两种方法检测血清人附睾分泌蛋白在盆腔疾病诊断中的研究
贾丽张鹏
两种方法检测血清人附睾分泌蛋白在盆腔疾病诊断中的研究
贾丽张鹏
目的:探讨血清人附睾分泌蛋白(human epididymis protein 4,HE4)在盆腔疾病诊断及鉴别诊断中的应用价值,比较电化学发光法(electrochemiluminescence immunoassay,ECLIA)及酶联免疫吸附法(Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)检测人附睾分泌蛋白的诊断准确性。方法:采用ECLIA检测211例患者血清HE4水平,包括85例卵巢癌、42例子宫内膜癌、21例子宫内膜异位症、33例盆腔良性疾病及30例健康对照者。结果以中位数表示,分析血清HE4在盆腔疾病诊断及鉴别诊断中的意义,并分别探明诊断卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌的最佳判定值。采用ELISA对其中卵巢癌组及卵巢良性疾病组血清HE4进行检测,绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC),计算曲线下面积(ROC-AUC),比较两种方法鉴别诊断卵巢良恶性疾病的准确性。结果:卵巢癌组、子宫内膜癌组血清HE4水平显著高于健康对照组、卵巢良性疾病组及子宫内膜异位症组;卵巢良性疾病组及子宫内膜异位症组与健康对照组比较,无显著性差异;HE4在鉴别诊断卵巢良恶性疾病、子宫内膜良恶性疾病时,其ROC-AUC分别为0.869和0.931,最佳诊断点分别为86.02 pmol/L和74.6 pmol/L。以卵巢良性肿瘤组作为对照,ECLIA法及ELISA法检测卵巢癌患者血清HE4的ROC-AUC分别为0.869和0.794。结论:HE4在盆腔疾病的诊断及良恶性鉴别中具有较高的诊断价值,ECLIA法检测卵巢癌的诊断准确性优于ELISA法。
人附睾分泌蛋白 卵巢癌 子宫内膜癌 子宫内膜异位症 电化学发光
近年来,卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌的发病率呈逐年上升的趋势,卵巢癌是女性生殖系统死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤,半数以上诊断时已为晚期。5年生存率仅为35%[1],远远低于早期卵巢癌90%的5年生存率,因此早期诊断是改善卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌预后的关键。CA125是传统的盆腔肿瘤标志物[2],其特点是敏感性高,尤其对晚期卵巢癌的诊断效果良好,但其特异性较低,影响其临床诊断的准确性。Moore等[3-4]报告新型肿瘤标志物人附睾分泌蛋白,与CA125相比对早期疾病具有高敏感性及高特异性的优点,弥补了CA125早期诊断敏感性低、特异性较差的缺点。本文旨在通过检测健康体检者及盆腔疾病患者血清HE4水平,探讨HE4在卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌诊断以及良恶性鉴别诊断中发挥的重要作用。目前,临床常用的HE4的检测方法有两种,即电化学发光法和酶免法。本文分别应用两种方法检测卵巢癌患者血清HE4水平,通过绘制受试者工作特征曲线并计算曲线下面积比较两种方法检测卵巢癌的效能。
1 材料与方法
1.1 标本来源及分组
选择2012年6月至11月因妇科盆腔疾病入院,并拟行手术治疗的患者,剔除存在其他原因影响肿瘤标志物检测合并症的患者,且临床资料完整。以术后病理诊断为金标准,其中包括卵巢癌组85例、子宫内膜癌组42例子宫内膜异位症组21例、卵巢良性疾病组33例,同时收集女性健康体检者血清30例作为健康对照组。本研究获患者知情同意,符合伦理委员会相关规定。
清晨空腹抽取肘部静脉血3 mL,3 000 r/min离心机中离心3 min,取上层血清待用。
1.2 仪器与方法
采用德国罗氏E170电化学发光检测仪及其配套的试剂(lot:168554)、定标液(lot:167348)、质控液(lot:168721)及其他耗材,实验前按常规对试剂进行定标及室内质控的检测;酶免法检测HE4采用康乃格公司生产的HE4检测试剂盒,依次加入随盒附带标准品、质控品及各检测标本,具体步骤参照肿瘤标志物室人附睾分泌蛋白检测SOP文件。
1.3 统计学方法
血清HE4水平频数分布不对称,呈偏态分布,以中位数表示。采用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计学处理,对不同疾病组间HE4的比较,分别采用多个独立样本的秩和检验及两组间的秩和检验。比较两种方法检测准确性时绘制受试者工作曲线,并计算ROC-AUC,用以反映诊断试验的准确性,其结果越接近1,说明诊断实验的价值越高。电化学发光法与酶免法检测结果的比较采用两相关样本秩和检验。当P<0.05时,为有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 各临床分组血清HE4检测浓度的比较
卵巢癌组及子宫内膜癌组,血清HE4水平增高。卵巢癌组血清HE4水平明显高于卵巢良性疾病组及健康对照组,子宫内膜癌组血清HE4水平明显高于子宫内膜异位症组及健康对照组,而卵巢良性疾病组、子宫内膜异位症组及健康对照组三组差异无统计学意义(表1)。
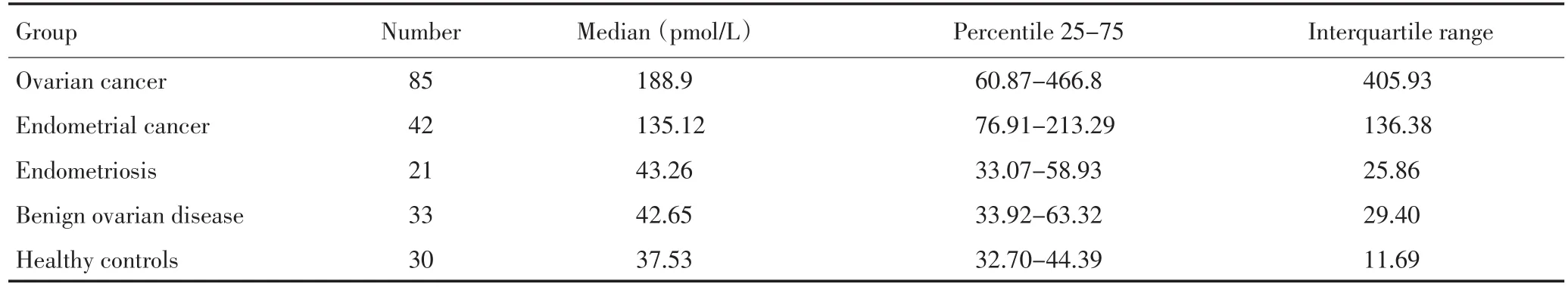
表1 各临床分组ECLIA法检测血清HE4浓度比较Table 1 HE4 concentrations in different groups as detected by ECLIA
2.2 HE4在卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌的鉴别诊断中的性能评价
血清HE4检测在鉴别诊断卵巢癌与卵巢良性疾病及子宫内膜癌与子宫内膜异位症中均具有很好的诊断准确性(ROC-AUC),由此分析其最佳判读点及最佳判读点时的敏感性及特异性(表2)。
2.3 电化学发光法与酶免法的比较
分别采用电化学发光法及酶免法检测血清HE4浓度(表3)。比较两种方法检测血清HE4水平是否相同,采用两相关样本的秩和检验,两种方法检测血清HE4水平有差异(P<0.001)。以卵巢良性疾病组作为对照组,分别绘制电化学发光法及酶免法两种方法的受试者工作曲线(图1,2),电化学发光法检测血清HE4的ROC-AUC为0.869,酶免法ROC-AUC为0.794。两种方法的最大约登指数分别为0.647和0.576,说明电化学发光法的检测效果优于酶免法。两种方法鉴别诊断卵巢癌的最佳判读值分别为86.02 pmol/L和76.76 pmol/L。

表2 ECLIA法检测HE4在卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌的鉴别诊断中的性能评价Table 2 HE4 concentrations of the differential diagnosis of ovarian and endometrial cancers by ECLIA
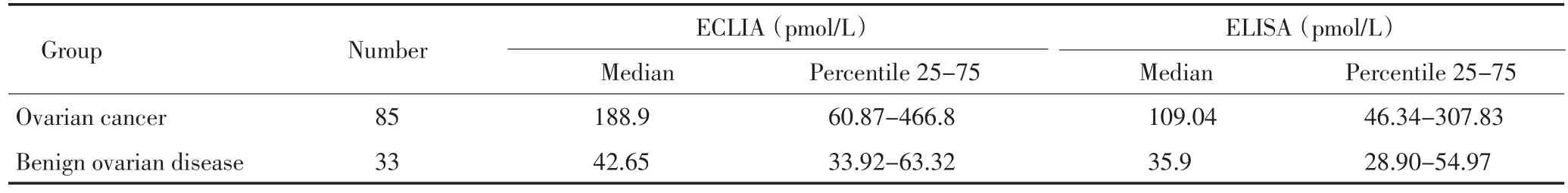
表3 两种方法血清HE4检测浓度比较Table 3 HE4 concentrations as detected by ECLIA and ELISA
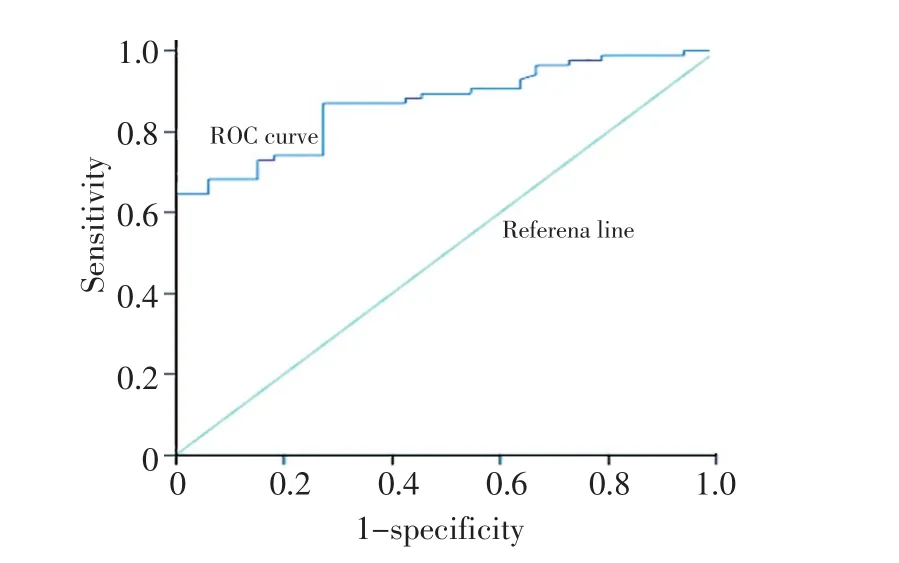
图1 电化学发光法检测HE4诊断卵巢癌的ROC曲线Figure 1 ROC curve of HE4 in the ovarian cancer group as detected by ECLIA
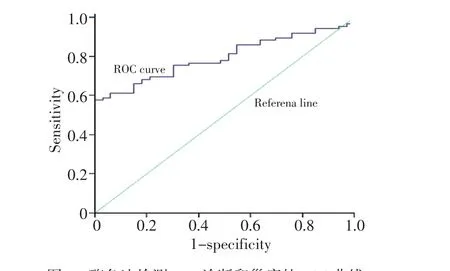
图2 酶免法检测HE4诊断卵巢癌的ROC曲线Figure 2 ROC curve of HE4 in the ovarian cancer group as detected by ELISA
3 讨论
CA125为传统的盆腔肿瘤标志物,广泛的应用于卵巢癌的诊断、复发转移的判断及疗效评估中,但在盆腔疾病的鉴别诊断中,其诊断准确性较低,在很多盆腔良性疾病中都有增高,如子宫内膜异位症、子宫腺肌症、盆腔炎症等[5-6],因此临床迫切需要一种灵敏度和特异度均较高的检测项目,以利于卵巢癌的早期诊断及盆腔疾病的鉴别诊断。
人附睾分泌蛋白(HE4)基因是由Kirchhoff等[7]发现的,其编码的蛋白质在正常的卵巢组织几乎不表达,在其他恶性肿瘤中低表达或不表达,在卵巢恶性肿瘤中表达上调[7],尤其对早期卵巢癌的诊断具有重要的诊断意义[3]。此外,有报道HE4也可作为诊断子宫内膜癌的良好血清学标志物[8]。
本研究通过对211名女性血清HE4的检测发现,卵巢癌组血清HE4水平明显高于卵巢良性疾病组及健康对照组;子宫内膜癌组血清HE4水平明显高于子宫内膜异位症组及健康对照组;卵巢良性疾病组、子宫内膜异位症组及健康对照组三组差异无统计学意义。为了探讨HE4在良恶性盆腔疾病中的诊断价值,分别以卵巢良性疾病组及子宫内膜异位症组作为对照组,计算卵巢癌及子宫内膜癌组ROC-AUC,子宫内膜癌组ROC-AUC为0.931,卵巢癌组ROC-AUC为0.869,说明HE4在鉴别子宫内膜癌与子宫内膜异位症、卵巢癌与卵巢良性疾病中均具有很高的诊断意义,这与Nolen等学者的研究结果一致[9-11]。在卵巢癌的诊断中若能联合检测CA125,根据绝经状态,计算出ROMA值,更有利于卵巢癌的风险评估。
若以0~140 pmol/L作为生物参考区间时,本研究中检测的126例非癌标本特异性为100%,均远远的低于此参考值上限。本研究通过绘制受试者工作特征曲线,在约登指数最大的点筛查实验的效果最好,在鉴别诊断卵巢癌与卵巢良性疾病时,HE4的最佳判读值为86.02,在鉴别诊断子宫内膜癌与子宫内膜异位症时,HE4的最佳判读值为74.6,而此时的特异性也均为100%。说明适当的降低血清HE4的生物参考区间,可以在不降低特异性的情况下提高检测的敏感性,所以建议实验室通过大样本的检测,建立合理的人附睾分泌蛋白生物参考区间,以提高检测的准确性。
本研究分析了电化学发光法和酶免法两种检测方法的差异,结果示同一样本ECLIA法检测值高于ELISA法检测值。通过比较两种方法鉴别诊断卵巢癌的ROC-AUC,得知ECLIA法的曲线下面积更大,说明ECLIA法的诊断准确性高于ELISA法。
1 卢仁泉,郭 林,胡 娟.人附睾上皮分泌蛋白4在卵巢癌诊治中的应用价值[J].中华检验医学杂志,2009,32(12):1379-1383.
2 Moore RG,MacLaughlan S,Bast RC Jr.Current state of biomarker development for clinical application in epithelial ovarian cancer[J].Gynecol Oncol,2010,116(2):240-245.
3 Moore RG,Brown AK,Miller MC,et al.The use of multiple novel tumor biomarker for the detection of ovarian carcinoma in patients with a pelvic mass[J].Gynecol Oncol,2008,108(2):402-408.
4 Moore RG,McMeekin DS,Brown AK,et al.A novel multiple marker bioassay utilizing HE4 and CA125 for the prediction of ovarian cancer in patients with a pelvic mass[J].Gynecol Oncol,2009,112(1):40-46.
5 Park Y,Lee JH,Hong DJ,et al.Diagnstic performances of HE4 and Ca125 for the detection of ovarian cancer from patients with various gynecologic and non-gynecologic diseases[J].Clin Biochem,2011,44(10-11):884-888.
6 Escudero JM,Auge JM,Filella X,et al.Comparison of serum human epididymis protein 4 with cancer antigen 125 as a tumor marker in patients with malignant and nonmalignant diseases[J].Clin Chem,2011,57(11):1534-1544.
7 Kirchhoff C,Habben I,Ivell R,et al.A major human epididymis-specific cDNA encodes a protein with sequence homology to extracellular proteinase inhibitors[J].Biol Reprod,1991,45(2):350-357.
8 Moore RG,Brown AK,Miller MC,et al.Utility of a novel serum tumor biomarker HE4 in patients with endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus[J].Gynecol Oncol,2008,110(2):196-201.
9 Nolen B,Velikokhatnaya L,Marrangoni A,et al.Serum biomarker panels for the discrimination of benign from malignant cases in patients with an adnexal mass[J].Gynecol Oncol,2010,117(3):440-445.
10 Anastasi E,Granato T,Marchei GG,et al.Ovarian tumor marker HE4 is differently expressed during the phases of the menstrual cycle in healthy young women[J].Tumour Biol,2010,31(5):411-415.
11 Moore RG,Jabre-Raughley M,Brown AK,et al.Comparison of a novel multiple marker assay vs the Risk of Malignancy Index for the prediction of epithelial ovarian cancer in patients with a pelvic mass[J].Am J Obstet Gynecol,2010,203(3):228.e1-228.e6.
(2012-12-28收稿)(2013-02-15修回)
Diagnosis of pelvic tumors by detecting human epididymis secretory protein via two methods
Peng ZHANG;E-mail:laopang.56@126.com
Department of Clinical Laboratory,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Treatment of Tianjin City,Tianjin 300060,China
Objective:This study aimed to evaluate the importance of human epididymis protein 4(HE4)in both simple diagnosis and differential diagnosis of pelvic diseases.This study also aimed to compare the diagnostic results of electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay(ECLIA)and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA).Methods:HE4 in serum specimens of the following groups was subjected to ECLIA:malignant ovarian tumor(85 cases);endometrial cancer(42 cases);endometriosis(21 cases);benign ovarian disease(33 cases);and healthy women(30 cases).Median scores of these groups were compared.HE4 detected by simple diagnosis and differential diagnosis of pelvic tumors were analyzed.The most accurate interpretation of the diagnosis of ovarian and endometrial cancers was evaluated.To detect HE4 in the serum specimens of the groups with malignant ovarian tumor(85 cases)and benign ovarian diseases(33 cases),ECLIA and ELISAwere performed,respectively.Areceiver operating characteristic(ROC)curve was drawn and the area under the curve(AUC)was calculated.Benign and malignant ovarian tumors were also detected by the two methods and results were analyzed.Results:The median scores of HE4 were significantly higher in malignant ovarian tumor and endometrial cancer groups than in healthy women,benign ovarian disease,and endometriosis groups.Ovarian benign disease and endometriosis groups did not have a significant difference compared with the healthy control group.For the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant ovarian tumors,ROC-AUC of HE4 was 0.869.For the differential diagnosis of endometrial benign and malignant disease,ROC-AUC of HE4 was 0.931.The most accurate interpretations of HE4 were 86.02 and 74.6 pmol/L.For HE4 detected by ECLIAand ELISA,the benign ovarian tumor group was considered as the control group.The ROC-AUCs of HE4 detected by ECLIAand ELISAwere 0.869 and 0.794,respectively.Conclusion:High diagnostic and differential diagnostic results of HE4 were observed in the benign and malignant pelvic disease groups.ECLIA was more effective than ELISA in detecting HE4 for the diagnosis of ovarian canner.
human epididymis protein 4,ovarian cancer,endometrial cancer,endometriosis,electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2013.06.004
天津医科大学附属肿瘤医院检验科,天津市肿瘤防治重点实验室(天津市300060)
*本文课题受国家“863”课题(编号:2011AA02A111)资助
张鹏 laopang.56@163.com
Li JIA,Peng ZHANG
This study was supported by the State 863 Projects of China(Grant No.2011AA02A111)
(本文编辑:周晓颖)

