DPP-4抑制剂单药治疗和联合治疗方案及疗效分析
中国人民解放军总医院内分泌科 陆菊明
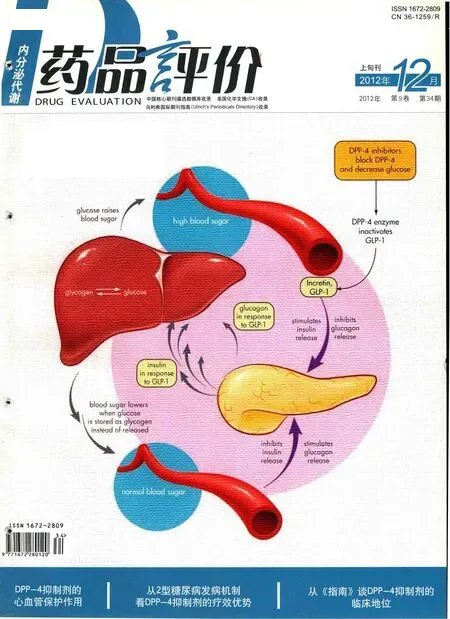
多种因素导致的胰岛素抵抗和胰岛细胞功能进行性减退是2型糖尿病的主要发病机制,其中胰岛细胞功能逐步衰竭在2型糖尿病的发生、发展过程中起着主导作用,因此,对2型糖尿病的治疗需要针对同时存在的多种病理生理缺陷。肠促胰素通过改善胰岛A和B细胞的敏感性,在葡萄糖稳态的调节中起重要作用。
两种主要的肠促胰素——胰高血糖素样肽1(GLP-1)和葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(GIP),在体内半衰期极短,迅速被二肽基肽酶-4(DPP-4)降解而失活。DPP-4抑制剂通过抑制DPP-4的活性,增加循环中活性GLP-1和GIP的水平,呈葡萄糖依赖性调节胰岛B、A细胞分泌胰岛素和胰高血糖素,同时抑制肝糖产生,并增加细胞对葡萄糖的摄取,进而有效降低血糖。
DPP-4抑制剂
在我国已经有3种DPP-4抑制剂被SFDA批准上市,分别为西格列汀、维格列汀和沙格列汀,本文仅介绍这3种药物的使用情况。
西格列汀在2006年被批准用于2型糖尿病的治疗,是第一个获批用于临床的DPP-4抑制剂。单剂量口服100mg后,西格列汀吸收迅速,口服后达峰时间1~4h,半衰期12.4h,生物利用度87%。西格列汀100mg对DPP-4活性的抑制作用可达96%,24h仍高于80%[1,2]。约79%的西格列汀以原型由肾脏排出体外,轻度肾功能不全的患者(肌酐清除率≥50ml/min)不需调整剂量,中度和重度肾功能不全者(肌酐清除率﹤50ml/min和30ml/min),西格列汀的每日剂量分别需减少至50mg和25mg[3]。
维格列汀是一种底物样DPP-4抑制剂,以共价键与DPP-4结合,吸收迅速。口服后1~2h达到最大血药浓度,半衰期2h,生物利用度85%[4]。文献报道维格列汀100mg口服后对DPP-4活性的抑制作用为95%[5]。维格列汀主要以无活性代谢产物形式经尿液排出(85%),少部分经粪便排出(15%)[6]。
沙格列汀同样以共价键的形式与DPP-4结合,5mg口服后达到最大血浆药物浓度的时间为2h,半衰期为2.5h。沙格列汀主要经肝脏细胞色素P450同工酶CYP3A4/5代谢,与CYP3A4/5强抑制剂同时用药时可能需要调整沙格列汀的剂量[7]。
DPP-4抑制剂单药治疗疗效分析
饮食和运动方案控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者,给予DPP-4抑制剂单药口服治疗,其疗效已经得到了充分证实。
在一项为期24周的随机对照试验(RCT)中,741例饮食和运动控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.0%)随机接受西格列汀100mg、200mg或安慰剂治疗24周,西格列汀100mg和200mg组HbA1c分别下降0.79%和0.94%。与安慰剂相比,标准餐负荷后2h血糖水平(2h-PPG)降低47mg/dl[8]。在亚洲人群中,530例饮食和运动控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.7%)随机接受西格列汀100mg或安慰剂治疗18周,与安慰剂相比,西格列汀组HbA1c下降1.0%,空腹血糖(FPG)和2h-PPG分别下降1.7mmol/L和3.1mmol/L[9]。1050例未经药物治疗的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c7.2%)随机分配到西格列汀100mg qd或二甲双胍1000mg bid治疗24周,西格列汀100mg组HbA1c下降0.43%,非劣效于二甲双胍1000mg bid组(HbA1c下降0.57%)[10]。
一项为期24周的RCT结果显示,维格列汀50mg qd、50mg bid、100mg qd用于354例未经药物治疗的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.4%),可使HbA1c分别下降0.5%,0.7%和0.9%[11]。在另一项为期52周的RCT研究中,780例2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.7%)随机接受维格列汀每日100mg或二甲双胍加量至每日2000mg治疗,52周后HbA1c分别下降1.0%(维格列汀100mg组)和1.4%(二甲双胍2000mg组),但两组间非劣效性检验未达到[12]。
Rosenstock等[13]评估了未经药物治疗的2型糖尿病患者接受不同剂量沙格列汀单药治疗12周的疗效,338例患者(基线HbA1c7.9%)随机接受沙格列汀2.5mg、5mg、10mg、20mg或40mg单药治疗,12周后与安慰剂组相比,HbA1c下降0.45%~0.63%。401例未经药物治疗的2型糖尿病患者分别接受沙格列汀2.5mg qd、5mg qd、10mg qd或安慰剂治疗,24周后接受沙格列汀单药治疗组HbA1c分别下降0.43%、0.46%和0.54%[14]。
DPP-4抑制剂联合治疗方案及疗效分析
1.DPP-4抑制剂与二甲双胍联用
Charbonnel等[15]评估了701例应用稳定剂量二甲双胍(≥1500mg/d)血糖控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.0%)加用西格列汀100mg qd治疗24周的疗效,结果与安慰剂组相比,西格列汀组HbA1c下降0.65%,FPG下降1.4mmol/L。1172例二甲双胍单药控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c7.5%)随机分别加用西格列汀100mg qd或格列吡嗪最大日剂量20mg,治疗52周后两组HbA1c分别下降0.67%,西格列汀联合二甲双胍治疗的疗效非劣效于格列吡嗪联合二甲双胍,两治疗组HbA1c达标率<7%,和FPG下降(0.56mmol/L vs 0.42mmol/L)相似,而西格列汀组低血糖明显少于格列吡嗪组(5% vs 32%)。西格列汀组体重减轻1.5kg,而格列吡嗪组体重增加1.1kg[16]。在另一项研究中,二甲双胍稳定剂量控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者随机加用西格列汀100mg/d或格列美脲加量至6mg/d治疗30周,两治疗组HbA1c下降相似(0.47% vs 0.54%),但西格列汀组低血糖更少(7% vs 22%)且体重减轻0.8kg[17]。一项为期18周的研究显示,二甲双胍稳定剂量治疗的基础上分别加用西格列汀100mg或罗格列酮8mg治疗,可使HbA1c分别下降0.51%(西格列汀组)和0.57%(罗格列酮组),两组HbA1c达标率相似(55% vs 63%)。罗格列酮组体重增加1.5kg,而西格列汀组体重减轻0.4kg[18]。在近期的一项研究中,395例二甲双胍稳定剂量控制不佳的中国2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.5%)加用西格列汀100mg qd治疗,24周后可使HbA1c进一步下降0.9%,FPG和2h-PPG分别下降
1.2mmol/L和1.9mmol/L[19]。
二甲双胍单药(≥1500mg/d)控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.4%)加用维格列汀50mg qd、50mg bid治疗24周,与加用安慰剂相比可使HbA1c分别下降0.7%和1.1%,FPG分别下降0.8mmol/L和1.7mmol/L[20]。576例二甲双胍单药控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.4%),加用维格列汀50mg bid或吡格列酮 30mg qd治疗24周,HbA1c下降相似(0.9% vs 1.0%)[21]。在一项为期2年的RCT中,3118例二甲双胍单药控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c7.3%)分别加用维格列汀50mg bid或格列美脲 6mg qd治疗,两治疗组HbA1c均下降0.1%,而维格列汀组低血糖少于格列美脲组(2.3% vs 18.2%)。维格列汀组体重减轻0.3kg,而格列美脲组增加1.2kg[22]。
在二甲双胍稳定剂量(1500~1700mg/d)控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者中,对比加用沙格列汀5mg/d或二甲双胍加量至2500mg/d的疗效。治疗24周之后,加用沙格列汀组HbA1c下降0.47%,二甲双胍加量组HbA1c下降0.38%,两组FPG均下降1.1mmol/L[23]。在另一项RCT中,858名二甲双胍单药控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者随机加用沙格列汀5mg/d或格列吡嗪5~20mg/d治疗,52周后两组HbA1c下降相似(0.74% vs 0.80%),但沙格列汀组低血糖少于格列吡嗪组(3.0% vs 36.3%)。沙格列汀组体重减轻1.1kg,而格列吡嗪组体重增加1.1kg[24]。
2.DPP-4抑制剂与磺脲类药物联用
Hermansen等[25]评估了格列美脲(>4mg/d)单药控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者分别加用西格列汀100mg qd或安慰剂治疗24周的疗效,结果发现与安慰机组相比,格列美脲加用西格列汀可使HbA1c进一步下降0.57%,但低血糖发生率有所增加(7.5% vs 2.8%)。
在515例格列美脲单药(4mg/d)治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者中,分别加用维格列汀50mg qd、100mg qd或安慰剂治疗24周,维格列汀两个剂量组HbA1c与加用安慰剂组相比分别降低0.6%和0.7%。低血糖发生率分别为3.6%(维格列汀100mg组)、1.2%(维格列汀50mg组)和0.6%(安慰剂组)[26]。
在一项为期24周的研究中,格列本脲单药(7.5mg/d)治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者分别加用沙格列汀2.5mg/d或5mg/d,治疗24周后,与格列本脲加量至10mg/d相比,沙格列汀联用组HbA1c分别下降0.54%(2.5mg/d组)和0.64%(5mg/d组),且低血糖在沙格列汀联用组的发生率与格列本脲加量组相当[27]。在随后进行的52周延长试验中,相比于格列本脲加量组,HbA1c在各沙格列汀联用组分别下降0.59%和0.67%[28]。
3.DPP-4抑制剂与噻唑烷二酮类药物联用
Rosenstock等[29]评估了353例接受稳定剂量吡格列酮单药(30mg/d或45mg/d)治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者随机加用西格列汀100mg qd或安慰剂治疗的疗效,治疗24周后加用西格列汀组HbA1c相比于安慰剂组下降0.7%,FPG下降1.0mmol/L,两治疗组低血糖(1.1% vs 0%)和水肿(5.1% vs 3.9%)的发生率相似。134例日本2型糖尿病患者接受吡格列酮单药15~45mg/d治疗的基础上随机加用西格列汀50mg/d(可增量至100mg/d)或安慰剂治疗的疗效,与加用安慰剂组相比,加用西格列汀组治疗12周时HbA1c下降0.8%[30]。另一项为期12个月的研究对比了吡格列酮单药(30mg/d)的基础上分别加用西格列汀100mg/d或二甲双胍850mg/d的疗效,结果显示两治疗组HbA1c均下降1.4%[31]。
463例吡格列酮单药治疗(45mg/d)控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.7%)分别加用维格列汀50mg qd或bid治疗24周,使HbA1c相对于较安慰剂组分别下降0.8%和1.0%。加用维格列汀两个剂量组外周水肿的发生率均高于安慰剂组(8.2%、7.0% vs 2.5%)[32]。
565例吡格列酮(30mg/d或45mg/d)或罗格列酮(4mg/d或8mg/d)单药治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者随机加用沙格列汀(2.5mg或5mg qd)或安慰剂治疗24周,结果显示与安慰剂组相比,加用沙格列汀分别可使HbA1c下降0.36%(2.5mg组)和0.63%(5mg组),但加用沙格列汀5mg剂量组外周水肿的发生率(8.1%)高于沙格列汀2.5mg组(3.1%)和安慰剂组(4.3%)[33]。在随后进行的52周延长试验中,相比于安慰剂组,HbA1c在沙格列汀各剂量组分别下降0.39%和0.89%[34]。
4.DPP-4抑制剂与胰岛素联用
接受胰岛素治疗控制不佳的641例2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.7%)随机加用西格列汀100mg qd或安慰剂治疗,24周后加用西格列汀组HbA1c与安慰剂组相比下降0.6%,但低血糖发生率在西格列汀组有所增加(16% vs 8%)[35]。另一项研究在140例胰岛素治疗控制不佳的韩国2型糖尿病患者中评估了加用西格列汀100mg qd与胰岛素加量治疗的疗效,24周后加用西格列汀组观察到更显著的HbA1c下降(0.6% vs 0.2%),且西格列汀联用组低血糖(8.2% vs 17.5%)及严重低血糖(1.6% vs 4.8%)的发生率均低于胰岛素加量组[36]。
在Fonseca等人的研究中,接受胰岛素治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c8.4%)加用维格列汀50mg bid治疗24周可使 HbA1c较安慰剂组下降0.3%,维格列汀组与安慰剂组低血糖的发生率分别为2%和3%[37]。近期的另一项研究也得到了类似的结果,接受胰岛素治疗的基础上加用维格列汀50mg bid,治疗24周HbA1c较基线下降0.8%,且低血糖发生率与安慰剂组相似(8.4% vs 7.2%)[38]。
455例胰岛素治疗控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者分别加用沙格列汀5mg qd或安慰剂治疗24周,沙格列汀组HbA1c较安慰剂组下降0.41%,低血糖发生率与安慰剂组相似(5.3% vs 3.3%)[39]。
5.DPP-4抑制剂的三药联合治疗
在二甲双胍与格列美脲联用控制不佳的基础上,添加西格列汀100mg qd或安慰剂治疗24周,与安慰剂组相比加用西格列汀组HbA1c下降0.89%,但低血糖发生率有所升高(16.4% vs 0.9%)[25]。另一项为期54周的研究评估了西格列汀与二甲双胍、罗格列酮三药联用的疗效,结果显示加用西格列汀组HbA1c相比于加用安慰剂组下降0.8%,同时低血糖发生率与安慰剂组相似[40]。37名二甲双胍与磺脲类药物联用的2型糖尿病患者(基线HbA1c9.3%),添加维格列汀100mg/d治疗6~15个月,HbA1c较基线下降1.6%[41]。
6.DPP-4抑制剂起始联合治疗
除了在其他降糖药物的基础之上加用DPP-4抑制剂之外,此类药物用于2型糖尿病的起始联合治疗,其疗效也已经得到了证实。
在一项为期24周的研究中,西格列汀100mg/d与二甲双胍1000mg/d起始联合治疗可使HbA1c较基线(HbA1c8.8%)下降1.4%,而西格列汀100mg/d与二甲双胍2000mg/d起始联合则可以降低HbA1c达1.9%[42]。在随后进行的延长试验中(30周+50周),与基线相比HbA1c在两个联合治疗组分别下降1.4%和1.7%[43]。可见,西格列汀与二甲双胍起始联合可持续有效降低血糖。在Yoon等人的研究中,西格列汀100mg qd与吡格列酮30mg qd起始联合治疗24周,HbA1c较基线(HbA1c9.5%)降低2.4%,HOMA-β较基线升高31%,HOMA-IR较基线降低2.7,有效改善血糖的同时也可显著改善B细胞功能[44]。在随后进行的30周延长试验中,吡格列酮日剂量增加至45mg,与西格列汀100mg qd联用,HbA1c较基线下降2.4%[45]。
Bosi等观察了初诊的2型糖尿病患者分别接受维格列汀50mg bid与二甲双胍500mg或1000mg bid起始联合治疗的疗效,结果显示治疗24周后,维格列汀联合二甲双胍可使HbA1c降低1.6%(50mg/500mg组)和1.8%(50mg/1000mg组)[46]。
未经药物治疗的2型糖尿病患者,随机接受沙格列汀5mg或10mg与二甲双胍加量至2000mg/d联合治疗,24周后两个剂量组HbA1c较基线均下降2.5%[47]。在随后进行的52周延长试验中,两个联合剂量组HbA1c较基线均下降2.3%[48]。
综上所述, 无论是饮食和运动方案控制不佳的基础上单药治疗,或是与二甲双胍、磺脲类药物、噻唑烷二酮类药物或胰岛素联合应用,DPP-4抑制剂均能持续有效地降低HbA1c、FPG和PPG,不增加体重和低血糖风险,且不良反应少见。尽管在上述研究中HbA1c的下降值有所不同,但在分析中发现,在矫正基线HbA1c值后,多种DPP-4抑制剂的降糖效应是相近的。目前,DPP-4抑制剂已经得到了包括《中国2型糖尿病防治指南》、美国糖尿病协会(ADA)和美国临床内分泌医师协会(AACE)糖尿病《指南》在内的多个国家糖尿病治疗《指南》的推荐。作为一种新型口服降糖药,DPP-4抑制剂有望成为治疗2型糖尿病的重要选择。
[1] Bergman AJ, Stevens C, Zhou Y, et al.Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of multiple oral doses of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor:a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in healthy male volunteers[J].Clinical therapeutics, 2006, 28:55-72.
[2] Alba M, Sheng D, Guan Y, et al.Sitagliptin 100mg daily effect on DPP-4 inhibition and compound-specific glycemic improvement[J].Current medical research and opinion, 2009, 25:2507-2514.
[3] Bergman AJ, Cote J, Yi B, et al.Effect of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor[J].Diabetes care, 2007, 30:1862-1864.
[4] He YL, Sadler BM, Sabo R, et al.The absolute oral bioavailability and population-based pharmacokinetic modelling of a novel dipeptidylpeptidase-IV inhibitor, vildagliptin, in healthy volunteers[J].Clinical pharmacokinetics, 2007, 46:787-802.
[5] He YL, Serra D, Wang Y, et al.Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Clinical pharmacokinetics, 2007, 46:577-588.
[6] He H, Tran P, Yin H, et al.Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of [14C]vildagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, in humans[J].Drug metabolism and disposition:the biological fate of chemicals, 2009, 37:536-544.
[7] Bristol-Myers Squibb.Onglyza (saxagliptin) tablets:US prescribing information.Available at:http://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_ onglyza.pdf.Accessed 2009.
[8] Aschner P, Kipnes MS, Lunceford JK, et al.Effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes care, 2006, 29:2632-2637.
[9] Mohan V, Yang W, Son HY, et al.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes in China, India, and Korea[J].Diabetes research and clinical practice, 2009, 83:106-116.
[10] Aschner P, Katzeff HL, Guo H, et al.Efficacy and safety of monotherapy of sitagliptin compared with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2010, 12:252-261.
[11] Pi-Sunyer FX, Schweizer A, Mills D, et al.Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes research and clinical practice, 2007, 76:132-138.
[12] Schweizer A, Couturier A, Foley JE, et al.Comparison between vildagliptin and metformin to sustain reductions in HbA(1c) over 1 year in drug-naive patients with Type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetic medicine:a journal of the British Diabetic Association, 2007, 24:955-961.
[13] Rosenstock J, Sankoh S, List JF.Glucose-lowering activity of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2008, 10:376-386.
[14] Rosenstock J, Aguilar-Salinas C, Klein E, et al.Effect of saxagliptin monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Current medical research and opinion, 2009, 25:2401-2411.
[15] Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, et al.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone[J].Diabetes care, 2006, 29:2638-2643.
[16] Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, et al.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone:a randomized, double-blind, noninferiority trial[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2007, 9:194-205.
[17] Arechavaleta R, Seck T, Chen Y, et al.Efficacy and safety of treatment with sitagliptin or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy:a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2011, 13:160-168.
[18] Scott R, Loeys T, Davies MJ, et al.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2008, 10:959-969.
[19] Yang W, Guan Y, Shentu Y, et al.The addition of sitagliptin to ongoing metformin therapy significantly improves glycemic control in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes[J].J Diabetes, 2012, 4:227-237.
[20] Bosi E, Camisasca RP, Collober C, et al.Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin[J].Diabetes care, 2007, 30:890-895.
[21] Bolli G, Dotta F, Rochotte E, et al.Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin vs pioglitazone when added to metformin:a 24-week, randomized, double-blind study[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2008, 10:82-90.
[22] Matthews DR, Dejager S, Ahren B, et al.Vildagliptin add-on to metformin produces similar efficacy and reduced hypoglycaemic risk compared with glimepiride, with no weight gain:results from a 2-year study[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2010, 12:780-789.
[23] Hermans MP, Delibasi T, Farmer I, et al.Effects of saxagliptin added to sub-maximal doses of metformin compared with uptitration of metformin in type 2 diabetes:the PROMPT study[J].Current medical research and opinion, 2012, 28:1635-1645.
[24] Goke B, Gallwitz B, Eriksson J, et al.Saxagliptin is non-inferior to glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin alone:a 52-week randomised controlled trial[J].International journal of clinical practice, 2010, 64:1619-1631.
[25] Hermansen K, Kipnes M, Luo E, et al.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on glimepiride alone or on glimepiride and metformin[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2007, 9:733-745.
[26] Garber AJ, Foley JE, Banerji MA, et al.Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with a sulphonylurea[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2008, 10:1047-1056.
[27] Chacra AR, Tan GH, Apanovitch A, et al.Saxagliptin added to a submaximal dose of sulphonylurea improves glycaemic control compared with uptitration of sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes:a randomised controlled trial[J].International journal of clinical practice, 2009, 63:1395-1406.
[28] Chacra AR, Tan GH, Ravichandran S, et al.Safety and efficacy of saxagliptin in combination with submaximal sulphonylurea versus uptitrated sulphonylurea over 76 weeks[J].Diabetes &vascular disease research :official journal of the International Society of Diabetes and Vascular Disease, 2011, 8:150-159.
[29] Rosenstock J, Brazg R, Andryuk PJ, et al.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing pioglitazone therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes:a 24-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallelgroup study[J].Clinical therapeutics, 2006, 28:1556-1568.
[30] Kashiwagi A, Kadowaki T, Nonaka K, et al.Sitagliptin added to treatment with ongoing pioglitazone for us to 52 weeks improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes[J].J Diabetes Invest, 2011, 2:381-390.
[31] Derosa G, Maffioli P, Salvadeo SA, et al.Effects of sitagliptin or metformin added to pioglitazone monotherapy in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J].Metabolism:clinical and experimental, 2010, 59:887-895.
[32] Garber AJ, Schweizer A, Baron MA, et al.Vildagliptin in combination with pioglitazone improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes failing thiazolidinedione monotherapy:a randomized, placebo-controlled study[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2007, 9:166-174.
[33] Hollander P, Li J, Allen E, et al.Saxagliptin added to a thiazolidinedione improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate control on thiazolidinedione alone[J].The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 2009, 94:4810-4819.
[34] Hollander PL, Li J, Frederich R, et al.Safety and efficacy of saxagliptin added to thiazolidinedione over 76 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Diabetes &vascular disease research:official journal of the International Society of Diabetes and Vascular Disease, 2011, 8:125-135.
[35] Vilsboll T, Rosenstock J, Yki-Jarvinen H, et al.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2010, 12:167-177.
[36] Hong ES, Khang AR, Yoon JW, et al.Comparison between sitagliptin as add-on therapy to insulin and insulin dose-increase therapy in uncontrolled Korean type 2 diabetes:CSI study[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2012, 14:795-802.
[37] Fonseca V, Schweizer A, Albrecht D, et al.Addition of vildagliptin to insulin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetologia, 2007, 50:1148-1155.
[38] Kothny W, Foley J, Kozlovski P, et al.Improved glycaemic control with vildagliptin added to insulin, with or without metformin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2012, doi:10.1111/dom.12020.
[39] Barnett AH, Charbonnel B, Donovan M, et al.Effect of saxagliptin as add-on therapy in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes on insulin alone or insulin combined with metformin[J].Current medical research and opinion, 2012, 28:513-523.
[40] Dobs AS, Goldstein BJ, Aschner P, et al.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin and rosiglitazone combination therapy in a randomized, placebo-controlled, 54-week trial in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].J Diabetes, 2012.doi:10.1111/j.1753-0407.2012.00223.x.
[41] Vilar L, Gusmao A, Albuquerque JL, et al.Effectiveness of adding vildagliptin to the treatment of diabetic patients nonresponsive to the combination of metformin and a sulphonylurea[J].Arquivos brasileiros de endocrinologia e metabologia, 2011, 55:260-265.
[42] Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, et al.Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes care, 2007, 30:1979-1987.
[43] Williams-Herman D, Johnson J, Teng R, et al.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and metformin as initial combination therapy and as monotherapy over 2 years in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2010, 12:442-451.
[44] Yoon KH, Shockey GR, Teng R, et al.Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and pioglitazone on glycemic control and measures of beta-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].International journal of clinical practice, 2011, 65:154-164.
[45] Yoon KH, Steinberg H, Teng R, et al.Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes:a 54-week study[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2012, 14:745-752.
[46] Bosi E, Dotta F, Jia Y, et al.Vildagliptin plus metformin combination therapy provides superior glycaemic control to individual monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2009, 11:506-515.
[47] Jadzinsky M, Pfutzner A, Paz-Pacheco E, et al.Saxagliptin given in combination with metformin as initial therapy improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with either monotherapy:a randomized controlled trial[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2009, 11:611-622.
[48] Pfutzner A, Paz-Pacheco E, Allen E, et al.Initial combination therapy with saxagliptin and metformin provides sustained glycaemic control and is well tolerated for up to 76 weeks[J].Diabetes, obesity &metabolism, 2011, 13:567-576.