FGF2 promotes the chemotherapy resistance in colon cancer cells through activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Xiao-Lan Jian,Pu-Hua Zeng,Ke-Xiong Li,Wei Peng
Abstract Background: To investigate the role of fibroblast growth factor 2(FGF2)in chemotherapy resistance of colon cancer.Methods: An HCT116/5-fluorouracil(5-FU)-resistant cell line was established,and FGF2 levels were detected in a sensitive cell group(HCT116)and a resistant cell group(HCT1116-R)using different methods.Fibroblast growth factor 2 levels in the medium were determined by enzyme-linked immunoassay.The protein expressions of FGF2,fibroblast growth factor receptor 1(FGFR1),and phospho-FGFR1 were assessed by Western blotting,and FGF2 mRNA levels were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.Fibroblast growth factor 2 recombinant protein was added to sensitive cells,and FGFR inhibitor AZD4547 was added to resistant cells,and the cell survival rate was determined using the cell counting kit-8 method and the protein expressions of PI3K(phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase),p-PI3K(phospho-PI3K),Akt(protein kinase B),p-Akt(phospho-Akt),mammalian target of rapamycin(mTOR),p-mTOR(phospho-mTOR),Bad(Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter),NF-κB(nuclear factor κB),GSK-3(glycogen synthase kinase-3),FKHR(forkhead box protein O1),and PTEN(phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten)were detected by Western blotting.Results: Fibroblast growth factor 2 protein and mRNA expression levels in the HCT116-R group were significantly higher than those in the HCT116 group. Fibroblast growth factor 2 increased the survival rate of HCT116 cells; improved tolerance to 5-FU; upregulated p-PI3K,p-Akt,and p-mTOR;and downregulated Bad.The FGFR inhibitor AZD4547 decreased cell survival rate and tolerance to 5-FU;downregulated p-PI3K,p-Akt,and p-mTOR expression;and upregulated Bad.Conclusions: Fibroblast growth factor 2 promotes chemotherapy tolerance in colon cancer cells by activating the Akt/mTOR and Akt/Bad signaling pathways downstream of PI3K.
Keywords:Chemotherapy drug resistance;Colorectal cancer;Fibroblast growth factor;PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
1.Introduction
Colorectal cancer is a common cancer.Despite improvement in living standards and dietary habits,its incidence has increased and is ranked the third in the word.The mortality rate is high,ranking fifth in the world.[1,2]This type of cancer easily relapses and metastasizes,which is the main cause of death.[3]
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for advanced intestinal cancers;however,drug resistance often occurs.[4]Drug resistance is an important factor leading to chemotherapy failure.The development of different degrees of drug resistance in tumors is the main obstacle to chemotherapy, which greatly affects the curative effect, leading to tumor recurrence or metastasis and reduced survival rate.[5]To overcome drug resistance and improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs,the targets of drug resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs have been investigated,and this has become a key problem to be solved.
Tumor cells secrete fibroblast growth factor (FGF), which promotes tumor angiogenesis and leads to drug resistance.The specific binding of FGF to fibroblast growth factor receptor(FGFR)blocks the action of FGFR,inhibits the growth of existing tumor vascular lesions,promotes the normalization of tumor vessels,decreases the pressure between tumor tissues,and promotes drug delivery to improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs. Fibroblast growth factor regulates several signaling pathways, including RAS/ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase(PI3K)/Akt.[6]
PI3K/Aktsignalingisactivatedintumorcells,anditsexpressionishigher in colorectal cancer tissues.[7]PI3K/Akt can be activated by the Ras pathway,growth factors,cytokines,and hormones[8]to regulate the cell cycle,apoptosis,proliferation,metastasis,and drug resistance.Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten(PTEN)negatively regulates PI3K and acts as a phosphatase that dephosphorylates Akt and inhibits its activation,thereby preventing downstream signaling events.
Tumor drug resistance is a multifactor and multistep process that is affected by both the tumor itself and tumor microenvironment.This study aimed to assess fibroblast growth factor 2's(FGF2's)role in drug resistance of colorectal cancer.
2.Materials
2.1.Cells
The human colon cancer cell line HCT116 was purchased from the Chinese Academy of Sciences(Tchu 99)and cultured in RPMI 1640 medium. When the cells reached 90% confluence, they were passaged,and the cells in the logarithmic phase at 80%confluence were used for the experiment.
2.2.Drugs
The following drugs were used:FGF2 recombinant protein(R&D Systems),R&D Systems(America),Selleck(America),Beyotime Biotechnology(China),Gibco(America),Abcam(America),CellSignaling(America),Proteintech(China),ThermoScentific(America),Sigma(Germany),Thermo(America),Hoefer(America),Tanon(China),BioTek(America),Roche (Switzerland). FGFR inhibitor (AZD4547; Selleck, S2801, lot no.5623),and 5-fluorouracil(5-FU)(Selleck,S1209,lot no.4823).
2.3.Reagents
Reagents used were cell counting kit-8 (Beyotime Biotechnology;C0038 lot no.: 2316), RPMI 1640 medium (ATCC modification;Gibco,C11875500BT,lot no.8121027),newborn calf serum(Gibco,26010-074, lot no.: 2296205), D-PBS (Beyotime Biotechnology,C0221G, lot no.: 1203), anti-FGF2 (EPR20145-219, ab208687,lot no.:GR3175972-2),human FGF2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)kit(Abcam,ab246531),phospho-FGFR(p-FGFR1)(Tyr653/654)mAb(Cell Signaling,52928,lot no.:6),FGFR mAb(Cell Signaling,#9740,lot no.:7),PI3 kinase p110α(C73F8)(Cell Signaling, #4249, lot no.: 4), phospho-PI3K (p-PI3K) (Abcam,ab182651, lot no.: BP71232-06), phospho-Akt (p-Akt) (Ser473)(Cell Signaling,#4060,lot no.:2),Akt(pan)(Cell Signaling,#4691,lot no.:5),phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin(p-mTOR)antibody(S2448)(Proteintech,67778-1-Ig,lot no.:30195914),mTOR antibody(Proteintech,66888-1-Ig,lot no.:30245823),nuclear factor κB p65 antibody(Proteintech,10745-1-AP,lot no.:30543412),BAD antibody(Proteintech,10435-1-AP,lot no.:30678345),forkhead box protein O1/FOXO1 Antibody (Proteintech, 18592-1-AP, lot no.:34356712),glycogen synthase kinase-3β(D5C5Z)XP Rabbit mAb(Cell Signaling,#12456,lot no.:5),PTEN(Abcam,ab170941,lot no.:ER35901-12), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH) antibody (Proteintech, 60004-1-Ig, lot no.: 30320674),radioimmunoprecipitation assay (Sigma R0278-50 mL, lot no.:SCBF7966V),SuperSignal West Pico PLUS Chemiluminescent Substrate(ThermoScentific,34580,lot no.:VF304342),GE Healthcare Life Science Amersham Protran (0.45 μm, 10600002, lot no.A15030279),and Trizol(Sigma,15596018,lot no.:290310).
2.4.Instruments
A cell incubator (Thermo, model: Heracell 2401), Hoefer electrophoresis apparatus(Hoefer,model:SE300),Hoefer film transfer apparatus(Hoefer,model:SE300),automatic chemiluminescence imaging analysis system (Tanon, Tanon5200), automatic enzyme marker(BioTek Synergy2),and real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction(PCR)(Roche LC480)were used.
3.Methods
3.1.Establishment of drug-resistant cell lines
This was induced by increasing the 5-FU concentration.At <0.1 μg/L 5-FU,the majority of HCT116 cells can continue to survive,which is a relatively safe concentration and was selected as the initial concentration,and the drug was changed every 48 hours.Subsequently,the dead cells were removed and subcultured. After no cell death was observed,the cells were subcultured in the logarithmic phase,and the drug concentration was increased by 25%to 50%.No cell death was observed when the cells survived at a concentration of 5 mg/L and were continuously cultured. This was defined as an HCT116/5-FU-resistant cell strain.To ensure the persistence of drug resistance,5-FU of 5 mg/L was provided to the cell strain. Drug-resistant cell lines were provided a 2-week drug-eluting culture prior to detection.
3.2.Detection of drug resistance using the cell counting kit-8 method
HCT116 and HCT116/5-FU(HCT116-R)cells were inoculated into 96-well plates at a density of 5000 cells per well and assigned to the HCT116, HCT116 + FGF2 recombinant protein, HCT116-R, and HCT116-R+FGFR inhibitor(AZD4547)groups and media containing FGF2 recombinant protein,inhibitors,and different concentrations of 5-FU.Three composite wells were used for each drug concentration gradient.After 72 hours,10 μL of cell counting kit-8(CCK-8)was added for 2 hours followed by measuring absorbance at 450 nm.The formula for cell survival rate was as follows:cell survival rate=mean absorbance of the administration group/control group×100.
3.3.Detection of FGF2 expression in the culture medium by ELISA
Sensitive HCT116 and HCT116-R cells were cultured for 24 hours,and the supernatant was collected.According to the instruction of ELISA kit,FGF2 standard and cell culture supernatant were added to the reaction well coated with FGF2 antibody,incubated at 37°C for 1 hour, and washed 3 times, and then freshly diluted enzymelabeled antibody was added for 1-hour incubation.Subsequently,it was rinsed 3 times, a temporary preparation of substrate solution was added for 20 minutes, the absorption value was measured at 450 nm,and a standard curve was drawn for analysis.
3.4.Detecting PI3K/Akt and FGF2/FGFR protein expression by Western blotting
Each group of cells was collected,rinsed 3 times with ice-precooled phosphate-buffered saline,and added to radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer 400 μL containing phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride 4 μL,lysed on ice for 30 minutes,and centrifuged at 4°C,12,000 revolutions per minute for 15 minutes to collect the supernatant(protein),which was quantified using a bicinchoninic acid kit and separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for Western blotting.GAPDH was used as a reference.
3.5.Detection of FGF2 mRNA expression by quantitative real-time PCR
After 24 hours of culturing sensitive HCT116 cells and HCT116/5-FU-resistant cells,total RNA was extracted using the 1-step TRIzol method, and cDNA was synthesized,followed by quantitative realtime PCR.Gene level was analyzed by 2△△Ct,and the difference of expression was calculated and repeated 3 times. qGAPDH-F,GCACCACCAACTGCTTA;qGAPDH-R,AGTAGAGGCAGGGATGAT;qFGF2-F, ACCTGCAGACTGCTTTTTGCCCA; qFGF2-R,GGTGCCACGTGAGAGCAGAGC.
4.Results
4.1.Establishment of HCT116/5-FU-resistant cells
This was established by increasing drug concentrations of 5-FU.The initial concentration of 5-FU was 0.1 μg/L,and finally,it could grow stably in a 5.0 mg/L 5-FU culture medium.Under light microscopy,colon cancer-sensitive HCT116 cells demonstrated depithelioid monolayers with uniform size,clear borders,fusiform-like morphology,and adherent growth.After 5-FU treatment,the drug-resistant cells exhibited evident changes with an irregular shape,and most of them had a round shape with a clear outline(Figure 1).
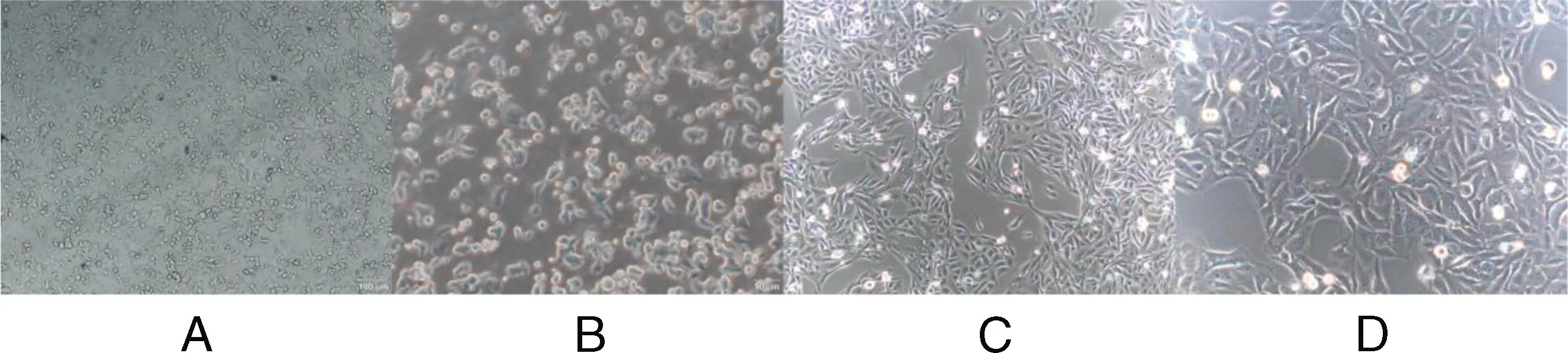
Figure 1. A,HCT116/5-FU-resistant strain(×100).B,HCT116/5-FU resistant strain(×200).C,HCT116(×100).D,HCT116(×200).5-FU,5-fluorouracil.
4.2.IC50 values of each group
The CCK-8 method was used to detect the cell survival rate and calculate the concentration of 5-FU under IC50after drug intervention.The cells were divided into 4 groups:HCT116,FGF2 recombinant protein,HCT116-R,and HCT116-R(FGFR inhibitor,AZD 4547).The concentrations of 5-FU were 3.486 μmol/L in the HCT116 group,39.09 μmol/L in the HCT116(FGF2)group,26.06 μmol/L in the HCT116-R group, and 5.119 μmol/L in the HCT116-R(AZD4547)group.
4.3.Drug resistance
To observe the effects of FGF2 on cell survival,the CCK-8 method was used to detect the cell survival rate.After addition of FGF2 recombinant protein (150 pg/nL) to sensitive HCT116 cells, the cell survival rate increased,suggesting improvement of the tolerance to 5-FU.The addition of FGFR inhibitor (AZD4547, 1 μM/L) in the HCT116 drug-resistant cell group decreased the cell survival rate,suggesting the decreased tolerance to 5-FU. This indicates that FGF2 is related to drug resistance and that its inhibition can reduce drug resistance in HCT116 cells(Figure 2).

Figure 2. Drug resistance.
4.4.FGF2 expression in the cell culture medium
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect FGF2 expression in the cell culture medium.Fibroblast growth factor 2 expression in the HCT116-resistant cell culture medium was upregulated compared with that in sensitive HCT116 cells(P <0.01)(Figure 3).
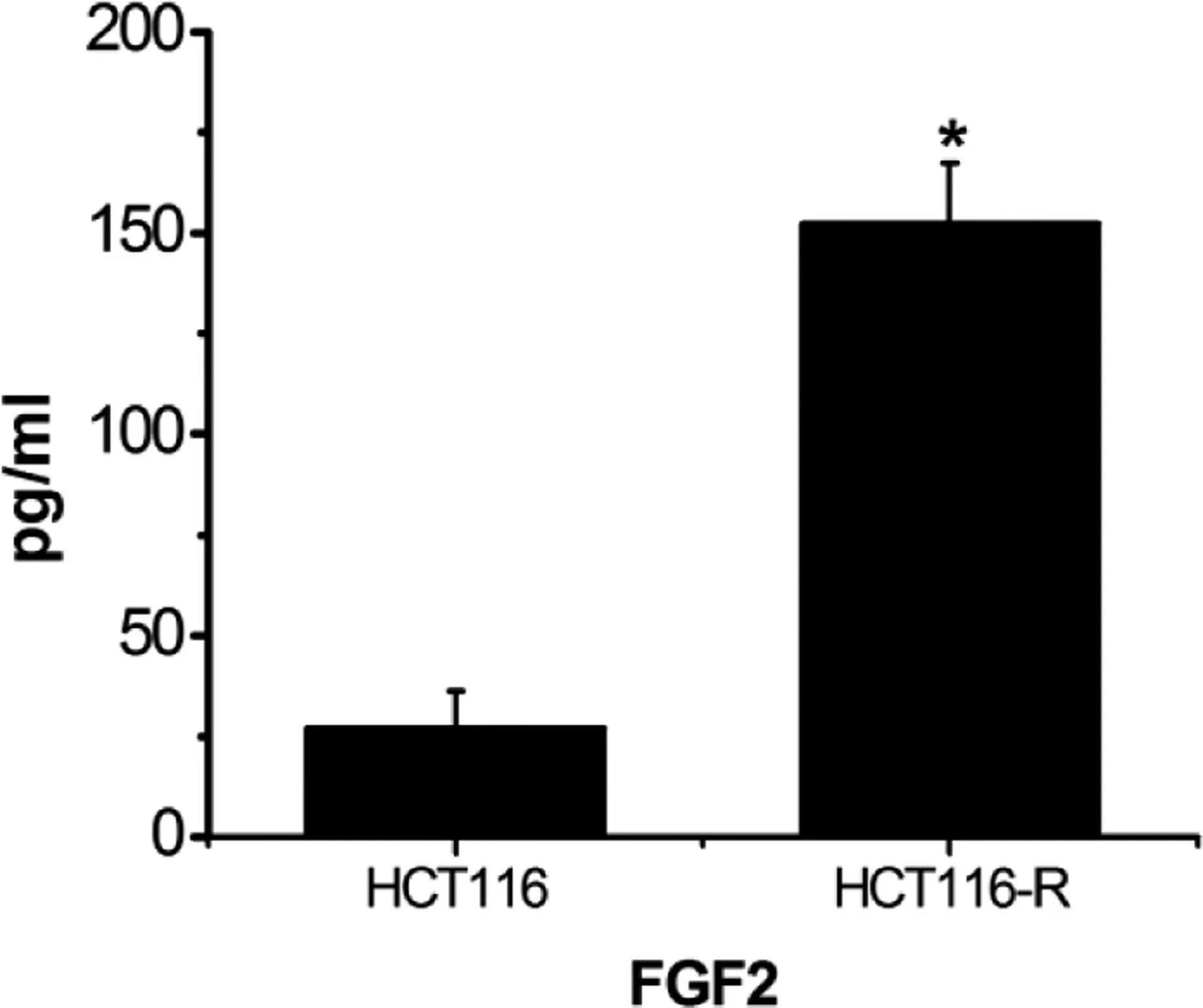
Figure 3. Expression of FGF2 in cell culture medium. *P <0.01,compared with the control group.
4.5.Protein expressions of FGF2,FGFR1,and p-FGFR1 in the cell
Western blotting was performed to detect the expression levels of FGF2,FGFR1,and the p-FGFR1;FGF2 and p-FGFR1 protein levels in HCT116-resistant cells were higher than those in sensitive cells(P <0.05)(Figure 4).
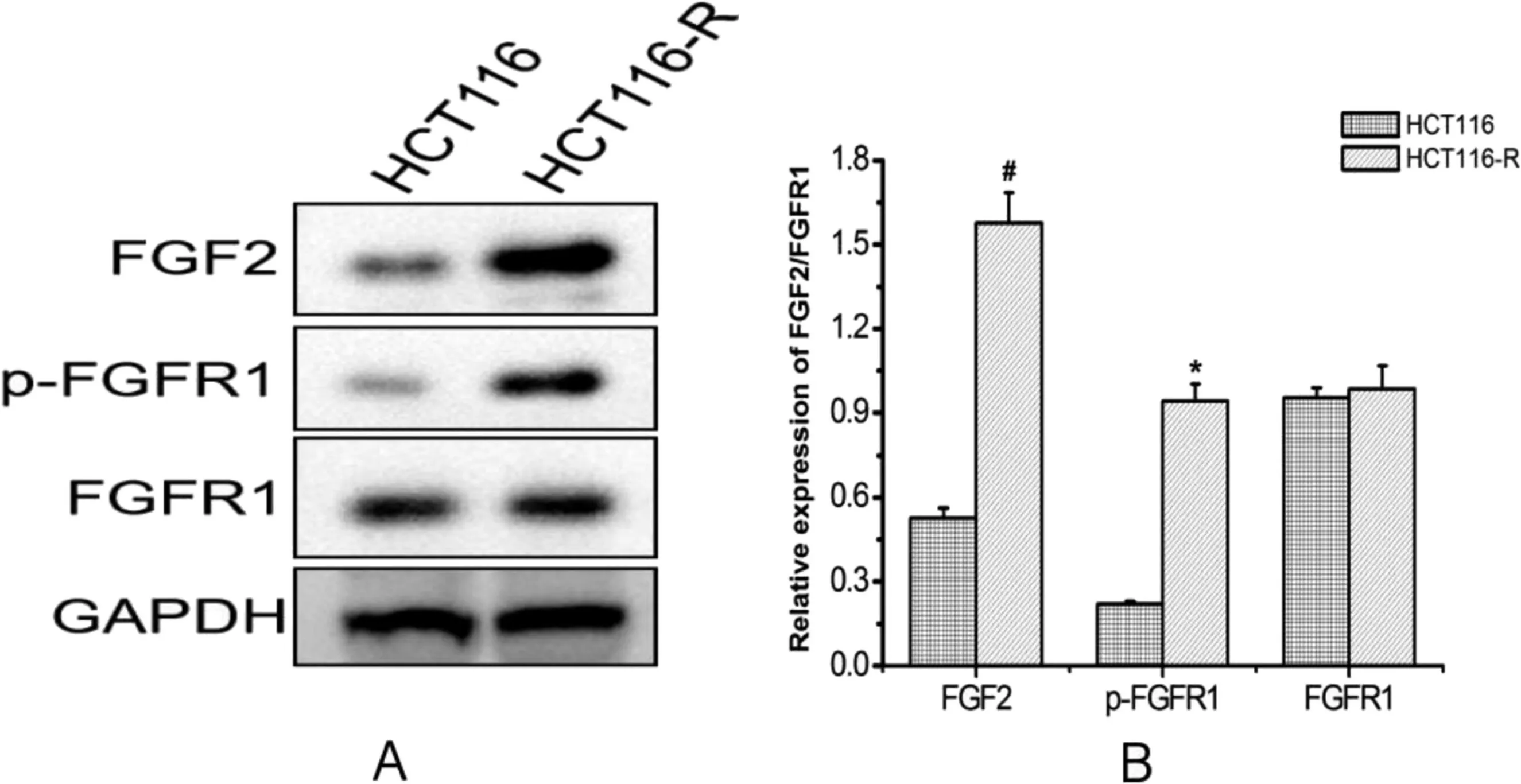
Figure 4. Protein expression of FGF2/FGFR1 in cell(*P <0.05, #P <0.01 compared with the control group).
4.6.FGF2 mRNA expression
Real-time PCR was used to detect the FGF2 mRNA expression level in HCT116-resistant cells, which was higher than that in HCT116-sensitive cells(P <0.05)(Figure 5).
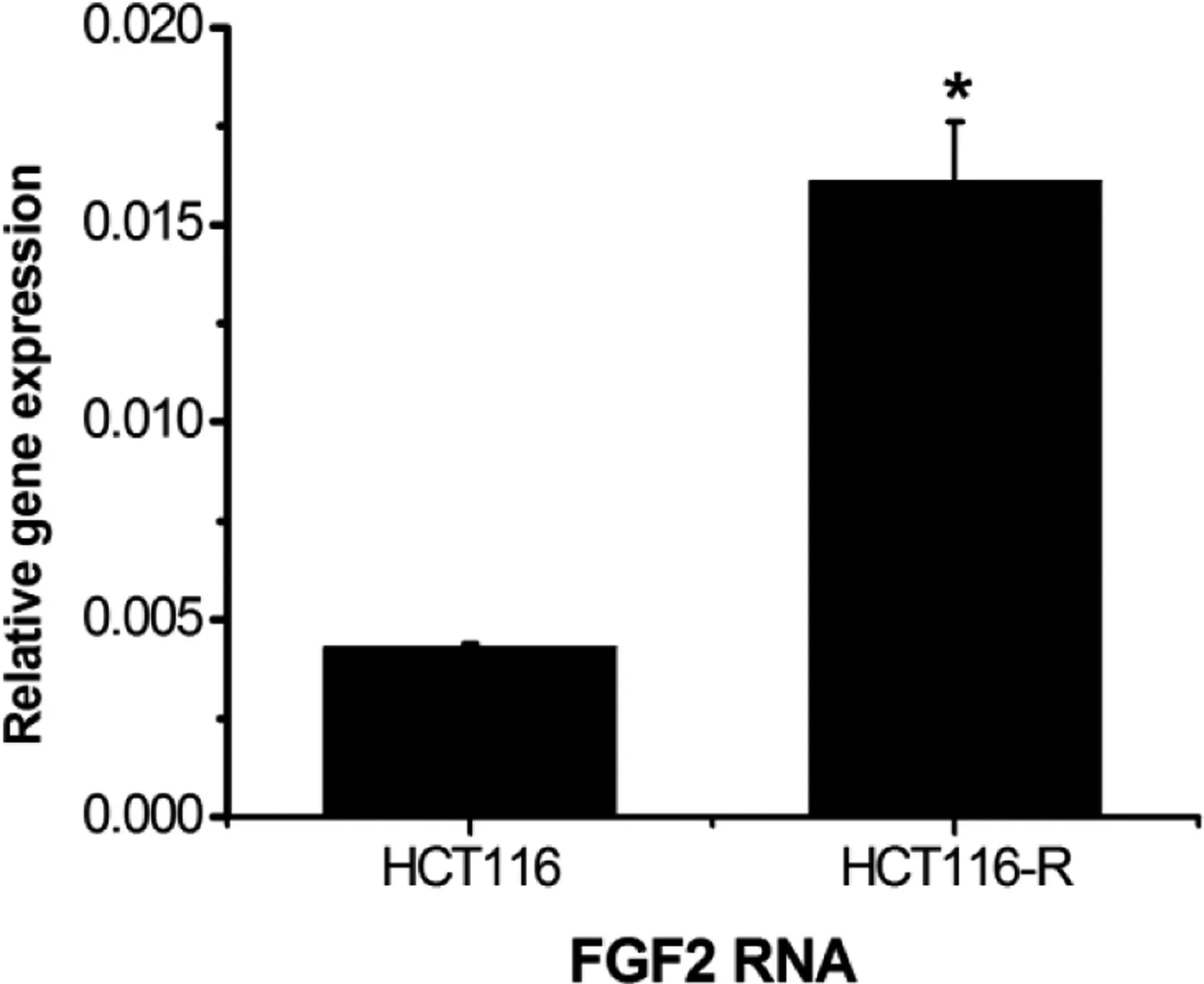
Figure 5. Expression of FGF2 mRNA.*P <0.05,compared with the control group.
4.7.Protein expression of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Western blotting was used to detect the expression of the PI3K/Akt protein.The expression of p-PI3K,p-Akt,and p-mTOR was upregulated, and Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter (Bad) was downregulated in the drug-resistant cell group and FGF2 recombinant protein group, which was significantly different from that in the HCT116-sensitive cell group (P<0.05). In the FGFR inhibitor group, the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt, and p-mTOR was downregulated,whereas that of Bad was upregulated,suggesting the involvement of FGF2 in drug resistance by regulating the AKT/mTOR and AKT/Bad pathways(Figure 6).
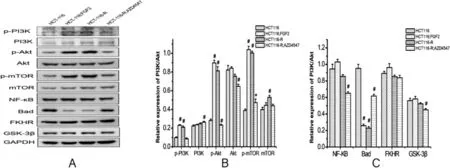
Figure 6. Protein expression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway(*P <0.05, #P <0.01,compared with the control group).
4.8.Protein expression of PTEN
A Western blot analysis was performed to detect PTEN protein expression. The PTEN expression revealed no significant differences among the groups (P >0.05), suggesting that the activation of PI3K/Akt in drug-resistant cells was not affected by PTEN signaling(Figure 7).
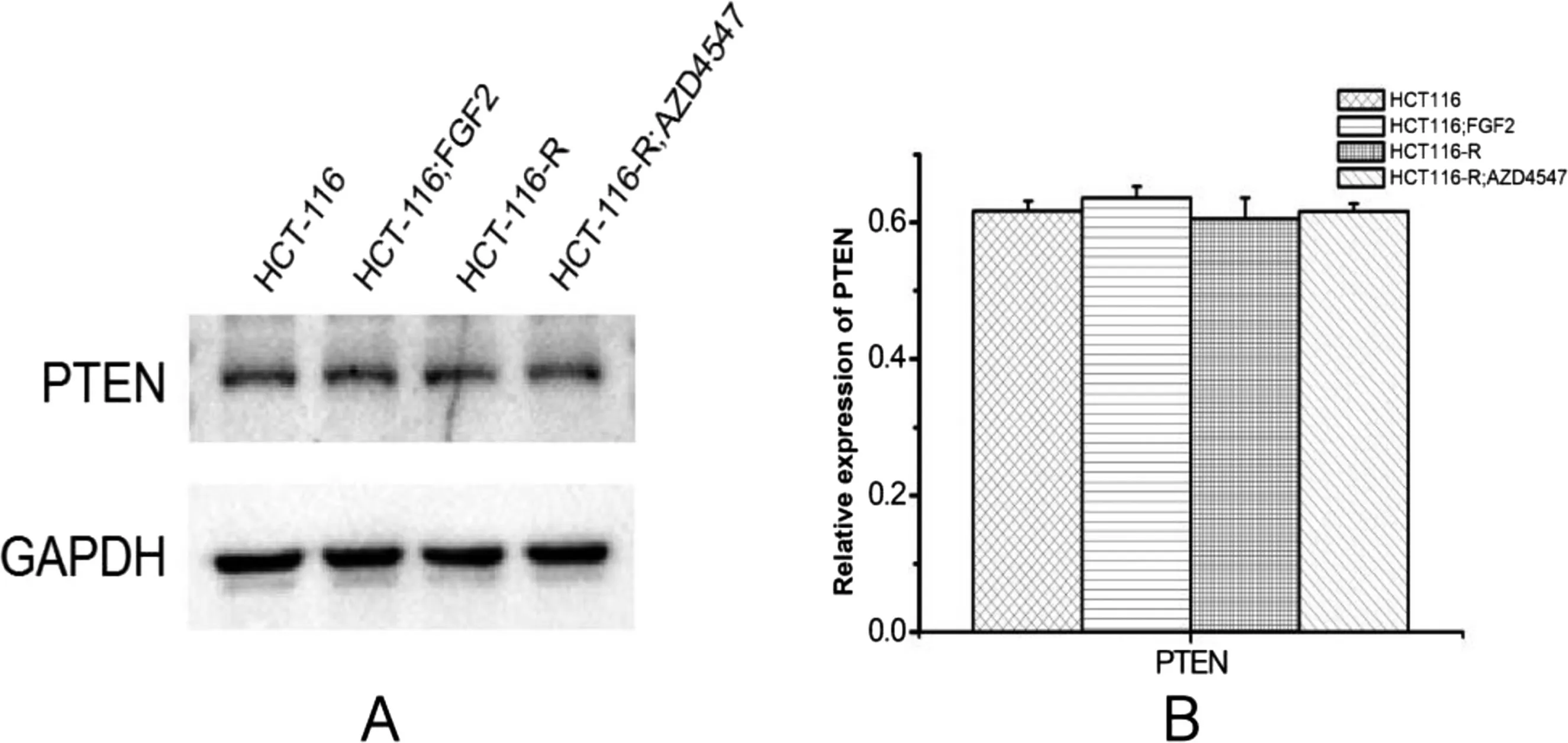
Figure 7. Protein expression of PTEN.
5.Discussion
In 2020,1.932 million cases of colorectal cancer and 935,000 colon cancer-related deaths worldwide were recoded,resulting in a serious social burden.[1]Currently,chemotherapy remains the main treatment approach for colorectal cancer,and the most commonly used effective chemotherapy drugs are fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and topotecan.[9]Drug resistance severely limits the efficacy of colorectal treatment.Resistance to chemotherapy leads to tumor recurrence or metastasis and affects patient survival. Therefore, the mechanism of resistance to chemotherapy is a core research topic that needs to be investigated.
Fibroblast growth factor is a mitogen of mesoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells that participate in several processes such as embryonic development, cell differentiation, neuronal growth, wound healing,tumor growth,cell survival,migration,infiltration,transformation, and angiogenesis.[10]Our results revealed that FGF2 was highly expressed in HCT116 drug-resistant cells,and the addition of FGF2 recombinant protein to HCT116-sensitive cells increased drug resistance, and inhibition of its expression in drug-resistant cells decreased drug resistance.
The activation of PI3K/Akt signaling promotes drug resistance and is abnormally activated in drug-resistant cells. Specific inhibition of this pathway can increase cellular sensitivity to drugs and reduce drug resistance. Some studies have reported a correlation between the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and colorectal cancer resistance.Akao et al[11]demonstrated that the aberrant expression of microRNA-34a can cause resistance to 5-FU in colon cancer cells.Lin et al[12]has reported that Scutellaria barbata inhibited the proliferation of HCT-8/5-FU cells and promoted apoptosis, possibly by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling.Downregulation or inhibition of PI3K/AKT increases colorectal cancer cell sensitivity to 5-FU,and inhibitors targeting PI3K/Akt signaling exhibit multiple antitumor effects. Chen et al[13]treated colon cancer HCT116 cells with magnesium-aluminum layered hydroxide-loaded 5-FU in combination with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ-235 and observed an 8%reduction in survival compared with that associated with BEZ-235 alone.Hu et al[14]reported that nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and BEZ-235 synergistically inhibited the growth of colon cancer cells.
PTEN is a classic tumor suppressor gene that inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway. Thus, PTEN inhibition can promote cell survival,growth,proliferation,metabolism,and migration.[15,16]This study identified no significant difference in PTEN expression among the 3 groups (P <0.05), suggesting that the activation of PI3K in HCT115-resistant cells was not affected by PTEN signaling.
PI3K/Akt signaling participates indrug resistance,whereas FGFcould regulate it.The mechanism of FGF2 in drug resistance may be through PI3K/Akt signaling.We observedthatp-PI3K,p-Akt,andp-mTORwere upregulated, and Bad was downregulated in the drug-resistant cell group,which was significantly different from the sensitive HCT116 cell group (P < 0.05). In the FGF2 recombinant protein group,p-PI3K,p-Akt, and p-mTOR were upregulated, Bad was downregulated,and cell survival rate was elevated,indicating increased drug resistance. In the AZD4547 group, the expressions of p-PI3K,p-Akt, and p-mTOR were downregulated, Bad expression was upregulated, and the cell survival rate was downregulated,suggesting the involvement of FGF2 in the drug resistance of intestinal cancer cells through the activation of the Akt/mTOR and Akt/Bad pathways downstream of PI3K.
6.Conclusion
Fibroblast growth factor 2 promotes chemotherapy tolerance in colon cancer by activating the Akt/mTOR and Akt/Bad signaling pathways downstream of PI3K. However, this study was limited to in vitro cell experiments, and further in vivo experiments are needed to verify this resistance mechanism.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all investigators and supporters involved in this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81904109) and the Natural Science Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (no.2023JJ30361,no.2019JJ50344).
Conflicts of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Author contributions
X.-L.Jian and P.-H.Zeng designed the project.X.-L.Jian and K.-X.Li performed the experiments. X.-L. Jian and W. Peng processed and wrote the manuscript.
Data availability statement
All data are true and reliable. Data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Ethical approval
There are no ethical issues.
 Oncology and Translational Medicine2023年6期
Oncology and Translational Medicine2023年6期
- Oncology and Translational Medicine的其它文章
- Pancreatic cystic neoplasms:a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management
- Development of therapeutic cancer vaccines using nanomicellar preparations
- Immunotherapy for mucosal melanoma
- Proposal of a modified classification for hilar cholangiocarcinoma
- Chinese expert consensus on laparoscopic hepatic segmentectomy and subsegmentectomy navigated by augmented-and mixed-reality technology combined with indocyanine green fluorescence imaging
- Xiao-Ping Chen:the “Master of the Scalpel” who saves lives by entering the forbidden territory of hepatopancreatobiliary surgery
