混纺比对涤棉平纹面料导湿排汗性能的影响

摘 要: 面料的原材料和组分对服装导湿、排汗性能影响较大。为探究面料混纺比与导湿、排汗性能间的关系,选择不同混纺比的涤棉平纹面料,通过电阻法评估汗液在各面料上的扩散及蒸发行为,采用动态水分管理测试仪和织物透湿量仪分别对面料水分扩散速率和透湿性进行测试。结果表明:混纺面料经纬向紧度是影响汗滴在面料经纬方向上扩散速率的主要因素,两者呈线性正相关;混纺面料中涤棉纤维混纺比、织物紧度和厚度影响面料的导湿及排汗性能,混纺面料中棉纤维含量越大,面料紧度值和厚度越大,则面料中汗液扩散速率和蒸发速率越小;随着混纺面料中棉纤维含量增大,面料的透湿性也会增大。研究结果对开发导湿、排汗面料具有一定参考价值,能够为夏季服装产品的选择提供理论参考。
关键词: 混纺比;涤棉面料;导湿排汗;电阻测试;滴液法;夏季服装
中图分类号: TS102.5""" 文献标志码: A""" 文章编号: 1009-265X(2025)01-0030-06
混纺纱线与面料在纺织领域应用越来越广泛,其产品特质显著依赖混纺纤维的种类及其配比。在混纺产品加工过程中,通过优选纤维组合,可以提高面料的物理机械性能、优化手感、改善穿着舒适度等。在混纺产品机械性能方面,高春燕等[1]、张陈恬等[2]探究了混纺比对混纺纱线力学性能的影响;田西西等[3]、梁巧敏等[4]分析了混纺比对纱线条干、纱疵、毛羽等指标的影响;吴佳庆等[5]建立了混纺纱强度预测模型。在混纺产品舒适性能方面,徐梦梦等[6-7]通过研究得到棉/丝光羊毛纱及混纺织物的吸湿性与棉纤维有关;尚润玲等[8]测试了棉/莫代尔/氨纶混纺织物的耐皂洗色牢度、摩擦色牢度、尺寸稳定性、透气吸湿性性能,得到相关性能与混纺织物中的莫代尔纤维含量有关;王玉新等[9]分析了丙纶磁性纤维/棉/竹浆混纺织物湿舒适性能,得到丙纶磁性纤维/棉/竹浆含量为60/10/30时织物湿舒适性能最好;罗小芹等[10]分析了6种不同混纺比针织物的主要服用性能指标,得出不同混纺比对其针织物服用性能影响的函数关系式;何海洋"等[11]用熵权TOPSIS法分析棉麻混纺织物的透气性、透湿性、导湿性,得出苎麻混纺织物的综合舒适性能优于亚麻和汉麻混纺织物;孙浪涛等[12]分析了Coolmax与棉混纺面料的吸湿速干性能,得出Coolmax纤维含量显著影响混纺面料吸湿速干性能;焦真等[13]发现亚麻/Modal混纺面料的纱线粗细、织物组织对面料导湿、透湿性能有影响,而混纺比对其影响不大。
上述 研究说明面料的成分及混纺比对其机械性能和舒适性能都有影响,因此分析混纺纱线和面料的性能时,需结合产品实际使用需求,优选最佳混纺比。在面料舒适性上,如人体大量出汗后,混纺服装对吸收以及导湿性能很大程度受到面料成分及混纺比的影响,通过对混纺面料湿舒适性进行测试评估,优选合适的面料成分及最佳混纺比是夏季导湿排汗面料新品开发的关键。本文基于电阻法自制一套面料导湿排汗测试仪,使用该仪器测试分析涤棉混纺面料的导湿、排汗性能,总结面料导湿排汗的性能变化规律,以期为夏季服装产品的选择和使用提供理论参考。
1 实验
1.1 材料与仪器
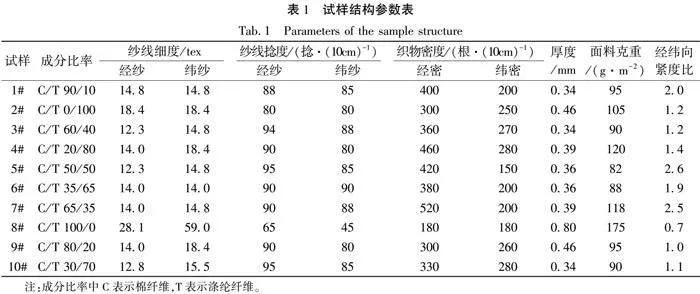
夏季机织服装面料多为平纹或简单斜纹组织,为避免面料组织结构对其导湿排汗性能影响,选择10块不同混纺比的涤棉平纹机织面料(面料经纬纱成分完全相同),测试其导湿排汗性能,试样参数如表1所示。
仪器:YG(B)141D数字式织物厚度仪(温州市大荣纺织仪器有限公司)、YG(B)511B型织物密度镜(温州市大荣纺织仪器有限公司)、织物电阻自动测试系统(自制)、FA2104电子天平(上海精密仪器仪表有限公司)。
1.2 测试方法
1.2.1 电阻测试法
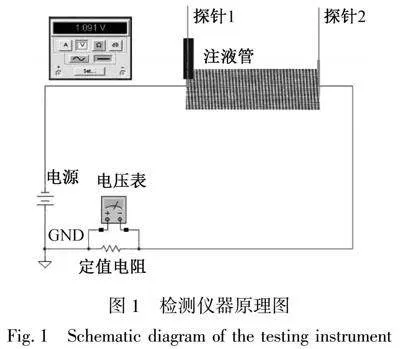
采用滴液法评价各试样导湿排汗性能,自制织物电阻自动测试系统,仪器原理如图1所示。
将调配好的含0.9%质量分数的NaCl溶液的模拟汗液(简称汗液),通过可调式移液器精确量取0.2 mL,经注液管注入,随后开始计时。汗液沿服装面料由探针1渗透至探针2位置后,探针间电阻由GΩ数量级下降至MΩ,与探针串联的20 MΩ定值电阻两端的电压表出现电压信号,由于探针2位置固定,只需记录汗液由滴入时刻到迁移至探针2的时间,可间接获得汗液扩散速率。随着汗液蒸发,探针1和2之间电阻逐渐增大,电压表之间电压值减小,当趋近于0 V,则说明汗液已蒸发完毕。
以探针1为中心,沿着试样经向、纬向、30°、45°和60°(角度为与试样经纱方向的夹角),每间隔4 mm布置1根探针,探针分布如图2所示。沿着试样经向上下两个方向都设置探针,通过检测探针与探针1间电阻变化,可得汗液沿试样不同方向的导湿、排汗性能。
1.2.2 纺织品吸湿速干性测试
参照 GB/T 21655.2—2019《纺织品 吸湿速干性的评定 第2部分:动态水分传递法》,采用锡莱-亚太拉斯有限公司动态水分管理测试仪(MMTⅡ)测试试样面层与里层扩散速率,每个试样测试5次,取平均值。
1.2.3 织物透湿性测试
参照GB/T 12704.1—2009《纺织品 织物透湿性试验方法 第1部分:吸湿法》,采用上海际发仪器设备有限公司YG216G型织物透湿量仪测试各试样透湿性能,每个试样测试5次,取平均值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 面料各向导湿性能差异分析
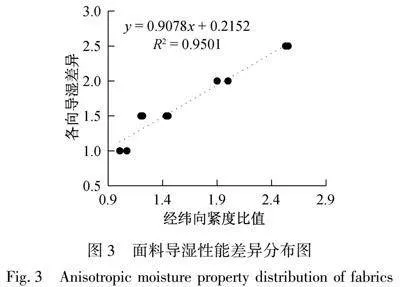
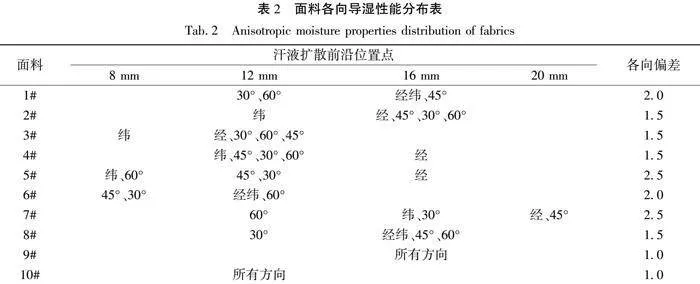
当插入面料的探针之间含有液态水时,探针间电阻值为MΩ数量级,不含有液态水或者液态水未 完全分布在探针之间时,探针间电阻值为GΩ数量级,标记探针板上各探针与中心探针1之间电阻值,可得汗液扩散情况。记录试样经向、纬向、30°、45°和60°方向上所有电阻值为MΩ数量级的探针,选取其中距离滴汗液落位置最远的探针,将该探针位置作为汗液扩散最前沿位置。汗液沿着试样扩散情况统计结果如表2所示。同时为定量评价试样不同方向扩散差异,引入各向偏差参数指标,其值以某一位置点角度数量最多的方向为标准位置点,如汗液沿着试样各向扩散前沿位置点相同,则各向偏差值为1,如汗液沿着某一方向前沿位置低于或者高于标准位置点时,则加0.5。如1#试样标准位置点为16 mm,12 mm位置点有30°和60°方向低于标准位置点,1#试样各向偏差为2;5#试样标准位置点取位于中间的12 mm,低于标准位置点有2个方向,高于标准位置点有1个方向,5#试样各向偏差为2.5。
由表2可得,对于5#与7#试样,汗液沿着各向扩散差异较大,9#与10#试样各向扩散差异较小,由于汗液扩散时一部分水分沿着纱线内部毛细孔芯吸扩散,一部分水分沿着纱线之间扩散,因此面料经纬纱线粗细与面料经纬密度差异会显著影响面料导湿性能差异。采用面料经纬向紧度比表征面料结构差异,其值如表1所示,如面料经向紧度小于纬向紧度,如8#试样,采用纬向紧度与经向紧度比。将经纬向紧度比与面料各向导湿性能偏差作对比,如图3所示。随着面料经纬向紧度比增大,面料各向导湿性能偏差也越大,将二者线性拟合后的相关系数达到0.9501,具有较高的相关性。因此当面料经纬纱原料相同时,其经纬向紧度差异会显著影响面料各向导湿性能。
2.2 混纺比对面料导湿排汗性能影响
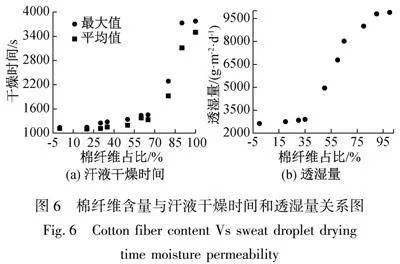
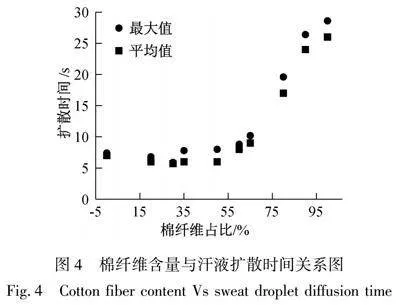
由表2可知,各试样导湿扩散位置各不相同,但8 mm位置处,汗液沿着各试样不同方向扩散前沿位置都达到了,因此以汗液沿着试样各向扩散至8 mm时所需时间来作为评价面料导湿性能优劣的指标,其值越大说明面料导湿性能越差。随着涤棉混纺面料中棉纤维含量增加,汗液扩散至8 mm处所需时间如图4所示,其中最大值为汗液沿着面料5个方向扩散到8 mm处所需最长时间,平均值为5个方向扩散到8 mm位置处平均时间。
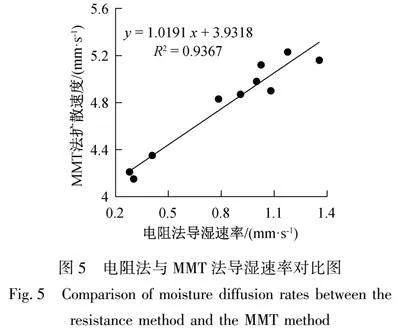
由图4可得,当棉纤维含量在0%~50%,汗液扩散时间总体变化不大,当棉纤维含量在60%以上时,汗液扩散时间有所增加,当棉纤维含量超过80%后,其汗液扩散时间明显增大,即面料导湿性能下降明显,主要原因是棉纤维比涤纶纤维吸湿能力强,当棉纤维含量超过涤纶后,可以明显抑制了水分迅速扩散,导致面料导湿性能下降。液态水分管理测试仪(MMT)评价面料导湿性能主要是通过测试样品面层与里层扩散速率,为便于与电阻法比较,将MMT仪器测得的面层与里层扩散速率取平均值,汗液扩散至8 mm位移除以汗液扩散至8 mm处所需时间最大值得到电阻法导湿速度,两者对比如图5所示。
图5中电阻法与MMT仪器测得的面料导湿速率在数量级上接近,但二者数值有一定差异,主要原因是测试和评价方法的差异。将两者的数值作线性拟合,相关性达到0.9367,说明两种方法都能明显区分面料导湿性能优劣。因此自制的测试仪测试结果稳定可靠,可满足面料导湿性能测试分析。
由图1的探针分布可知,当注液管周围最近的探针处(4 mm位置)的水分蒸发后,残留在面料中的水分很少,可以这些探针位置处的水分蒸发时间作为评价基准,其值越大,说明面料中汗液干燥越慢。将面料中汗液蒸发时间用干燥时间来表征,分析混纺面料中汗液干燥时间与棉纤维含量之间关系,如图6(a)所示,其中最大值与平均值含义与图4中表示的含义相同。由图6(a)可得,随着涤棉混纺面料中棉纤维含量增加,汗液在面料上干燥时间也变大,蒸发速率下降。当棉纤维含量超过80%时,干燥时间明显增大,说明棉纤维含量越大,混纺面料中汗液蒸发速率越小。选择透湿性能评价混纺面料的舒适性,面料透湿量与混纺面料中棉纤维含量关系如图6(b)所示。由图6(b)可得,随着棉纤维含量增加,试样透湿量逐渐增大。当棉纤维含量超过50%时,试样透湿性提升显著,主要原因可能是由于棉纤维表 面天然转曲,易形成丰富的毛细孔;同时棉纤维内部孔隙也比涤纶多,当棉纤维含量多时,有利于水分透过试样。结合图3和图4可知,当棉纤维含量低于50%时,汗液扩散时间与干燥时间相对较小,表明试样导湿排汗性能优异。结合透湿性能以及导湿排汗性能综合分析,涤/棉混纺比为50/50时产品综合性能 最佳。
2.3 结构参数对面料导湿排汗性能影响
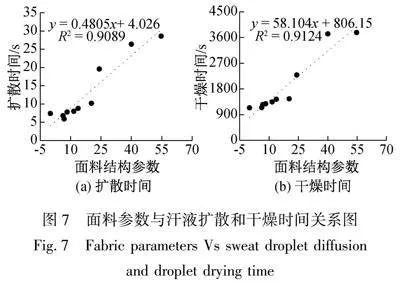
影响面料导湿排汗性能主要因素包括纤维成分、混纺比、纱线细度、捻度、织物结构和厚度等。依据表1中纱线细度和捻度数值分别计算经、纬纱特数制捻系数,得到10款试样 经纱捻系数范围为329.7~344.6,纬纱捻系数范围为327.0~345.7,说明纱线加捻程度差异不大;而经纬纱粗细和经纬向密度参数可合并到织物紧度参数中。结构参数对面料导湿排汗性能影响只需考虑面料中棉纤维含量、面料厚度及紧度,将三者相乘,得到面料结构参数值。以扩散时间和干燥时间作为面料导湿和干燥性能参数,两者与面料结构参数关系分别如图7所示。
图7中的面料结构参数都显著影响汗液扩散时间及干燥时间,分别将其与面料结构参数作线性拟合,其相关性分别为0.9089和0.9124,说明棉纤维含量、织物紧度、厚度都能显著影响面料导湿排汗性能,即棉纤维含量越多、织物越紧密、厚度越大则面料对汗液传导和蒸发性能越差。
3 结论
本文基于电阻法原理自制面料导湿、排汗性能测试仪,测试了汗液在面料不同方向上扩散速率及蒸发时间的差异,并采用动态水分管理测试仪和织物透湿量仪对面料水分扩散速率和透湿性进行了系统评估,主要结论如下:
a)当面料经纬纱原料相同时,面料经纬向紧度比显著影响其各向导湿性能,紧度比值越大,汗液沿着面料各向扩散性能差异也越大,二者呈线性正相关。
b)涤棉面料纤维混纺比、面料紧度和厚度对混纺面料的导湿及排汗性能影响较大,随着混纺面料中棉纤维含量提升,面料紧度和厚度增加,汗液沿着面料扩散时间及蒸发时间变长,导湿及排汗性能变差。
c)为保证面料具备较好的导湿排汗性能,棉纤维含量需要控制在50%以下。
本文研究结果为涤棉混纺面料的开发提供有一定的指导价值,期望推动市场生产出更多优质的服装产品,也为消费者选择和使用夏季服装产品提供了参考和建议。
参考文献:
[1] 高春燕,周宇阳,王旭斌,等.混纺比对亚麻/棉混纺纱拉伸性能的影响[J].上海纺织科技, 2023, 51(8):26-28.
GAO Chunyan, ZHOU Yuyang, WANG Xubin, et al. Effect of blended ratio on tensile properties of flax/cotton blended yarn[J]. Shanghai Textile Science amp; Technology, 2023, 51(8): 26-28.
[2] 张陈恬,赵连英,顾学锋,等.混纺比对中空咖啡碳/棉混纺纱性能的影响[J].丝绸,2021,58(1):27-33.
ZHANG Chentian, ZHAO Lianying, GU Xuefeng, et al. Effect of blending ratio on the hollow coffee carbon/cotton blended yarn[J]. Journal of Silk, 2021, 58(1): 27-33.
[3] 田西西,方萌,陈倩钰,等.混纺比对备长炭/棉混纺纱及其针织物性能的影响[J].产业用纺织品,2023,41(5):33-37.
TIAN Xixi, FANG Meng, CHEN Qianyu, et al. Effect of blending ratio on properties of Binchotan fiber/cotton blended yarns and knitted fabrics[J]. Technical Textiles, 2023, 41(5):33-37.
[4] 梁巧敏,崔益怀,张娣,等.基于不同混合工艺的棉/舒弹丝纤维混纺纱性能研究[J].丝绸,2022,59(2):25-30.
LIANG Qiaomin, CUI Yihuai, ZHANG Di, et al. Study on the properties of cotton/SUSTANS fiber blended yarn based on different blending processes[J]. Journal of Silk, 2022, 59(2): 25-30.
[5] 吴佳庆,王怡婷,何欣欣,等.混纺比对生物基锦纶56短纤/棉混纺纱力学性能的影响[J].纺织学报,2023,44(3):49-54.
WU Jiaqing, WANG Yiting, HE Xinxin, et al. Influence of blending ratio on mechanical properties of bio-polyamide 56 staple fiber/cotton blended yarn[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2023, 44(3): 49-54.
[6] 徐梦梦,吉宜军,崔益怀,等.不同混纺比和纺纱方式对棉/丝光羊毛混纺纱性能影响的分析[J].毛纺科技,2023,51(8):1-6.
XU Mengmeng, JI Yijun, CUI Yihuai, et al. Analysis of the influence of different blending ratios and spinning methods on the properties of cotton/mercerized wool blended yarn[J]. Wool Textile Journal, 2023, 51(8):1-6.
[7] 徐梦梦,武金余,崔益怀,等.混纺比对棉/丝光羊毛针织物性能的影响[J].毛纺科技,2023,51(5):7-12.
XU Mengmeng, WU Jinyu, CUI Yihuai, et al. Effect of blending ratio on the property of cotton/mercerized wool knitted fabric[J]. Wool Textile Journal, 2023, 51(5):7-12.
[8] 尚润玲,李朗.不同混纺比的棉/莫代尔/氨纶针织物的性能研究[J].轻纺工业与技术,2023,52(2):8-10.
SHANG Runling, LI Lang. Study on properties of cotton/modal/spandex knitted fabrics with different blending ratios[J]. Light and Textile Industry and Technology,2023, 52(2):8-10.
[9] 王玉新,荆妙蕾,闫妍,等.丙纶磁性纤维仿毛织物舒适性的多元回归分析及混纺比优化[J].毛纺科技,2013,41(2):15-18.
WANG Yuxin, JING Miaolei, YAN Yan, et al. Multiple regression analysis on comfort property of PP magnetic fiber wool-like fabrics and blended ratio optimization[J]. Wool Textile Journal, 2013, 41(2):15-18.
[10] 罗小芹,吴佳林.不同混纺比Tencel/苎麻混纺针织物服用性能的测试与分析[J].现代纺织技术,2012,20(3):42-45.
LUO Xiaoqin, WU Jialin. Study of knitted fabrics weara-bility of tencel/ramie yarns with different blend ratio[J]. Advanced Textile Technology, 2012, 20(3): 42-45.
[11] 何海洋,李心如.棉麻混纺机织物舒适性评价[J].棉纺织技术,2023,51(8):43-48.
HE Haiyang, LI Xinru. Suitability evaluation of cotton bast fiber blended woven fabric[J]. Cotton Textile Technology, 2023, 51(8):43-48.
[12] 孙浪涛,李建华,何小玲,等.Coolmax/棉混纺织物的吸湿速干性分析[J].中原工学院学报,2022,33(1):1-5.
SUN Langtao, LI Jianhua, HE Xiaoling, et al. Analysis of moisture absorption and quick drying performance of Coolmax/cotton blended fabric[J]. Journal of Zhongyuan University of Technology, 2022, 33(1):1-5.
[13] 焦真,邢富强,王学武,等.亚麻Modal混纺抗紫外织物湿热舒适性分析[J].棉纺织技术,2003,31(5):32-34.
JIAO Zhen, XING Fuqiang," WANG Xuewu, et al. Analysis of heat amp; wet comfortability of flax and modal blended ultraviolet resistance fabric[J]. Cotton Textile Technology, 2003, 31(5):32-34.
Influence of the blending ratio on moisture diffusion and perspiration of polyerster/cotton blended plain fabrics
ZHANG" Caiqian1," MENG" Shaoni1," MA" Haiyan2
(1.Institute of Art and Art Design, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang 473061, China;
2.Yuanpei College, Shaoxing University, Shaoxing 312000, China)
Abstract:
The most important factors affecting the moisture diffusion and perspiration performance of blended yarns or fabrics are the types of fibers and the blending ratio. In this paper, the resistance method was adopted to test the moisture diffusion and perspiration performance of summer polyester/cotton blended woven fabrics with different composition ratios. At the same time, the moisture diffusion rate and moisture permeability of the fabric were tested by dynamic moisture management tester and fabric moisture permeability meter, differences in moisture diffusion and perspiration performance of fabrics with different parameters were analyzed, and the performance variation law was obtained.
The test objects were ten polyester/cotton plain woven fabrics with different blend ratios. Some metal probes were inserted into the fabric sample as a resistance sensor. A precise volume of 0.2ml of simulated human sweat was measured by using an adjustable pipette and injected into the fabric through a dispensing tube. The data acquisition card was used to monitor the changes in resistance values between the probes after the simulated sweat diffused on the surface and inside the fabric. If the resistance value decreased from the order of GΩ to MΩ, the sweat had transferred to the probe position; if the resistance between the probes increased from the order of MΩ to GΩ, it indicated that the sweat had evaporated. The probes were distributed in the warp, weft, 30°, 45°, and 60° directions of the fabric. By detecting the resistance changes between these probes, the diffusion and evaporation properties of simulated sweat along different directions of the fabric could be obtained. A dynamic moisture management tester was used to test the moisture diffusion velocity of each fabric, and the drop diffusion time was compared with that of the resistance method. The fabric permeability meter was used to test the moisture permeability of the fabric, and the comfort performance of the fabric was evaluated comprehensively.
The conclusions are as follows: when the warp and weft yarns of the fabric are made of the same material, the tightness ratio between the warp and weft significantly affects the differences in moisture diffusion property in various directions. As the tightness ratio increases, the differences in sweat diffusion performance along various directions of the fabric also increase, showing a linear relationship; the fiber blending ratio, fabric tightness, and thickness of polyester/cotton blended fabrics have a significant impact on their moisture diffusion and perspiration performance. Due to the strong moisture absorption capability of cotton fibers but relatively weak water transport capability, as the proportion of cotton fibers in the blended fabric increases, the moisture diffusion and evaporation performance deteriorate, leading to longer diffusion and evaporation time for sweat along the fabric. Both the moisture diffusion and perspiration performance of the fabric worsen, and the fabric thickness and tightness also greatly affect its moisture diffusion and perspiration performance; as the cotton fiber content in polyester/cotton blended fabric increases, the moisture permeability of the fabric gradually improves. When the cotton fiber content in polyester/cotton blended fabric exceeds 50%, the moisture diffusion and perspiration performance lead to significant declines. Therefore, to ensure that the fabric has better moisture diffusion and perspiration performance, the cotton fiber content needs to be controlled below 50%. The results of this study can provide reference for the development of polyester/cotton fabrics, and also provide a basis for the selection and use of comfortable summer clothing.
Keywords:
blending ratio; polyester/cotton fabric; moisture diffusion and perspiration; resistance method; dropping" method; summer clothing
基金项目: 2024年度南阳师范学院博士专项科研项目(2024ZX034)
作者简介: 张才前(1979—),男,江苏盐城人,副教授,博士,主要从事纺织品测试技术及新产品开发方面的研究

