文拉法辛与选择性五羟色胺再摄取抑制剂对抑郁症转换策略疗效的Meta分析
何如东陈美玲周欢
·论 著·
文拉法辛与选择性五羟色胺再摄取抑制剂对抑郁症转换策略疗效的Meta分析
何如东*陈美玲*周欢*
目的 系统评价文拉法辛 (venlafaxine)与选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂 (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor,SSRI)对抑郁症转换策略疗效的差异。方法 检索1990~2010年的MEDLINE和中文文献,纳入文拉法辛与SSRI对抑郁症转换策略治疗效果的随机对照试验并进行Meta分析。结果 8个随机对照试验符合纳入标准,共5350例抑郁症患者。Meta分析结果显示,文拉法辛的临床治愈率是52.5%,SSRI的临床治愈率是43.3%,二者的差异有统计学意义(OR=1.38,95%CI:1.20~1.58,P<0.01);文拉法辛的有效率是67.8%,SSRI的有效率是59.6%,二者的差异有统计学意义(OR=1.33,95%CI:1.15~1.53,P<0.01)。 结论 文拉法辛较SSRI对抑郁症转换策略有更高的临床治愈率与有效率。
文拉法辛 SSRI 转换策略 难治性抑郁症
随着精神药理学的发展,特别是选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂 (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor,SSRI)的广泛应用,抑郁症治疗已经得到了明显的进展,但临床上仍有40%~50%的抑郁症患者首次治疗疗效不佳甚至无效[1-2]。而某些难治性抑郁症 (treatment-resistant depression, TRD)经历两种类型的抗抑郁药足量足程治疗无效。对于上述两类患者实施转换策略是较优的选择[3]。目前抗抑郁药有几大类作用机制不同的药物可以选择,在转换药物的选择上,不同作用机制的药物在疗效上是否存在差异?近年来,5-羟色胺与去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂(serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors,SNRI)文拉法辛已在临床一线广泛应用。有证据表明文拉法辛在疗效上比SSRI更好[4-5]。在转换药物的选择上,首选文拉法辛是否会比SSRI更有优势?为了探讨文拉法辛与SSRI在转换策略疗效的差异,本研究对既往研究的文献进行系统评价。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究文献 纳入标准:①随机对照试验(randomized controlled trials,RCT);②研究对象符合美国精神障碍诊断与统计手册第4版(DSM-IV)、国际疾病分类系统(ICD-10)和中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准第3版(CCMD-3)的抑郁症诊断标准,有明确的排除标准;③对象入组前经历一次或以上足量足程的抗抑郁药治疗无效后接受转换治疗,转换药物包括文拉法辛与SSRI类药物;④纳入的文献要有明确的评定工具、结局指标、药物不良反应统计与退出原因说明。排除标准:①非随机对照试验;②结局指标数据不完整。
1.2 文献检索 计算机检索MEDLINE与万方数据库的核心期刊,检索年限1990~2010年。英文检索关键词:treatment-resistant depression、refractory depression、difficult-to-treat depression、antidepressant、switching、switching strategies、venlafaxine、SSRI;中文检索关键词:难治性抑郁症、转换治疗、转换策略、文拉法辛、SSRI。
1.3 文献质量评估 采用Jadad评估标准:①随机:描述了具体的随机方法且随机方法合理2分,只描述随机1分;②双盲:描述了具体的双盲方法并且方法合理2分,只描述双盲1分;③退出与失访:对退出与失访的例数与理由进行描述1分,没描述0分。
1.4 统计学处理 采用Revman4.2软件进行检索文献的数据处理和统计学分析,计数资料用比值比(odds ratio,OR)与95%可信区间(CI)表示。采用卡方检验分析各研究间的异质性,如各研究间有统计学同质性时(P≥0.05)时,采用固定效应模型(fixed effects model)作 Meta分析;如各研究间有统计学异质性时(P<0.05)时,采用随机效应模型(randomized effects model)作Meta分析。
2 结果
2.1 文献检验结果 初步检索出25篇文拉法辛与SSRI类药物对抑郁症转换策略疗效的文献,有8篇文献符合纳入标准[6-13],中文核心期刊无相关文献。
2.2 纳入文献的特征与方法学质量评估 8篇文献共纳入5350例抑郁症患者,总计接受文拉法辛治疗人数2288例,接受SSRI治疗人数1772例。见表1。
2.3 结局指标的Meta分析 纳入文献中有6个试验提供临床治愈率与有效率,1个试验提供临床治愈率,1个试验提供有效率。提取7个文献临床治愈率数据进行Meta分析,森林图结果示各研究间异质性检验无统计学意义(I2=0%,P=0.48),采用固定模型作Meta分析。以临床治愈率为结局指标,文拉法辛组治愈人数为1115例,治愈率52.5%(1115/2122);SSRI治愈人数694例,治愈率43.3%(694/1604),差异有统计学意义(OR=1.38,95%CI:1.20~1.58,P<0.01)。见图1。
提取7个文献有效率数据进行Meta分析,森林图结果示各研究间异质性检验无统计学意义 (I2=11.6%,P=0.34),采用固定模型作Meta分析。以有效率作为结局指标,文拉法辛有效人数1512例,有效率67.8%(1512/2231);SSRI有效人数1023例,有效率59.6%(1023/1717),差异有统计学意义(OR=1.33,95%CI:1.15~1.53,P<0.01)。见图2。
需要治疗人数 (number needed to treatment,NNT)的计算:提取文献的临床治愈率与有效率的数据Meta分析计算风险差异(RD),NNT=1/RD。以临床治愈率为结局指标,两组的临床治愈率差异有统计学意义(RD=0.07,95%CI:0.04~0.11,P<0.01),NNT=14(95%CI:9~25)。以有效率为结局指标,两组的有效率差异有统计学意义(RD=0.06,95%CI:0.03~0.09,P<0.01),NNT=17(95%CI:11~33)。
退出率的Meta分析:提取8个文献的退出率数据进行Meta分析,森林图结果示各研究间异质性检验无统计学意义(I2=3.2%,P=0.40),采用固定模型作Meta分析,以退出率作为结局指标,两类药的差异无统计学意义 (OR=0.88,95%CI:0.78~1.00,P=0.05)。
3 讨论
抗抑郁治疗无效是一个难题,为此目前提出了一些治疗策略与步骤,例如抑郁症序贯治疗(sequenced treatment alternatives to relieve depression,STAR*D),目的是通过转换策略、增效策略、联合策略等治疗步骤提高患者的疗效,特别是临床治愈率。因为临床治愈较临床有效有更好的功能恢复与良好预后、更少的复发和复燃风险、更少的卫生资源使用率、低自杀和酒精药物依赖风险率、更少的致残症状[14]。

表1 文拉法辛与SSRI对抑郁症转换策略疗效对照文献特征
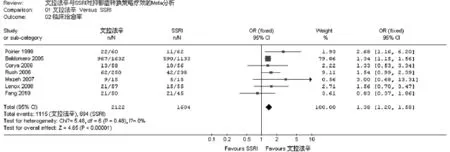
图1 文拉法辛与SSRI对抑郁症转换策略的临床治愈率的Meta分析
基于安全与耐受性的原因,SSRI类药物目前已经是抗抑郁治疗的首选用药。纳入的8个试验的对象入组前SSRI使用率超过50%,其中有5个试验的对象入组前均经历SSRI治疗无效[8-12]。对于SSRI治疗无效的患者如采用转换策略会面临着同类与异类转换的选择,因为换用另一个SSRI或其它类型的抗抑郁药都有一定的效果[15-17],没有明显的证据证明哪类抗抑郁药更有优势。至今转换策略的对照研究仍少,所以有必要进行系统评价。

图2 文拉法辛与SSRI对抑郁症转换策略的有效率的Meta分析
本Meta分析纳入的随机对照试验中有5个试验采用双盲设计,方法学质量良好。2个试验[7-8]虽然未采用盲法设计,由于样本量大,在转换策略疗效方面的结果仍有一定代表性。纳入分析的试验有相同的结局指标,疗效评定工具基本一致。需指出的是纳入分析的试验间有一些特征上的差异:Poirier等[6]疗程只有4周。Fang等[13]采用固定剂量治疗,其中文拉法辛225 mg,帕罗西汀20 mg。Mazeh等[10]研究对象是老年抑郁症。Brent等[11]研究对象是青少年抑郁症。此外,本分析纳入的试验统计学的同质性好,合并效应量的结果具有良好的证据的强度,故本研究对于文拉法辛与SSRI对转换策略的疗效的系统评价可信。
本Meta分析以临床治愈率与有效率为结局指标系统评价文拉法辛与SSRI对抑郁症转换策略疗效的差异。纳入分析的试验中,文拉法辛的临床治愈率为24.8%~60%,有效率为28%~80%;SSRI的临床治愈率为17.6%~52.1%,有效率为26.4%~71.1%。Meta分析结果显示两种药物存在差异,文拉法辛较SSRI对抑郁症转换策略有更高的临床治愈率(OR=1.38)与有效率(OR=1.33)。NNT计算结果显示,与SSRI对照,抑郁症患者采用文拉法辛治疗增加1例得到临床治愈的获益需要治疗的人数是14例,采用文拉法辛治疗增加1例得到有效的获益需要治疗的人数是17例。结果显示在转换策略中采用文拉法辛治疗更能让抑郁症患者在治疗中获益。Bauer等[18]纳入5个试验Meta分析文拉法辛与其它类型抗抑郁药 (主要是SSRI类药物)对首次治疗无效与TRD患者的疗效差异,结果示文拉法辛有更高的临床治愈率(OR=1.35,95%CI:1.20-1.52)与有效率(OR=1.35,95%CI:1.19-1.54)。Papakostas等[19]以相对危险度(RR)为合并效应量纳入3个试验Meta分析文拉法辛与SSRI对SSRI治疗无效患者的疗效差异,结果示文拉法辛有更高的临床治愈率 (RR=1.31,95%CI:1.02-1.67)。这2个Meta分析的结果都显示文拉法辛在转换策略上较SSRI更有优势,本研究结果与二者一致。
抑郁症治疗决策是基于有效、安全与耐受的原则[20]。文拉法辛是一种5-羟色胺与去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂,其双重活性的作用机制对抑郁症的治疗效果较选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂更有优势[4-5],在转换策略上较SSRI有潜在的优势[21]。在安全性与耐受性方面,纳入的试验统计文拉法辛与SSRI的副反应主要是恶心、呕吐、口干等消化系统症状;头昏、头痛等神经系统症状。Fang等[13]报告文拉法辛食欲不振与头昏的发生率较SSRI高,其它试验无差异。需指出的是Rush等[8]报告文拉法辛与SSRI各有2例自杀意念或自杀企图。Brent等[11]报告文拉法辛有11例自杀意念或自杀企图,SSRI有6例。各试验因严重药物副作用的退出率无差异,提示文拉法辛是一种具有良好安全性与耐受性的抗抑郁药。
由于目前转换策略的对照研究较少,本Meta分析纳入的文献较少。2个大样本试验的方法学设计上仍存不足,部分试验样本量过小,结果难免偏倚。结论仍需要大样本方法学设计合理的试验补充评价。
[1]Trivedi MH,Rush AJ,Wisniewski SR,et al.Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurementbased care in STAR*D:implications for clinical practice[J].Am J Psychiatry,2006 163(1):28-40.
[2]Kroenke K,West SL,Swindle R,et al.Similar effectiveness of paroxetine,fluoxetine,and sertraline in primary care:a randomized trial[J].JAMA,2001,286(23):2947-2955.
[3]American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder (revision).American Psychiatric Association[J].Am J Psychiatry,2000,157(4 suppl):1-45.
[4]Thase ME,Entsuah AR,Rudolph RL.Remission rates during treatment with venlafaxine or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors[J].Br J Psychiatry,2001,178(3):234-241.
[5]Nemeroff CB,Entsuah R,Benattia I,et al.Comprehensive analysis of remission(COMPARE)with venlafaxine versus SSRIs[J].Biol psychiatry,2008,63(4):424-434.
[6]Poirier MF,Boyer P.Venlafaxine and paroxetine in treatmentresistant depression.Double-blind,randomised comparison[J].Br J Psychiatry,1999,175(7):12-16.
[7]Baldomero EB,Ubago JG,Cercos CL,et al.Venlafaxine extended release versus conventional antidepressants in the remission of depressive disorders after previous antidepressant failure:ARGOS study[J].Depress Anxiety,2005,22(2):68-76.
[8]Rush AJ,Trivedi MH,Wisniewski SR,et al.Bupropion-SR,sertraline, or venlafaxine-XR after failure of SSRIs for depression[J].N Engl J Med,2006,354(12):1231-1242.
[9]Corya SA,Williamson D,Sanger TM,et al.A randomized,double-blind comparison of olanzapine/fluoxetine combination,olanzapine, fluoxetine, and venlafaxine in treatment-resistant depression[J].Depress Anxiety,2006,23(6):364-372.
[10]Mazeh D,Shahal B,Aviv A,et al.A randomized,singleblind,comparison of venlafaxine with paroxetine in elderly patients suffering from resistant depression[J].Int Clin Psychopharmacol,2007,22(6):371-375.
[11]Brent D,Emslie G,Clarke G,et al.Switching to another SSRI or to venlafaxine with or without cognitive behavioral therapy for adolescents with SSRI-resistant depression: the TORDIA randomized controlled trial[J].JAMA,2008,299(8):901-913.
[12]Lenox-smith AJ,Jiang Q.Venlafaxine extended release versus citalopram in patients with depression unresponsive to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor[J].Int Clin Psychopharmacol,2008,23(3):113-119.
[13]Fang Y,Yuan C,Xu Y,et al.Comparisons of the efficacy and tolerability of extended-release venlafaxine, mirtazapine,and paroxetine in treatment-resistant depression: a double-blind,randomized pilot study in a Chinese population[J].J Clin Psychopharmacol,2010,30(4):357-364.
[14]McClintock SM,Husain MM,Wisniewski SR,et al.Residual symptoms in depressed outpatients who respond by 50%but do not remit to antidepressant medication[J].J Clin Psychopharmacol,2011,31(2):180-186.
[15]Thase ME,Blomgren SL,Birkett MA,et al.Fluoxetine treatment of patients with major depressive disorder who failed initial treatment with sertraline[J].J Clin Psychiatry,1997,58(1):16-21.
[16]Thase ME,Rush AJ,Howland RH,et al.Double-blind switch study of imipramine or sertraline treatment of antidepressant-resistant chronic depression[J].Arch Gen Psychiatry,2002,59(3):233-239.
[17]Reynaert-Dupuis C,Zdanowicz N,Leyman S,et al.Efficacy and tolerance of venlafaxine in depressed patients switched from prior antidepressant treatment[J].Prim Care Psychiatry,2002,8(2):63-68.
[18]Bauer M,Tharmanathan P,Volz HP,et al.The effect of venlafaxine compared with other antidepressants and placebo in the treatment of major depression:a meta-analysis[J].Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2009,259(3):172-185.
[19]Papakostas GI,Fava M,Thase ME.Treatment of SSRI-resistant depression:a meta-analysis comparing within-versus across-class switches[J].Biol Psychiatry,2008,63(7):699-704.
[20]Schatzberg AF.Safety and tolerability of antidepressants:weighing the impact on treatment decisions[J].J Clin Psychiatry,2007,68(Suppl 8):26-34.
[21]Connolly KR,Thase ME.If at first you don't succeed:a review of the evidence for antidepressant augmentation, combination and switching strategies.Drugs,2011,71(1):43-64.
The efficacy of venlafaxine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in antidepressant switching strategies:a meta-analysis.
HE Rudong,CHEN Meiling,ZHOU Huan.The Chronic Disease Prevention and Treatment Center of Maoming,GuangDong,No 10 Lane 1 Jixing Road,Maoming 525000.China.Tel:0668-2305133.
Objective To systematically review the difference in efficacy between venlafaxine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors(SSRI)in antidepressant switching strategies.Methods We conducted a meta-analysis comparing the efficacy between venlafaxine and SSRI in antidepressant switching strategies.The randomized controlled trials (RCT) were identified through searches of MEDLINE and Chinese publications for the years 1990 to 2010.Results Eight RCTs involving 5350 patients with maior depressive met inclusion criteria.Results of meta-analysis showed that the remission rates were 52.5%and 43.3%for venlafaxine and SSRI, respectively.There were statistically significant difference(OR=1.38,95%CI:1.20~1.58,P<0.01)in remission rates between the two treatment groups.The response rates were 67.8%and 59.6%for venlafaxine and SSRI, respectively.There were statistically significant difference(OR=1.33,95%CI:1.15~1.53,P<0.01)in response rates between the two treatment groups.Conclusions Remission and response rates are significantly higher in venlafaxine than in SSRI in antidepressant switching strategies.
Venlafaxine SSRI Switching strategies Treatment-resistant depression
R794.4
A
2011-03-28)
(责任编辑:曹莉萍)
* 广东省茂名市慢性病防治中心(茂名 524500)
(E-mail:hurudong@sina.com)

