台湾地区樟芝研究概况与发展趋势
徐泰浩 林芳仪
(台湾大叶大学生物产业科技学系/药用植物与保健学系)
1 前言
樟芝 (Antrodia camphorata;Antrodia cinnamomea;Taiwanofungus camphorata)为台湾牛樟树 (Cinnamomum kanehirae)上所发现的相当特殊的药用真菌,自1990年初次被正式命名[1]发表至今已超过20年。由于樟芝仅在台湾地区被发现,目前国际期刊有关樟芝的研究报告几乎都为台湾研究学者所发表。由于原生樟芝的神秘性、稀有性及口碑,原生性子实体的售价相当昂贵,而人工培养子实体或液态培养菌丝体的价格则较低。樟芝中有超过78种化合物,包括三萜类 (terpenoids)、苯酸类(benzenoids)、木脂素 (lignans)、苯醌及其衍生物 (benzoquinone derivatives)、琥珀酸与马来酸及其衍生物 (uccinic and maleic derivatives)及多糖体等。[2]
近年来樟芝在抗发炎、[3~9]保肝 、[10~12]抗肝癌 、[13~15]抗肺癌 、[16]抗乳癌、[17,18]抗卵巢癌、[19]抗结肠癌、[20,21]抗口腔癌、[22]抗氧化、[9,23]降低系统性红斑狼疮性肾炎[24]及抗血小板凝集[25]等方面的研究皆显示其未来具有高度发展潜力。樟芝也已被证实不具有基因毒性,[26]口服90天亚急性毒性试验也未显示其具安全疑虑。[27]
近年发表的樟芝生物活性成分,包括:①Antroquinonol,保肝、抗氧化与抗发炎;[9~10]②羊毛甾烷三萜类Lanostane triterpenoids,保肝;[11]③Antrocin,抗乳癌;[17]④4-Acetylantroquinonol B,抗肝癌;[13~14]⑤Methyl anteinate A,抗肝癌;[28]⑥Methylantcinate A,抗口腔癌;[22]⑦5-Substituted 4,7-dimethoxy-1,3-benzodioxole衍生物,抗结肠癌;[21]⑧Ergostane-type triterpenoids and polyacetylenes,抗发炎;[3]⑨Benzocamphorins AE, 抗发炎;[4]○10Camphoratins A-J, 抗发炎 ;[5~29]○11 Antcin A, 抗发炎;[6]○12 Antrocamphin A, 抗发炎/抗血小板凝集[25]等,显示樟芝生物活性成分应有开发为新药原料之价值。
本文主要有下列4个构面。
2 樟芝学名变迁与国际发表研究论文数量变化
樟芝为台湾所发现的特有药用真菌,早于1990年被命名为Ganoderma camphoratum,[1]1997年吴声华等人在 《Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica》期刊重新将其命名为Antrodia camphorata,[30]2004年张东柱与周文能在前述期刊再次修正其学名为Antrodia cinnamomea;[3]同一年,吴声华等人另于 《Fungal Sciences》期刊发表 Taiwanofungus新属,认为 A.camphorata应归于Taiwanofungus,其学名应为 Taiwanofungus camphorate。[32]2007年Chiu以樟芝rDNA内转录间隔区基因分析仍采用Antrodia camphorata为樟芝学名。[33]
以 《Web of Knowledge》 数据库分别就 “Antrodia camphorate” 、“Antrodia cinnamomea” 及 “Taiwanofungus camphorata”为搜寻词,限于文献 “标题”检索2001—2011年发表的相关论文数,截止2011年10月16日,Antrodia camphorata 129篇、Antrodia cinnamomea 56篇、Taiwanofungus camphorate 10篇,Antrodia camphorata论文发表的高峰期在2007年,并未受2004年修正学名的影响。Antrodia cinnamomea论文发表的高峰期在2006年,以Antrodia cinnamomea为学名发表的论文11篇,以Antrodia camphorata为学名发表的论文12篇,前者略少。2006年以后以Antrodia camphorata为学名发表的论文皆多于Antrodia cinnamomea。不论采用何种学名,樟芝国际研究热潮主要集中于2007—2008年,2009年相关的研究论文发表已开始减少。
台湾 “财团法人食品工业研究所生物资源保存及研究中心”于2005年1月13日公告,将其现有樟芝菌种BCRC 35396、BCRC 35398、BCRC 35716及BCRC 36401均更名为 Antrodia cinnamomea T.T.Chang&W.N.Chou。樟芝采用何种学名目前学术界仍未取得一致。
3 台湾樟芝硕博士论文数量与研究领域分布
1992—2010年台湾樟芝相关博硕士研究论文数量变化如图1所示,2001—2007年为台湾樟芝硕博士论文研究的快速成长期,2007年单年的论文篇数达36篇。自1992年至今台湾樟芝硕博士研究论文共计229篇,亦即平均每年有12篇。依主题,共可分为13类。樟芝“生物活性”研究论文数量远高于其他类别,显示出樟芝功能特别受到重视。樟芝 “液态培养”与 “成分分析”研究排名为第 2及第3位,显示台湾地区研究学者仍相当重视应用性的研究。樟芝“分子生物”与“作用机制”方面研究排序虽为第4位与第5位,其研究篇数也不少,显示有不少台湾地区研究学者重视基础研究。进一步分析 “生物活性”相关研究,共可分24类 (表1),其中研究最多的前5类依其排序为:(1)抗肿瘤/抗癌,(2)保肝,(3)抗氧化,(4)免疫调节,(5)抗发炎,显示了该5项为樟芝主要生物活性。樟芝对心血管疾病,如降血糖、降三酸甘油脂与预防动脉硬化方面,也有其生物活性。
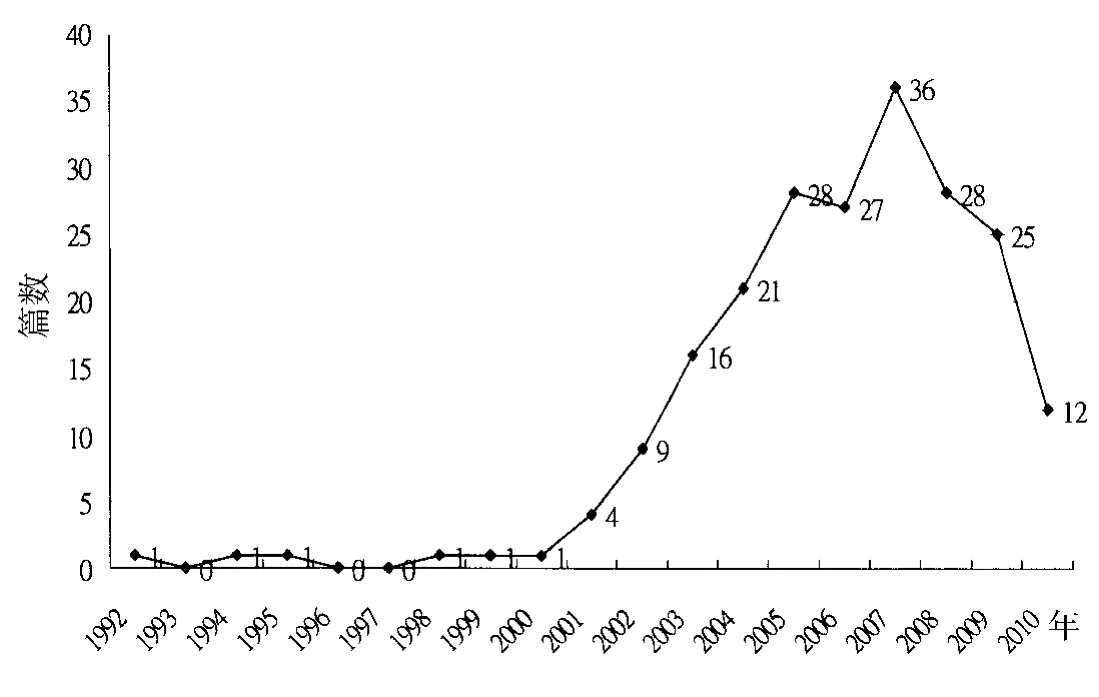
图1 1992—2010年台湾樟芝相关博硕士研究论文数量变化
4 2000—2011年台湾樟芝研究计划的件数与经费变化
2000—2011年台湾地区樟芝研究计划的数量与经费变化如图2所示,就研究计划件数而言,自2000年8件开始逐渐增加至2004年19件,2005年减少为12件,其后逐渐增加至2009年的26件为高峰期;就研究计划经费而言,2000—2008年期间相关研究经费,以 2003年与2005年较高,2009年显著增加至最高,达新台币7000万元。2000—2011年樟芝研究计划件数与经费累计分别为208件与新台币3.5亿元。与前述台湾硕博士论文篇数的发展趋势比较,除2006年外,2000—2007年论文篇数持续增加,然其与研究计划件数和经费并无相关性。
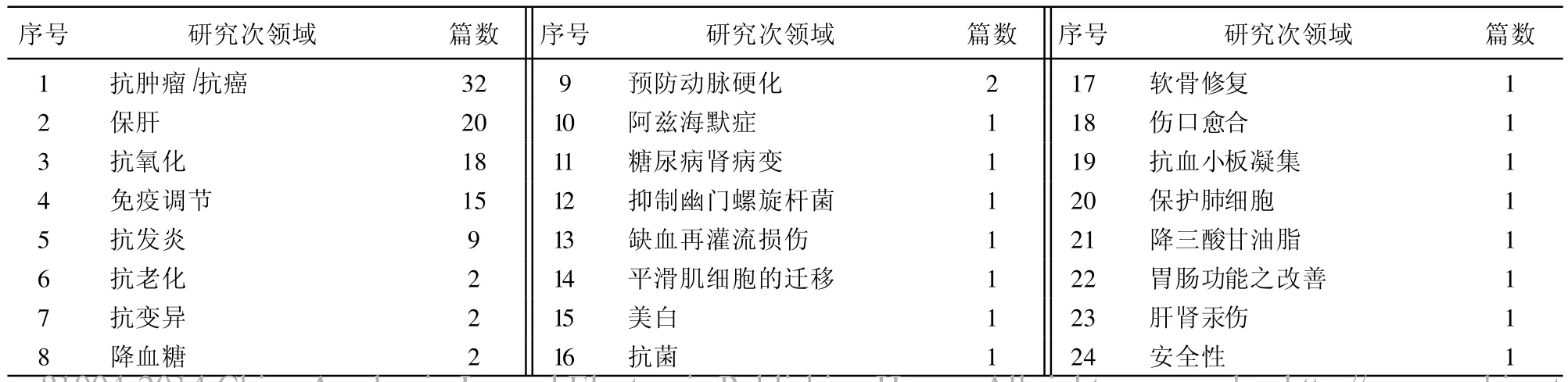
表1 台湾樟芝相关硕博士论文有关生物活性次领域与篇数
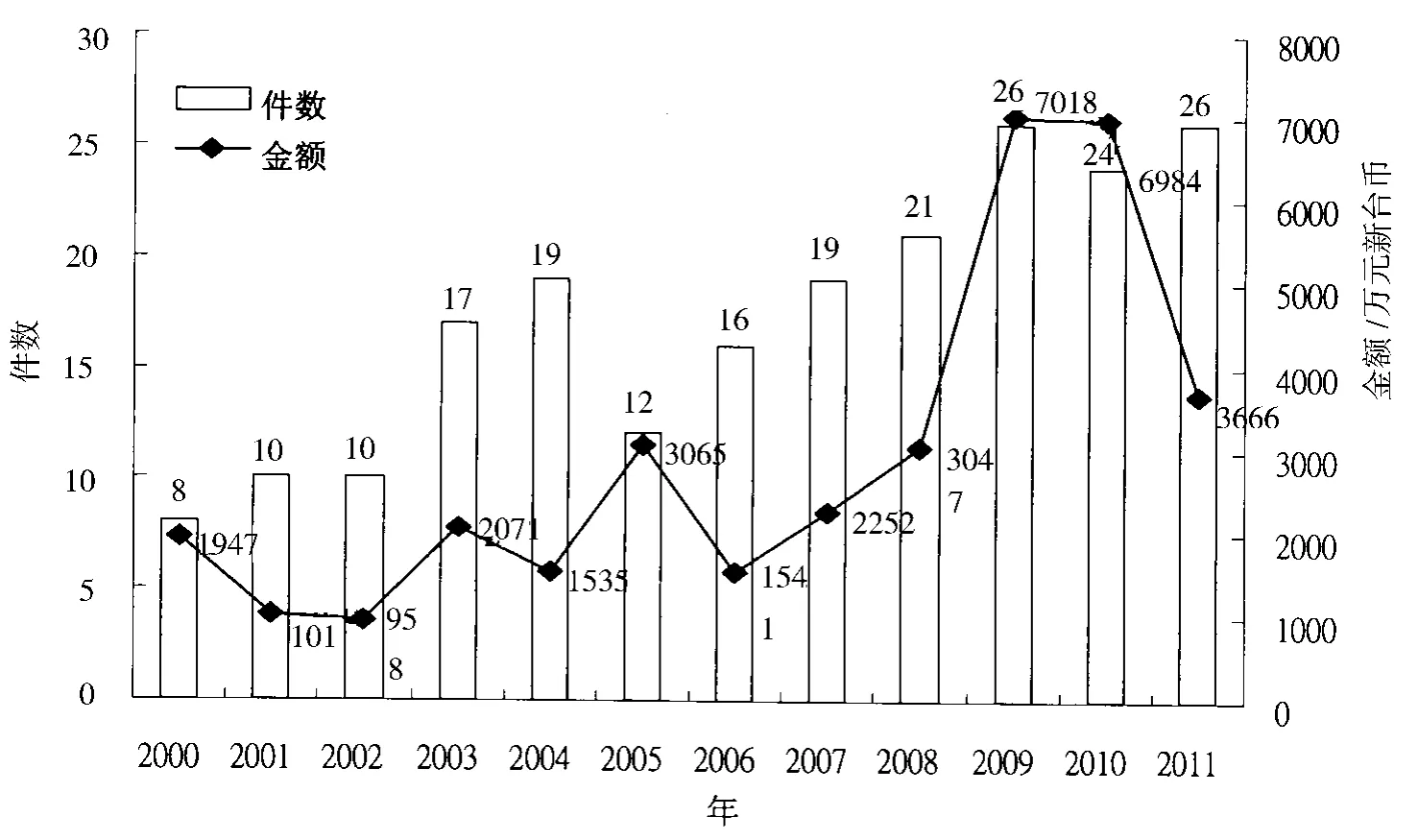
图2 2000—2010年台湾樟芝相关研究计划数量与经费变化
5 2003—2011年台湾有关樟芝发明专利公报的数量变化及特定化合物种类
台湾第一件樟芝发明专利为2003年的 《樟芝之固体培养方法及其所得固体培养物》(公告号565430),2009年樟芝发明专利6件,为高峰期,其后获得专利件数开始减少,至目前总计有26件。台湾樟芝新型专利仅有1件,为2009年的 《牛樟芝栽培箱》。近年来虽然樟芝发明专利件数并无显著增加,然值得注意的是自2007年以后樟芝 《发明公开公报》的数量自9件显著增加为2009年的25件,2010年与2011年亦分别有17件与22件,显示未来仍可能有相当的专利被核定。迄今已核定的29件樟芝相关专利,可分为8类,其专利主题与数量依序为:①生物活性成分组合物13件,②制造方法8件,③制剂配方2件,④液态培养方法2件,⑤固体培养方法1件,⑥人工栽培方法1件,⑦废弃物再利用1件,⑧用途1件。
台湾樟芝相关专利中 “专利范围”含源自特定化合物的专利基本资料如表2所示,目前可分3类:①多糖体2种,②蛋白质2种,③三萜类5种以上,共计9种以上,这9种为:①β-(1-6)-葡萄糖基支链的β-(1-3)-D-喃葡聚糖 (分子量范围为50~200万之间),②多糖体 (分子量范围为1000~30000之间),③蛋白阿卡安1(ACA1),④谷胱甘肽依赖型甲醛脱氢酶 (glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase,GFD),⑤3-isobutyl-4-{4-[(3-甲基-2-butenyl)oxy]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-2,5-pyrroledione,⑥4,7-二甲氧基-5甲基-1,3-苯并二氧环 (4,7-dimethoxy-5-methy-1,3-benzodioxole),⑦3-异丁基-4-[4-(3-甲基-2-丁烯氧基)苯基]-1H-吡咯-1-醇-2,5-二酮及相关衍生物,⑧4-羟基-2,3-二甲氧基-6-甲基-5(3,7,11-三甲基-2,6,10-十二碳三烯)-2-环己烯酮 (4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5(3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl)-cyclohex-2-enone),⑨Antroquinonol B与Antroquinonol C等。前述樟芝特定化学组成专利权人主要为葡萄王企业股份有限公司、国鼎生物科技股份有限公司及善笙生物科技股份有限公司。
6 樟芝研究发展趋势
6.1 与产业研究发展相结合 由2000—2011年台湾樟芝研究计划的件数与经费变化显示,于2009年相关研究达高峰,学术界的研究能量未来将逐渐转入产业,其中主要包括从事相关研究的研究生所累积的研究经验导入产业,研究成果落实于产业应用,与学界研究和产业研究的结合。目前在台湾地区从事樟芝生产、制造、代理与销售的厂商相当多,也有不少厂商自行投入研发经费,或与学术界合作,或争取政府研发补助从事樟芝相关研究,主要研究多以验证产品的生物活性为主。虽然近两年政府补助研究计划件数与经费并未显著持续增加,但并不表示相关研究活动减少;而产业界自行投入研发活动的费用无法呈现于政府补助研发经费统计之中。
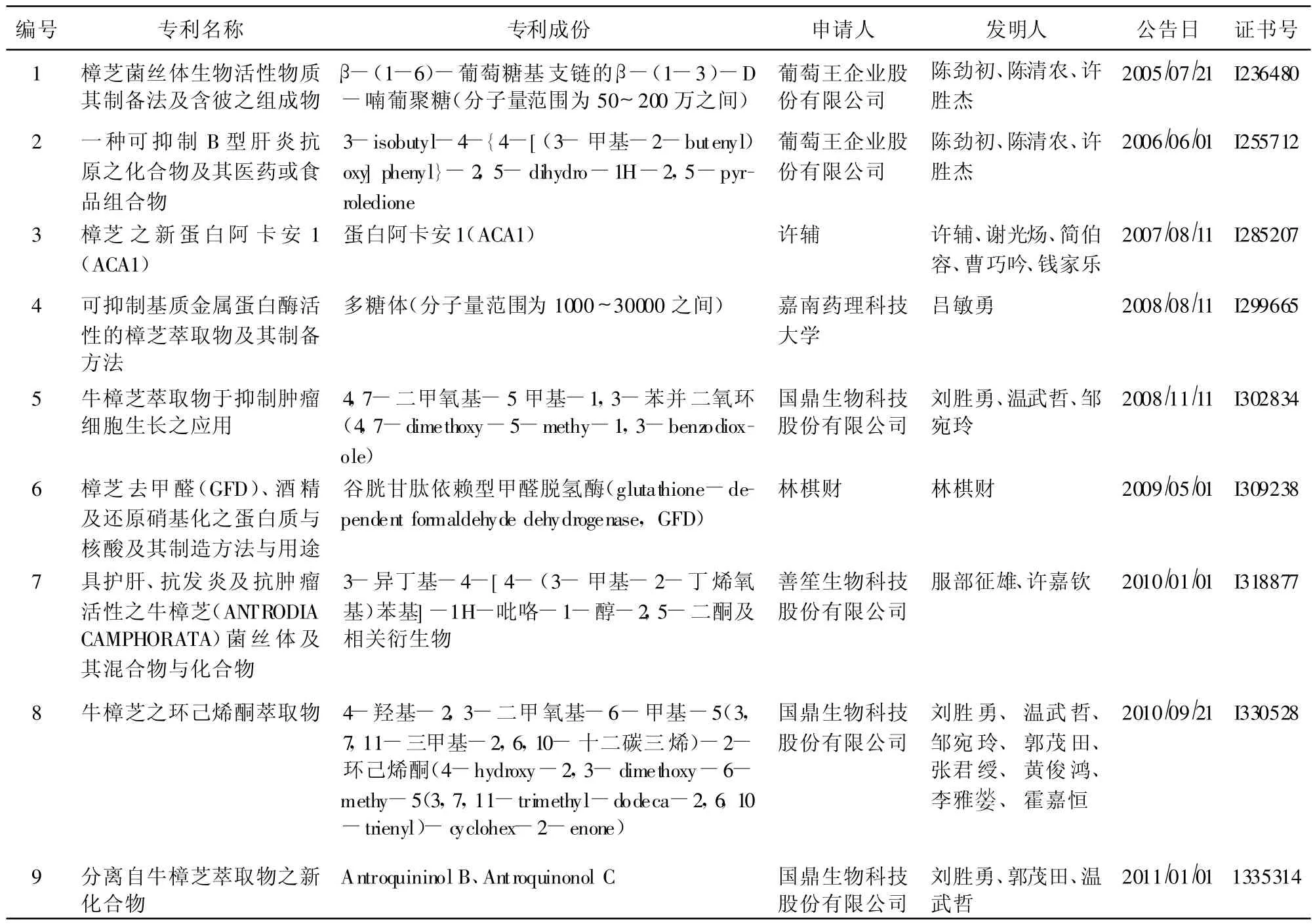
表2 台湾樟芝相关专利中 《专利范围》含源自特定化学组成的专利基本数据
6.2 研究成果以智慧财产权保护 由于樟芝具有高度的产业价值与发展潜力,部分研究是以生物活性成分的发现、结构确认与生物活性验证为主,期能为未来保肝、抗癌、抗发炎新药开发找出发展机会。由台湾专利 《发明公开公报》近十年数量显著持续增加,显示出学术研究逐渐重视智能财产权保护与未来的产业价值。
6.3 验证樟芝特定成分的生物活性与药理机制 过去虽然已有许多从事樟芝生物活性的研究,以萃取物为主,主要因特定成分需经分离纯化、结构鉴定与大量制备,方能有足够材料进行后续动物试验,以樟芝“特定成分”进行生物活性研究较为不易。于2010—2011年的国际期刊论文中,已发现不少研究以樟芝“特定成分”进行生物活性研究,多数仍以 “活体外”的细胞培养试验为主。而未来以樟芝 “特定成分”或 “特定成分组合物”的细胞培养试验、动物试验、药理机制研究或属于樟芝临床的研究报告将有助于产业发展。
6.4 樟芝培养方式与培养条件对特定活性成分的影响 樟芝培养方式包括固态培养与液态培养两类,固态培养可分:①牛樟木培养,②非牛樟段木培养,③太空包培养,④固态培养基培养4类。液态培养产出物包括:①菌丝体,②发酵液,③菌丝体与发酵液3种。菌株品系、培养方式、培养基材种类、培养基配方组成、培养条件及培养周期与樟芝生物活性成分产出的种类和数量具有密切关联性。樟芝不同制程产品的 “生物活性成分”与 “品管指标成分”在未来仍有相当大的研究空间。
7 结 语
樟芝为台湾地区所发现的特有药用真菌,20年来的研究发展基础是促成今日台湾樟芝产业蓬勃发展的重要原因。樟芝的命名与学名鉴定,也体现了分子生物技术对樟芝物种分类与鉴定的影响。近20年生物科技对产业发展影响既深且广,新兴生技与传统产业有高度连动性。因为有足够学术研究的基础,对于樟芝培养技术、生物活性成分、生物活性与安全性都有广泛与充分的认识。展望未来,樟芝研究仍将是产业发展不可或缺的要素。从学术的角度,樟芝仍有许多有待探讨的课题,例如由原生牛樟木所产生的樟芝,种源与栽培期对其生物活性的影响;从产业的角度看,不同菌株与不同制程,对于樟芝生物活性成分组成物的比例与含量,也是值得深入研究的课题。
[1]Zang,M.and Su,Q.H.G anoderma comphoratum,a new taxon in genus G anoderma from Taiwan.Acta BotanicaYunnanica 1990.12:395-396.
[2]Geethangili,M.and Tzeng,Y.-M.Review of pharmacological effects of Antrodia camphorata and its bioactive compounds.Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2011:1-17.
[3]Lin,T.-Y.,Chen,C.-Y.,Chien,S.-C.,Hsiao,W.-W.,Chu,F.-H.,Li,W.-H.,Lin,C.-C.,Shaw,J.-F.andWang,S.-Y.Metabolite profiles for Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies harvested at different culture ages and from different wood substrates.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2011.59(14):7626-7635.
[4]Shi,L.-S.,Chao,C.-H.,Shen,D.-Y.,Chan,H.-H.,Chen,C.-H.,Liao,Y.-R.,Wu,S.-J.,Leu,Y.-L.,Shen,Y.-C.,Kuo,Y.-H.,Lee,E.J.,Qian,K.,Wu,T.-S.and Lee,K.-H.Biologically active constituents from the fruiting body of Taiwanofungus camphoratus.Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry.2011.19(1):677-683.
[5]Shung,T.W.Camphoratins A-J,potent cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory triterpenoids from the fruiting body of Taiwanofungus camphoratus.Planta Medica.2010.76(12):1239-1239.
[6]Chen,Y.-c.,Liu,Y.-l.,Li,F.-y.,Chang,C.-l.,Wang,S.-y.,Lee,K.-y.,Li,S.-l.,Chen,Y.-p.,Jinn,T.-r.and Tzen,J.T.AntcinA,a steroid-like compoundfrom Antrodia camphorata,exerts anti-inflammatory effect via mimicking glucocorticoids.Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2011.32(7):904-911.
[7]Hsieh,Y.-H.,Chu,F.-H.,Wang,Y.-S.,Chien,S.-C.,Chang,S.-T.,Shaw,J.-F.,Chen,C.-Y.,Hsiao,W.-W.,Kuo,Y.-H.and Wang,S.-Y.AntrocamphinA,an anti-inflammatory principal from the fruiting body of Taiwanofungus camphoratus,and its mechanisms.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2010.58(5):3153-3158.
[8]Kumar,V.B.,Yuan,T.-C.,Liou,J.-W.,Yang,C.-J.,Sung,P.-J.and Weng,C.-F.2011.Antroquinonol inhibits NSCLC proliferation by altering PI3K/mTOR proteins and miRNA expression profiles.Mutation Research-Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 707(1-2):42-52.
[9]Tsai,P.-Y.,Ka,S.-M.,Chao,T.-K.,Chang,J.-M.,Lin,S.-H.,Li,C.-Y.,Kuo,M.-T.,Chen,P.and Chen,A.Antroquinonol reduces oxidative stress by enhancing the Nrf2signaling pathway and inhibits inflammation and sclerosisinfocal segmental glomerulosclerosismice.Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2011.50(11):1503-1516.
[10]Kumar,K.J.S.,Chu,F.-H.,Hsieh,H.-W.,Liao,J.-W.,Li,W.-H.,Lin,J.C.-C.,Shaw,J.-F.and Wang,S.-Y.Antroquinonol from ethanolic extract of mycelium of Antrodia cinnamomea protects hepatic cells from ethanol-induced oxidative stress through Nrf-2 activation.Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2011.136(1):168-177.
[11]Kuo,Y.New lanostane triterpenoids from Antrodia camphorata.Planta Medica.2011.77(12):1333-1333.
[12]Wu,M.-T.,Tzang,B.-S.,Chang,Y.-Y.,Chiu,C.-H.,Kang,W.-Y.,Huang,C.-H.and Chen,Y.-C.Effects of Antrodia camphorata on alcohol clearance and antifibrosis in livers of rats continuously fed alcohol.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2011.59(8):4248-4254.
[13]Lin,Y.-W.,Pan,J.-H.,Liu,R.H.,Kuo,Y.-H.,Sheen,L.-Y.and Chiang,B.-H.The 4-acetylantroquinonol B isolated frommycelium of Antrodia cinnamomea inhibits proliferation of hepatoma cells.Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2010.90(10):1739-1744.
[14]Lin,Y.-W.and Chiang,B.-H.4-Acetylantroquinonol B isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea arrests proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma hepg2 cell by affecting p53,p21 and p27 levels.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2011.59(16):8625-8631.
[15]Chang,C.-Y.,Cheng,T.-J.,Chang,F.-R.,Wang,H.-Y.,Kan,W.-C.,Li,S.-L.,Huang,L.-H.,Chen,Y.-C.,Tsai,W.-C.,Huang,C.-H.,Cheng,C.-H.,Lee,G.-Y.,Shyue,S.-W.,Chen,Y.-P.,Lin,K.-C.and Chuu,J.-J.Macrophage mediated anti-proliferation effects of Anthodia camphorata non-polysaccharide based extracts on human hepatoma cells.Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry.2011.75(4):624-632.
[16]Chiou,J.-F.,Wu,A.T.H.,Wang,W.-T.,Kuo,T.-H.,Gelovani,J.G.,Lin,I.H.,Wu,C.-H.,Chiu,W.-T.and Deng,W.-P.A preclinical evaluation of Antrodia camphorata alcohol extracts in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancerusing non-invasive molecularimaging.Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2011:1-12.
[17]Rao,Y.K.,Wu,A.T.H.,Geethangili,M.,Huang,M.-T.,Chao,W.-J.,Wu,C.-H.,Deng,W.-P.,Yeh,C.-T.and Tzeng,Y.-M.2011.Identification of antrocin from Antrodia camphorata as a selective and novel class of small molecule inhibitor of Akt/mTOR signaling in metastatic breast cancerMDA-MB-231 Cells.Chemical Research in Toxicology 24(2):238-245.
[18]Yang,H.-L.,Kuo,Y.-H.,Tsai,C.-T.,Huang,Y.-T.,Chen,S.-C.,Chang,H.-W.,Lin,E.,Lin,W.-H.andHseu,Y.-C.Anti-metastatic activities of Antrodia camphorata against human breast cancer cells mediated through suppression of the MAPK signaling pathway.Food and Chemical Toxicology.2011.49(1):290-298.
[19]Liu,F.-S.,Yang,P.-Y.,Hu,D.-N.,Huang,Y.-W.and Chen,M.-J.Antrodia camphorata induces apoptosis and enhances the cytotoxic effect of paclitaxel in human ovarian cancer cells.International Journal of G ynecological Cancer.2011.21(7):1172-1179.
[20]Yeh,C.-T.,Yao,C.-J.,Yan,J.-L.,Chuang,S.-E.,Lee,L.-M.,Chen,C.-M.,Yeh,C.-F.,Li,C.-H.and Lai,G.-M.Apoptotic cell death and inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human colon cancercells by an active fraction(HS7)from Taiwanofungus camphoratus.Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2011:1-13.
[21]Lien,H.-M.H.M.,Kuo,P.-T.P.T.,Huang,C.-L.C.L.,Kao,J.-Y.J.Y.,Lin,H.H.,Yang,D.-Y.D.Y.and Lai,Y.-Y.Y.Y.Study of the anti-proliferative activity of 5-substituted 4,7-dimethoxy-1,3-benzodioxole derivatives of SY-1 from Antrodia camphorata on Human COLO 205 colon cancer cells.Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine:eCAM.2011:450529-450529.
[22]Tsai,W.-C.,Rao,Y.K.,Lin,S.-S.,Chou,M.-Y.,Shen,Y.-T.,Wu,C.-H.,Geethangili,M.,Yang,C.-C.and Tzeng,Y.-M.Methylantcinate A induces tumor specific growth inhibition in oral cancer cells via Bax-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry Letters.2010.20(20):.6145-6148.
[23]Yang,C.-T.,Kuo,J.-T.and Lin,E.-S.Screening of medium composition forthe free radical-scavenging properties by Antrodia cinnamomea.International Journal of Food Science and Technology.2010.45(2):305-311.
[24]Chang,J.-M.,Lee,Y.-R.,Hung,L.-M.,Liu,S.-Y.,Kuo,M.-T.,Wen,W.-C.and Chen,P.An extract of Antrodiacamphorata mycelia attenuates the progression of nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus-prone NZB/W F1Mice.Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2011:1-7.
[25]Lee,C.-L.,Huang,C.-H.,Wang,H.-C.,Chuang,D.-W.,Wu,M.-J.,Wang,S.-Y.,Hwang,T.-L.,Wu,C.-C.,Chen,Y.-L.,Chang,F.-R.and Wu,Y.-C.First total synthesis of antrocamphin A and its analogs as anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet aggregation agents.O rganic&biomolecular chemistry.2011.9(1):70-73.
[26]Wu,M.-F.,Peng,F.-C.,Chen,Y.-L.,Lee,C.-S.,Yang,Y.-Y.,Yeh,M.-Y.,Liu,C.-M.,Chang,J.-B.,Wu,R.S.-C.,Yu,C.-C.,Lu,H.-F.and Chung,J.-G.Evaluation of genotoxicity of Antrodia cinnamomea in the Ames test and the in vitro chromosomal aberration test.2011.25(3):419-423.
[27]Chen,T.-I.,Chen,C.-C.,Lin,T.-W.,Tsai,Y.-T.and Nam,M.-K.A 90-day subchronic toxicological assessment of Antrodia cinnamomea in Sprague-Dawley rats.Food and Chemical Toxicology.2011.49(2):429-433.
[28]Hsieh,Y.-C.,Rao,Y.K.,Wu,C.-C.,Huang,C.-Y.F.,Geethangili,M.,Hsu,S.-L.and Tzeng,Y.-M.Methyl anteinate a from Antrodia camphorata induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells through oxidant-mediated cofillin-and bax-triggered mitochondrial pathway.Chemical Research in Toxicology.2010.23(7):1256-1267.
[29]Wu,S.-J.,Leu,Y.-L.,Chen,C.-H.,Chao,C.-H.,Shen,D.-Y.,Chan,H.-H.,Lee,E.J.,Wu,T.-S.,Wang,Y.-H.,Shen,Y.-C.,Qian,K.,Bastow,K.F.and Lee,K.-H.Camphoratins A-J,potent cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory triterpenoids from the fruiting body of Taiwanofungus camphoratus.Journal of Natural Products.2010.73(11):1756-1762.
[30]Wu,S.-H.Ryvarden,L.andChang,T.-T.Antrodia camphorata(’niu-chang-chih’),new combination of a medicinal fungus in Taiwan.Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica.1997.38(4):273-275.
[31]Chang,T.-T.and W.-N.Chou.Antrodia cinnamomea reconsidered and A.salmonea sp.nov.on Cunninghamia konishii in Taiwan.Bot.Bull.Acad.Sinica.2004.45:347-352.
[32]Wu,S.-H.,Yu,Z.-H.and Dai Y.C.Taiwanofungus,a polypore new genus.Fungal Sciences.2004.19:109-116.
[33]Chiu,H.-H.Phylogenetic analysis of Antrodia species and Antrodia camphorata inferred from internal transcribed spacer region.Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.2007.91(3):267-276.

