白藜芦醇分子印迹聚合物微球的制备及特性评价
洪美花,陈元涛,王 婧,王晓兰,蔡林森
青海师范大学化学系,西宁 810008
Introduction
Molecularly imprinted polymers(M IPs)have been tailor-made materials with high selectivity for a target molecule,widely used in solid-phase separation,membrane separation,environmental application,and reaction catalysis[1-4].ConventionM IPs have been prepared in the form of bulk monolith[5,6].The copolymers are then ground and sieved to obtain appropriate size particleswith irregularly shape for further use.This procedure is time-consuming and results in onlymoderate amounts of useful product.Lots of efforts have been made to prepare M IPs with regular size and shape for wide application[7].Recently,molecular imprinted polymeric microspheres(M IPMs)have been received much concern due to their potentional applications, which can be prepared by emulsion polymerization[8], suspension polymerization[9],precipitation polymerization[10],Multi-step s welling and polymeri zation[11], and surface molecular imprinting[12].Of course,various methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. Compared with the above mentioned methods,a singlestep s welling and polymerization might be the easiest methods because this procedure is facile and the obtainedM IPMs have good monodispersity.
Chloroform and cyclohexcanol are usually used as solventfor a single-step s welling and polymerization[13,14],however,most template molecule such as active herbal ingredients,environmental pollutants and pesticides are not soluble in above-mentioned non-polar solvents.Thus,it will be very interesting to prepare M IPMs in polar solvent system,suitable to polar tem-plate molecule.
Resveratrol is an interesting compound found in berries,wine,peanut and grapes.This natural phytoalexin isexpressed in plants in response to fungal infections and stress factors such as nutrient deprivation.Recent studies have shown that it has a variety of biological properties,such as anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory,cardioprotective and chemopreventive activities,and resveratrol has also been shown to extend the lifespan of yeast calls[15-17].
In this study,M IPMs have been prepared by a singlestep swelling and polymerization using polystyrene as seeds in polar solvent.The factors of preparing microsphere have been studied in detail;it was found that variation of the s welling time and the solvent polarity played vital role on controlling morphology of microspheres.Itwas found that the adsorption rate ofM IPMs was very fast,due to their unique groove-style spatial structure.
Exper imental
Materials
Resveratrol(TCM038-080715,purity>98%)was from Nanjing Institute of ChineseMateriaMedica.Polydain(08071022,purity>98%)was from Shanghai Tauto Biotech Company.Water was deionized and distilled.All other chemicals and solvents were obtained from commercial sources with AR grade.Styrene was distilled to remove inhibitor before use.All othermaterialswere used without further purification.
Preparation of polystyrene seeds
Polystyrene seedswere synthesized as follows.21.24 g styrene,0.29 g sodium chloride and 0.14 g potassium peroxodisulfate were added to 160 mL of ultra-pure water.The polymerization was carried out under nitrogen atmosphere at 70℃for 20 h with magnetic stirring at 380 r mp.After purification by repeated centrifugation and dispersion,the purified seedwas dispersed intowater to reach a final particle concentration of 0.2 g/mL for further use.
Preparation ofM IPM s
In a 100 mL three-necked flask,1 mmol resveratrol,4 mmol acrylamide,20 mmol ethylene glycol d imethacrylate,1.00 g dibutyl phthalate,0.20 g azobisisobutyronitrile,and 5.00 g N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF) were mixed with 50 mL aqueous solution of 0.1%(w/ w)sodium dodecanesulphonate and 1.0%(w/w)polyvinyl alcohol,emulsified under ultrasonic conditions until the size of oil drops became,atmost 0.5μm(observed by optical microscope),then 1.5 mL polystyrene seed dispersed in water was added dropwise,the mixture was stirred at room temperature until the emulsified organic phase was completely absorbed by the seed particles.The mixture was degassed with nitrogen for 20 min.The polymerization was carried out at 70℃for 20 h with continuous stirring.The obtained microspheres were washed with water,methanol and tetrahydrofuran.Then the micropheres were eluted by the mixed solvent ofmethanol and acetic acid(9:1,v/v) for several times to extract the template molecules until no resveratrol could be detected byUV spectrometer in the eluent.Finally,the obtained micropheres were rinsed with ethanol for one time to remove the remaining acetic acid,and dried in the vacuum desiccators for 24 h before used.As a control,the non-molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres(NM IPMs)were prepared and treated in the same way,except that the template molecule was omitted from the polymerization process.
B inding exper iments
Ten milligramsM IPMs orNM IPMs were added into 10 mL tubes,and mixed with 2.0 mL of resveratrol-DMF solution with specific initial concentration ranging from 0 to 5.0 mmol·L-1.After the samples were shaken at 25℃for 40 min,the solution was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min.The concentration of free resveratrol in the supernate was measured by UV spectrophotometry at 306 nm.The amount of resveratrol bound to the M IPMswas calculated by subtracting the amountof free resveratrol from the amount of resveratrol initially added.Meanwhile,the adsorption kinetics of the M IPMs was perfor med at the different adsorption t ime intervals.
Results and D iscussion
Preparation of polystyrene m icrospheres Polystyrene seedswere prepared by emulsifier-free polymerization.The morphology and size were characterized by scanning electronic microscopy(SEM)with a JEOL JS M-5610LV scanning electronic microscope. Fig.1 indicated the resulting polystyreneweremonodisperse and unifor m spherical morphology with about 2 μm in diameter.
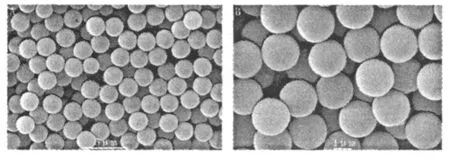
Fig.1 SEM images of polystyrene m icrospheres
Preparation ofM IPM s
The SEM images indicated thatM IPs prepared in DMF system were spherical structure as shown in Fig.2.The microsphereswere uniform and had good dispersibility with 5μm in diameter.It was excited to find that the obtained microspheres had lots of concave-dipression or cracks.

Fig.2 SEM images ofM IPM s,DM F as solvent.
Effect of solvent polarity on m icrosphere m orphology
In order to examine the effect of the solvent,tetrahydrofuran and acetonitrile were used as solvent and other conditionswere kept unchanged.It could be seen that theM IP Ms prepared in different solvent system had almost the same size with about 5μm in diameter,whereasM IPMs prepared in N,N-dimethylfor mamide system had a big hole running through micropheres,and M IP Ms prepared in acetonitrile system had deep cracks as shown in Fig.3.That is to say,the morphologies of M IP Ms could be controlled by changing the polarity of solvent.

Fig.3 SEM images ofM IPM s,(A)tetrahydrofuran as solvent;(B)aceton itrile as solvent.
Effect of swelling t im e on m icrosphere m orphology
Itwas also found that the swelling time played vital role on the morphology ofM IPMs.A few polystyrene seeds could be seen and the size ofM IPMs was not unifor m as shown in Fig.4A,when swelling time was 2 h.Some ruptured M IPMs could be seen as shown in Fig.4B, when the swelling time increased up to 6 h.
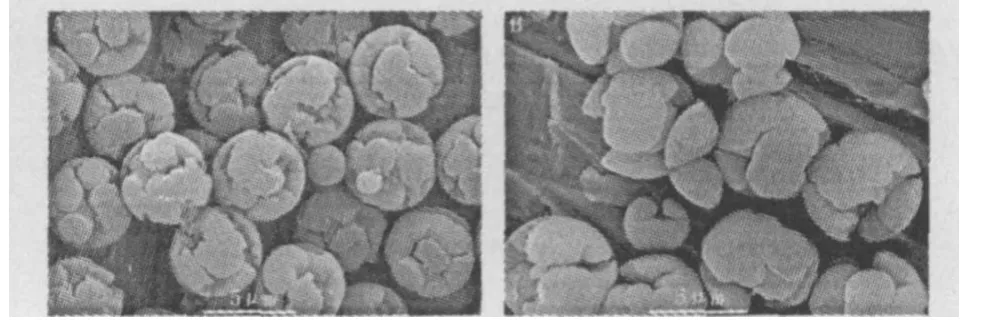
Fig.4 SEM of the M IPM s,the swell ing t ime was for (A)2 h;(B)6 h.
Adsorption kinetics ofM IPM s
The adsorption kinetics of theM IPMs for template molecule was carried out by adding 10 mg M IPMs into 2 mL DMF solution with template molecule concentration of 1.5 mmol/L.The curve of the adsorption kinetics was shown in Fig.5.It can be seen that the adsorption amount of resveratrol increased with the increase of adsorption time.In the early 20 min,the adsorption rate increased quickly.After 30 min,the adsorption almost reached equilibrium,indicating that the imprinted cavities were saturated with the template molecules.It was worthymentioning the adsorption equilibrium time was much shorter[18-20].In this communication,it was suggested the concave-dipression spatial structure played vital role on the short equilibrium time.In this structure,the template moleculeswere easy to reach the imprinted cavities of theM IPMs.Thus,the adsorption rate was faster.
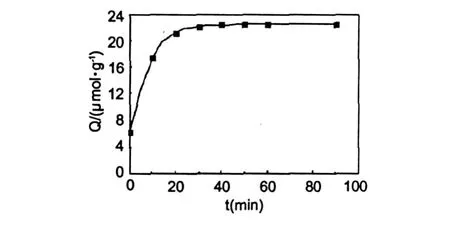
Fig.5 Adsorption k inetics curves of resveratrol on M IP M s.
Binding property ofM IPM s
The adsorption capacity is an important factor,which deter mines the amount of adsorbent for a given solution.The range of resveratrol solution with the concentration of 0-5 mmolwas studied.As can be seen in Fig. 6,the amount of resveratrol adsorbed per unit mass of M IP Ms increased with the initial concentrations of resveratrol.
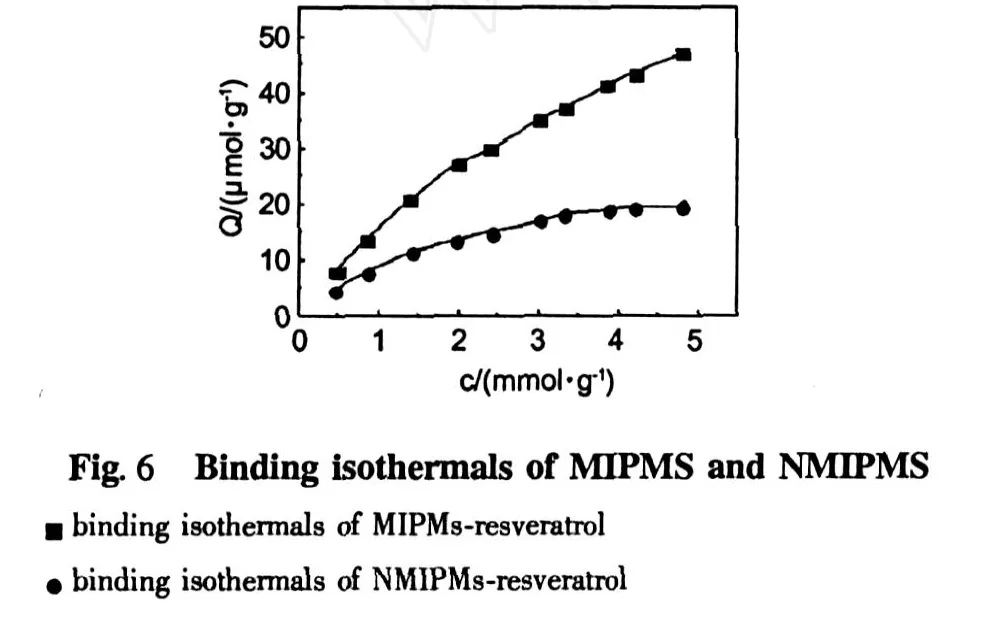
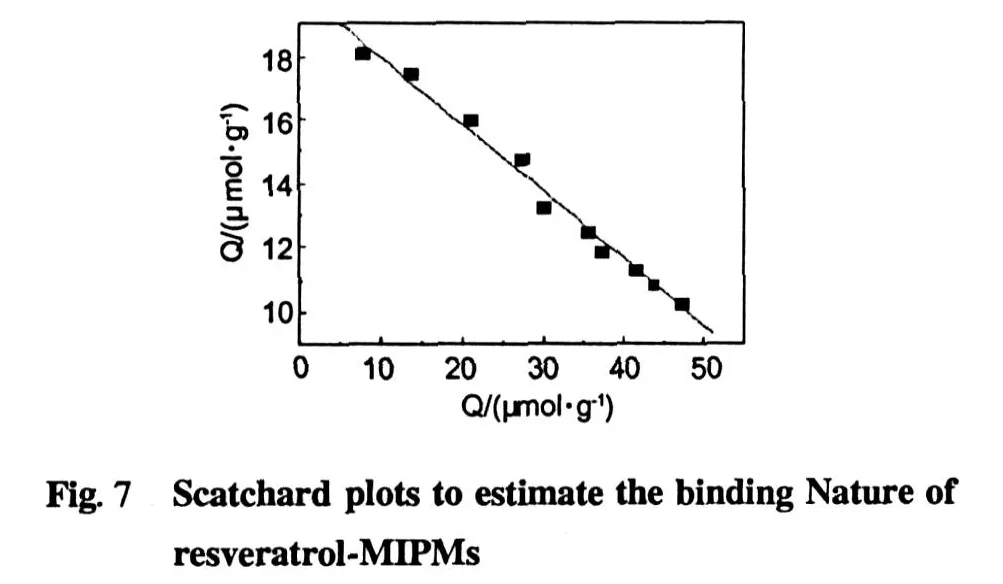
The obtained data were further processed with Scatchard equation to est imate the binding properities of M IP Ms.Scatchard equation was as follows[21].
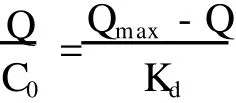
Where Kdis an equilibrium dissociation constant,Qmaxis an apparent maximum number of binding sites.Q is M IPMs adsorption capacity for resveratrol(μmol/g) and C0is quantitatively concentrate from resveratrol solution.As shown in Fig.7,Scatchard curve was a good straight line so that the M IPMs recognizing resveratrol only had one equivalent binding sites.The linear equation was as follows. y=20.092-0.21053x,R=0.99508
The apparentmaximum numberQmaxof binding sites is 95.435μmol/g,nearly twice as many as literature (48.50μmol/g)[15].It was speculated the larger adsorption capacities may be resulted from their unique concave-dipression structure,which effectively reduced the binding sites buried in theM IP Ms.Thus,there were more binding sites to be utilized.
Recogn ition properties ofM IPM s
In order to verify the selectivity of the M IPMs for resveratrol,polydatin was used as competitive substrate. The reason was that polydatin are also the active ingredients of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.Et Zucc.,and has similar structure with resveratrol.The molecular structures of resveratrol and polydatin are shown in scheme 1.The selectivity of the polymerswas estimated by Kdandαsame as Zheng’s reports[14].The obtained data was listed in Table 1.
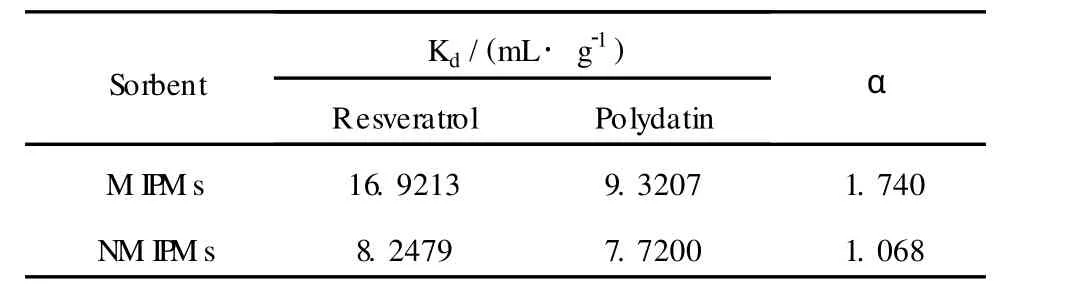
Table 1 Separation results of M IPM s and NM IPM s from resveratrol and polydat in
The separation factorαwas 1.74 indicated the M IPMs exhibited specific selectivity for resveratrol.That is to say,the template molecule could be easily seperated from its analogues by the obtainedM IPMs.
Conclusions
The single-step swelling and polymerization was developed to synthesize resveratrolM IPMs in polar solvent. Here,the unique concave-dipression spatial structure has successfully been prepared using DMF as the solvent.The obtainedM IPMs possessed the fast adsorption kinetics and large adsorption capacities.The M IPMs exhibit good recognition properties for the resveratrol.
1 ZhangML,Xie JP,Zhou Q,et al.On-line solid-phase extraction of ceramides from yeast with ceramide III imprinted monolith.J ChromatogrA,2003,984:173-183.
2 Wulff G.Enzyme-like catalysis bymolecularly imprinted polymers.Chem Rev,2002,102:1-27.
3 Ebarvia BS,Binag CA,Sevilla F.Biomimetic piezoelectric quartz sensor for caffeine based on a molecularly imprinted polymer.Anal B ioanal Chem,2004,378:1331-1337.
4 Dirion B,Lanza F,Sellergren B,et al.Selective solid phase extraction of a drug lead compound usingmolecularly imprinted polymers prepared by the target analogue approach.Chrom atographia,2002,56:237-241.
5 Lu Y,Li CX,Zhang HS,et al.Study on the mechanis m of chiral recognition with molecularly imprinted polymers.Anal Chim Acta,2003,489:33-43.
6 Ye L,Mosbach K.Molecularly imprinted microspheres as antibody bindingm imics.React Funct Polym,2001,48:149-157.
7 Li Y,Yin XF,Chen FR,et al.Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanowires using a nanoporous alumina template.M acrom olecules,2006,39:4497-4499.
8 Qi JY,Li X,Bian J.Preparation and property ofmicrospheric Fe(III)imprinted polymer.M aterials Science and Technology,2007,6:765-773.
9 Lai JP,Lu XY,Lu CY,et al.Preparation and evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres by aqueous suspension polymerization for use as a high-performance liquid chromatography stationary phase.Anal Chim Acta,2001, 442:105-111.
10 Chen FQ,Liu SX,Fang Y,et al.Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres and their recognition for chenodeoxycholic aacidChem J Chin Univ,2007,11:2195-2199.
11 Haginaka J,Sanbe H.Unifor mly sized molecularly imprinted polymer for(S)-naproxen-retention and molecular recognition properties in aqueous mobile phase.J Chrom atogr A, 2001,913:141-146.
12 JoshiVP,KulkamiMG,MashelkarRA.Molecularly imprinted adsorbrents for positional isomer separation.J Chrom atogrA, 1999,849:319-330.
13 Zheng XM,Tu WP.Study of binding characteristics of quinazoline molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres.Fine Chem,2006,9:833-840.
14 Zheng XM,Tu WP.Preparation of monodisperse molecularly imprinted polymer beads by a single-step polymerization method.J Chem Engineering Chin Univ,2007,1:116-121.
15 PrestaMA,BruyneelB,Zanella R,et al.Determination of flavonoid and resveratrol inwine by turbulent-flow chromatography-LC-MS.Chromatographia,2009,69:S167-S173.
16 Sapino S,CarlottiME,Caron G.In silico design,photostability and biological properties of the complex resveratrol/ hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin.J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem, 2009,63:171-180.
17 Park HJ,Jeong SK,Kim SR,et al.Resveratrol inhibitsPorphyromonas gingivalislipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial adhesion molecule expression by suppressing NF-κB activation.A rch Phar m Res,2009,32:583-591.
18 Kan XW,Zhao Q,Zhang Z,et al.Molecularly imprinted polymers miccrosphere prepared by precipitation polymerization for hydroqunone recognition.Talanta,2008,75:22-26.
19 Yang KG,Liu ZB,Mao M,et al.Molecularly imprinted polyethersulfone microspheres for the binding and recongnition of bisphenolA.Analytica Ch im ica Acta,2005,546:30-36.
20 WangB,LiuMZ,Liang R,et al.MMTCA recognition bymolecular imprinting in interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on poly(acrylic acid)and poly(vinyl alcohol). M acrom ol B iosci,2008,8:417-425.
21 LideDR.CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics.Boca Raton:CRC Press,1994.9-42.
22 Cheng CM,Vanderhoff JW,El-AasserMS.Monodisperse porous polymer particles:formation of the porous structure.J Polym Sci Part A,Polym Chem,1992,30:245-256.
23 YangM,Huai LF,Zhao T,et al.Preparation of monodispersed molecularly imprinted microspheres by one-step swelling polymerization.Fine Chem,2008,6:550-557.

