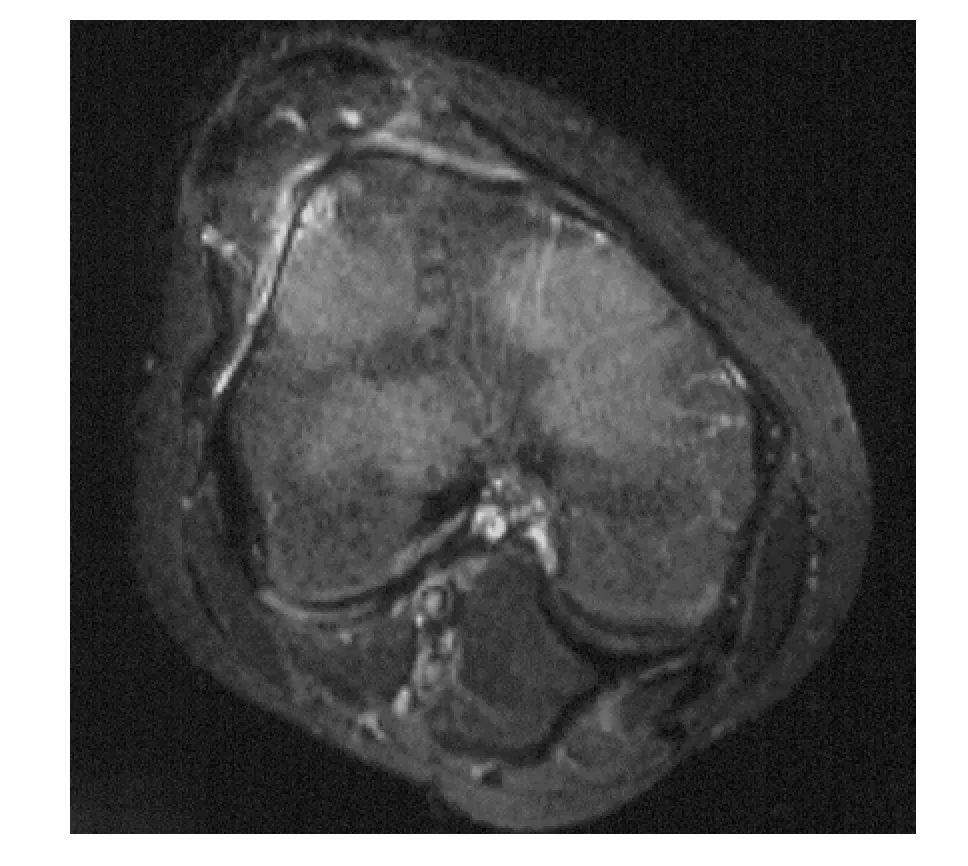
图1 髌骨脱位的MRI表现
基于手术探查或MRI检查的研究发现,髌骨脱位 后 关 节 内 软 骨 损 伤 的 发 生 率 在 40%~76%[8,9]。 早期的骨软骨损伤会逐步加重,有文献报道,22%的患者 最 终 发 展 为 骨 关 节 炎[5-7]。 因 此 ,早 期 辨 别 骨 软 骨损伤并合理治疗对髌骨脱位的预后至关重要。本研究中,髌骨脱位后骨软骨骨折的发生率为39%,与文献报道相似。髌骨软骨损伤较股骨髁骨软骨损伤更为常见,原因可能是髌骨软骨损伤在脱位和复位时都有可能发生,而股骨外侧髁软骨损伤仅在脱位阶段。
由于脱位的髌骨与股骨外髁外侧壁发生撞击,将会造成股骨外髁骨髓水肿,这是MRI上的特异征象,也是MRI优于其他影像学检查之处。而膝关节外翻损伤也会造成内侧支持结构的撕裂并在股骨外髁造成骨髓水肿,不过二者的部位不同。髌骨脱位发生股骨外髁骨髓水肿的部位更高,位于股骨外上髁附近;而外翻损伤的骨髓水肿部位接近关节面,并且在胫骨平台对应部位也会有骨髓水肿发生。
股骨外髁高度是限制脱位的主要骨性因素,当存在髌股关节发育不良的情况时,脱位所需的力量较小,因此脱位更容易发生。当存在髌股关节发育不良时,再脱位的发生率上升至 85%[10]。不过由于脱位复位较为容易,因此损伤程度相对较轻。
髌股内侧支持带是限制脱位的主要软组织因素,脱位时可以发生支持带撕裂或髌骨内侧缘撕脱骨折。当存在髌股关节发育不良的情况时,髌骨脱位所需的外力较小,因此支持带的损伤反而较轻。当存在髌骨高位或股骨滑车浅平的情况时,内侧支持带损伤和髌骨内缘骨折的发生率为31%,明显低于髌股关节发育正常患者(P<0.05),因此诊断更多地依赖股骨外髁骨挫伤等间接征象。
总之,MRI可以较好地诊断髌骨脱位;但当髌股关节发育不良时,内侧支持带损伤和髌骨内缘骨折的发生率降低。
[1]Cotield RH,Bryan RS.Acute dislocation of the patella:results of conservative treatment.J Trauma,1977,17(7):526-531.
[2]Ahmad CS,Brown GD,Stein BS.The docking technique for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction:surgical technique and clinical outcome.Am J Sports Med,2009,37 (10):2021-2027.
[3]Guerrero P,Li X,Patel K,et al.Medial patellofemoral ligament injury patterns and associated pathology in lateral patella dislocation:an MRI study.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol,2009,1(1):17.
[4]Sanders TG,Paruchuri NB,Zlatkin MB.MRI of osteochondral defects of the lateral femoral condyle:incidence and pattern of injury after transient lateral dislocation of the patella.AJR Am J Roentgenol,2006,187(5):1332-1337.
[5]Sillanpää PJ,Peltola E,Mattila VM,et al.Femoral avulsion of the medial patellofemoral ligament after primary traumatic patellar dislocation predicts subsequent instability in men:a mean 7-year nonoperative follow-up study.Am J Sports Med,2009,37(8):1513-1521.
[6]Nomura E,Inoue M.Second-look arthroscopy of cartilage changes of the patellofemoral joint,especially the patella, following acute and recurrent patellar dislocation.Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2005,13(11):1029-1036.
[7]Mäenpää H,Lehto MU.Patellofemoral osteoarthritis after patellar dislocation.Clin Orthop Relat Res,1997,(339): 156-162.
[8]Stanitski CL,Paletta GA Jr.Articular cartilage injury with acutepatellardislocationinadolescents.Arthroscopicandradiographiccorrelation.AmJSportsMed,1998,26(1):52-55.
[9]Nomura E,Inoue M,Kurimara M.Chondral and osteochondral injuries associated with acute patellar dislocation.Arthroscopy,2003,19(7):717-721.
[10]Dejour H,Walch G,Nove-Josserand L,et al.Factors of patellar instability:an anatomic radiographic study.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,1994,2(1):19-26.
Magnetic resonance imaging features of dysplasia of patellofemoral joint after patellar dislocation
WEI Min*,LIU Yujie,LI Zhongli,WANG Zhigang,CAI Xu
(Department of Orthopaedics,Chinese PLAGeneral Hospital,Beijing 100853,China)
Patellar dislocation;Dysplasia of patellofemoral joint;Magnetic resonance imaging
*通信作者:魏民,E-mail:weim301gk@sina.com

