溶剂萃取-差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中的邻苯基苯酚
李 静,李红波,,*,杜 诗,任艳艳,胡效亚
(1.盐城工学院化学与生物工程学院,江苏 盐城 224051;2.扬州大学化学化工学院,江苏 扬州 225002)
溶剂萃取-差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中的邻苯基苯酚
李 静1,李红波1,2,*,杜 诗2,任艳艳2,胡效亚2
(1.盐城工学院化学与生物工程学院,江苏 盐城 224051;2.扬州大学化学化工学院,江苏 扬州 225002)
建立溶剂萃取-差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中的邻苯基苯酚(OPP)的方法。为避免橘皮中大量抗坏血酸和香精油等物质的影响,采用甲苯萃取橘皮中的OPP,在优化实验条件下,运用差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中OPP含量。结果表明,OPP氧化峰电流与其浓度在2.0×10-9~4.0×10-6mol/L范围内呈良好的线性关系,检出限达到8.1×10-10mol/L,回收率为106.7%~112.2%。该法操作简单、快速、灵敏、准确。
电化学;溶剂萃取;邻苯基苯酚;橘皮
邻苯基苯酚,又名2-羟基联苯(OPP),是一种强有效的杀真菌剂,在蔬菜和水果特别是柑橘类水果的储存、运输和配送过程中起杀真菌作用的活性成分。由于它能够抑制收后果实因微生物菌而腐烂,所以可以用作为果实箱的消毒剂[1]。OPP被认为可能是一种潜在的致癌物,在动物体内的实验[2]证明它诱发并干扰生物体的生长,降低产量,损坏肾脏。GB 2760—96《食品添加剂使用卫生标准》规定,OPP作为食品添加剂最大允许残留量为12mg/kg。
目前,已经有若干种检测OPP在柑橘类水果中残留量的方法,如带有荧光检测器(FLD)的液相色谱法(LC)[3-7]、质量选择检测器(MSD)液相色谱检测法[8-9]、紫外(UV)高效液相色谱法(HPLD)[10]和二极管阵列检测器[11]液相色谱法;气相色谱法(GC)(有时会衍生使用火焰离子化检测器[12-13]、质谱选择检测器[14-16]),以及光谱法[17-18]等。但是已报道的检测方法具有耗时长、仪器昂贵、灵敏度较低等缺点。本实验为避免橘皮中大量抗坏血酸和香精油等物质对电化学法测定OPP的影响,故采用溶剂(甲苯)萃取-差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中的OPP,以期为邻苯基苯酚测定方法的建立提供一定的参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料、试剂与仪器
橘子 超市采购。
OPP(纯度99.5%) 盐城华业医药化工有限公司;鳞片石墨 上海国药试剂有限公司。OPP标准溶液的配制:将OPP溶于95%乙醇配成浓度为1.0×10-3mol/L的溶液,保存于容量瓶中并放置黑暗处,使用之前再用缓冲溶液稀释至所需浓度。不同pH值磷酸盐缓冲溶液(由不同比例的 0.1mol/L Na2HPO4、NaH2PO4和 H3PO4配制而成)。所有试剂均为分析纯;实验用水均为二次蒸馏水。
CHI760D电化学分析仪(三电极体系:工作电极为石墨电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),对电极为铂丝电极) 上海辰华仪器有限公司;KQ118型超声波清洗器 中国昆山市超声波仪器有限公司;pHS-25精密pH计 中国上海雷磁仪器厂。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 样品中邻苯基苯酚的提取
将橘皮切成碎末,然后称取其1.0g 碎末于容量瓶中,加入甲苯100mL(分5次萃取),每次超声振荡1h后抽滤,将滤液集中到梨形瓶中旋转蒸发。蒸发结束后,用95%乙醇润洗梨形瓶3次,将润洗液倒入容量瓶中并定容为100mL供样品分析使用。
1.2.2 伏安法测定
在0.3~1.0V区间内以100mV/s的扫速对稀释后的OPP分别作循环伏安(CV)和差示脉冲溶出伏安测试。采用差示脉冲伏安法进行OPP的定量及样品分析,其工作条件为:振幅为0.05V;脉冲持续时间为0.05s;脉冲周期为0.2s。
2 结果与分析
2.1 橘皮中邻苯基苯酚提取方法的选择
橘皮中含有大量的抗坏血酸和香精油等物质,其中大量存在的抗坏血酸和部分香精油成分对电化学测定OPP有干扰,因此避免其干扰成为用电化学法测定橘皮中OPP的关键问题。综合考虑到抗坏血酸的水溶性、香精油成分的较低沸点和OPP具有微溶于水而易溶于有机溶剂且具有一定极性等特点。本实验采用合适极性的非水溶剂甲苯作为萃取溶剂,使得橘皮中含有大量的香精油等物质溶于其中,而水溶性的大量抗坏血酸则可以被隔离出萃取剂中。5次萃取后,通过旋转蒸发使甲苯和较低沸点的香精油得到回收。整个萃取过程由气相色谱-质谱跟踪以保证待测物得到完全萃取。蒸发结束后,用95%乙醇润洗梨形瓶3次,将润洗液倒入容量瓶中并定容为100mL供分析使用。
2.2 缓冲溶液及其pH值的选择
考察乙酸-乙酸钠、柠檬酸-柠檬酸钠和磷酸盐缓冲液,发现在磷酸盐缓冲液中峰电流最大且峰形好。图1为pH3.0~8.0时的磷酸盐缓冲液循环伏安图。由图2可见,pH值与峰电位呈线性关系,随着pH值的增大峰电流达到最大然后逐渐变小,说明电化学过程伴随着质子参与反应;当pH8.0时,体系中质子数最少,因此在电极表面发生氧化反应的OPP浓度就最小。其中,pH 4.0时峰电流最大;因此,本实验选择pH4.0的磷酸盐缓冲液为底液。

图1 pH3.0~8.0磷酸盐缓冲溶液中邻苯基苯酚的循环伏安曲线Fig.1 Circulated voltammery curve of OPP in PBS buffer at a pH ranging from 3.0 to 8.0

图2 峰电位、峰电流随pH值的变化关系Fig.2 Effect of pH on peak potential and peak current
2.3 差示脉冲溶出伏安测定橘皮的邻苯基苯酚
2.3.1 富集电位和富集时间的确定
当pH4.0时,1.0×10-9mol/L的OPP于电极上的最佳富集电位和富集时间分别为0V和120s。在富集电位为0V时考察富集时间(60、80、100、120、160、240s)对峰电流的影响,结果发现,120s后OPP氧化峰电流变化不大;在富集时间为1 20 s时,考察富集电位(-0.2、-0.1、0、0.1、0.2、0.3V)对峰电流的影响,结果发现,随着富集电位的增大,峰电流随着增大,当富集电位大于0V时,峰电流逐渐减小,因此,0V和120s作为电极富集的最佳条件。
2.3.2 线性范围和检出限
在优化的实验条件下,应用差示脉冲溶出伏安法对OPP进行测定。图3为不同浓度的OPP在石墨电极上的差分脉冲伏安曲线,可看出OPP浓度与峰电流的线性关系。OPP的氧化电流Ip/μA与OPP的浓度/(mol/L)在2.0×10-9~4.0×10-6mol/L范围内呈良好的线性关系,线性方程为Ipa=113.8156+0.9523c,r= 0.9924;检出限为8.1×10-10mol/L,比气相色谱法[3]报道的检出限低一个数量级。对含有5.0×10-9mol/L OPP的PBS缓冲液,连续9次测定,相对标准偏差(RSD)为3.54%,表明该检测方法重现性好。

图3 不同浓度OPP的差示脉冲溶出伏安曲线Fig.3 Differential pulse stripping voltammetry curves of OPP at various concentrations
2.3.3 样品的测定及回收率实验
对橘皮萃取液用PBS缓冲液适当稀释后,用本法对其进行测定;为了验证本方法的可行性,进一步地做了回收率实验(表1)。结果表明,回收率106.7%~112.2%,本方法可以用来测定橘皮中的OPP。
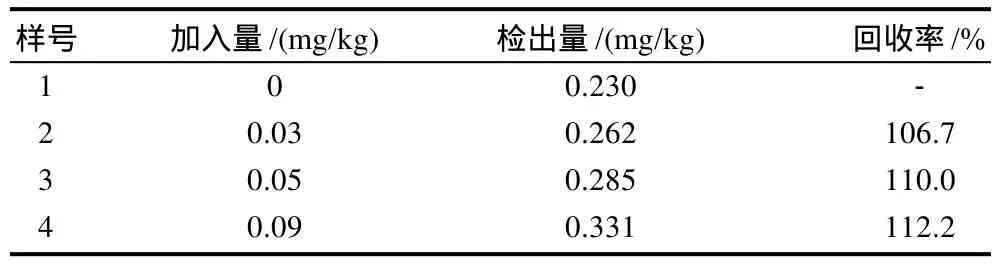
表1 橘皮中邻苯基苯酚的回收率Table 1 Recovery rate of OPP in orange peel
3 结 论
运用甲苯萃取橘皮中的OPP避免了橘皮中大量抗坏血酸和香精油等物质对电化学法测定该物质的影响;差示脉冲溶出伏安法测定橘皮中OPP含量具有试样用量少、灵敏度高、检出限低、反应速度快、稳定性好和操作简单等特点。这为橘皮中OPP的痕量检测提供了一种新方法。
[1] CAPITAN-VALLVEY L F, DEHEIDEL M K A, AVIDAD R. Solidphase spectrophosphorimetric determination of the pesticideophenylphenol in water and vegetables[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2003, 375(5): 685-691.
[2] APPEL K E. The carcinogenicity of the biocide ortho-phenylphenol[J].Archives of Toxicology, 2000, 74(2): 61-71.
[3] KOLBE N, ANDERSSON J T. Simple and sensitive determination ofo-phenylphenol in citrus fruits using gas chromatography with atomic emission or mass spectrometric detection[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2006,54(16): 5736-5741.
[4] SAAD B, HANIFF N H, SALEH M I, et al. Determination of orthophenylphenol, diphenyl and dphenylamine in apples and oranges using HPLC with fluorescence detection[J]. Food Chem, 2004, 84(2): 313-317.
[5] YAMAZAKI Y, NINOMIYA T. Determination of benomyl, diphenyl,o-phenylphenol, chlorpyrifos, methidathion, and methyl parathion in oranges by solid-phase extraction, liquid chromatography[J]. J AOAC Int, 1999, 82(6): 1474-1478.
[6] MOTOHASHI N, NAGASHIMA H, MEYER R. High-performance liquid chromatography of fungicides in citrus fruits[J]. J Liq Chromatogr,1991, 14(19): 3591-3602.
[7] ZAMORA T, HIDALGO C, LOPEZ F J, et al. Determination of fungicide residues in fruits by coupled-column liquid chromatography[J]. J Sep Sci, 2004, 27(9): 645-652.
[8] BLASCO C, PICO Y, FONT G. Monitoring of five postharvest fungicides in fruit and vegetables by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry[J]. J AOAC Int, 2002, 85(3): 704-711.
[9] YOSHIOKA N, AKIYAMA Y, TERANISHI K. Rapid simultaneous determination ofo-phenyphenol, diphenyl, thiabendazole, imazalil and its major metabolite in citrus fruits by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry using atmospheric pressure photoionzation[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2004, 1022(1/2): 145-150.
[10] PROUSALIS K P, POLYGENIS D A, SYROKOU A, et al. Determination of carbendazim, thiabendazole, ando-phenylphenol residues in lemons by HPLC following sample clean-up by ion-pairing[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2004, 379(3): 458-463.
[11] 牛增元, 包艳, 叶曦雯, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定水性涂料中的酚类防霉剂[J]. 分析试验室, 2008, 27(3): 48-51.
[12] WOOD R. MAFF validated methods for the analysis of foodstuffs No.V4. Biphenyl and 2-hydroxybiphenyl in citrus fruits[J]. J Assoc Public Anal, 1992, 28(1): 43-49.
[13] HERNANN T S, POST A A. Quamtitative determination of traces of indole ando-phenylphenol by direct aqueous-injection gas chromatography[J]. Anal Chem, 1968, 40(10): 1573-1576.
[14] JOHNSON G D, HARSY S G, Geronimo J, et al. Orthophenol and phenylhydroquinone residues in citrus fruit and processed citrus products after postharvest fungicidal treatments with sodium orthophenylphenate in California and Florida[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2001, 49(5): 2497-2502.
[15] YU L, SCHOEN R, DUNKIN A, et al. Determination ofo-phenylphenol,diphenylamine, and propargite pesticide residues in selected fruits and vegetables by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry[J]. J AOAC Int,1997, 80(3): 651-656.
[16] BARTELS M J, BRZAK K A, BORMETT G A. Determination of ortho-phenylphenol in human urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr B, 1997, 703(1/2): 97-104.
[17] CAULFIED P H, ROBINSON R J. Spectrophotometric determination ofo-phenylphenol with titanium sulfate[J]. Anal Chem, 1953, 25(6):982-983.
[18] GARCIA REYES J F, LLORENT MARTINEZ E J, ORTEGA BARRALES P, et al. Continuous flow separation and pre-concentration coupled on-line to solid-surface fluorescence spectroscopy for the simultaneous determination ofo-phenylphenol and thiabendazole[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2004, 378(2): 429-437.
Determination ofO-Phenlyphenol in Orange Peel by Solvent Extraction Coupled with Differential Pulse Stripping Voltammetry
LI Jing1,LI Hong-bo1,2,*,DU Shi2,REN Yan-yan2,HU Xiao-ya2
(1. College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Yancheng Institute of Technology, Yancheng 224051, China;2. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225002, China)
The solvent extraction-differential pulse stripping voltammetry method was developed to determineO-phenlyphenol(OPP) in orange peel. In order to avoid the influence of ascorbic acid and essential oil, OPP was extracted by toluene from orange peel. Under the optimal conditions, differential pulse stripping voltammetry was used to determine OPP in orange peel. The results demonstrated that the oxidative peak current of OPP was linearly correlated with the OPP concentrations in the range of 2.0 × 10-9- 4.0 × 10-6mol/L. The detection limit and recovery rate of this developed method were 8.1 × 10-10mol/L and 106.7%-112.2%, respectively. Therefore, this developed method is characteristics of simple operation, fast detection, high sensitivity and accuracy.
electrochemistry;solvent extraction;O-phenlyphenol;orange peel
O657. 1
A
1002-6630(2011)06-0195-03
2010-06-16
国家自然科学基金项目(20875081;21075107);盐城工学院自然科学基金项目(XKY2009009)
李静(1978—),女,讲师,硕士,主要从事重金属离子检测研究。E-mail:hnzklhz@yahoo.com.cn
*通信作者:李红波(1979—),男,讲师,博士研究生,主要从事食品电化学检测研究。E-mail:lhbchem@163.com
- 食品科学的其它文章
- 超临界CO2萃取紫苏叶挥发油的工艺优化
- 超临界CO2流体萃取-GC-MS分析南北五味子挥发油成分
- 沙葱籽油的超临界CO2萃取及成分分析
- Central Properties of the Metabolites ofHouttuynia cordataThunb.Populations from Different Altitudes in Guizhou
- Effects of Deformation Rate and Degree of Compression on Texture Profile Analysis of Hard-boiled Egg
- 紫薯色素两种提取方法的比对研究

