BMSCs transplantation inhibits neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-mediated autophagy
CUI Cai-ling, XU Xin-yu, ZHANG Yu, CUI Bo-wen, HU Ai-hui, LIU Jun-jie,2, LI Jianmin,2✉
1.College of Clinical Medicine, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, China
2.Department of Neurosurgery, the Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the impacts of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)intervention on the neuronal withering and autophagy in rats after subarachnoid hemorrhage(SAH) in rats and its process.Methods: forty-eight SD rats (males), were randomly assigned to the followings: sham surgery (Sham) group, modeling (SAH) group, modeling group +bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) group, the modeling group + BMSCs +AMPK inhibitor (Compound C) group, twelve rats in each group.Except Sham group, other groups formed SAH samples with intravascular points.Separate groups Compound C and BMSCs, respectively Compound C and 10 μL of normal saline were injected into the left lateral ventricle of rats using a stereoscope brain machine 30 minutes before modeling, and 2 μL concentration is 1×108/mL cell suspension was injected into the ventricles of the brain 1 hour after the model was established.Observe whether the rats have severe brain swelling.Garcia were used to test the neural function of rats.TUNEL staining was used to monitor neuronal apoptosis in the rat hippocampal gyrus.Immunohistochemical fluorescence reflected the expression of two proteins, LC3-II and Beclin-1, in rat hippocampal gyrus.Western blotting is applied to measure the expressions of autophagy-associated proteins in the AMPK pathway.Results: Compared with the group undergoing sham-surgery, brain edema worsened in the model group, neuronal apoptosis rate was increased, neural function was weakened,Protein granules decreased (P<0.05) and expression levels of p-AMPK and other proteins decreased (P<0.05); brain swelling and neuronal apoptosis were reduced in the BMSCs group by comparison with the modeling group’s, with substantial elevation in the expression of proteins comprising LC3-Ⅱ, Beclin-1, and p-AMPK.And the standard of p-mTOR protein expression was considerably lessened (P<0.05); rats belonging to group compound C showed increased brain swelling which is relative to that of BMSCs group, increased neuronal apoptosis, decreased neuronal function (P<0.05), increased p-AMPK protein expression, and decreased LC3-Ⅱ, Beclin-1, and p-mTOR protein expression (P<0.05).Conclusion: BMSCs transplantation can reduce neuronal apoptosis after SAH; its principle may be to activate AMPK/mTOR pathway, strengthen autophagy of neurons, and thus inhibit their transformation to apoptosis.
1.Introduction
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a clinical syndrome caused by the rupture of superficial blood vessels in the brain parenchyma and the infusion of blood into the subarachnoid space.It has a high mortality and disability rate in clinical practice.Yu Zhiqiang et al.[1] believed that after the occurrence of SAH, nerve microglia were stimulated, immune cells gathered, causing microcirculation disorders, and then the blood brain barrier was destroyed, leading to direct or indirect apoptosis of neurons.Therefore, neuronal apoptosis is considered to play an important role in the pathophysiological process of early brain injury (EBI)[2-4].Autophagy is an important decomposition pathway that depends on abnormal proteins in lysosomes and proteins produced or exposed by damaged organelles.Among them, AMPK/mTOR (adenosine phosphate activated protein kinase)/(mammalian rapamycin target protein) pathway is a key pathway upstream of autophagy.When the body has sufficient energy supply, mTORC1 phosphorylates ULK1, thereby blocking its activation with AMPK, thus inhibiting autophagy initiation[5].When the body is in energy deficit, AMPK phosphorylates Raptor and inhibits it, thereby downregulating the activity of mTORC1.In addition, ULK1 can also be activated by phosphorylation, triggering the initiation of autophagy cascade[6]; previous studies have shown that the AMPK/mTOR and PI3K Akt/mTOR pathways can play a protective role in the regulation of autophagy intensity after subarachnoid hemorrhage[7].These experiments indicate that AMPK/mTOR pathway may play an indispensable role in the regulation of neuronal apoptosis and autophagy after SAH.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) have the ability to cross the blood brain barrier, migrate to the central nervous system, and differentiate into neural cells after transplantation.At present, some studies have shown that transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can promote the recovery of nervous system function in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).On the one hand, transplantation of stem cells can reduce neuronal apoptosis, strengthen tissue repair after injury, improve the internal environment of the injured site,and play a role in protecting the tissues around the hematoma[8-10]; on the other hand, the activation of PI3K Akt mTOR related pathway can be detected in the brain tissue around the hemorrhage after ICH; after BMSCs treatment, the activation of this pathway was strengthened, and autophagy and axonal regeneration were also enhanced[11].However, whether BMSCs transplantation can induce autophagy through AMPK/mTOR pathway to reduce neuronal apoptosis after SAH has rarely been reported.Therefore, this experiment intends to establish a rat model of SAH and explore the extent and mechanism of autophagy and apoptosis of neurons after BMSCs transplantation treatment induces SAH through AMPK/mTOR pathway, aiming to provide a better experimental basis for other related research, and provide new ideas for clinical diagnosis and treatment of SAH and drug development.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Material Science
2.1.1 Experimental animals
Healthy male SD rats, weighing 280-300 g.The rats in the experimental group were artificially raised in the animal experimental base of North China University of Science and Technology.They were given free food every day, and their drinking water and environment were well ventilated.Before the experiment,the rats were fed adaptively for one week.
2.1.2 Experimental reagents and instruments
AMPK inhibitor Compound C was purchased from Sigma Company in the United States; anti Beclin-1 monoclonal antibody,anti LC3-Ⅱ polyclonal antibody and anti GAPDH monoclonal antibody were purchased from Protein-tech Company; the second antibody and color rendering products were purchased from KPL in the United States; anti p-mTOR monoclonal antibody, anti mTOR polyclonal antibody, anti p-AMPK monoclonal antibody and anti AMPK monoclonal antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology in the United States.TP-1 tablet spreader (Hubei Kangqiang Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.), 820-Ⅱ slicer (German Leica Company), rat brain stereotaxic locator (Shanghai Yuyan Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.).
2.2 Experimental methods
2.2.1 Animal grouping and model construction
Forty-eight Sprague Dawley rats (male) were randomly divided into sham operation (Sham) group, model (SAH) group, model group + bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) group,model group + BMSCs + AMPK inhibitor (Compound C) group with 12 rats in each group.Before making the model, all animals were forbidden to eat within 12 h and water within 4 h.According to the reference[12], the SAH rat model was established, and the blood vessel puncture technique was used.The materials were taken 24 hafter the operation.The clinical manifestation of the successful SAH operation model was that there was a blood clot in the subarachnoid space; if it is unqualified, the test will be rejected[13].In the sham operation group, the vessel wall was not pierced, and there was no significant difference in other operations.Compound C (100 nmol dissolved in 10 μL normal saline) and 10 μL normal saline (2 μL dimethyl sulfoxide soluble in 8 μL 0.1 mol/L phosphate buffer) was injected into the left lateral ventricle (1 mm behind the anterior fontanelle, 1.5 mm behind the lateral fontanel, 3.5 mm deep)with the stereotaxic device of the rat brain.1 h after the successful modeling, 2 μL of cell suspension at a concentration of 1×108/mL was injected into the cerebral ventricle.
2.2.2 Evaluation of neurological function in rats
Twenty four hours after the successful modeling, six rats in each group were randomly evaluated for nervous system defects according to Garcia scoring scale[14], including autonomic activity, limb movement, forelimb extension, climbing, and responses to trunk and limb touch.Among them, 0~3 points for autonomous activity,symmetry of limb movement and forelimb extension respectively;1~3 points for climbing, reaction to trunk touch and reaction to axial running respectively.Calculate the total score.The lower the score,the more serious the damage to the nervous system.
2.2.3 Detection of brain water content in rats
Six rats in each group were taken for modeling, and continued to feed for 24 h after success.The model rats of SAH were anesthetized with chloral hydrate, and their cervical vertebrae were dislocated and their brains were taken out, and the hippocampal tissues on both sides were quickly stripped.Take 200 mg of cerebral cortex,place it on the electronic balance, record the wet weight (accurate to 1 mg), and then dry it at constant temperature for 48 h until the constant weight.Weigh the dry weight and analyze the brain tissue water content of each group according to Elliott formula: brain water content (%) = (mass before drying - mass after drying)/mass before drying 100%.The water content of brain tissue of four groups of rats was measured and compared.
2.2.4 Neuron apoptosis in rats
Part of the hippocampus was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,embedded with paraffin and divided into consecutive slices.After regular dewaxing, washing and other treatments, drop hydrogen peroxide to eliminate the activity of peroxidase, and soak at 20~25℃ for 25~30 min.After completion, wash the specimens, and process and dye the specimens according to the instructions on TUNEL staining kit.Observe the number of apoptotic cells under the microscope and take photos.In each section, randomly select five image fields in the hippocampal CA1 area for counting, and take the average value as the number of apoptotic cells.
2.2.5 Immunohistochemical staining
Routine dewaxing, heating with hydrogen peroxide for 10 min in dark conditions, correcting antigen with trypsin for 20 min, dropping antibody LC3-Ⅱ (dilution 1:300) and antibody Beclin-1 (dilution 1:200) into a wet container, and incubating overnight at 4 ℃.Then add the second antibody solution and incubate it at room temperature for half an hour.After that, it was washed with PBS, dyed with diaminobenzidine, dehydrated, transparent, and covered with slides.In this experiment, PBS was used as the control group instead of the primary antibody.The positive cells in hippocampal CA1 region were observed under light microscope, and five different visual fields were randomly selected in each slice to calculate the average number of positive cells[15].
2.2.6 Expression level of related proteins in rat hippocampus
Hippocampal tissue of rats was taken, and RIPA lysate was added to grind and lyse the tissue at 4 ℃, and protein was extracted by centrifugation.Take the prepared protein extract, sample 30 μg protein-poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis, transfer to PVDF film.Place PVDF membrane in incubation box, add 5% skimmed milk powder, and seal it for 2 h at room temperature.After the closure,TBST was used to wash the membrane, and different proportion of diluted primary antibody 1:500 diluted AMPK was added; 1: 1 000 Diluted LC3-Ⅱ, Beclin-1, p-AMPK , mTOR, p-mTOR; 1: 1 500 diluted GAPDH diluent, 4 ℃ overnight.After that, use TBST to wash at room temperature, and then add horseradish peroxidase labeled secondary antibody to incubate for 2 h.After incubation,use TBST to wash.Drop ECL super sensitive luminous solution for development.Image J was used to determine the optical density value and quantitative analysis of protein bands.
2.2.7 Statistical analysis
All data are built with Excel, and SPSS 23.0 and GraphPad Prism 8.0 statistical analysis software are used to process the data and draw graphs.All values are expressed by.One way ANOVA was used to compare multiple samples, and t-test was used to compare the data between the two groups.When P<0.05, the difference was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Comparison of neurological deficit scores of rats in each group
Compared with rats in the SAH group, the Garcia score of rats in the Sham group was higher (P<0.05), and the neurological function was normal, while the Garcia score of rats in the BMSCs group was lower, and the neurological function was significantly defective(P<0.05).Compared with BMSCs group, the neurological function of Compound C group was further reduced (P<0.05).The data on neurological deficit scores of rats in each group are provided in Table 1.
3.2 Comparison of brain water content of rats in each group
Compared with Sham group, the water content of brain tissue in SAH group was significantly increased (P<0.05).Compared with SAH group, BMSCs group reduced the brain water content of rats(P<0.05).Compared with BMSCs group, Compound C group was slightly higher (P<0.05); there was no significant difference between Sham group and BMSCs group (P>0.05).In the course of the experiment, edema of different degrees can be observed in each group.The results are shown in Table 2.
Tab 1 The results of the neurological score content in each group of rats (n=6,)
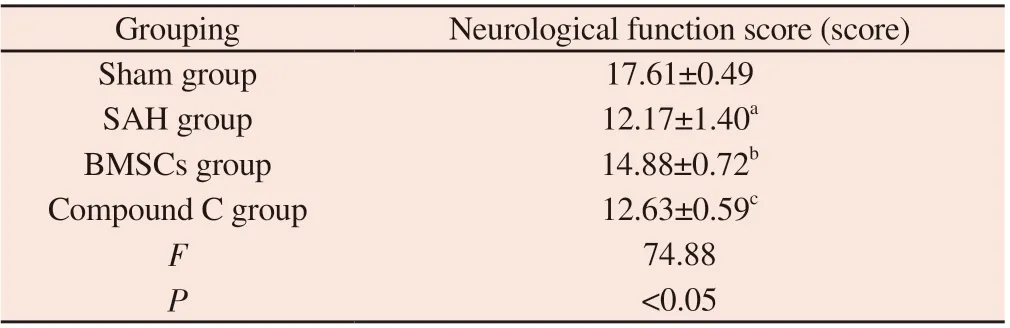
Tab 1 The results of the neurological score content in each group of rats (n=6,)
Note: SAH group compared with Sham group, aP<0.05; BMSCs group compared with SAH group, bP<0.05; Compound C group compared with BMSCs group, cP<0.05.
Grouping Neurological function score (score)Sham group 17.61±0.49 SAH group 12.17±1.40a BMSCs group 14.88±0.72b Compound C group 12.63±0.59c F 74.88 P<0.05
Tab 2 The results of brain water content in each group of rats (n=6,)
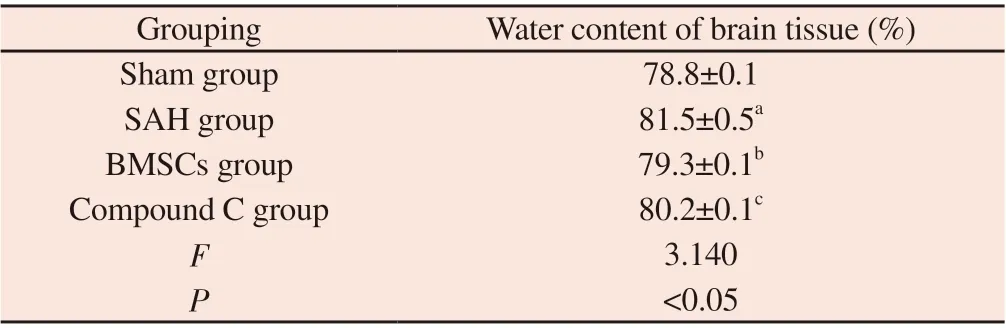
Tab 2 The results of brain water content in each group of rats (n=6,)
Note: SAH group compared with Sham group, aP<0.05; BMSCs group compared with SAH group, bP<0.05; Compound C group compared with BMSCs group, cP<0.05.
Grouping Water content of brain tissue (%)Sham group 78.8±0.1 SAH group 81.5±0.5a BMSCs group 79.3±0.1b Compound C group 80.2±0.1c F 3.140 P<0.05
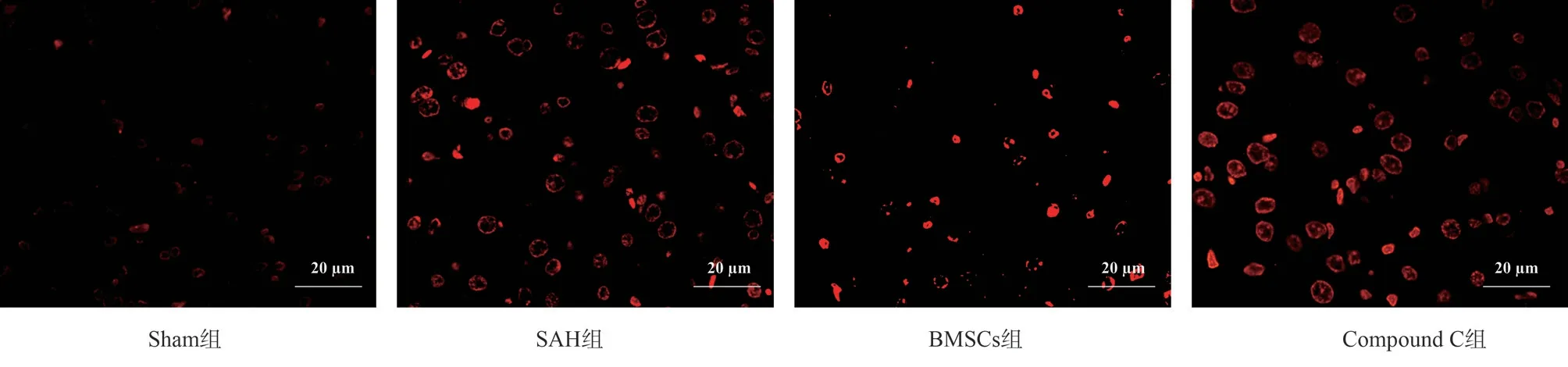
Fig 1 TUNEL staining (× 400)
3.3 Neuron apoptosis in hippocampus of rats in each group
TUNEL staining was used to observe the results of rat hippocampal tissue slices: compared with Sham group, SAH group had greater neuronal apoptosis and significantly higher apoptosis rate (P<0.05);compared with SAH group, the apoptosis of neurons in BMSCs group was significantly reduced (P<0.05); compared with BMSCs group, the apoptosis rate of neurons in hippocampus of rats in Compound C group showed a relatively upward trend (P<0.05).The data on neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampal tissue of rats in each group are shown in Table 3, Figure 1.
Tab 3 The number of neuronal apoptosis in rats in each group(n=6, )

Tab 3 The number of neuronal apoptosis in rats in each group(n=6, )
Note: SAH group compared with Sham group, aP<0.05; BMSCs group compared with SAH group, bP<0.05; Compound C group compared with BMSCs group, cP<0.05.
Grouping CA1 area Sham group 1.61±0.22 SAH group 45.25±3.79a BMSCs group 29.47±1.52b Compound C group 39.38±1.72c F 17.44 P<0.05
3.4 Expression of Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ protein in hippocampus of rats in each group
To study the expression level of Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ protein in rat hippocampus, it was found that the expression level of autophagy protein in SAH group was lower than that in Sham group; compared with rats in SAH group, the expression level of autophagy protein in BMSCs group was significantly higher; compared with BMSCs group, the level of autophagy protein in Compound C group decreased.All the above were statistically different (P<0.05).The results are shown in Table 4, Figure 2, Figure 3.
Tab 4 Thenumberofpositive cellsof Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ in hippocampal tissue ofdifferentgroups(n=6, )
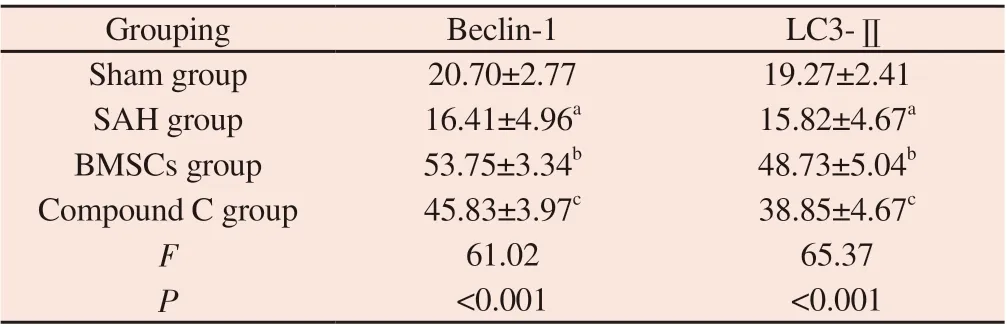
Tab 4 Thenumberofpositive cellsof Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ in hippocampal tissue ofdifferentgroups(n=6, )
Note: SAH group compared with Sham group, aP<0.05; BMSCs group compared with SAH group, bP<0.05; Compound C group compared with BMSCs group, cP<0.05.
Grouping Beclin-1 LC3-ⅡSham group 20.70±2.77 19.27±2.41 SAH group 16.41±4.96a 15.82±4.67a BMSCs group 53.75±3.34b 48.73±5.04b Compound C group 45.83±3.97c 38.85±4.67c F 61.02 65.37 P<0.001 <0.001
3.5 Changes of AMPK pathway related proteins in rats of each group
Western blot showed that compared with Sham group, SAH group decreased the ratio of p-AMPK to AMPK and increased the ratio of p-mTOR to mTOR (P<0.05); compared with SAH group, the ratio of p-AMPK to AMPK in BMSCs group increased, and the ratio of p-mTOR to mTOR decreased (P<0.05).Compared with BMSCs group, Compound C group decreased the ratio of p-AMPK to AMPK and increased the ratio of p-mTOR to mTOR (P<0.05).It suggests that BMSCs may activate AMPK/mTOR pathway.The results are shown in Figure 4.
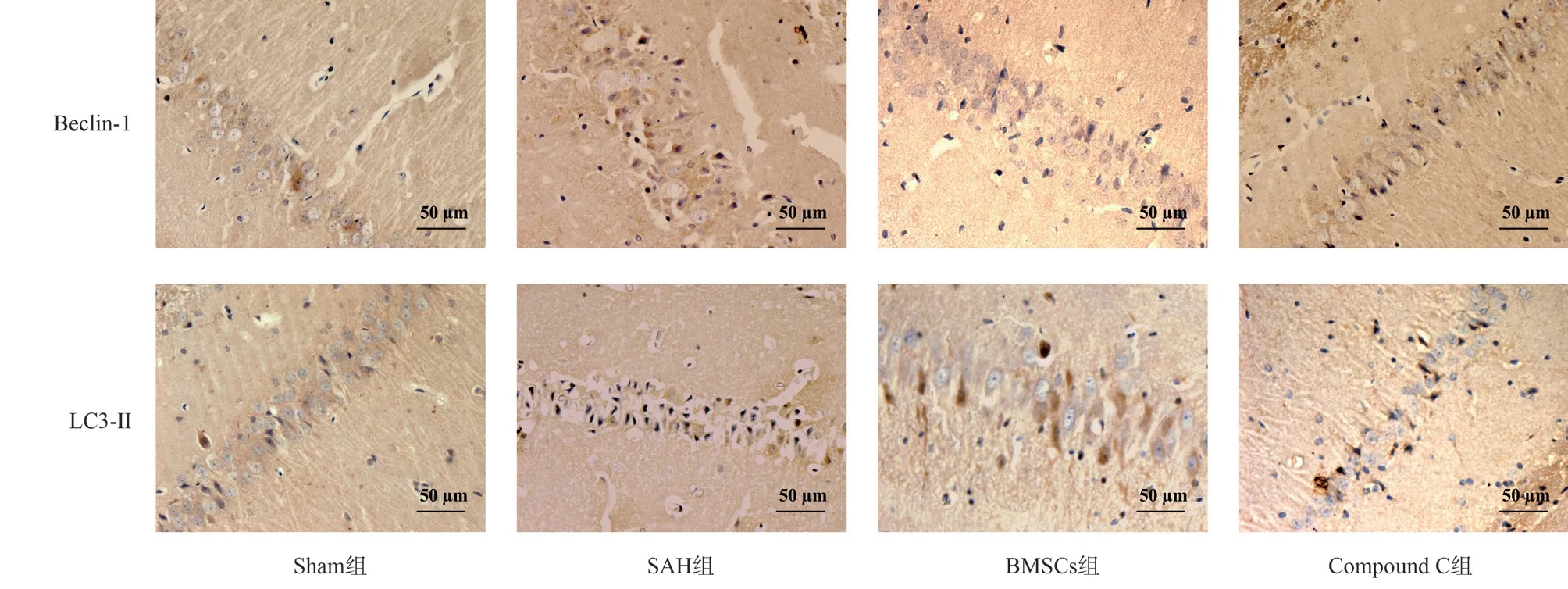
Fig 2 Beclin-1 and LC3-Ⅱ staining of hippocampal tissue in different groups (DAB, ×400)
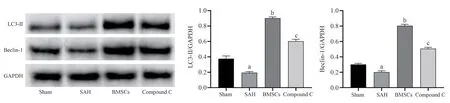
Fig 3 Expression levels of autophagy-related proteins in different groups of rats
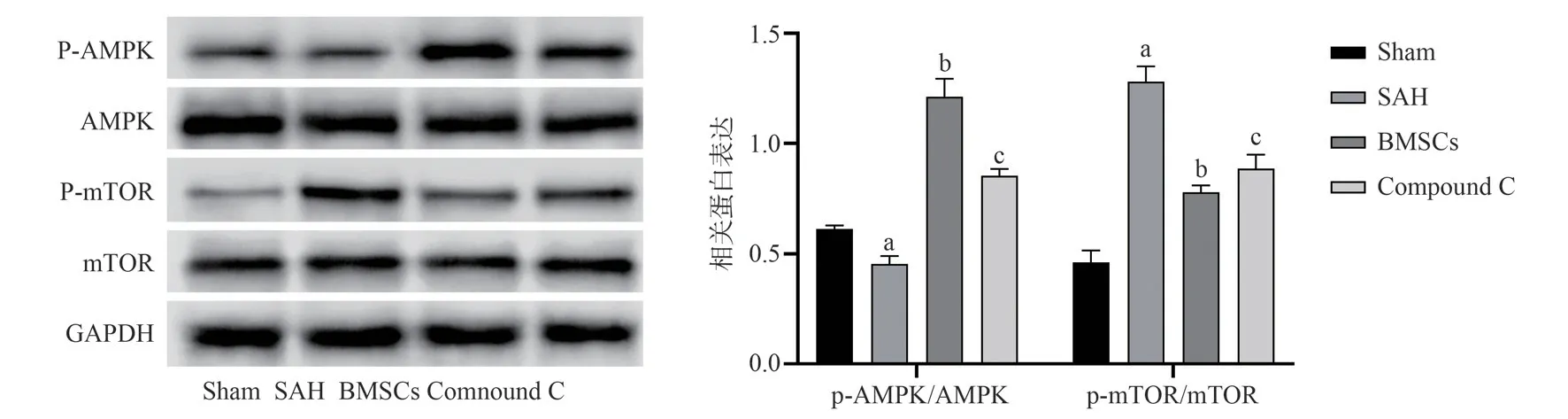
Fig 4 Expression levels of proteins associated with the AMPK signaling pathway in different groups of rats
4.Discussion
Autophagy is a phenomenon that maintains the intracellular environment by digesting and degrading damaged organelles,pathogens, etc.The effect and mechanism of autophagy on neuronal apoptosis after SAH has become an important research hotspot.Li’s several studies[16] have confirmed that if apoptosis is induced in rats through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, the synthesis of rat BMSCs may affect autophagy of neural cells.Appropriate autophagy helps cells to expel toxins and damaged substances,increase the number of surviving neurons, and inhibit cell apoptosis.A large number of experimental studies have shown that the auto phase of neurons after SAH may be activated and further induce autophagy.Strengthening autophagy can reduce the apoptosis of neurons after SAH, and alleviate the damage of neural function.In the process of auto-phage formation, LC3-Ⅱ is a marker protein[17]for the formation and localization of auto-phage membrane.In this study, we found that in the determination of autophagy factor LC3-Ⅱ and Beclin-1 protein, compared with the SAH group, the protein expression level in the hippocampus of rats in the BMSCs group was significantly increased.By observing the neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats, we found that the number of TUNEL positive cells in the SAH group was significantly increased, but not significantly in the sham operation group; the number of TUNEL positive cells in BMSCs group was significantly lower than that in SAH group, indicating that the level of neuronal apoptosis was reduced.The experimental study showed that the transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells could improve the degree of autophagic neurons and restrain their apoptosis in SAH rats,and at the same time, strengthen the repair of neural function and improve brain edema in rats.These results suggest that BMSCs may inhibit early neuronal apoptosis after SAH by increasing autophagy.However, the potential mechanism of BMSCs inhibiting low amplitude neuronal apoptosis after SAH test has not been fully confirmed.
Previous studies have shown that the neurons of rats after SAH can be protected to some extent by activating autophagy[18].In the present experimental study, after making a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage by using carotid artery puncture method like Sun et al.[12], we found that the neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of SAH rats was serious, and the neurological function score was significantly reduced.After adding BMSCs, the neurological function score of rats increased relatively, suggesting that sensory and motor functions were restored to a certain extent.At present,studies have shown that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can promote the recovery of damaged nerve cells in SAH rats[19] and BMSCs can affect autophagy of SAH through PI3K-Akt/mTOR pathway[11].mTOR is a key substance regulating autophagy.Its upstream regulatory pathways mainly include PI3K/Alt and LKBl/AMPK, which inhibit neuronal autophagy through the activation of mTOR.As a negative regulator of mTOR, AMPK activation can promote autophagy[20].AMPK is a key cell energy sensor.After activation, AMPK maintains cell energy balance and promotes cell survival by regulating anabolism and catabolism and inducing autophagy[21].
AMPK/mTOR is one of the most important self-phase control approaches.Among them, AMPK is phosphorylated into p-AMPK,which further inhibits the phosphorylation of mTOR kinase and eventually triggers autophagy[22-23].The experimental results showed that the addition of BMSCs could significantly increase the level of p-AMPK and reduce the expression level of p-mTOR in the hippocampus of rats after SAH, indicating that the transplantation of BMSCs activated the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway.At the same time, we intervened with AMPK inhibitor (Compound C), the p-AMPK activity of Compound C group was significantly lower than that of BMSCs group at almost all stages, while the mTOR protein activity was higher than that of BMSCs group, and the p-mTOR expression was increased.Therefore, we speculate that SAH in rats after BMSCs transplantation may enhance the effect of autophagy of neurons in the hippocampus of rats by regulating the AMPK/mTOR pathway, thereby reducing its apoptosis.
In conclusion, BMSCs may inhibit neuronal apoptosis by promoting AMPK/mTOR pathway activation and opening autophagy.Autophagy and activation of AMPK/mTOR pathway were found in neurons in the damaged hippocampus of SAH rats;transplantation of BMSCs can further activate the AMPK/mTOR pathway, enhance autophagy in damaged tissues, inhibit neuronal apoptosis, and further improve the neurological damage in SAH rats, which provides a new reference for BMSCs transplantation in treating nerve damage after SAH.However, this study has not yet clarified the specific role of BMSCs in regulating the AMPK/mTOR pathway, which needs further research and description in the later stage.
Author’s contribution
Cui Cai-ling: experiment design, experiment implementation,data analysis, and thesis writing; Xu Xinyu, Zhang Yu: assist in experimental design, analyze data, and write papers; Cui Bowen, Hu Ai-hui: experiment implementation, data collection; Liu Junjie, Li Jian-min: Design experiments and guide writing.Conflict of interest statement
All authors of this article declare that there is no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年21期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年21期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Assessment of gastric cancer prognosis, immune infiltration based on cuproptosis-related LncRNAs and prediction of traditional Chinese medicine
- Mechanism of AiTongXiao granule in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology and rat transplanted liver cancer model
- The effect and mechanism of stilbene glycosides on improving neuronal injury in Alzheimer's disease rats by regulating ASK/MKK7/JNK pathway
- Meta-analysis of the acupoint application therapy for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Preparation of adhesive resveratrol micelles and determination of drug content
- Research progress of necroptosis and ferroptosis in knee osteoarthritis
