Screening for Enterobacteriaceae Bacteria in Infant Formula Powder
Lu Yan, Qi Feng, Sun Mei-ling and Wang Wei
1 National Diary Testing Center, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
2 3M China, lnz, Shenyang 110001, China
3 Heilongjiang Beingmate Dairy Co. Ltd, Anda 151400, Heilongjiang, China
Introduction
FAO/WHO convoked joint conference about "Enterobacter sakazakii (E. sakazakii)and other microbiology in infant powder" in Geneva on May, 2004. The conditioned pathogen in infant powder was classified into A, B, and C three classes, meanwhile, the A and B classes are more pathogenic for the infants. The typical A class contains E. sakazakii and Salmonella enterica;the typical B class contains Klebsiella pneumoniae(K. pneumoniae), Klebsiella oxytoca (K. oxytoca),Enterobacter cloacae (E cloacae.), Escherichia coli(E. coli), and Escherichia vulneris (E. vulneris).
E. sakazakii is a gram negative, sporeless bacterium, lived in the intestinal canal of human and animal,it will cause some diseases in controlled condition(Farmer et al., 1980). The first report are two cases meningitis in Britain (Urmenyi and Franklin, 1961).The susceptible population is new arrival, premature,the common contracts are new life meningitis,necrotizing enterocolitis of newborn, septicemia(Muytjens et al., 1983; 1988). When the newborns are infected, the therapeutic effect by antibiotics is unconspicuous, the death rate is up to 40%-80%.Milk Accident in Fuyang, China, the infection rate of E. sakazakii is 12.6% (Liu et al., 2004). Other Enterobacteriaceae is an important conditioned pathogen, and has the strong pathogenicity for human,especially for the low immunity crowd, infants,K. pneumoniae, and K. oxytoca will cause the diseases,such as pneumonia, hepatophyma, meningitis, myelitis, septicemia, colonitis and food poisoning (Xu and Shu, 2002; Biering and Karlsson, 1989).
Materials and Methods
Materials
Bacterial strains for testing
E. sakazakii Strip: ATCC29544; K. pneumoniae Strip:CMCC46117; and K. oxytoca Strip: ATCC49334.
Experimental instruments and reagents
The common instruments in microbiology lab, centrifuge; ABI7300 real-time PCR; ultraviolet specrophotomet (DV800); transilluminator (T2A); DNA extract kit (TaKaRa); TSA, EE, mLST, VRBGA,SCAI , MIAC; API20E; and VITEC GNI.
Methods
Detection of Enterobacter sakazakii
The usual detection methods for E. sakazaki: the traditional culture (Gao et al., 2005; SN /T 1632. 1-2005, 2005.)and real-time PCR.
Traditional detection of Enterobacter sakazakii
All the detection processes referred to GB4789.40-2010 as the followings. Weighed the samples 100, 10,and 1 g in the sterile operation, put into the preheated(about 44℃)900, 90, and 9 mL BPW respectively with 1 : 10 uniform liquid, (36±1)℃ about (18±2)h,extracted 1 mL to 9 mL mLST, (44±0.5)℃ about (24±2)h, mixed, then inoculated the enrichment broth on Chromogenic medium, (36±1)℃ about (24±2)h, the single charac-teristic colony (about 1-5)was inoculated on TSA, (25±1)℃ about (48±4)h, the suspicious colony was processed biochemical identification.
PCR detection of Enterobacter sakazakrii
All the detection process referred to SN/T1632.3-2005.The 1 : 10 uniform liquid was cultivated at (36±1)℃about 18-22 h, extracted 10 mL to 90 mL EE broth,(36±1)℃ about 18-22 h. The extracted template DNA was proceeded to real-time PCR, and transferred the positive samples to the traditional methods.
Detection of other Enterobacteriaceae
The detection method of K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca referred to SN/T 1962-2007. Prepared 1 : 10 uniform liquid, (36±1)℃ about 18-22 h, extracted 10 mL to 90 mL EE broth, (36±1)℃ about 18-22 h, then inoculated the enrichment broth on VRBGA and MIAC, the single characteristic colony was processed biochemical identification.
Results
Colonial morphology and biochemistry identifi cation of E. sakazakii
E. sakazakii was the G- bacillus, the optimum growth temperature was 37-44℃, asporous and atrichosis.
As shown in Fig. 1, E. sakazakii produced a kind of round, protuberant purple colony surrounded by cholicacid aureole on VRBG agar, formed a yellow colony about 2-3 mm on TSA, presented the green colony about 1-2 mm on X-α- glucoside agar.
The good identification of API 20E is shown in Fig. 2, the results had accorded with the biochemical character of E. sakazakii, the detection results reported as the most probable number (MPN)in 100 g samples.
Colonial morphology and biochemistry identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca
K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca were the G- bacillus,0.5-0.8×1-2 um, the optimum growth temperature was 37℃, the optimum pH is 6.5-8.5, asporous and atrichosis, the majority had the pili. This kind bacterium had the low demand for the nutrition, it would grow well on the common agar medium, form major offwhite mucoidcolony. It would be killed on 55℃ for 30 min.
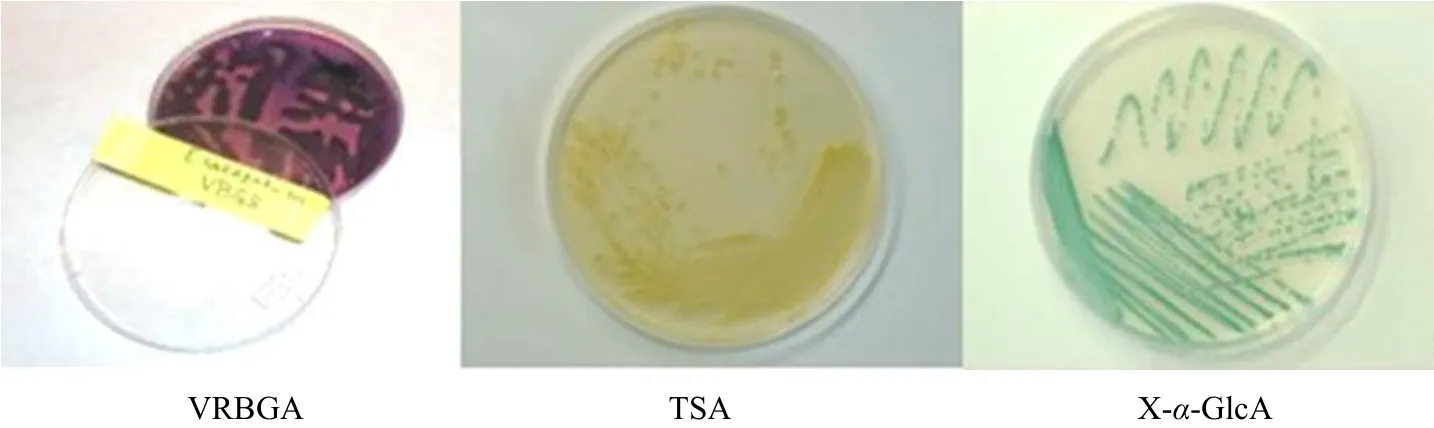
Fig. 1 Colonial morphology of Enterobacter sakazakii in different media culture

Fig. 2 Representative API 20E Strip for E. sakazakii
The neighboring colony would mix together on the common agar, blood agar plate and SS agar. It would produce the obvious colony on MIAC (MacConkey inositol ribitol penicillin agar), moist, smooth, red colony with deep red core, 2-3 mm, easy fusion, the crimson heart would be observed from the back of the plate as shown in Fig. 3.
The good identification of API 20E is shown in Figs. 4 and 5, the results had accorded with the biochemical characters of K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca.
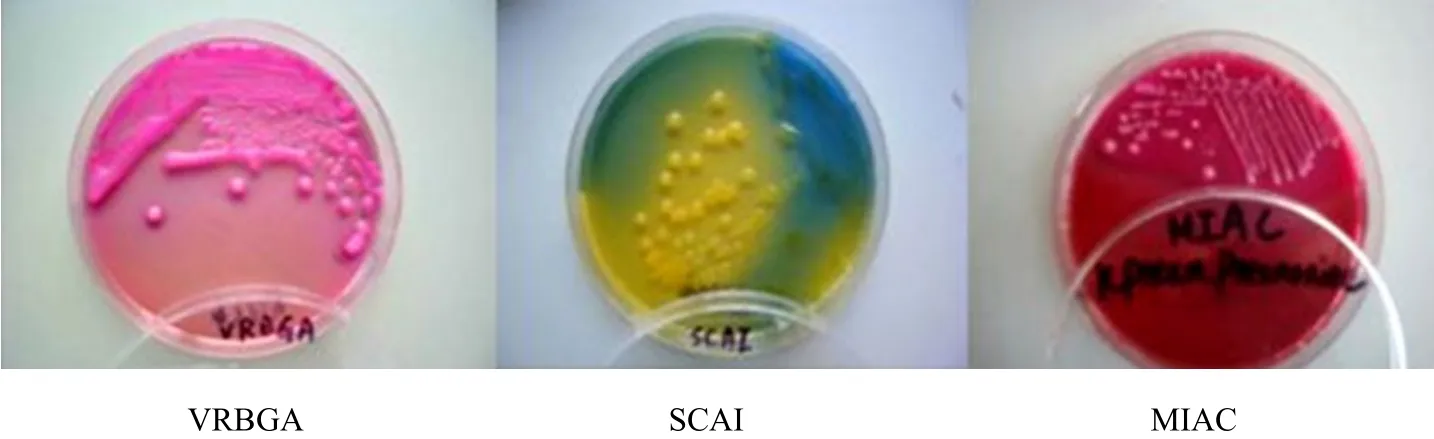
Fig. 3 Colonial morphology of K. pneumoniae in different media culture

Fig. 4 Representative API Strip for K. pneumoniae
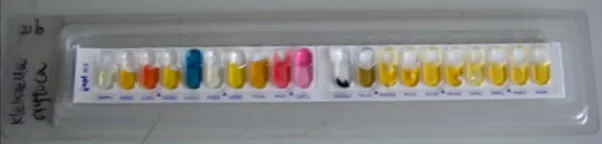
Fig. 5 Representative API Strip for K. oxytoca
Discussion
General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine (GAQSIQ)announced New Zealand Fonterra Co-operative Group, the global biggest supplier for dairy raw material, whose multibatches had been checked pathogenic E. sakazakii in July, 2007.
In 2009, GAQSIQ announced 852 batches imported disqualification food from 8 to 11 month in 2008. The formula powder of Wei Quan Food were checked E.sakazakii among it.
The morbidity of the disease by the infection of E.sakazakii is low, but it will lead to higher death rate,the national standard GB 4789.40-2010 has come on.The sensitivity of real-time PCR is higher than the traditional methods and the common PCR, and the whole operation is simple, fast, the PCR method can reduce the testing time and improve the veracity, and so was widely used for for mechanism detection of E. sakazakii and by milk powder manufacturer, if the first screening was positive, we would return to the traditional methods for the last identification.
Harry used the method such as: BPW and EE broth,VRBGA separation, surveyed the Enterobacteriaceae contamination situation for 141 infant formula powder samples from 35 countries. The contamination rate of E. sakazakii, E. cloacae, K. pneumoniae and K.oxytoca were 14.2%, 21.3%, 9.2%, and 2.8% among it(Harry, 2006).
These conditioned pathogens had been detected long time before, K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca in Klebsiella has stronger pathogenicity for adults and infants, especially for the low immunity population,once infected, it would cause terrible consequences,such as bronchitis, pneumonia, suppurative inflammation, urinary system and wound infection, even septicemia, meningitis, peritonitis and food poisoning(Harry, 2006). No standard required the inspection on E. sakazakii for the infant supplementary food (Lai,2001)now, but the contamination level is far higher than the infant powder.
The relevance ratio of E. sakazakii is lower than the Enterobacteriaceae, declared that the environment of diary product enterprises was not the only channel to production contamination, maybe, other effect factors existed. If the environmental factors were eliminated,perhaps, the contaminated diary production connected with the workers in the surroundings. The microbes on the producers' hands and coats can reflect the environment and perch characteristics. They come from the soil, water, dust and other surrounding,in addition, the nostril, mouse and skin are all the important sources of these microbes, the enteric microorganisms can contaminate the food by means of unhygienic operation, all these will arise the attention of diary processors.
Enterobacteriaceae bacteria widely distributed in the environment, common in the dried one, and easily detected, it could be regarded as an indicator(indicating bacteria)for the process and sanitary condition of the environment. Easily understand, the negative samples can avoid many hazards. Therefore,we should regard Enterobacteriaceae as the indicator to carry out effective management, and then the neglected mild and discontinuity contamination can be easily found. The quality of the infant powder can be guaranteed safety for the special group.
Biering G, Karlsson S, Clark N C, et al. 1989. Three cases of neonatal meningitis caused by Enterobacter sakazakii in powdered milk. J Clin Microbiol, 27: 2054-2056.
Farmer J J, Asbury M A, Hickman F M, et al. 1980. Enterobacter Sakazakii: a new species of "Enterobacteriaceae". Clinical Specimens,30: 569-584.
Xu H S, Shu M A. 2002. The cause of disease pathogeny on Klebsiella pneumoniae sick about Pelodiscus sinensis. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science Edition, 11: 702-706.
Harry J. 2006. Enterobacter sakazakii and Salmonella inpowdered infant formula. Meeting Report, 10: 35-38.
Lai K. 2001. Enterobacter sakazakii infections among neonates,infants,children and adults. Case Report and a Review of the Literature Medicine, 80: 113-122.
Muytjens H L, Roelofs-Willemse H, Jaspar G H. 1988. Quality of powdered substitutes for breast milk with regard to members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol, 26: 743-746.
Muytjens H L, Zanen H C, Sonderkamp H J, et al. 1983. Analysis of eight cases of Neonatal Meningitis and Sepsis due to Enterobacter sakazakii. J Clin Microbiol, 18: 115-120.
Gao Q L, Zhang X, Luo M F. 2005. The test method and study about Enterobacter sakazakii in milk powder. Inspection and Quarantine Science, 15(4): 4-8.
SN /T 1632. 1-2005. 2005. The test method of Enterobacter sakazakii in milk powder (the first part): the separation and counting method of Enterobacter sakazakii in milk powder. China Standards Press,Beijing. pp: 3-4.
SN /T 1632. 3-2005. 2005. The test method of Enterobacter sakazakii in milk powder (the third part): real-time PCR method. China Standards Press, Beijing. pp: 1-3.
Urmenyi A M C, Franklin A W. 1961. Neonatal death from pigment edcoliform infection. Lancet, 1: 313-315.
Liu X M, Pei X Y, Guo Y C. 2004. The contamination of Enterobacter sakazakii in inferior infant powder in Fuyang, China. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 17(1): 10-12.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年1期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年1期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Actuality and Inf l uencing Factors of Integrated Production Capacity of Foodstuff in Heilongjiang Province
- Developing Potential of Low-carbon Agriculture in Heilongjiang Province
- Crop Yield Forecasted Model Based on Time Series Techniques
- Study on Lysine and Methionine Content Promotion of Soybean Meal by Probiotic Fermentation Process
- Application of Radio Frequency Identif i cation (RFID)in Dairy Information Management
