Study of oxidation characteristic on copper surface exposed by surface wave plasma
Keisuke YOSHIDA,Yoshiharu MEGA,Hiromitu KAWAZOE,Takashi MATSUNO,Gohji YAMADA,Shin TAKEUCHI
(1.Tottori University,4-101 Minami,Koyama,Tottori,680-8552,Japan; 2.Nissin inc.,10-7 Kamei,Takarazuka,Hyogo,665-0047,Japan)
Study of oxidation characteristic on copper surface exposed by surface wave plasma
Keisuke YOSHIDA1,Yoshiharu MEGA1,Hiromitu KAWAZOE1,Takashi MATSUNO1,Gohji YAMADA1,Shin TAKEUCHI2
(1.Tottori University,4-101 Minami,Koyama,Tottori,680-8552,Japan; 2.Nissin inc.,10-7 Kamei,Takarazuka,Hyogo,665-0047,Japan)
Surface wave plasma(SWP)is a kind of low temperature plasma which can be utilized for material development.In this research,argon and oxygen were used as a working gas for an SWP experiment and the influence of the plasma irradiation on a copper surface was examined.Particular,relation between the spatial characteristics of SWP and wetting characteristics was examined.As a result,it was found that spatial characteristics of the SWP affected the wetting characteristics and the oxidation characteristics.
surface wave plasma;material surface reformation;wetting characteristics
The chemical reaction of plasma in recent years has been notable for the plasma processing technology such as the piling up and etching technique of thin film.The need in the industry is especially turned to making semiconductor-integrated-density and to getting high performance.The low temperature plasma technology dose not influence the characteristics of IC substrate material and has various effects on the processing the working gases.Furthermore,CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)can be achieved individually in the generated plasma field,because the low temperature plasma permits plural electronic excited temperature distributions.Therefore,the low temperature plasma technology has been developed widely in an IC substrate processing technology.SWP(Surface Wave Plasma)was used as low temperature plasma technologies in this study,which can easily control an etching shape and selection ratio of an irradiated material because SWP is the type of inductively coupled plasma source.However,the influence of SWP on the irradiated material has not examined sufficiently.Therefore,in this study,SWP was irradiated on a copper-plate surface with the working gas of argon and oxygen and their mixture,and the relation between the wetting characteristics of a copper-plate surface and the characteristics of SWP,was investigated.
1 Experimental apparatus and principle
1.1 Experimental apparatus
Fig.1 shows the schematic diagram of the surface wave plasma device and the spectrum measurement system.The electric power can be controlled in the range from 0.5 to 2 kW.The plasma chamber of 728 mm in width,350 mm in depth and 100 mm in height was made of stainless steel.The chamber was evacuated with the rotary pump,and the working gaseous pressure was set to 100 Pa during the experiments.Spectra of the plasma were measured every 0.4 nm from 338 nm to 1 029 nm.Table 1 shows the experimental condition for this research.

Table 1 Experimental condition
1.2 Generation process of surface wave plasma
A microwave generated by a magnetron is transmitted into a chamber through a slotted antenna and a quartz glass plate where a working gas is filled.Atthe early stage,the gas is ionized by the power of the microwave and this stage momentarily continues.The electron density in the chamber goes up due to the electron avalanche phenomenon.When this electron density exceeds a cut-off frequency,the microwave is reflected and the plasma behaves in a metallic characteristic.The surface wave,namely electromagnetic radiation,spreads between the high density plasma and the quartz glass.Flat boardshaped plasma is formed in the chamber in proportion to the surface wave transition.An electron is accelerated by the surface wave and high-density plasma is maintained in the chamber[1].

Fig.1 Schematic diagram of surface wave plasma and measuring system for spectra
1.3 Wetting characteristic
Wetting characteristic is evaluated by a contact angle θ between a material and a liquid droplet surface as shown in Fig.2.It is assumed that a wetting characteristic is better as θ is smaller.Fig.2 also shows the balance of the forces acting on these surfaces as follows
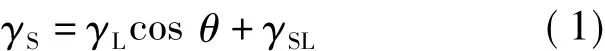
where γSis the material surface tension,γLis the liquid surface tension of the droplet and γSLis the solid and liquid boundary tension.

Fig.2 Force valance on a droplet and material
2 Results and discussions
2.1 Influence of spatial characteristics of plasma on the wetting characteristics
Emission spectrum and contact angle on the coppur surface were measured with different distance z in three experimental conditions.The volume fraction of O2in the O2and Ar mixture are 0%,25%,and 50%.Fig.3 shows the typical measured spectrum in the case of φ(O2)=50%.The measured emission intensity was normalized by the maximum value of emission intensity.Spectrum lines of OI: 777.1,844.6 nm,ArI:750.3,763.5,810.3 nm were selected and their average values of Io and IArwere used for the evaluation of the spatial characteristics of plasma.Fig.4 shows the relation between distance z and contact angle on the copper surface with different mole ratio of oxygen.Contact angle on the copper surface tends to decrease with increasing the mole ratio of oxygen.This is caused by the oxidation reaction on the copper surface.With increasing the mole ratio of oxygen,oxidation is more activated on the copper surface and the hydroxyl is more formed,resulting in the increase of the hydrophilicity.Therefore,contact angle on the copper surface decreases with increasing the mole ration of oxygen.In the case of φ(O2)=0%,the contact angle on the copper surface hardly depends on the distance z.On the other hand,in the case of φ(O2)=25%, and 50%,the contact angle on the copper surface depends on the distance z.Fig.5 shows relation between the intensity ratio Io/IArand the distance z.From Fig.5,the intensity ratio Io/IArtends to increase with decreasing the distance z.This result shows the degree of dissociation increases with decreasing the distance z.This is caused by the increase of the power of the microwave near the quartz glass.From these results,oxidation process is more activated near the quartz glass,resulting in the decrease of the contact angle on the coppuer surface.

Fig.3 Light emission intensity of the SWP spectra for 50%oxygen
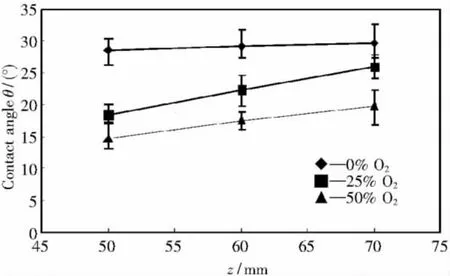
Fig.4 Relation between z and contact angle
2.2 Influence of the radiation time on the wetting characteristics
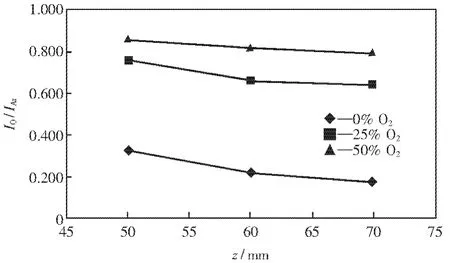
Fig.5 Relation between z and intensity ratio

Fig.6 Relation irradiation time and the contact angle
Contact angle on the copper surface was measured with different irradiation time at the condition of 100%of O2.Fig.6 shows the relation between irradiation time and contact angle on the copper surface.Contact angle on the copper surface decreases rapidly for the irradiation time from 0 to 20 s.On the other hand,the contact angle on the copper surface was almost same for the irradiation time from 30 to 60 s.Fig.7 shows the pictures of the copper surface with each irradiation time.The color of copper surface varies depending on the irradiation time.This is caused by the interference of light corresponding to the thickness of the oxidation film.For the irradiation time from 0 to 20 s,the colors of the copper surface are almost same.Therefore,the film thickness is considered to be thin.On the other hand,for the irradiation time over 30 s,the colors of the copper surface are quite different from that for the irradiation time of 0 s.Therefore,film thickness is considered to be thick for this irradiation time.These results suggest that the contact angle on the copper surface is influenced by the formation process of the oxidation film.For the irradiation time from 0 to 20 s,oxidation film is not formed completely and the surface of the film is not considered to be uniform.Therefore,the contact angle decreases rapidly because of the increase of the effective solid surface area.On the contrary,for the irradiation time from 30 to 60 s,oxidation film is formed completely and the surface of the films is considered to be uniform.Therefore,the contact angle on the coppper surface is almost same.

Fig.7 Plasma-treated copper surface
3 Conclusion
In this study,oidation characterisc on copper furface was evaluated by the spectroscpic measurement and wetting characteris.With increasing the mole ratio of O2,the contact angle on the copper surface decreases because the oxidation reaction is more activated and hydroxyl is more formed on the copper surface.Contact angle on the copper surface decreases near the quartz glass because the degree of dissociation of O2increses and the oxidation reaction is more activated.This result suggest the spatial characteristics of SWP affects the wetting characteristics on copper surface.
With increasing the irradiation time of plasma,contact angle on the copper surface tends to decrease.For the irradiadtion time from 0 and 20 s,contact angle decreases rapidly because the oxidation film is not considered to be uniform.On the other hand,for the irradiation time from 30 to 60 s,contact angle is almost samle becaus the oxidatio film is considered to be uniform.This result suggest the formation process of the oxidation film affects the contact angle on the copper surface.
[1]Nonaka S.Surface waves and plasma production:excitation and propagation of surface waves(in japanese)[J].Journal of the Japan Society of Plasma Science and Nuclear Fusion Research,1996,72:622-628.
[2]Ono S.Surface tension(in japanese)[M].Kyouritsu Publishers,1980:64,71.
TG 17
A
1671-6620(2011)01-0058-03
2010-05-20.
吉田圭佑(1986—),男,日本国鸟取县人,日本鸟取大学大学院生,E-mail:k_y_19861023@yahoo.co.jp;川添博光(1954—),男,日本国三重县人,日本鸟取大学教授,E-mail:kawazoe@mech.tottori-u.ac.jp.

