The effect and mechanism of stilbene glycosides on improving neuronal injury in Alzheimer's disease rats by regulating ASK/MKK7/JNK pathway
LI Yue, KANG Bi-qian , HE Xiao-xuan , HU Rui , XIAO Zhen , LUO Chen-liang , WU Gui-you , HUANG Zhong-shi✉
1.School of Basic Medicine,Youjiang Medical Univ for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
2.School of Pharmacy, Guangxi Univ of Chinese Medicine, Baise 533000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the mechanism of action of tetrahydroxy stilbene glycosides(TSG)in ameliorating neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease rats by regulating MKK7 and JNK kinases.Methods: A total of 24-month-old 42 SD rats were randomly selected for the experiment in 7 groups: normal group, sham-operated group, model group, positive drug group, low, medium and high dose TSG group at 0.033 g/kg, 0.1 g/kg, 0.3 g/kg.The Model Group and the TSG groups were established by stereotaxic Aβ25-35 solution.After 28 days, the model rats were selected by passive avoidance test.After screening, each dosage group of TSG and positive drug group was given intragastrically according to the corresponding dosage, and the experiment was carried out after 28 days.The pathological changes of hippocampal CA1 region were observed by tissue staining, and the amount of MKK7 and JNK proteins and the expression content of MKK7 and JNK mRNA by histochemical method of protein, and qRTPCR assay.Results: (1) He staining observation: Compared with the normal group and the sham-operated group, the number of nerve cells in the model group decreased and arranged irregularly, the cell membrane shrank, and the nucleus deformed and dissolved.The number of neurons in the positive drug group and TSG Group also increased significantly, the order is also relatively well.(2) From the results of the Tunel staining experiments:the positive apoptotic cells in the model group were higher than control group and sham-operated group, positive drug group and TSG drugs group was significantly smaller than that in the model group (P <0.05).(3) Compared with the control group and the Virtual Operation Group, the MKK7 and JNK protein concentrations in the brain of the model group were increased(P<0.05) by data analysis of immunohistochemistry: Compared with the model group, the protein expression of positive drug and TSG each dose group were reduced (P<0.05).(4)The results of QRTPCR data showed that the levels of MKK7 and JNK mRNA in the brain tissue of the model group were increased compared with the normal group and sham-operated groups(P<0.05).Conclusion: Stilbene glycoside has a certain effect on neuronal injury and repair which may be related to the changes of mRNA transcription and protein expression of MKK7 and JNK kinases.
1.Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and is emerging as a major global health and Social Health Challenge.However, the pathogenesis of AD is still poorly understood and there is no known drug therapy for early diagnosis and radical cure of the disease[1].Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that is characterized by the formation of amyloid betaβ(Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphoric tau tangles in the limbic regions of the human brain, inflammation occurs in association with the formation of oxygen free radicals, which are characterized by memory loss and progressive neurocognitive impairment and affect daily activities of life and social function[2].With increasing life expectancy and population ageing, global prevalence is expected to continue to rise, particularly in developing countries, resulting in a costly disease burden[3].
2,3,5,4-tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside (TSG) , also known as stilbene glucoside, plays a major pharmacological role in radix polygoni multiflori, such as anti-inflammatory repair, anti-oxidation,anti-apoptosis and scavenging free radicals, it can protect the nervous system, improve the ability of learning and memory, repair the brain damage, and have certain curative effect on the improvement of Alzheimer's disease (AD).It can relax the blood vessels and promote the proliferation of Endothelium, lowering cholesterol and arteriosclerosis[4,5].It has been shown that TSG can increase the expression of several AD-related proteins, thereby reducing the over-production of APP and A-B in the brain of mice, thus playing a role in the prevention and treatment of AD[6].In the current situation of aging, it is of great practical significance to study it[7].In this study, we observed the changes of MKK7 and JNK in order to further explore the mechanism of TSG in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
SPF RAT, SD male, 24 months old, Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., License No.SCXK (Hunan)2019-0014.Feeding, material collection and experiment were carried out in SPF animal experiment center of Youjiang Medical College of Guangxi Baise City.This experiment was examined and approved by the Ethics Committee of Youjiang Medical College for nationalities in Baise City, Guangxi, and then related experiments were carried out, the whole experimental process is strictly in accordance with the“Guidelines on the treatment of experimental animals,” the norms and requirements.
2.2 Major reagents
Stilbene glycoside extract (batch number: CHB180810, Chengdu Keloma
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) , dye-based quantitative PCR premix(Mona Biology Co., Ltd., batch number: 100649), blocking with normal goat serum (Beijing Solebo Technology Co., Ltd., batch number: SL038) amyloid beta protein solution 25-35(Sigma Corporation, USA, batch number: 118M4893V), mKK7 and JNK polyclonal antibodies (batch number: AB08284512).
2.3 Major methods
2.3.1 Animal modeling
Male SD rats were randomly divided into 7 groups.The model of Alzheimer’s disease was established by injecting Aβ25-35solution into the hippocampus.The rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% pentobarbital (40 mg/kg) , the Rat’s head was placed on a brain stereotaxic instrument, and the Bregma and Bregma were fully exposed to make them in a straight line.After shaving and skin preparation, sterile iodophor was used to sterilize the skin preparation area, the surgical area was selected[8] , the skull was perforated with a 0.3 mm diameter syringe, and 5 μL of Aβ25-35solution was injected into the left and right hippocampus at a rate of 1 μL/min, after the operation, stay for about 5 min to passively diffuse the liquid at the tip of the needle tube.To avoid the liquid overflow, the needle should be slowly drawn out after fully immersing in the solution, and the wound should be kept clean.The sham-operated group was injected with the same amount of saline in the above-mentioned areas of the brain, and the normal group was fed daily without any other operations[9].
2.3.2 Model selection
The passive avoidance experiment was used as a behavioral test,and the experiment was used as a marker to screen whether the modeling was successful or not.In the first stage, the experimental rats were put into the experimental box through the entrance of the light chamber, and the entrance between the light and dark chamber was communicated with each other, and the animals were allowed to adapt freely for 10 min.The rats were put into the bright room with their heads facing the wall of the ventricle.When the rats entered the dark room completely, they were given electrical stimulation after closing the entrance to make the rats form memory.In the second stage, the rats were subjected to passive avoidance test.The rats were put into the dark room through the entrance of the bright room.The latency of rats was recorded as rat latency, the incubation period of the rats that did not enter the darkroom was recorded at 300 s, and the experimental data of the rats in each group were analyzed.
2.3.3 Grouping and administration
Forty-two male rats were divided into normal group, Sham Operation Group, model group, positive drug group, low, middle and high dose TSG groups with 6 rats in each group.After screening,the positive drug huperzine a (0.15 mg/kg) was administered in low,middle and high dose groups after administration of TSG solution at the concentrations of 0.033 g/kg, 0.1 g/kg and 0.3 g/kg, respectively,the other groups were given 25 mL/kg normal saline for 4 weeks [10].
2.3.4 The pathological changes of hippocampus and cortex in mice were observed (HE staining)
Three rats in each group were randomly selected and injected with paraformaldehyde into the heart.The whole brain tissues of the rats were taken out on ice.The hippocampus of rats was fixed with paraformaldehyde, and the slices were made with the thickness of 4 μm.The slices were serially sectioned after paraffin embedding, and the slices were dewaxed and dehydrated in a 60 ℃ oven overnight,the slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin dye and the morphological changes in the hippocampus were observed under the microscope.
2.3.5 Tunel staining
Paraffin-embedded sections were stained by TUNEL staining.The sections were dewaxed three times, dehydrated with ethanol,washed with NaCl and washed with PBS.After rehydration, sections were incubated with protease K (20 μg/mL) at room temperature to prepare a TUNEL reaction mixture, which was subjected to endlabeling reaction and immersed in stop buffer for 15 min, after blocking, staining, gradient dehydration, transparent and the sealing piece was dried, the apoptosis of the hippocampal area was observed under the microscope.
2.3.6 The expression of MKK7 and JNK protein was detected by immunohistochemistry
After paraffin sections were dewaxed with xylene and dehydrated with ethanol gradient, antigen pretreatment with Sodium Citrate buffer was carried out (100 ℃ 20 min) , serum blocking; incubation of MKK7(1:150) , JNK (1:150) , 4 ℃ blocking overnight; incubation of secondary antibodies; staining with DAB reagent and stopping reaction after sufficient staining under microscope; counterstaining of tap water with hematoxylin to control reaction time; After gradient dehydration and transparency, the expression of proteins in hippocampal CA1 region was detected, the data were analyzed by Image Pro plus 6.0 using the average optical density value as the statistical result of protein relative expression amount.
2.3.7 Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay (qRT-RCR)
Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction method (QRT-RCR) was used to extract 50 mg of total RNA from the hippocampus of rats in each group, the concentration, purity(OD260/OD280) and integrity of total rat RNA were detected.After reverse transcription into cDNA, the reaction system was set up according to the instructions of the Premix.2-ΔΔCTmethod was used to calculate the expression of target mRNA.
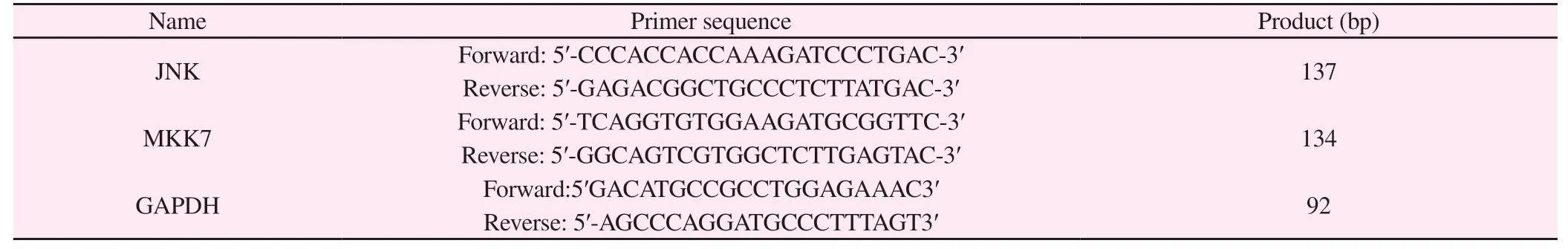
Tab 1 Sequences of the primers
2.4 Statistical treatment
SPSS 23.0 was used for data processing and Image Pro plus 6.0 for Image analysis.All experimental data were expressed as mean, and one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison among groups.When P < 0.05, the experimental data had statistical significance.
3.Results
3.1 Passive avoidance test of experimental behavior
Compared with the normal group, the number of errors in the model group was significantly increased (P < 0.01) , the latency was significantly shortened (P < 0.05) , and the number of errors in the model group was significantly increased (P < 0.01) , the incubation period was significantly shortened (P < 0.05).The model rats were divided into two groups, and no special operation was performed in the normal group and Sham Operation Group.
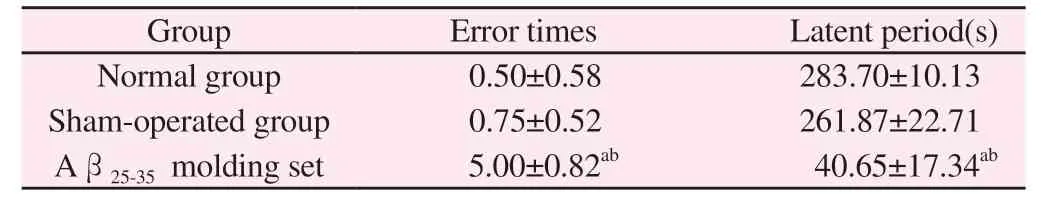
Tab 2 Behavioral test results
3.2 HE staining results
In the hippocampal CA1 region of the normal group and the shamoperated group, the number of normal cells was more, the edge of cells was clear, the shape of cells was plump and abundant, and the nucleoli were obvious, compared with the normal group and the sham-operated group, compared with the model group, the number of normal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region of the model group was significantly decreased, the structure of neurons was disordered, and the cell morphology was shriveled, compared with the positive drug group, TSG low, middle and high dose groups,the number of neurons in hippocampal CA1 area increased and the structure and morphology of neurons were improved, the number and morphological structure of neurons in hippocampal CA1 region of rats in low, middle and high dose TSG groups were obvious, as shown in Figure 1.
3.3 TUNEL staining
Compared with the normal group and Sham Operation Group, the number of TUNEL positive cells and the number of apoptotic cells in the hippocampal CA1 region of the model group were significantly increased (P < 0.05) Compared with the model group, the number of TUNEL positive cells and the number of apoptosis cells in the positive drug group, TSG low, middle and high dose groups were significantly decreased (P < 0.05) , the number of TUNEL-positive cells was increased in low and middle dose TSG groups (P < 0.05) ,but there was no significant change in high dose TSG group (Figure 2).
3.4 Immunohistochemical results
Compared with the normal group and the Sham Operation Group,the expression of MKK7 and JNK protein in the hippocampal CA1 region of the model group was significantly higher (P < 0.05)Compared with the model group, the expression levels of MKK7 and JNK protein in the hippocampus of TSG low, middle and high dose groups were significantly down-regulated (P < 0.05) Compared with the positive drug group, the expression of MKK7 protein in the low-dose group was higher (P < 0.05) , the expression of MKK7 protein in the middle-dose group had no significant change, and the expression of JNK protein in the high-dose group was lower (P <0.05) , the expression of TSG was up-regulated in low and middle dose groups (P < 0.05) , and the expression of TSG in high dose group was similar to that of positive drug group (Figs.3,4).
3.5 qRT-PCR results
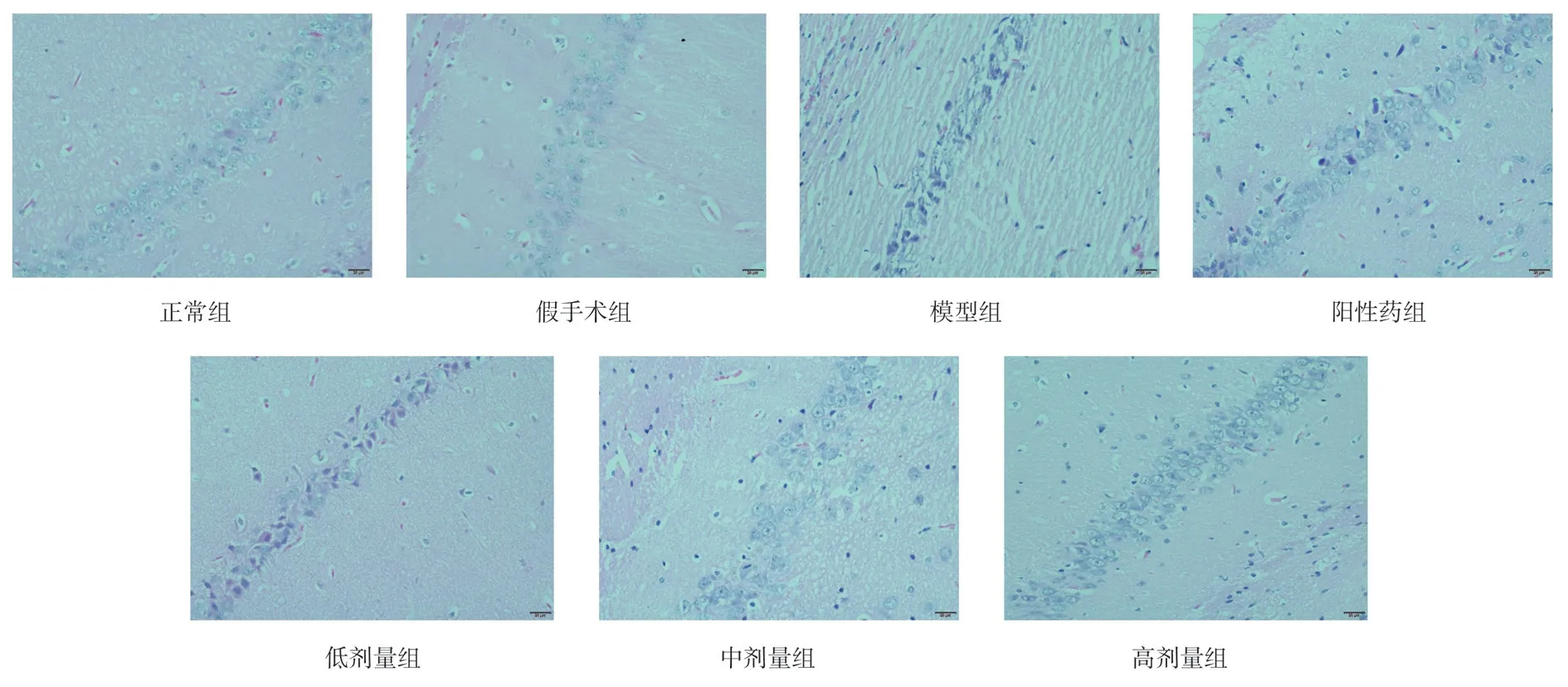
Figu 1 The results of pathological staining in hippocampal CA1 region of each group
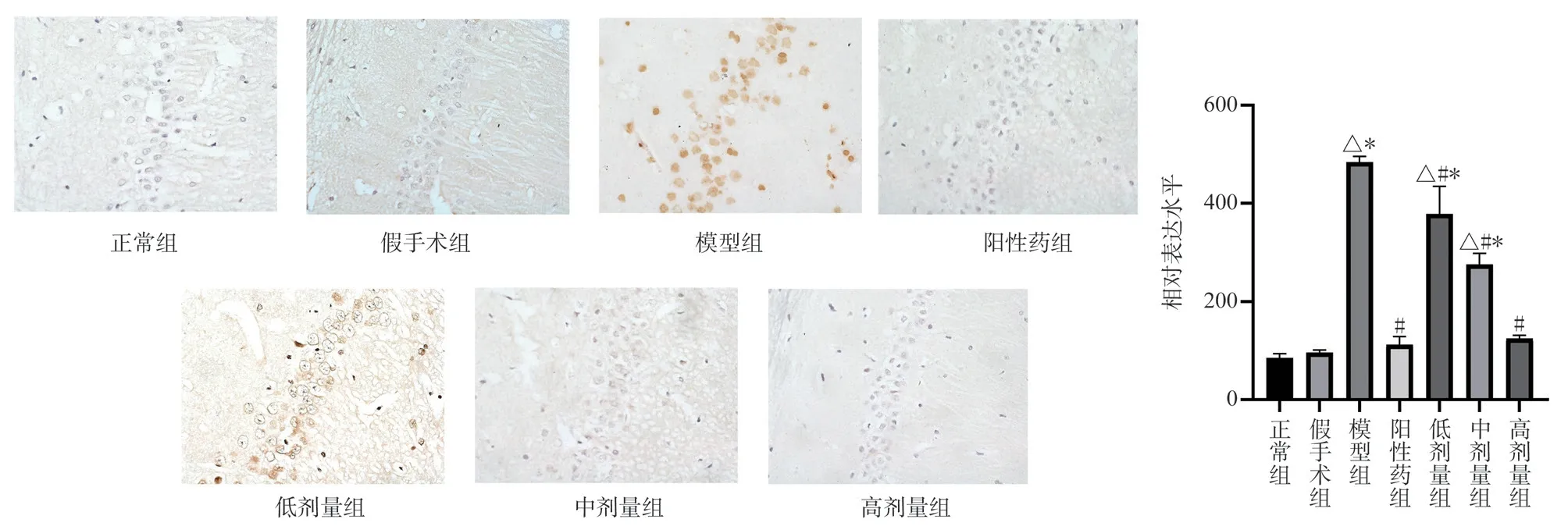
Fig 2 TUNEL staining of hippocampal neurons in each group (× 400,Bar=20 μm)
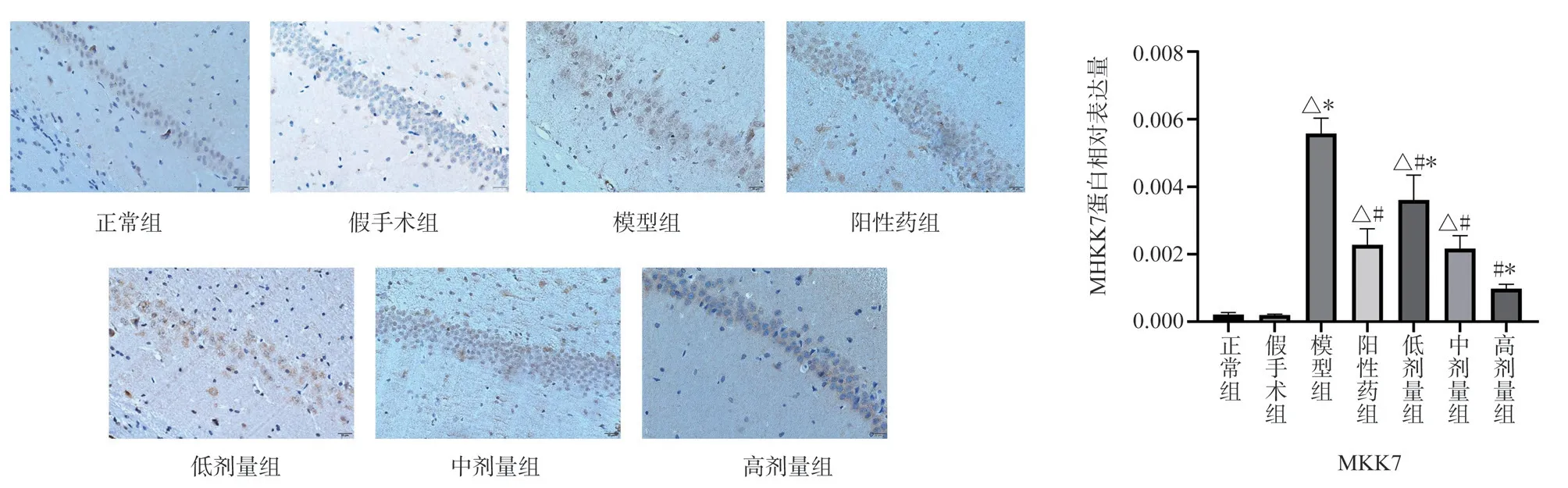
Fig 3 Expression of MKK7 protein in rat hippocampus (× 400)
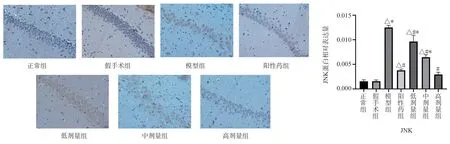
Fig 4 Expression of JNK protein in rat hippocampus (× 400)
Compared with the normal group and the Sham Operation Group,the expression of MKK7 and JNKmRNA in the model group increased significantly (P < 0.05) , while the expression of MKK7 and JNK mRNA in the positive drug group decreased significantly(P < 0.05) , the mRNA contents of MKK7 and JNK in the middle and high dose group of TSG were decreased (P < 0.05) , while the mRNA contents of MKK7 and JNK in the low dose group of TSG were decreased (P < 0.05) , and the expression of JNK mRNA was slightly decreased but not statistically significant Compared with the positive drug, the expression of MKK7 and JNKmRNA in the low-dose TSG group increased (P < 0.05) , while the expression of MKK7 and JNK in the middle and high-dose TSG groups decreased,however, only the high-dose TSG group showed significant expression of JNK (P < 0.05) , as shown in Figure 5.
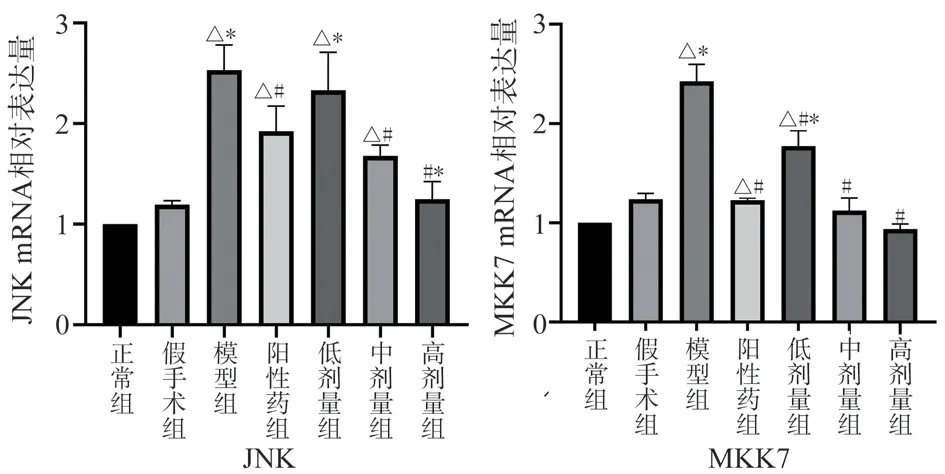
Fig 5 The relative expression levels of ASK1, MKK7 and JNK mRNA in the brain tissue of rats in each group
4.Discussion
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that occurs mainly in old age, its main performance for memory loss, aphasia,apraxia, loss of identity, thinking and Computing Ability Impaired,personality and daily behavior changes[11].The main pathological changes are the accumulation of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques,neurofibrillary tangle, loss of cholinergic neurons, inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.Whereas relevant studies have shown that a β accumulation and its associated inflammation are thought to be an early event prior to neurodegeneration and neuronal loss in the AD brain[13].
MKK7 is a member of the MAPKKS family and plays a key role in oxidative stress and apoptosis of the nervous system.Activation of MKK7 is regulated by both phosphorylation and ubiquitination, and activated MKK7 can activate JNK[14].MKK7, a specific upstream kinase of JNK that only activates JNK, is the most important MAP2K regulating JNK cascade activity[15].The importance of MKK7 for different intracellular functions, such as cell growth, proliferation,senescence, differentiation, and transformation, has been reported in many in vitro and in vivo studies, cell cycle regulation and tumor metabolism and their roles in the nervous system[16].Apoptotic stimuli such as TNF-α, ROS can act on MKK7 leading to JNK activation, thereby inducing apoptosis of cells.Some studies have studied the effects of drugs on brain diseases from the perspective of MKK7 and JNK signaling factors[17]
The JNK signaling pathway is a subtype of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway that plays a role in this pathway, the nervous system is mainly involved in the activation of Aβ-induced apoptosis, Synaptic plasticity dysfunction and tau Hyperphosphorylation, revealed to us that JNK may serve as a target for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease[18].JNK is a key mediator involved in a variety of physiological processes.The JNK pathway is active in the central nervous system system(CNS) and is involved in the regeneration and repair of cells that need to cope with pathophysiological injuries during development and adulthood, as well as Neurodegeneration and nerve cell death[19].It has three major subtypes, JNK1/JNK2/JNK3, and C-Jun N-terminal kinase 3(JNK3) , which is thought to play a critical role in Neurodegeneration disease headed by Alzheimer's disease (AD) , and is complex regulated by upstream kinases and phosphatases[20].In this experiment, the model of AD was established by injecting Aβ25-35solution into the rats.The results of immunohistochemistry and qRT-PCR showed that the expression of JNK in the model group was significantly higher than that in the normal group and Sham Operation Group, it is suggested that the upregulation of JNK may be related to the accumulation of amyloidbeta (Aβ) plaques and the induction of apoptosis in Alzheimer‘s disease.After treatment with TSG, the expression of JNK decreased with the increase of the dose of TSG, suggesting that TSG may be a therapeutic target for AD by down-regulating the content of JNK.
To sum up, it is inferred from the experiment that the protective effect of TSG on neurons may be achieved by down-regulating the transcription and protein expression of MKK7 and JNKmRNA to repair the damage of hippocampal neurons, however, its specific mechanism and target factors are not clear, and need further study.
Authors’ contribution
Li Yue: the design and operation of the overall experimental process, the collation and analysis of late data, as well as paper writing and literature review; Kang biqian, he Xiaoxuan, Hu Rui, Xiao Zhen, Luo Chenliang: to assist the completion of the experiment; Wu Guiyou: Literature Review; Huang Zhongshi:Revision of thesis ideas, funding support.
All authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年21期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年21期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Assessment of gastric cancer prognosis, immune infiltration based on cuproptosis-related LncRNAs and prediction of traditional Chinese medicine
- Mechanism of AiTongXiao granule in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology and rat transplanted liver cancer model
- Meta-analysis of the acupoint application therapy for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Preparation of adhesive resveratrol micelles and determination of drug content
- BMSCs transplantation inhibits neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-mediated autophagy
- Research progress of necroptosis and ferroptosis in knee osteoarthritis
