直接PCI患者LVEF与BNP的相关性及其预后预测价值的临床研究
张鸿举 刘孝钧 尚咏琦 梁毅 丁少娟 王相智 吴慧敏 李文 李莉 叶兴
直接PCI患者LVEF与BNP的相关性及其预后预测价值的临床研究
张鸿举 刘孝钧 尚咏琦 梁毅 丁少娟 王相智 吴慧敏 李文 李莉 叶兴
目的研究直接PCI患者左室射血分数(LVEF)与脑型钠尿肽(BNP)之间的相关性,分析LVEF与血BNP对于直接PCI患者预后的预测作用。方法57例连续选入的接受直接PCI植入支架的急性心肌梗死患者,分别于入院后24 h内、1周、2周、1月和6月进行血BNP检测及超声心动图测定LVEF。所有患者随访1年,记录主要不良心脏事件(MACE)发生情况,分析MACE与BNP以及LVEF之间的相关性。结果患者入院后24 h内、1周、2周、1月和6月的血BNP与LVEF均呈显著负相关,相关系数 r分别为-0.896(P=0.000)、-0.891(P=0.000)、-0.887(P=0.000)、-0.871(P=0.000)和-0.876(P=0.000)。随访1 年,共发生MACE 36 例,MACE 与入院后24 h(r=0.742,P=0.000)、1 周(r=0.719,P=0.000)的血BNP水平呈显著正相关;MACE与入院后24 h(r=-0.813,P=0.000)、1周(r=-0.762,P=0.000)、2周(r=-0.867,P=0.000)的LVEF呈显著负相关。多元logistic回归分析显示,入院1周的BNP值以及入院24 h的LVEF是MACE的独立预测因子。入院1周BNP的ROC曲线下面积0.812(P=0.000),其面积95%可信区间为[0.729,0.893],不包括0.5;入院1周LVEF的ROC曲线下面积0.822(P=0.000),其面积95%可信区间为[0.764,0.923],也不包括0.5;入院1周的BNP值以及入院1周的LVEF的拐点分别为226.36ng/L和48%。结论对于接受直接PCI植入支架的急性心肌梗死患者,BNP与LVEF预后有密切的关系,尤其是入院1周的BNP值以及入院24 h的LVEF可有效预测入院后1年内的MACE事件发生情况。
直接PCI;脑型钠尿肽;左室射血分数;预后
急性心肌梗死(AMI)是常见中老年急症,直接PCI能够尽早尽快恢复梗死心肌的血流供应,是目前治疗AMI最有效最安全的方法[1-2]。AMI患者心功能及BNP都可能发生改变,LVEF是临床上最常用的心功能指标,BNP是心力衰竭的一大特征性指标[3-6],因而我们推测,LVEF及 BNP与直接PCI患者的远期预后有关联。本研究的目的就是探索直接PCI患者BNP及LVEF的相互关系,及其对患者远期预后的预测作用。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 2010年1月至2011年10月在我院行直接PCI植入雷帕霉素洗脱支架的AMI患者中,连续选入57例单支冠状动脉病变的患者。入选患者年龄51~71岁,平均(52.7±5.7)岁,其中79%为男性。
1.2 LVEF的测定 患者入院后24 h内、1周、2周、1月和6月分别行超声心动图检查,获得这5个时间的LVEF值。LVEF检测由超声科2名医师独立完成,结果取二者的平均值。
1.3 BNP测定 患者入院后24 h内、1周、2周、1月和6月采集静脉血用于BNP检测,方法:利用BNP检测板(变异系数CV<10%)和免疫荧光分析仪,采用免疫荧光法,按照说明说操作完成检测。
1.4 术后随访 术后随访1年,随访方法:电话随访或门诊随访。随访观察指标:死亡、再发心肌梗死、再发心绞痛、心力衰竭和心源性休克。支架内再狭窄确定标准为:冠状动脉造影显示原支架段直径狭窄≥50%。
1.5 统计学方法 所有资料采用SPSS 16.0统计软件包进行统计分析,连续变量以均数±标准差表示,分类变量以率表示;采用Spearman等级相关分析法进行关联分析,相关分析采用多元二分类logistic回归分析,ROC曲线确定指标的预测特性。
2 结果
57例患者平均年龄(56.3±4.6)岁,男性占79%,有、无心脏事件的患者在年龄、性别、高血压、高脂血症、糖尿病、病变血管及病变分布方面无显著差异。研究过程中共死亡3例,死亡时间分别为术后1周、2周、5周,原因不明。共发生主要心脏事件36例,包括死亡3例、再发心绞痛11例和急性心肌梗死15例,其中12例经冠脉造影证实为支架内再狭窄,行靶病变再次血运重建。
双变量相关分析显示,患者入院后24 h内、1周、2周、1月和6月的血BNP与LVEF均呈负相关,相关系数r分别为-0.896(P=0.000)、-0.891(P=0.000)、-0.887(P=0.000)、-0.871(P=0.000)和-0.876(P=0.000)。MACE与入院后24 h(r=0.742,P=0.000)、1 周(r=0.719,P=0.000)的血 BNP水平呈显著正相关,与入院后2周(r=0.225,P=0.000)、1月(r=0.309,P=0.000)、6 月(r=0.198,P=0.000)的血BNP水平呈弱正相关;MACE与入院后24 h(r=-0.813,P=0.000)、1 周(r=-0.762,P=0.000)、2 周(r=-0.867,P=0.000)的LVEF呈显著负相关,与入院后1月(r=-0.207,P=0.000)、6月(r=-0.297,P=0.000)的LVEF呈弱负相关。
多元logistic回归分析显示,入院1周的BNP值以及入院24 h的LVEF是MACE的独立预测因子(P=0.001;P=0.000)。相应的ROC曲线见图1和图2,入院1周 BNP的ROC曲线下面积0.812(P=0.000),其面积95%可信区间为[0.729,0.893],不包括0.5;入院1周 LVEF的ROC曲线下面积0.822(P=0.000),其面积95%可信区间为[0.764,0.923],也不包括0.5。入院1周的BNP值以及入院1周的LVEF的拐点分别为226.36ng/L和48%。
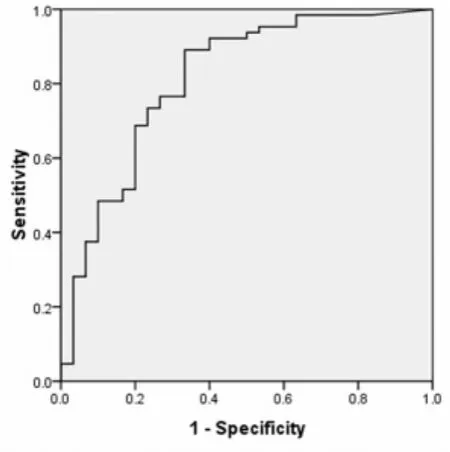
图1 入院1周BNP判定MACE的ROC曲线(拐点=226.36ng/L)

图2 入院1周LVEF判定MACE的ROC曲线(拐点=48%)
3 讨论
心力衰竭是各种心脏病晚期的共同结局,已有诸多研究证实,任何原发心脏疾病引起的心力衰竭都伴有血BNP的增高[3-7]。BNP的主要作用为利尿,利钠、增加肾小球滤过率,无利钾作用,扩张动脉、静脉,降低肺动脉锲压(PCWP)、体循环阻力(SVR)、平均右房压(MRAP),抑制血浆肾素和醛固酮水平[8-10]。BNP用于急性心肌梗死患者的预后研究已有多个报道[11-13]。研究显示,LVEF是直接PCI患者MACE的独立预测因子[14]。本研究旨在探讨直接 PCI患者不同时期血BNP与LVEF的关系及其对MACE的预测意义。
本研究显示,对直接PCI植入支架的患者,入院1周的BNP值以及入院24 h的LVEF是直接PCI患者术后1年MACE的独立预测因子;其拐点分别为226.36ng/L和48%。并且所测五个时间点的BNP和LVEF分别呈正相关关系,这与先前的报道[15,16]是一致的。BNP和LVEF检测操作简便快捷,对患者的临床预后有良好的预测价值,值得临床进一步推广。
[1] Wright RS,Anderson JL,Adams CD,et al.2011 ACCF/AHA Focused Update of the Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction(Updating the 2007 Guideline):a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines.Circulation,2011,123(18):2022-2060.
[2] Kushner FG,Hand M,Smith SC Jr,et al.2009 focused updates:ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction(updating the 2004 guideline and 2007 focused update)and ACC/AHA/SCAI guidelines on percutaneous coronary intervention(updating the 2005 guideline and 2007 focused update)a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines.J Am Coll Cardiol,2009,54(23):2205-2241.
[3] Hoekstra T,Jaarsma T,van Veldhuisen DJ,et al.Quality of life and survival in patients with heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail,2012 Sep 18.[Epub ahead of print].
[4] Guazzi M,Vitelli A,Arena R.The effect of exercise training on plasma NT-pro-BNP levels and its correlation with improved exercise ventilatory efficiency in patients with heart failure.Int J Cardiol,2012,158(2):290-291.
[5] Palazzuoli A,Caputo M,Calabrò A,et al.Clinical impact of BNP and other emerging biomarkers in heart failure evaluation and management.Minerva Cardioangiol,2012,60(2):183-194.
[6] Palazzuoli A,Gallotta M,Quatrini I,et al.Natriuretic peptides(BNP and NT-proBNP):measurement and relevance in heart failure.Vasc Health Risk Manag,2010,6:411-418.
[7] Smart NA,Steele M.Systematic review of the effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on systemic brain natriuretic peptide(BNP)and N-terminal BNP expression in heart failure patients.Int J Cardiol,2010,140(3):260-265.
[8] Mils R M,LeJ emtel T H,Horton D P,et al.Sustained hemodynamic effects of an infusion of nesiritide(human a-type natriuretic peptide)in heat failure.J Am coll Cardiol,1999,34:155-162.
[9] Colucci W S,Elkayam U,Horton DP,et al.Intravenous nesiritide,a natriuretic peptide,in the treatent of decompensated congestive heart failure.N Engl J Med,2000,343:246.
[10] Mair J,Lercher A H,Puschendort B.The impact of cardiac natriuretic peptide determination on the diagnosis and management of heart failure.Clin Chem Lab Med,2001,39(7):571-588.
[11] Lain B,SQUIRE,Russell J.O'BRIEN,Bettina DEMME,et al.N-terminal pro-atrial natriuretic peptide(N-ANP)and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide(N-BNP)in the prediction of death and heart failure in unselected patients following acute myocardial infarction.Clinical Science,2004,107:309-316.
[12] Braunwald E.Acute coronary syndromes:BNP measurement predicts AMI risk in the elderly.Nat Rev Cardiol,2009,6(8):503-504.
[13] Tycińska AM,Sawicki R,Mroczko B,et al.Admission B-type natriuretic peptide level predicts long-term survival in low risk ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients.Kardiol Pol,2011,69(10):1008-1014.
[14] Wang CH,Fang Q,Zhang SY,et al.Long-term effects of drug-eluting stents versus bare met al stents on patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention:outcomes of 3-year clinical follow-up.Chin Med J(Engl),2012,125(16):2803-2806.
[15] Kohno M,Kano H,Horio T,et al.Inhibition of endothelin production by adrenomedullin in vascular smooth muscle cells.Hypertension,1995,6:1185-1190.
[16] Sugo S,Minamino N,Shoji H,et al.Effects of vasoactive substances and cAMP related compounds on adrenomedullin production in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells.FEBS Lett,1995,369(2-3):311-314.
The correlation between BNP and LVEF and their predictive value on prognosis in patients received e-mergency PCI
ZHANG Hong-ju,LIU Xiao-jun,SHANG Yong-qi,et al.Department of Cardiology,The First People's Hospital of Xuzhou,Xuzhou 221002,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the correlation between BNP and LVEF,and to evaluate their predictive value on prognosis in patients
emergency PCI.Methods57 consecutive patients underwent primary PCI were selected for determining BNP level and LVEF at 24 hours,1 week,2 weeks,1 month and 6 months after the stent implantation.All cases were followed up for 1 year to record major adverse clinical events(MACE).Then the correlations of BNP and LVEF to MACE were analyzed.ResultsBNP level and LVEF at 24 hours,1 week,2 weeks,1 month and 6 months after the stent implantation were negatively correlated respectively,of which correlation coefficient were-0.896(P=0.000),-0.891(P=0.000),-0.887(P=0.000),-0.871(P=0.000)and-0.876(P=0.000)respectively.36 MACEs occurred during the 1-year follow-up.MACE had a significantly positive correlation with BNP level of 24 hours(r=0.742,P=0.000)and 1week(r=0.719,P=0.000)after admission and a significantly negative correlation with LVEF of 24 hours(r=-0.813,P=0.000),1week(r=-0.762,P=0.000)and 2 weeks(r=-0.867,P=0.000)after admission.According to logistic regression analysis,BNP level of 1 week after admission and LVEF at 24 hours after admission were all independent predictors to MACE in patients underwent primary PCI during the first year after operation(P=0.001;P=0.000).The area under curve(AUC)of the BNP level of 1 week after admission and LVEF at 24 hours after admission on ROC were 0.812(P=0.000)and 0.822(P=0.000)respectively and 95%confidence interval were[0.729,0.893]and[0.764,0.923],respectively.According to ROC,inflection point of the BNP level of 1 week after admission and LVEF at 24 hours after admission were 226.36ng/L and 48%,respectively.ConclusionFor patients received primary PCI,BNP level and LVEF are significantly correlated with their prognosis and especially,BNP level of 1 week after admission and LVEF at 24 hours after admission are effective in predicting MACE during the first year after operation.
Emergency PCI;BNP;LVEF;Prognosis
221002徐州市第一人民医院心内科

