Numerical studyon the shock responses of submunition dropon various mediums
WANG Shu-you(王树有), JIANG Jian-wei(蒋建伟), NAN Yu-xiang(南宇翔),MEN Jian-bing(门建兵)
(State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing 100081,China)
When submunitions in a cluster warhead dispense and fall down to ground in a target area,the shock loads impact on submunitions and device attached.To protect the expensive mechanism inside the submunitions and keep the mechanism act reliablly it is necessary to ensure that the bearable drop peak overload of devices is higher than the actual drop peak overload of submunitions[1].
Recently,lots of scholars have studied the antidrop performance of electric products through finite element method and experimental tests[2-7],but references on submunitions drop on ground are hardly published.
In this paper,submunition impact on ground with various drop velocities,different drop angles,attack angles and various mediums are calculated with LS-DYNA[8-9].The law of various drop velocities,drop angles and attack angles related to peak overload are obtained.The investigation results have a significant meaning to strength mechanism design inside the submunitions and the accurate modeling of submunition dynamic response.
1 Numerical simulation model
The submunition is simplified as a column in this problem,the submunition weights 3kg,and is equivalent to steel 45#with the premise condition as major parts positions have not been changed.In order to keep submunition size unchanged according to test requirements,the submunition is modeled as an inner cavum case.Impact targets are concrete surface,gravel ground or sand.The problem is studied by using LS-DYNA,Lagrange algorithm is adopted to model the submunition,three dimensional model of submunition and ground medium are meshed,they have 32 000elements(grids of submunition)and 640 000elements(grids of target ground)respectively.The symmetrical method is used in this problem to reduce computation time.The calculation model is shown in Fig.1.According to real conditions,the drop velocity,drop angleθ(angle of velocity vector to the horizontal ground)and at-tack angleδ(angle of velocity vector to the axis of submunition)against concrete surface,gravel ground or sand are studied respectively.
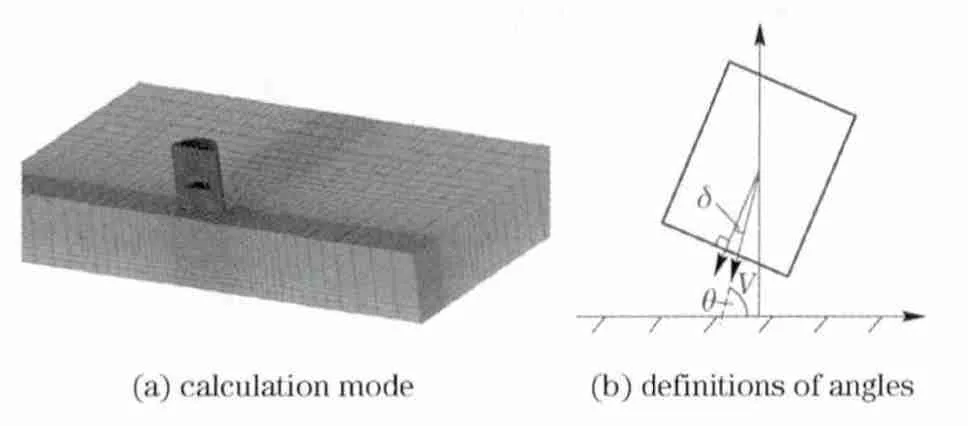
Fig.1 Calculation model and the definitions of angles
Constitutive Plastic_Kinematic is adopted for submunition material strength calculation,and strain rate effect is calculated by using Cowper-Symonds model in the paper.Parameters of submunition material are listed in Tab.1.
The constitutive JHC (Johnson_Holmquist_Concrete)is used for strength calculation of con-crete;the equivalent von-mises stress is used to predict the loads on submunition.The parameters of concrete are list in Tab.2.Gravel and soil are calculated with constitutive Mat_Soil_and_Foam,the different bulk modulus and pressure parameters are listed in Tab.3.
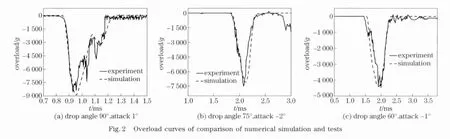
In order to validate the computation results of numerical model,overload sensors are set up inside the submunitions.When the submunitions drop to ground,the sensor device DRT0 1 0inside the submunition will collect data over the loading time.The submunition hangs on the tower with definite height,and concrete plate are set up oblique to the vertical drop line of submunition.The velocity camera is used to record submunition attack angle.
Fig.2is the submunition overload curvecomparisons from three typical cases,the numerical simulation curves agree well with recorded test data from sensor device DRT010.

Tab.1 Parameters of 45# steel material model

Tab.2 Parameters of constitutive JHC[8]

Tab.3 Parameters of constitutive Mat_Soil_and_Foam[9]
2 Analysis on numerical simulation results
The following cases are studied by using a finite element program LS-DYNA,the three drop velocities,respectively,are 15m/s,20m/s and 25m/s,the drop angles,respectively,are 60°,75°and 90°,and the attack angles,respectively,are 0°,1°,2°,3°,4°,5°.Three types of ground medium are calculated:the concrete,gravel and soil.
2.1 Analysis of drop velocity effect on shock response
Fig.3is the law of submunition overload on different drop velocities impacting on ground of concrete,gravel and soil medium respectively.In these cases,the drop angle of submunition is 90°and the attack angle of submunition is 0°.From the curves,the overload of submunition increases with submunition drop velocity,the relationship between drop velocity and overload is almost linear.The reason is that submunition will have more kinetic energy and more momentum with drop velocity increases,and drop shock will usually have more overloading.

The interaction time of submunition impacting on concrete ground and gravel ground decreases with the increase of drop velocity,because the compression strength and Young's modulus of concrete and gravel are greater than those of soil.Submunitions finished the impact response behavior instantaneously,especially in comparatively high velocities.On the contrary,the interaction time on soil medium increases as the drop velocity increases.It indicates that the penetration or indentation happens when the submunitions impact on soil medium,the displacement of submunition indent into medium enlarges and the response time increases by the penetration behavior.
2.2 Response analysis on different drop angle
Fig.4is the peak overload and interaction time of submunition impacting on ground with different impact angles.The curve fitted shows that the peak overload increases with the drop angle increases in range 60-90°.The tendency of peak overload keeps the same when impact on different mediums.For concrete,gravel or soil,the overload of submunition reduces 180g/(°),7g/(°)and 3g/(°)respectively,and meanwhile the interaction time decreases,respectively,0.009ms/(°),0.033ms/(°)and 0.015ms/(°).In the oblique impact process,the submunitions have a small interaction area with ground medium,the drop energy dissipated due to plastic deformation happens in the interaction area.The submunitions may rebound with overturning.The interaction time increases and peak overload reduces by these mechanical behaviors.Compared to concrete ground,the gravel ground and soil medium have less effects on the peak overload change.

2.3 Response effects of different attack angle
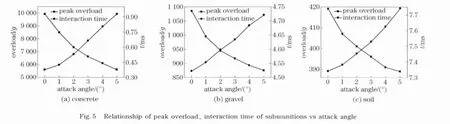
Fig.5shows that the peak overload and interaction time of submunition drop on three different ground mediums at velocity 15m/s.The results indicate that the relations between peak overload and attack angle,as well as the interaction time and attack angle are basically the same for different ground-mediums.The peak overload of submuniton reduced 862g/(°),42g/(°),6g/(°),respectively,impacting on concrete ground,gravel and soil.The interaction time increases with the increase of attack angle,respectively,the range are 0.11ms/(°),0.04ms/(°)and 0.08ms/(°).This is due to that the posture of submunition changes by the attack angle,and the interaction time increases by plastic deformation and velocity dissipation.
2.4 Effect of ground medium on submunition drop response
Fig.6illustrates the tendency of peak overload and interaction time of submunition drop on concrete ground,gravel ground and soil.The three cases are based on the drop velocity 15m/s and drop angle 90°.The concrete ground induces the largest peak overload,and the soil brings the least peak overload but the longest interaction time.Since the momentum of submuniton is constant,the interaction time decrease causes the stress increases sharply,which enhanced the peak overload.

3 Conclusions
In this paper,the impact responses of submuni-tion drop on different ground mediums are investigated numerically.The overload parameters and interaction time related to drop velocity,drop angle and attack angle are studied.In conclusion,the analysis results are presented as follow.
①When the submunition impacts on concrete ground,gravel and soil with the same drop angle and attack angle,the overload of submunition ramping increases with submunition drop velocity,and the relation of drop velocity with overload are almost linear.The interaction time of submunition impact on concrete ground and gravel ground decreases with the increase of drop velocity,but for soil,the interaction time of impact increases as the drop velocity increases.
②The peak overload of submunition increases as the drop angle increases,but the interaction time of submunition decreases.Compared to concrete ground,the gravel ground and soil medium have less effect on peak overload change.
③The peak overload of submuniton dropping on concrete ground reduces as the attack angle increases,but the interaction time increases.For the gravel ground and soil the attack angle has less effect on peak overload and interaction time.
④When submunition drops on different ground-mediums(concrete ground,gravel ground and soil)with the same drop velocity,drop angle and attack angle,change rule of the peak overload variation is:concrete ground has the biggest,followed by gravel ground and then soil.The interac-tion time,however,is the opposite.
[1] Zhang Ben,Lu Jun.The summary of spreading technology of primary-secondary bomb[J].Journal of Sichuan Ordnance,2006,3:26-29.(in Chinese)
[2] Li Min,Li Yulin.Drop-test study of parachute textile with embedded fiber optic sensors[R].Bellingham,WA:SPIE,2005:94-98.
[3] Liang Long.Dropping analysis and simulation of product package[D].Guangzhou:Jinan University,2009.(in Chinese)
[4] Du Zhenjie,Ning Jie,Zhang Yanjun.The drop-fall computer of medical kit based on MSC.Dytran [J].Machinery Design and Manufacture,2004,3:42-43.(in Chinese)
[5] Huang Tao,Zhu Ruoyan,Li Houmin.Drop simulation analysis of computer mainboard based on LS-DYNA[J].China Printing and Packaging Study,2010,1:57-58.(in Chinese)
[6] Kim Hanbala,Lee Jaijin,Park Sanghu.Application of drop-impact simulation for package cushioning material reduction[C]∥PUCA’97.1997:299-303.
[7] Kiselewiz L T,Ando K,Endo M.Numerical simulation of laptop computer drop tests[R].[S.l.]:Eng Systems Int,Asia,1993:111-119.
[8] Bai Jinze.Theoretic basis of LS-DYNA3Dand case study[M].Beijing:Science Press,2005.(in Chinese)
[9] Shi Dangyong.Dynamic explicit analysis based on ANSYS/LS-DYNA 8.1[M].Beijing:Tsinghua University Press,2005.(in Chinese)
 Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology2013年4期
Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology2013年4期
- Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology的其它文章
- Numerical simulations of stress wavepropagation and attenuation at arc-shaped interface inlayered SiC/Al composite
- Acylation of 3,4-Diaminofurazan
- Low spurious noise frequencysynthesis based on a DDS-driven wideband PLL architecture
- Simulation of multiphase boost DC-DC converter with the stable control strategy
- Fuzzycontrol method to minimize the needle deflection duringneedle insertion therapy
- Design,analysis and control for an antarctic modular manipulator
