Developing Potential of Low-carbon Agriculture in Heilongjiang Province
Yang Hui, Li Cui-xia*, Chen Yao, and Fu Rao
1 College of Economics and Management, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
2 Publishing Center, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
3 Harbin No.72 Middle School, Harbin 150056, China
Introduction
The concept of low-carbon economy was first proposed in 2003 by the United Kingdom, followed by the development of low-carbon economy and had gradually become a global consensus. The development of low-carbon economy made the United States out of economic crisis, releading the strategic choice of the world economy; the EU thought low carbon economy as a new industrial revolution(Levine, 2007). In 2007, China began to speed up the resource-saving and environment-friendly society;by 2020, bringing down CO2per unit of GDP from 40% to 45% as compared with 2005 in order to walk in the forefront of the world and commitment to the international obligations of the Third World Country(Ren, 2009). Although the Copenhagen Summit in 2009 adopted a non-legally binding agreement, the game around the world of low-carbon economy would exist for a long time and have a decisive impact in the multipolar world.
Concept of Low-carbon Agriculture
Low-carbon economy is referred to the development mode of the least greenhouse gas emissions and the maximum output in a community economy. Many people disagree to link agriculture and low-carbon economy that reduce greenhouse gas emission (Williams, 1987). In their views, planting and breeding produced agricultural products are not associated with green-house gas emission. It sounds reasonable, but with careful analysis, it might find that agricultural production and management do not match with the reality. Firstly, from the point of view of agricultural inputs, it includes both the agricultural outputs inputs to their activities, such as seeds, organic fertilizers,and the output of industrial production inputs, such as fertilizers, pesticides, and agricultural films. The former investment and greenhouse gas emission have little correlation, but the latter inputs and greenhouse gas emission have a great related degree. Secondly,from the point of view of manufacture and use of agricultural machinery, it is inseparable from power,oil, and other energy uses. Thirdly, from the point of view of the processing of agricultural products and circulation, and the energy use is essential. Product sales, packing whether or not, must use certain consumption, such as farmers' market, supermarket bags and so on. Finally, from the point of view of handling and utilizing agricultural waste, it must consume energy, even they do not use the processing power and energy, only low-level form of treatment.Through the above statements, it can be identified that energy consumption and green-house gas emission have great correlation with the whole agricultural production process (Gold, 1999). From the concept of low-carbon economy, low-carbon agriculture should be a specific model of agricultural production and business operations with minimal green-house gas emission and the maximum benefit of community economy. Low-carbon agriculture is the "three low"economy: low energy consumption, low pollution, and low emission (Qi, 2010). Its specific model is shown in Fig. 1.
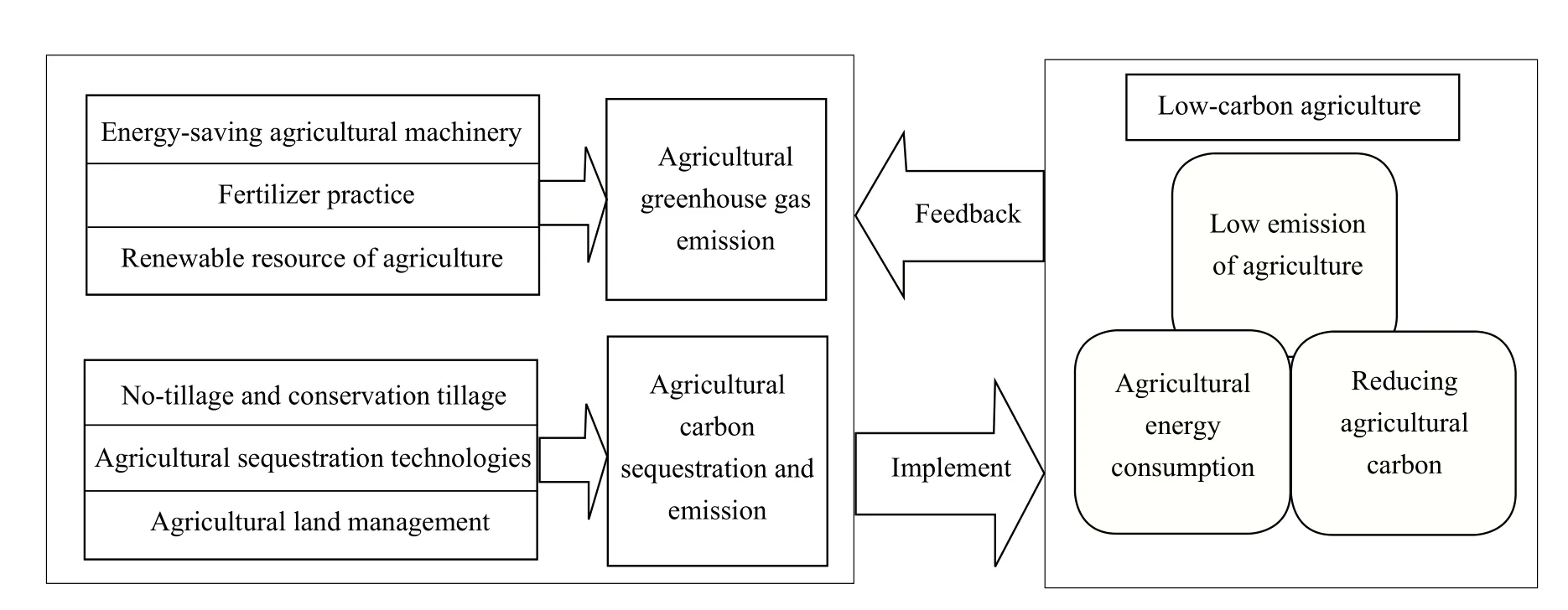
Fig.1 Agriculture low-carbon development model
Advantages of Low-carbon Agriculture in Heilongjiang Province
Superior geographical conditions
The geographical conditions of Heilongjiang Province mainly consists of mountain, plateau, plains, water,and other accessories. Mountains accounts for about 24.7% of the total area of Heilongjiang Province;the altitude of 300 m above the hilly areas accounts for about 35.8%; Sanjiang Plain in the northeast and Songnen Plain in the west account for 37% of the total area of Heilongjiang Province, which is from 50 to 200 m above the sea level.
According to the survey results of land use in 2007, agricultural land area was 39.583 million hm2,accounting for 83.69% of the total land area of Heilongjiang Province; construction land was 1.558 million hm2, accounting for 3.3% of the total land area;unused land was 6.155 million hm2, accounting for 13.01% of the total land area. The cultivated land was 11.9895 million hm2, accounting for 30.29% of the total agricultural land; garden land was 0.06 million hm2, accounting for 0.16%; forest land was 24.4301 million hm2, accounting for 61.72%; pasture land was 2.1623 million hm2, accounting for 5.47%; other agricultural lands were 0.942 million hm2, accounting for 2.38%.
Rich ecological resources
Heilongjiang Province with a vast territory and rich agricultural resources has great potential for development, because of the late developing history.Abundant natural resources and good ecological environment provide a favorable material foundation and natural conditions for the agriculture development and the establishment of ecological demonstration zones. There are many kinds of varieties of wild animals in Heilongjiang Province (mammals six orders, 20 families, 86 species), accounting for 21.6%of species, and the main protected species are sable,mink bear, leopard, tiger, and deer. The number of birds is up to 19 orders, 57 families and 343 species,accounting for 29% of species, and the main protected species are red-crowned crane, Chinese merganser,white stork, golden eagle, etc. There are more than 2 100 species of wild plants, including gymnosperms(four families, eight genera, 17 species), angiosperms(107 families, 636 genera, 1 747 species), and seed plants (111 families, 644 genera, 1 764 species). The economic value of wild plant resource reserves is about 2.5 million tons, including 0.25 million tons of edible wild grass section, more than 1 million tons of paper-making raw materials and 1.25 million tons of various herbs.
Excellent conditions for agricultural production
The land condition of Heilongjiang ranks first in the country. The total cultivated land areas and reserved resources of Heilongjiang Province account for more than 1/10 of the national land. There is one of the world famous three black land belts in Heilongjiang Province, so it is the important commodity grain production base and the amount of food commodities reserves ranks first in the country. Soybean production and export volume occupy the first, and its export account reaches 2/3 of the country. Livestock accounts for a considerable proportion of the number of dairy herds, milk and dairy production ranks first in the country too. Since the early 1990s of the last century,the total area of cultivated land of Heilongjiang Province began to stabilize from 0.17 to 0.18 billion hm2, the total grain output increased stably. In 2010,the cultivated land of Heilongjiang Province was close to 0.012 billion hm2and grain production had increased to nearly 500 billion kg.
Rich forest resources
The total area of forest in Heilongjiang Province is 31.26 million hm2, accounting for 68.9% of Heilongjiang Province's land areas. The area of woodland is 24.4301 million hm2, the total accumulation of wood is 1.5 billion m3accounting for 1/4 of the national total and the rate of forest covers up to 41.9%. Heilongjiang Province is the most important state-owned wood forest and the largest production base in China and its forest area, the total forest and timber production rank first in China. There are more than 100 species of forest trees, including more than 30 high-value species in Heilongjiang Province. The forest land of natural forest protection projects accounts for 28.3%,the forest area of 15.151 million hm2, accounting for natural forest protection project of natural forest resources 27.2%. The main forest resources in Heilongjiang Province are mainly in the Xing'anling Mountains and the Changbai Mountains and parts of the mid-levels mountains area. They are in the northeast of the main terrestrial natural ecosystems,and are the Northeast Plain agriculture and Hulunbeier league prairie animal husbandry production bases of natural barriers on the national economy, playing a vital role in the sustainable development.
Further improving eff i ciency by using straw
In 2008 microbial were produced in Heilongjiang, salt feed 18 million tons, 32.1% utilization rate of straw,straw feed rate of 42% of the total, respectively by 14.5% and 16.3% in 1991. Every year in the field,27 million tons of straw manure were equivalent to more than 1 million tons of fertilizer. Not only promote food production, but also fertilize the soil fertility and increase soil organic matter content(Wen, 2010). With the increased utilization of straw,which greatly eased the pressure of overgrazing of grasslands, the comprehensive grazing policy of grasslands of Songnen Plain in Heilongjiang Province had been thoroughly implemented, the average grass production increased by 30%, and grassland ecological environment was improved significantly. Meanwhile,with the "Renewable Energy Law" and "Renewable Energy Prices and the Cost-Sharing Management Pilot Xcheme", the introduction of straw power generation was concerned, and the current generation of straw was a rapid growth trend.
Disadvantages of Low-carbon Agricultural in Heilongjiang Province
A serious decline in soil fertility and erosion
In nearly 50 years in Heilongjiang Province, the average loss of the soil reached half, surface organic matter reduced by 1/3 of the land which had been the early days of organic matter content of 8%-11%to 2%-4%, and the pursuit of short-term benefits of chemicals, to decline soil fertility, and thin the black soil layer. Among them, the largest area of medium quality, to 3.421 million hm2, accounting for 33.18%of the total cultivated area. Soil and fertilizer in Heilongjiang, according to data from low-yielding fields in the area of the province's 6.1 million hm2,account for 54% of arable land, including soil erosion area of 5 million hm2, and account for 44% of the total area of cultivated land. In addition, with the black soil erosion and severe degradation, soil salinization and desertification are serious, and annual reduction in grain output is from 2 to 4 billion kg because of soil erosion.
Backward agricultural production in some areas
There is a concentration of contiguous land and fertile soil in Heilongjiang Province, however, because of different production methods, a large gap is made among the food production process. In the long run,the best method to reduce the gap is to explore the potential. If the reclamation levels of the cultivated land can up to 80%, it will increase 10 billion kg of grain.
Lack of sewage and garbage treatment facilities
With the rapid economic development, people's living standard has been improved greatly, resulting in the increase of the pollution. Currently, 96% of villages in Heilongjiang Province, there are no comprehensive drainage systems and sewage treatment systems, the untreated sewage are directly into rivers, lakes, and ponds, becoming the main source of water pollution. The lack of unified planning and management gives rise to rural solid waste without any treatment clutters. For example, if per person produces 0.5 kg garbage per day, 17.62 million rural people will produce about 8.8 thousand tons garbage per day, total waste per year will increase 3.212 million tons. Any of these open dumps, not only destroy environment, but also influence the breeding ground in all kinds of pathogenic microorganisms and breeding farms, easily lead to and spread epidemic diseases, directly endanger the health of farmers,seriously affect environmental health in rural areas.
Lack of methane and other new energy constructions
The development of biogas construction is very unbalanced, some counties in Heilongjiang Province have not begun to carry out the construction of biogas; in some farms and farming communities, the provincial coal saving stoves, curing of biomass, and bio-liquid fuel limit the use of solar energy and other inputs; meanwhile, biogas construction management and technology, research and education are lacking.
Low straw resource utilization
Heilongjiang Province exists total more than 56 million tons of straw, 40% of which are used for fuel,30% for feed, 10% for field, and other industrial raw materials account for about 20%, of which more than 20 million tons are for fuel and straw. However, the utilization of straw is relatively low, resource waste is greater, at the same time, burning of straw not only directly release carbon, but also accelerate the decomposition of soil organic carbon.
Countermeasures of Developing Low-carbon Agriculture in Heilongjiang Province
Stepping up publicity and try to carry out overall planning
Low-carbon agriculture, for many people, especially farmers, may not be heard of. Therefore, through newspapers, magazines, radios, televisions, internets,and other forms of publicity campaign, we can change the concept of the public and society to improve understanding of low-carbon agriculture, designing the master plan and improving the carbon productivity of social production and living activities. First, lowcarbon agriculture should be included in planning of agricultural production in Heilongjiang Province, to the overall arrangement for the deplopment. Second,the low-carbon technology research and development should be put into agricultural science and technology plans. Third, government should develop a special plan to put forward low-carbon agricultural statistics and evaluation indicators.
Promoting low-carbon agricultural technology and carrying out emission reduction technology demonstration model
In the agricultural production process, we should actively promote the use of ridge tillage technology,fertilization, animal health aquaculture, biogas,and straw utilization technology; enhance land use technology and green manure forage technology;breed new crops and excellent technical ruminant species, promote pest control, water-saving irrigation technology, ecological health of aquatic farming technology, agricultural machinery, and other energy saving technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the environment. And on that basis, selection mode aing low-carbon agricultural practice zone, business model, and model farmers will give fully play to promote emission reduction technology to provide data and technical support.
Strengthening basic research and carbon sequestration potential
It is a positive and effective way through the adjustment of land use and forestry measures will be stored in atmospheric greenhouse gase in the biological carbon emission reduction. Scientific research shows that an increase of 1% of the forest cover, can absorb fixed 0.06-0.71 billion tons carbon from the atmosphere (IPCC, 2007). The system collecting information and data about the number of breeding livestock and poultry, irrigation, pesticide use conditions, crop straw utilization, and land changes will contribute to strengthen agricultural carbon sink and further researches.
Adjusting energy structure and changing rural energy services thinking
Currently, agricultural and rural issues and potential energy savings haven't been paid, so they develop enough emphasis, relatively slowly. The main features:serious waste of energy crop cultivation, aquaculture pollution control space, and pollution control in rural life has just been started. Therefore, the energy structure must be adjusted to positive change in the thinking of rural energy services. It will change into emission reduction and increasing income in order to build a distributed, self-contained, and low-carbon of the rural energy service system. The development of biomass energy in rural areas will become agriculture new thinking (Appleby, 2005). We must make fully use of rural solar energy, wind energy, hydropower,geothermal, biomass energy and other renewable energies while increasing renewable energy and biomass energy in rural areas the proportion of energy consumption.
Conclusions
Low-carbon global climate change becomes a new thing, which is a green pattern. And this new model is driven by the development of low-carbon agricultural economy, which will be a new low power consumption and low pollution agricultural economy based on green energy (Wang, 2008). So far no country has achieved the world's agricultural modernization based on a lowcarbon economy model of development, China has been out of low-carbon agricultural development, and it will be a major national agricultural development innovations (Li, 2010). During economic development process, grasping a low-carbon agriculture, reducing greenhouse gas emission of agricultural production,and alleviating contradictions of energy structure will help us to optimize the ecological environment in Heilongjiang Province, to improve the quality of farmers' lives, and to promote a new socialist countryside construction, so as to promote the modern sustainable agricultural development.
Appleby M C. 2005. Sustainable agriculture is humane, humane agriculture is sustained. Journal of Agricultural and Environ-mental Ethics, 18: 9-11.
Gold M V. 1999. Sustainable agriculture: definitions and terms.Beltsville, Md: USDA, ARS, National Agricultural Library. pp.99-102.
IPCC. 2007. Climate change 2007: mitigation of climate change contribution of working group iii to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: United Kingdom. pp. 354-358.
Levine R. 2007. Commission of the European Communities (CEC),limiting global climate change to two degrees celsius: the way ahead for 2020 and beyond. Brussels: CEC. pp. 43-44.
Li X Y. 2010. The inevitability of the development of low-carbon ways of agriculture in Sichuan. Southwest University for Nationalities:Humanities and Social Sciences, 1: 21-23.
Qi Y B. 2010. A low-carbon impact of agricultural development. Rural Economy, 2: 45-48.
Ren L. 2009. Foreign policy and the development of low-carbon economy Enlightenment. Development Research, 2: 23-24.
Wen B Q. 2010. On circular economy development and low-carbon agriculture construction. Journal of Poyang Lake, 2: 45-48.
Wang Y. 2008, Agricultural economy of carbon. China Agri-cultural Information, 8: 15-17.
Williams J A. 1987. World commission on environment and development.Our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford. pp. 210-211.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年1期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年1期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Study on Lysine and Methionine Content Promotion of Soybean Meal by Probiotic Fermentation Process
- Screening for Enterobacteriaceae Bacteria in Infant Formula Powder
- Crop Yield Forecasted Model Based on Time Series Techniques
- Actuality and Inf l uencing Factors of Integrated Production Capacity of Foodstuff in Heilongjiang Province
- Application of Radio Frequency Identif i cation (RFID)in Dairy Information Management
