Free amino group-directed C(sp2)-H arylation of α-amino-β-aryl esters by palladium catalysis
Yue Gao ,Yu Du,* ,Weiping Su,*
a State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry,Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Fuzhou 350002,China
b Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China,Fuzhou 350108,China
c University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
Keywords: Native amino-directed Palladium catalyst C(sp2)-H arylation α-Amino-β-aryl ester Chiral α-amino acid
ABSTRACT Native amino-directed palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)-H activation/functionalization has been developed for modification of α-amino acids and peptides.Herein a palladium(II)-catalyzed C(sp2)-H arylation of αamino-β-aryl esters has been disclosed,using the native amino as the directing group.A variety of chiral α-amino-β-aryl esters can be functionalized to give the corresponding ortho-substituted mono-and diarylated products.
α-Amino acids (α-AAs) are an important class of natural chiral compounds which are essential building blocks of proteins and peptides.The modification of easily availableα-AAs that provides new molecules bears great practical potential in chemistry,chemical biology,drug discovery and other disciplines [1-4].In recent years,C-H activation catalysis has gradually emerged as a powerful tool forα-AAs [5-9] and peptides [10-12] modification in an atom-and step-economical manner.However,the existing methodsviaC-H activation often require installation of either directing auxiliaries or introducing protecting groups to manipulate the reactivity,the development of novel methods using native carboxyl or amino groups as directing groups has attracted substantial attention.In contrast to the steady progress of carboxylate-directed inert C-H activation [13-16] and its application in modifyingα-AAs [17-21],free NH2-directed transformation is less studied [22-23].
In order to suppress the high propensity to form strong binding and less active bis-amine complexes of primary amines with metal catalysts [24],a protonation strategy of using acetic acid as the solvent [25] was employed by Shi to realize the NH2-directedγ-C(sp3)-H acetoxylation of aliphatic primary amines (Scheme 1a)[26].Applying the same strategy toα-AAs modification,an effi-cient NH2-directedγ-C(sp3)-H arylation ofα-amino esters was developed by Yao (Scheme 1b) [27,28],and substrates were further expanded toN-terminus unprotected oligopeptides [29,30].Meanwhile,native amino-directed palladium-catalyzed C(sp2)-H arylation of primary amines had also been developed (Scheme 1c)[31,32].Aryl substitutedα-AAs are an important class of naturalα-AAs (e.g.,Phe,Trp,Tyr) and derivatives.However,at present,native NH2-directed C(sp2)-H functionalization of suchα-AAs has rarely been discussed [32].In this context,herein we report a native amino-directed palladium(II)-catalyzed C(sp2)-H arylation ofα-amino-β-aryl esters with various aryl iodides (Scheme 1d).A variety of chiralα-amino esters could be arylated by this method directly.

Scheme 1.NH2-directed C-H functionalization of primary amines.
As shown in Table 1,the research was commenced with exploring the coupling reaction of model substrates (S)-phenylalanine methyl ester1aand 4-methyliodobenzene2ain the presence of palladium acetate (Pd(OAc)2,5 mol%) andN-acetyl-glycine (NAc-Gly,40 mol%) as a ligand,along with 1.2 equiv.of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TfOH) as the proton source and 1.25 equiv.of silver carbonate (Ag2CO3),warmed at 120°C for 24 h in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) under air.The desiredortho-arylated products3a(mono-arylated) and4a(di-arylated) were obtained in yields of 48% and 25% separately (entry 1).Then lots of control experiments were performed to find the optimal conditions (see Supporting information for more reaction conditions evaluation).Various mono-N-protected amino acids (MPAAs) [1,33] were examined(entries 1-5),N-acetyl-valine (N-Ac-Val) is the superior one that affords the highest yields of3aand4a(entry 3).The screening of acid additives showed that TfOH is the best choice (entries 6-8).It should be noteworthy that no target molecules were obtained without the addition of acid,suggesting the critical role of acid in inhibiting the strong binding of the amino group with palladium.A survey of inorganic bases revealed that Ag2CO3significantly outperform others in promoting the reaction (entries 9-11),and silver salts play an irreplaceable role as iodide scavenger [34].Other polar or nonpolar solvents were also tested,however,no positive effect was observed (entries 12 and 13).Extending reaction time to 36 h led to a little increase of the combined yields of3aand4a(entry 14),further extending reaction time to 48 h failed to take effect (entry 15).Besides,the use of other palladium-catalysts instead of Pd(OAc)2led to an erosion in the yield (entries 16-18).The di-arylation increased significantly (>60% yield) with the catalyst loading of Pd(OAc)2increased to more than 20 mol%,while the mono-arylation was almost disappeared.The results indicate that the poor selectivity is caused by the lack of activity of the catalytic system.
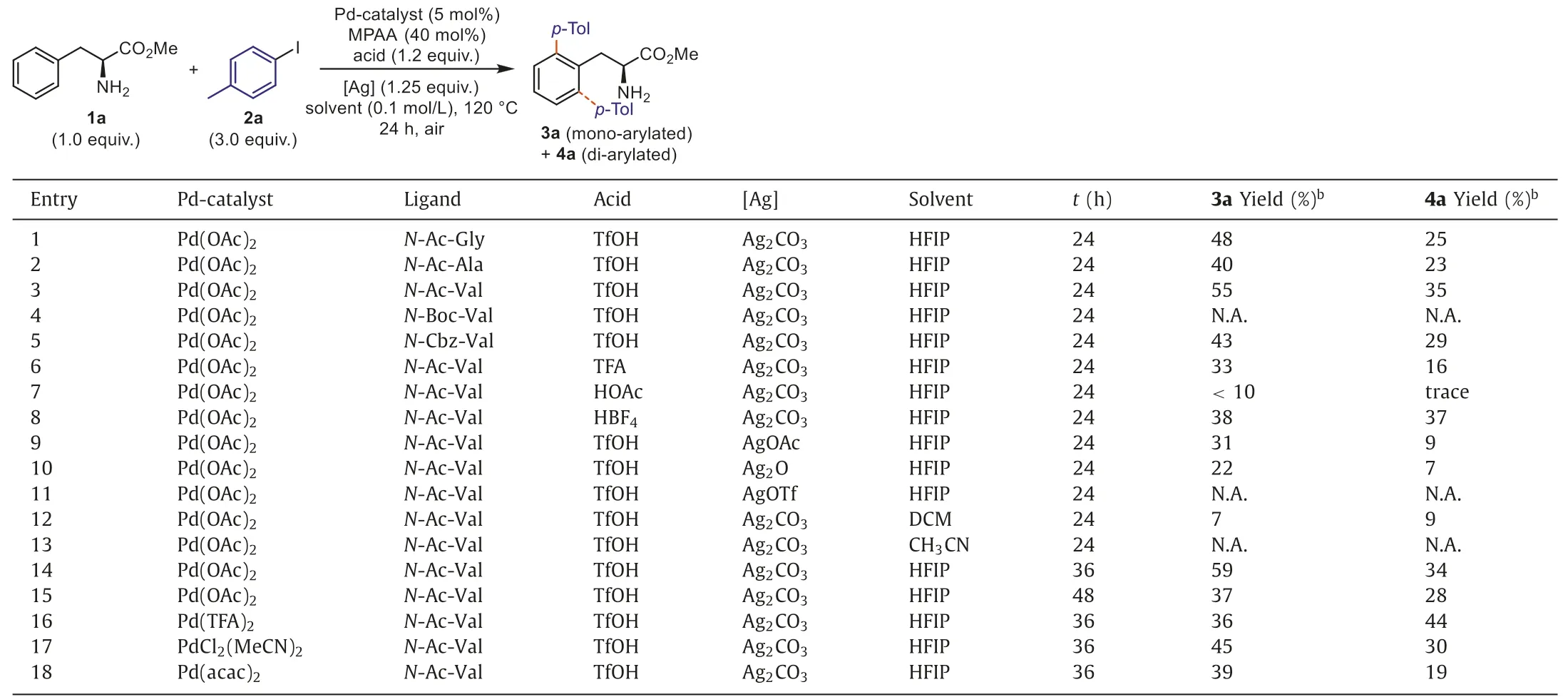
Table 1Optimization of reaction conditions.a
With the optimal conditions (Table 1,entry 14),the generality of this C(sp2)-H arylated method was first evaluated with variousα-amino-β-aryl esters (Scheme 2).In order to ensure the reliability of the yields,all data represent the average of (more than)two independent experiments.A variety ofα-amino esters with electron-rich or -deficient aryl groups (1b-1n),naphthyl (1o),could react under the optimal conditions to generate the corresponding arylated products3and4.Generally,the presence of an electron donating group (1b,1c,1h,1l) led to a higher yield than that derived from an electron withdrawing group (1e-1g,1i-1k,1m-1n),which probably because the former can promote the reductive elimination.α-Amino-β-aryl ester bearing apara-substituent(1b-1g) would give a mixture of mono-and di-arylated products(3b-3g&4b-4g),whileortho-andmeta-substituted substrates (1h-1o) led to only mono-arylation (3h-3o).By now the method appears not applicable for site-selective C-H functionalization of peptides containing Phe as the N-terminus,both C(sp2)-H and C(sp3)-H arylation were observed after reactions (details see Supporting information).
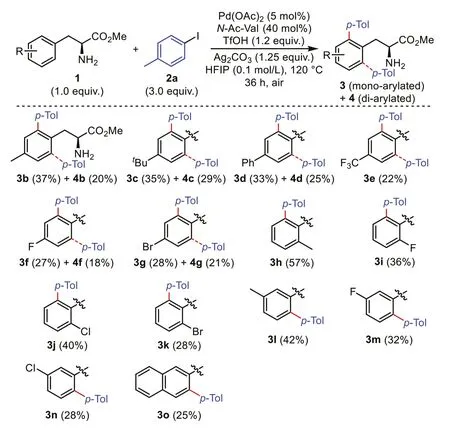
Scheme 2.Scope of α-amino-β-aryl esters.Reactions were performed on a 0.4 mmol scale.Yields are isolated yields.
Further investigation of coupling reagents,aryl iodides,was carried out under the optimal conditions with (S)-phenylalanine methyl ester1a(Scheme 3).Various functional groups such as methoxy,alkyl,phenyl,trifluoromethyl,ester and halogen groups at thepara-ormeta-position were tolerated,generating mixtures of mono-and di-arylated products (3b’-3n’&4b’-4n’).In contrast,ortho-substituted iodobenzene doesn’t work in this reaction.Fluorenyl derivative (2o) also worked well to give the corresponding mono-and di-arylated products (3o’&4o’) in a moderate combined yield.Regrettably,the method is not applicable to heteroaryl iodides orα-amino-β-heteroaryl esters (e.g.,Trp-OMe).

Scheme 3.Scope of aryl iodides.Reactions were performed on a 0.4 mmol scale.Yields are isolated yields.
Chiral HPLC analysis of arylated products derived from (R)-and(S)-phenylalanine methyl esters showed that there is a little erosion in enantiomeric excess (di-arylated product4a,88%ee,see Supporting information),revealing that partial racemization occurred during the reaction due to the basicity and high temperature.In order to verify the directing effect of the native NH2,as shown in Scheme 4,methyl 3-phenylpropanoate1pandN,Ndimethyl-Phe-OMe1qwere subjected to the reaction,and no observation of the desired C(sp2)-H arylation.The results exclude the possible ester-directed C-H activation.
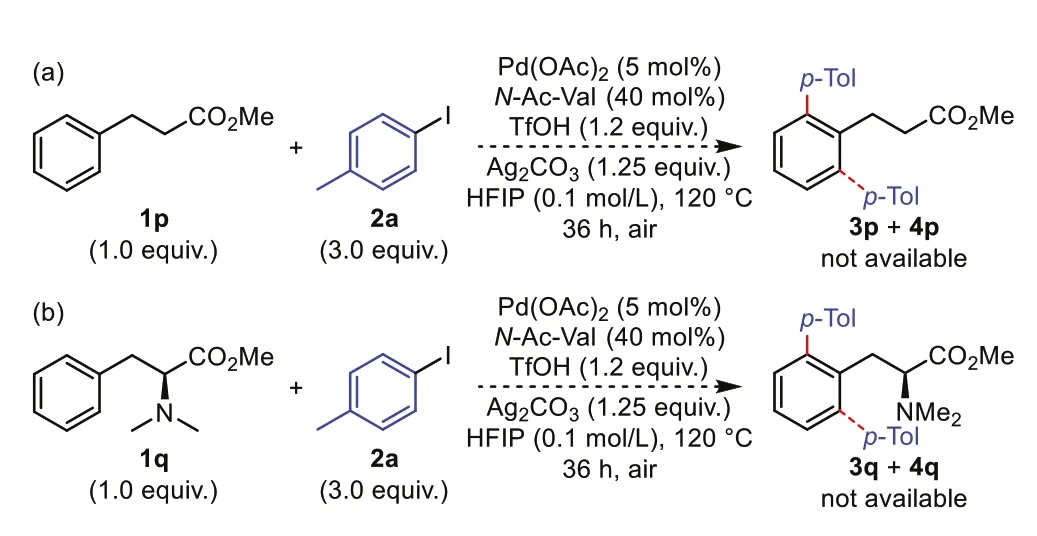
Scheme 4.Additional control experiments.
In summary,an efficient and practical Pd(II)-catalyzed C(sp2)-H arylation ofα-amino-β-aryl esters with various aryl iodides has been developed,using the native NH2as the directing group.A variety of chiralα-amino esters could be functionalized by this method to give the corresponding mono-and di-arylated products with a little erosion in enantiomeric excess.The method features broad substrate scope,excellent functional group tolerance and mild conditions.Further exploration of this protocol for C(sp2)-H arylation of oligopeptides and structure modification of polypeptide drugs is currently underway in our laboratory.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2018YFA0704502),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21871261,21931011),and Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China (No.2021ZZ105).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108505.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2024年2期
Chinese Chemical Letters2024年2期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- The 3rd Xihua Chemistry and Biomedicine Forum
- Professor Hualiang Jiang: A tribute to an esteemed visionary chemist and pharmacist
- Recent advances in visible light-mediated chemical transformations of enaminones
- Development of porphyrin-based fluorescent sensors and sensor arrays for saccharide recognition
- Recent advances of versatile reagents as controllable building blocks in organic synthesis
- Synthetic host-guest pairs as novel bioorthogonal tools for pre-targeting☆
