Study on Instable Combustion of Solid Rocket Motor with Finocyl Grain
HU Da-ning(胡大宁),HE Guo-qiang(何国强),LIU Pei-jin(刘佩进),WANG Zhan-li(王占利)
(1.Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710072,Shaanxi,China;2.The 210th Institute of Second Academy,China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation,Xi’an 710065,Shaanxi,China)
Introduction
With the development of missile technology and improvement of its performance,some higher requirements for the solidrocket motor were put forward,such as higher propellant capacity,larger length-diameter ratio and higher initial thrust.In today’s high performance rocket motors with higher operating pressure,HTPB composite propellant and complex finocyl grain are widely used.However,the acoustic instable combustion was found in several rocket motors.
The acoustic instable combustion of rocket motors is generally induced by the acoustic wave due to various disturbances in the combustion chamber.If the frequency of the pressure oscillation generated by the combustion disturbance is close to the intrinsic frequency of the chamber itself,a significant gas pressure oscillation will occur in the chamber and leads to vibration,spinning and motor case damage or even burst.The instable combustion can be divided into acoustic related and non-acoustic related.The acoustic related instable combustion can be divided into pressure and speed coupling instable combustions.There are three kinds of pressure oscillations,i.e.,high frequency(more than 1 000 Hz),medium frequency(100-1 000 Hz)and low frequency(less than 100 Hz).According to the propagation of acoustic wave in the combustion chamber,the vibration modes can be divided into three types,i.e.,longitudinal,radial and tangential[1].
As the essence of instable combustion is understood in the rocket technology development,some methods to suppress combustion oscillation are presented.The earliest methods include inserting a slab into the hole of the tubular grain,drilling a series of radial holes by spiral arrangement in the grain,or changing the internal hole of the grain from circular to non-circular[2].Lately,it is found that the instable combustion can be reduced by changing the geometry shape of the grain and adding aluminum or other metal particles into the propellant[3].
This paper discusses the instable combustion occurring in three high grain capacity motors with high energy composite propellant and finocyl grain.The methods,such as changing grain shape and modifying nozzle,are found to be effective to suppress the instable combustion.They can be applied to control the combustion instability in similar motors.
1 Analysis on Instable Combustion
The length-diameter ratio of tested Motor-1 is 6.6.HTPB propellant with aft end finocyl grain is used.In the test,significant instable combustion was found in the first stage and the transit stage,as shown in Fig.1.
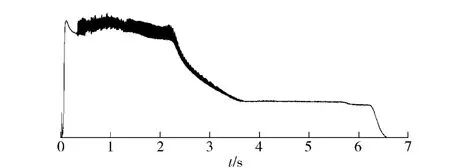
Fig.1 Pressure-time curve of Motor-1
Motor-2 uses a finocyl grain HTPB propellant,the same as that of Motor-1.Its length-diameter ratio is 7.But,it has anelliptical long tail nozzle with a 75°convergence angle at the convergence section.The instable combustion in this motor occurs at about 6.2 second after motor ignition,as shown in Fig.2.Motor-3 is also with finocyl grain,HTPB propellant,and single chamber with dual thrust.Its length-diameter ratio is 12.6.The front half of the grain is low burning rate propellant;while the aft end of the grain is high burning rate propellant.The motor is very stable in the first stage,but there is a slight pressure disturbance in the second stage,as shown in Fig.3.
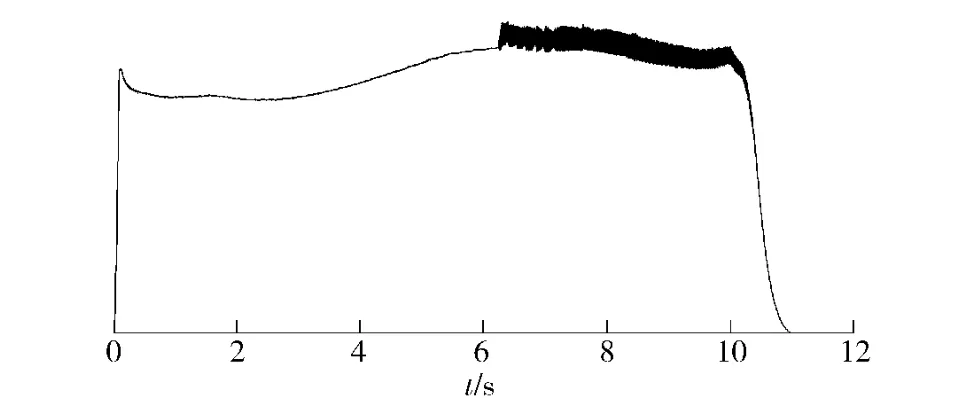
Fig.2 Pressure-time curve of Motor-2
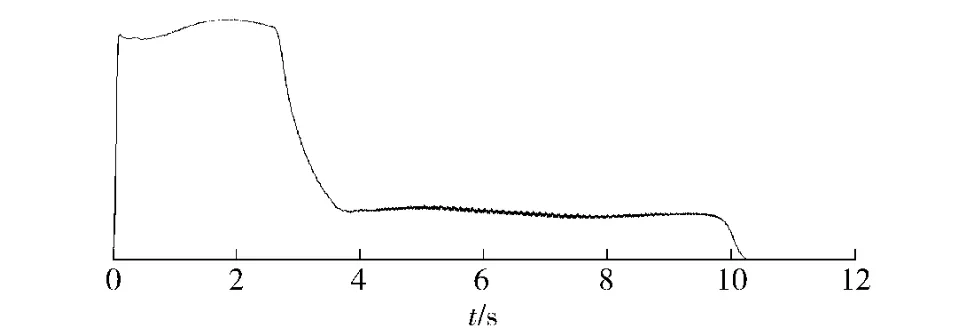
Fig.3 Pressure-time curve of Motor-3
The spectrums of pressure-time curves are obtained by using spectrum analyzer.The spectra indicate that the base frequencies of three motor’s pressure oscillations are close to the longitudinal fundamental frequencies of the grain cavities;therefore,they are longitudinal medium frequency instability.The base frequencies of three motor’s pressure oscillations are 406 Hz,265 Hz and 292 Hz,respectively.
2 Methods to Suppress Instable Combustion
The acoustic instable combustion is caused by the interaction between the combustion and acoustic processes in the combustion chamber.Pressure oscillation frequency is close to the intrinsic frequency of the combustion chamber acoustic.There are various damping and gaining factors inside the combustion chamber,which can dampen or amplify the propagation of the acoustic energy;they are all related to the frequency and vibration mode.The pressure oscillation will depend on the final result of amplifying or damping to each type of oscillations in the chamber.If the amplifying effect is stronger than the damping effect,the pressure oscillation will become stronger and stronger and the instable combustion will occur,otherwise,it will eventually disappear.
The velocity or pressure coupling exists in the combustion process of the solid rocket motor.Therefore,the propellant itself and its combustion characteristics will influence the combustion instability[4],and the grain that determines the natural frequency of the combustion chamber and the mass generation and flow rates of combustion gas also effects on the combustion instability.The instable combustions in all three motors mentioned above are longitudinal and in medium frequency.The basic ways to suppress this kind of insta-ble combustion are adjustment of the propellant composition and modification of the combustion chamber.
2.1 Increasing Nozzle Damping Effect
In solid rocket motors,the acoustic variation energy can be lost through the nozzle in the means of radiation and convection,this energy lost is very significant if the oscillation is longitudinal.In most cases,the energy lost is the same level as the increase of the propellant combustion surface.The acoustic energy attenuation factor through the nozzle is

where Atis the area of the nozzle throat,ACis the section area of the combustion flow,the absolute value of αnozincreases with the frequency increase.Meanwhile,the acoustic dispersion is different if the geometry and length of the nozzle convergent section is different.Generally speaking,the loss in a nozzle with convex convergent section is greater than that in a nozzle with a concave convergent section;the longer the nozzle convergent section is,the larger the energy loss will be.For the same inlet March number,the cone shape nozzle has a higher damping effect.
In order to eliminate instable combustion in three above-mentioned rocket motors,the nozzle structure of the motors can be modified.Its convergent section can be changed to increase the damping effect on the acoustic energy.The acoustics character of combustion chamber can also modified by changing the grain shape.
1)Modification of Motor-1
Before the modification,the transition section in front of the nozzle throat is very short,and the inner surface of the nozzle divergent section and the surface of throat downstream are whole special profiles.After the modification,the arc of the nozzle upstream section is increased,as shown in Fig.4.
2)Modification of Motor-2
The original ellipsoid nozzle of Motor-2 is changed as a cone nozzle.The cone angle is 45°.The convergent angle of the nozzle is reduced from 75°to 56°,as shown in Fig.5.
3)Modification of Motor-3

Fig.4 Motor-1 nozzle structure
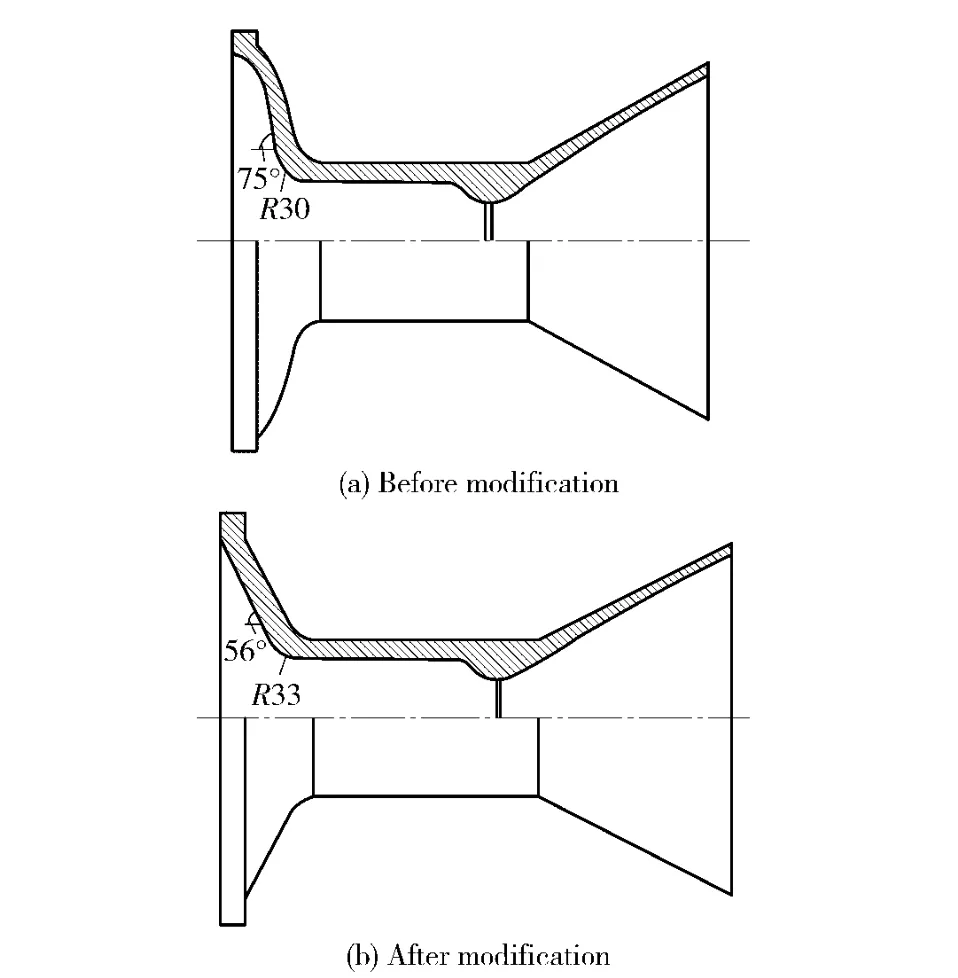
Fig.5 Motor-2 nozzle structure
For Motor-3,the convergent angle of the nozzle is changed from 59°to 45°in order to reduce the reflection of acoustic wave.The damping effect of the nozzle increases after the modification.However,since the length of the nozzle is not changed,decreasing the convergent angle will cause the increase of the divergent angle,and will increase the loss of combustion gas flow for given convergent shape;the divergent section of the nozzle can be modified to a special profile to reduce this loss.Fig.6 shows the nozzle before and after the modification.
2.2 AdjustmentofMassGeneration Rateof Combustion Gas
The variation of the propellant grain shape will greatly influence the acoustic wave propagation in the combustion chamber.The composite propellant is a kind of visco-elastic material;the acoustic energy will be absorbed significantly when transmitting within this kind of material,therefore,the solid propellant itself is very good damping material for the acoustic energy.The major source of the acoustic amplification in a solid rocket motor is the propellant combustion process.When there is a pressure oscillation inside the combustion chamber,the burning rate of the propellant also oscillates,and the oscillation of the propellant burning rate also amplifies the oscillation of the combustion pressure[5].The combustion flow,the disturbance of the flow,and the propagation of the acoustic wave inside the combustion chamber will all affect the propellant burning rate.

Fig.6 Motor-3 nozzle structure
In Ref.[4],an FEA calculation was carried out to analyze the acoustic field in the combustion chamber.The results show that the intrinsic frequency of the acoustic field can be changed significantly by increasing the section area in the front part of the grain.For example,the fundamental frequency of Motor-1 is 406 Hz before changing the grain shape,which is close to the propellant combustion oscillation frequency.The front part of the cylinder tube grain is changed to finocyl,and the combustion gas flow section area is also increased.After the change,the new first order longitudinal frequency is changed to 367 Hz,which is far from 396 Hz,and is good for preventing the instable combustion.The head of Motor-3’s grain can also be changed similarly to increase the combustion flow section area.
2.3 Improvement of Propellant Composition
The aluminum particles are widely used to increase the propellant’s specific impulse,and they also burn in the whole chamber and become condensed phase products in the main flow.They can also amplify or dampen the instable combustion in rocket motor.The experiment results show that they do not affect the response function greatly,but its combustion product,Al2O3,has a strong damping effect on the instable combustion,which is much stronger than those of the gas and surface,and can improve the combustion stability.Moreover,the aluminum combustion product also changes the sound speed in the chamber and affects the motor natural frequency indirectly.For most rocket motors,satisfactory results can be obtained by applying the above discussed estimation theory.Based on them,the aluminum and AP composition in the propellant can be adjusted,and the combustion performance can be improved.
3 Experimental Verification
After the modifications,the instable combustions in the redesigned motors are suppressed greatly.The typical test and the spectrum analysis results are shown below.
3.1 Motor-1
By analyzing the spectrum,the maximum peak of the first stage pressure is 0.000 68 MPa from 1.0 to 3.0 s;the maximum peak of the second stage pressure is 0.000 7 MPa from 4.5 to 6.6 s,therefore,the combustion instability has been eliminated.
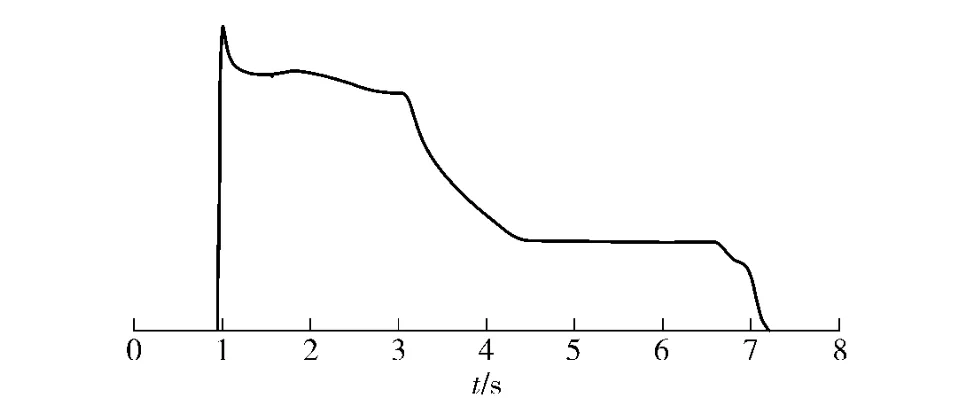
Fig.7 Pressure-time curve of modified Motor-1
3.2 Motor-2
By analyzing the spectrum,the maximum peak of the pressure is 0.000 6 MPa,and it indicates that the combustion instability has been eliminated.
3.3 Motor-3
By analyzing the spectrum,the maximum peak of the second stage pressure is 0.078 MPa.There is no abnormal pressure peak in both the first and the second stage,so the combustion instability is suppressed in this motor.
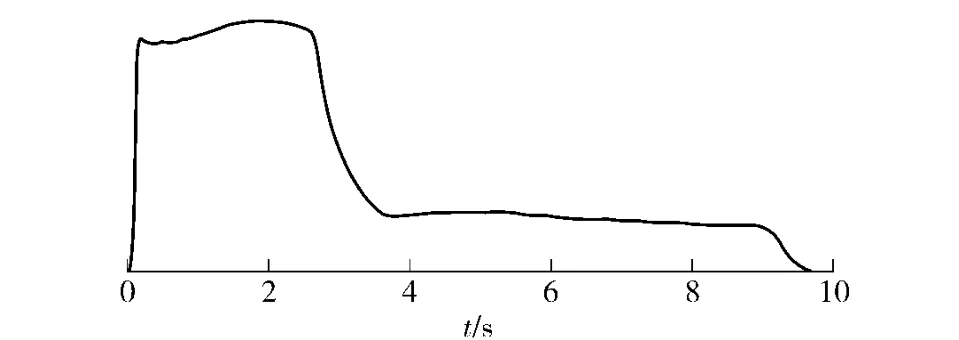
Fig.9 Pressure-time curve of modified Motor-3
4 Conclusions
1)For large length-diameter ratio motors with complex finocyl grain,most of the instable combustion are longitudinal oscillations.
2)For longitudinal oscillations,the best way to suppress the instable combustion is to increase the nozzle damping effect.The nozzle with convex shape convergent section has a better damping effect than that of concave shape.For a certain inlet March number,the cone nozzle has a better damping effect.
3)For propellant with metal particles,the particle damping effect is not significant,and more study should be done on the response function of the propellant[6].
4)Increasing the mass generation rate of combustion gas at the front part of the chamber can also help to suppress the instable combustion.
[1]XIE Wei-min.Solid rocket motor combustion instability,aerospace engineering textbook[M].Xi’an:Northwestern Polytechnical University Press,1984:2 - 20.(in Chinese)
[2]Blomshield Fred S.Lessens learned in solid rocket combustion instability[R].AIAA2007-5803,2007.
[3]Kuo K K,Summerrfield M.Fundamentals of solid-propellant combustion[M].Beijing:Astronautic Publishing House,1994:349-392.(in Chinese)
[4]YANG Xiang-ming,LIU Pei-jin.Analyse of acoustic with complicated grain shape in combustion chamber of solid rocket motor[J].Journal of Astronautics,2008,(9):1953-1957.
[5]Loncaric S,Greatrix D R,Fawaz Z.Star-grain rocket motor-nonsteady internal ballistics[J].Arospace Science and Technology,2004,(8):47 -55.
[6]Gallier S ,Godfroy F.Aluminum combustion driven instabilities in solid rocket motors[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2009,25(2):509 -521.
- Defence Technology的其它文章
- Deployable Antenna with Compact Ortho-mode Transducer and Feeding Systems
- Numerical Simulation on Flow Control for Drag Reduction of Revolution Body Using Dimpled Surface
- A Classification Algorithm for Ground Moving Targets Based on Magnetic Sensors
- Stability of Composite Braking Produced by Retarder and Braking System
- Study of Load Modeling Technology on Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulator of Gun Servo System
- A GNSS Signal Blind-decoding Algorithm at Low SNR

