Construction and validation of prognostic model of Cuproptosis-related LncRNA in osteosarcoma
FAN Yi-dong, QIN Gang, SU Guo-wei, XIAO Shi-fu, LIU Jun-liang, LI Wei-cai, WU Guang-tao
1.Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, China
2.The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530022, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Abstract: Cuproptosis is a newly discovered form of apoptotic process that is thought to play an important role in cancer therapy.Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is involved in regulating many physiological and pathological activities of cells.The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic significance of Cuproptosis-associated lncRNAs in osteosarcoma.Methods: The Gene expression profiling of osteosarcoma samples versus normal samples and corresponding clinical data were downloaded from the public databases UCSC Xena and GTEx, and the cuproptosis gene was obtained from the published literature, the prognostic model of osteosarcoma cuproptosis-related lncRNA was constructed by using coexpression network, minimum absolute contraction and selection algorithm (LASSO) and Cox regression model.Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and nomograms were used to assess the predictive power of the model.Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was used to explore the relationship between osteosarcoma immune cells and function in different risk groups.Results: 181 cuproptosis -related lncRNAs were obtained by co-expression analysis of 19 cuproptosis genes collected.Ten lncRNAs were screened out by differential analysis and single-factor Cox analysis.Three cuproptosis-related lncrnas (AC124798.1, AC090152.1,AC090559.1) were screened by Lasso and multivariate Cox regression to construct the prognostic model.Patients were divided into high and low risk groups based on the median risk score.The results of overall survival, risk score distribution and survival status in the lowrisk group were better than those in the high-risk group, and were verified in the internal data.Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses showed that risk score was an independent prognostic factor.Nomograms and ROC curves showed that the prognostic model had good predictive ability.The results of ssGSEA suggest that immune cells and function may be inhibited in the high-risk group.Conclusion: The 3 cuproptosis-related lncRNAs may be helpful to guide the prognosis of osteosarcoma patients and provide some theoretical basis for clinical decision.
1.Introduction
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary bone tumor originating from primary mesenchymal cells[1].It is most common in children and adolescents and is the third most common bone cancer in adults after chondrosarcoma and chordoma.The global total incidence rate is 3.4 per million per year[2].Currently, treatment of patients with OS usually includes surgery in combination with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and 5-year survival is estimated to be less than 20% in patients with metastatic OS[3].There has been no significant improvement in survival over the past 20 years despite numerous chemotherapy regimens.Prediction of prognostic biomarkers of OS, it can help to judge the possible clinical outcome of patients after treatment, improve the therapeutic effect of OS,reduce the treatment-related toxicity and provide a plan for clinical trial design in the future[4].Therefore, it is important to identify prognostic biomarkers of OS.
Copper is an indispensable micronutrient in all living things.It is mainly involved in energy metabolism, reactive oxygen species accumulation, iron uptake and signal transduction in eukaryotes,copper in cells has a direct effect on cell proliferation, differentiation or cell death[5].When the intracellular concentration of copper ion exceeds the threshold of maintaining steady state, it will lead to the appearance of cytotoxicity.The mechanisms involved include the accumulation of reactive oxygen species, anti-angiogenesis and proteasome inhibition[6].Recent studies have shown that copper is involved in the regulation of cell death in a way that is different from the known mechanisms of cell death, such as iron death,apoptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy, and is more closely related to mitochondrial respiration[7].Copper ions bind directly to the fatty acylation components of tricarboxylic acid cycle acid (TCA), causing these proteins to aggregate and deregulate, followed by the loss of iron-sulfur cluster proteins, which in turn triggers toxic stress and ultimately cell death.Tsvetkov named this process cuproptosis[8].
Long-chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a transcript over 200 nucleotides in length and is involved in many biological processes,including cell differentiation, development and apoptosis[9].Importantly, lncrnas have been shown to be important regulators of gene expression, and they can play key roles in a variety of biological functions and disease processes, including cancer[10].Lncrnas have been found to be associated with a variety of cancers,including breast[11], colorectal[12] and liver cancers[13].Currently, the role of cuproptosis-associated lncrnas in OS is unclear, and therefore,our study aimed to explore the role of cuproptosis-associated lncrnas in OS prognosis using bioinformatics.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Screening of cuproptosis -associated lncrnas
On October 19,2022, the Gene expression profiling of 88 osteosarcoma samples were downloaded from the UCSC Xena Database (http://Xena.UCSC.edu/) with corresponding clinical data (survival time, survival status, age, sex, metastasis or not).On October 20,2022, Gene expression profiling of 396 normal samples were obtained from the GTEX database (https://www.gtexportal.org/home/) and all gene expression data were log2(x + 1) transformed.We extracted 19 genes associated with cuproptosis from published articles[8,14].The R software“sva” package Combat function normalizes the merged data of UCSC and GTEX.mRNAs were distinguished from LncRNAs based on annotation information of genes in the pooled data.To screen for lncrnas potentially associated with cuproptosis, the R software“Limma” package was used for co-expression analysis of 19 cuproptosis genes with lncrnas using| R | > 0.4 and P < 0.05(R as correlation coefficient) as screening conditions.Finally, a differential analysis was performed for eligible lncrnas by | log2fc | 1, FDR < 0.05 conditions, resulting in differential cuproptosis-related lncrnas for follow-up analysis.
2.2 Establishment and validation of prognostic model of cuproptosis-associated lncRNA
Eighty-five patients (2 of whom did not have survival status and 1 of whom did not have overall survival time and therefore were not included in the study) were randomly divided into a 1:1 training group and a validation group.The training group was used to construct the prognostic model, and the validation group and total sample group were used for model validation (Table 1).Univariate Cox regression was used to screen prognostic lncrnas in cuproptosisrelated differences lncrnas.Then, the least absolute contraction and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression and multivariate Cox regression model were used to create the prognostic model for the training group.The risk value formula for each patient is calculated as RiskWhere χiand coefirepresents the expression amount and risk coefficient of each lncRNA.Patients with OS were divided into high-and low-risk groups according to the median risk score in the training group.Kaplan-meier (K-M)survival analysis compared overall survival between two different risk groups.The receiver operating characteristic (ROC-curves predicting 1, 3 and 5-year overall survival and clinical characteristics were further drawn to assess the predictive value of the model.The risk scores for each patient with OS in the validation and total sample groups were calculated using the same formula.
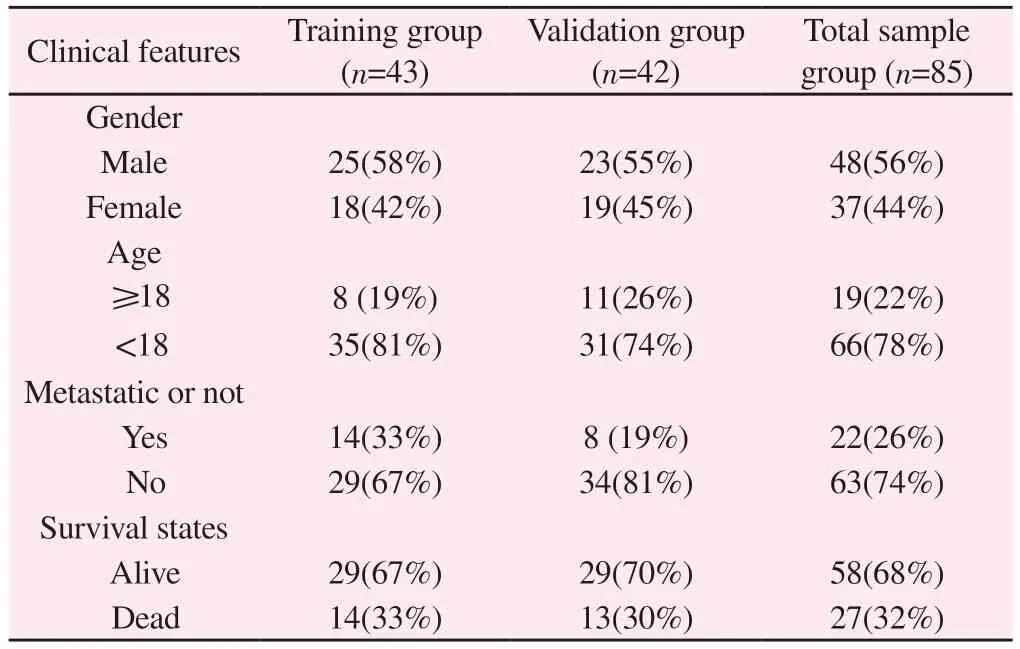
Tab 1 Grouped clinical information
2.3 Independent prognostic analysis
Risk score was combined with clinical information of patients with OS, including age, sex, and metastasis.Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were used to determine whether the risk score was an independent prognostic factor.
2.4 The construction of nomograms
To better enable the clinical application of our prognostic model,a prognostic nomogram model was constructed using the“RMS”and“Survival” packages of R software to assess 1, 3 and 5-year survival of patients with OS.The calibration curve visualizes the consistency between the actual results and the prediction results of nomograms.
2.5Analysis of differences in immune cells and function among different risk groups
Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (SSGSEA) in R software“GSVA” package was used to analyze 16 kinds of immune cell infiltration and 13 kinds of immune function in high and low risk groups.
2.6 Statistic analysis
All the statistical analysis and drawing were carried out in R (64X 4.1.2) software.The correlation of gene coexpression was obtained by Pearson correlation analysis.Wilcox test was used to compare the differential gene expression between tumor tissues and normal tissues.The Mann-whitney test was used to compare SSGSEA scores for immune cell content or function between high-and lowrisk groups.Kaplan-meier survival analysis and log-rank test were used to compare survival differences between high-and lowrisk groups.Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to identify independent prognostic factors.P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 To determine the prognostic model for construction of the copper-related death lncRNA
A total of 181 eligible lncrnas (| R | > 0.4 and P < 0.05) were obtained from coexpression analysis of 19 copper-death genes with 13425 lncrnas extracted from UCSC + GTEx pooled data, of which no relevant lncrnas were found in PDHA1.Differential analysis was then performed, resulting in 108 differential cuproptosisrelated lncrnas (| log2fc| 1, FDR < 0.05) , of which 33 were downregulated and 75 were upregulated.Sangeet visualized the co-expression relationship between cuproptosis gene and its associated lncrnas (figure 1A).A total of 85 patients with OS were randomly divided into the training group (N = 43) and the validation group (N = 42).For the training group, 108 cuproptosis-related lncrnas screened were subjected to univariate Cox analysis and 10 prognostic-related cuproptosis lncrnas were identified, of which 5 were high-risk lncrnas(AC124798.1, AC005277.2, LINC01549,LINC01060, AP000851.2)and 5 were low-risk lncrnas(PCOLCEAS1, AC090152.1, NKILA, AC090559.1, AL136162.1)( Figure 1B).Subsequently, Lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression analysis were used to determine the optimal 3 lncrnas involved in the model construction(AC124798.1, AC090152.1, AC090559.1)(Figure 1C, D, E).
3.2 Construction and validation of prognostic model
Risk Scores were calculated for each patient in the training,validation, and total sample groups using the 3 selected lncrnas,risk scores= AC124798.1*(1.14553168738236)+AC090152.1*(-1.13701301122647)+AC090559.1*(-1.83119937382105).Patients in the training group were divided into high-and low-risk groups according to the median risk score.Survival analysis showed that the overall survival of the low-risk group was significantly better than that of the high-risk group.The risk heatmap showed that AC124798.1 expression gradually increased from the low-risk group to the high-risk group, and AC090152.1 and AC090559.1 expression gradually decreased.The survival chart showed that the number of death increased gradually from low-risk group to high-risk group.Not only that, we also validated in the Validation Group and the total sample group.The results showed that both the validation group and the total sample group had similar trends to the training group (figure 2A-L).The ROC curves showed AUC values of 0.799,0.786, and 0.827 at 1,3 and 5 years, respectively (figure 3A).The AUC values for risk score and metastasis were 0.799 and 0.905, respectively,higher than those for age (0.461) and sex (0.467)(figure 3b).All in all, the above results show that the prognostic model we have built has better prognostic value.
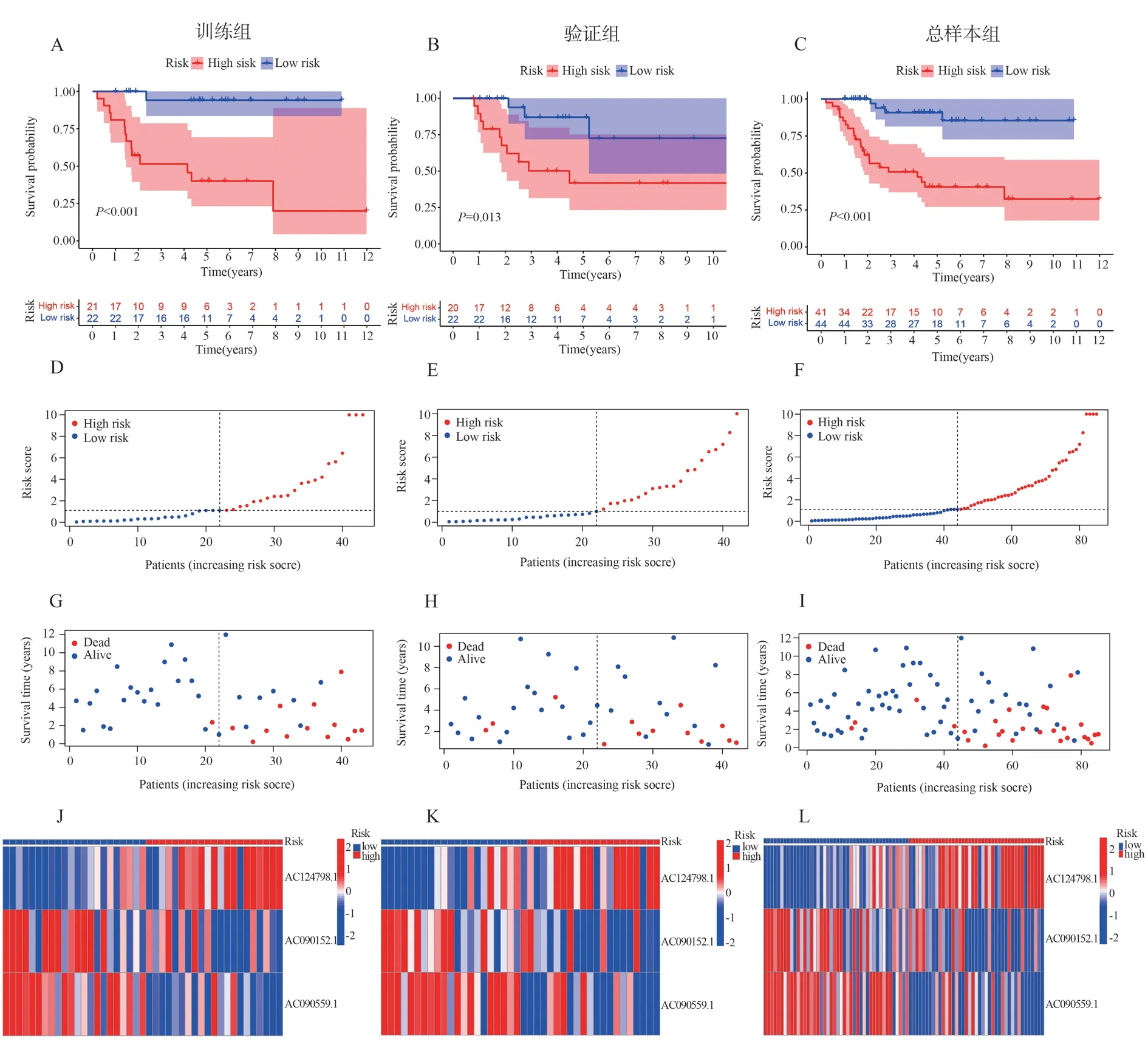
Fig 2 The prognostic model of Training Group, Validation Group and total sample group
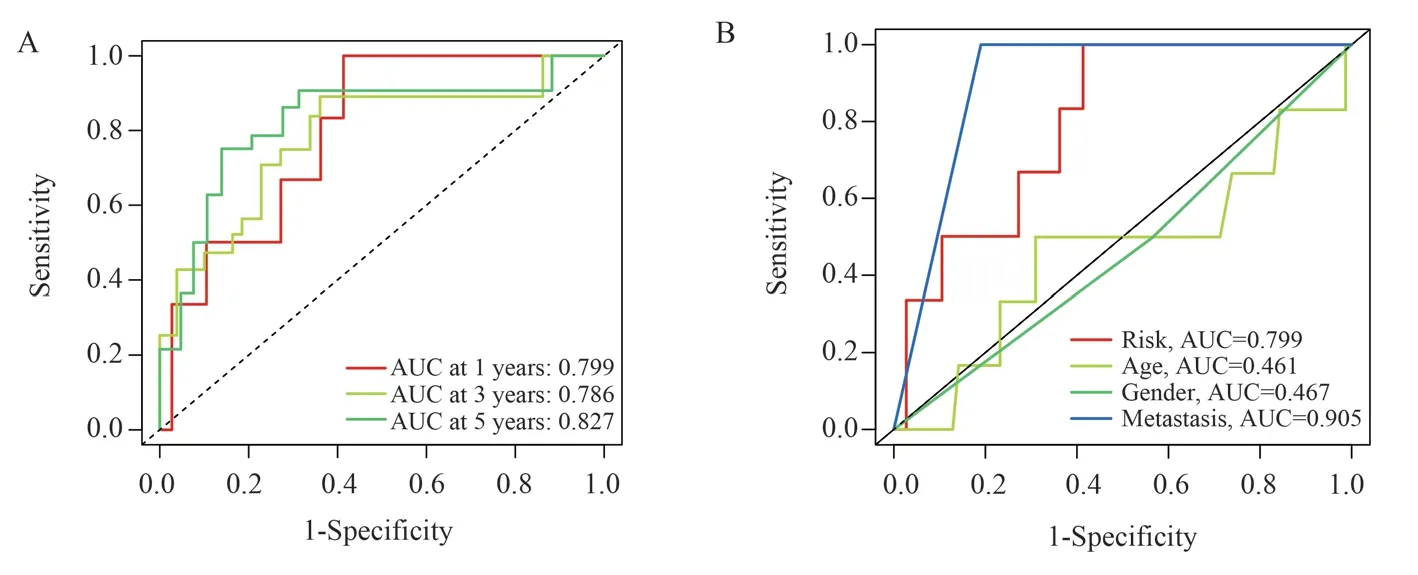
Fig 3 A: ROC curve for predicting 1, 3 and 5-year survival in the total sample group.B: ROC curve of risk score and clinical characteristics
3.3 Independent prognostic analysis
Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were used to determine whether the risk score was a prognostic factor that could be independent of other clinical features.The results showed that risk score and metastasis were independent prognostic factors in univariate and multivariate Cox analysis, and both were high risk factors.
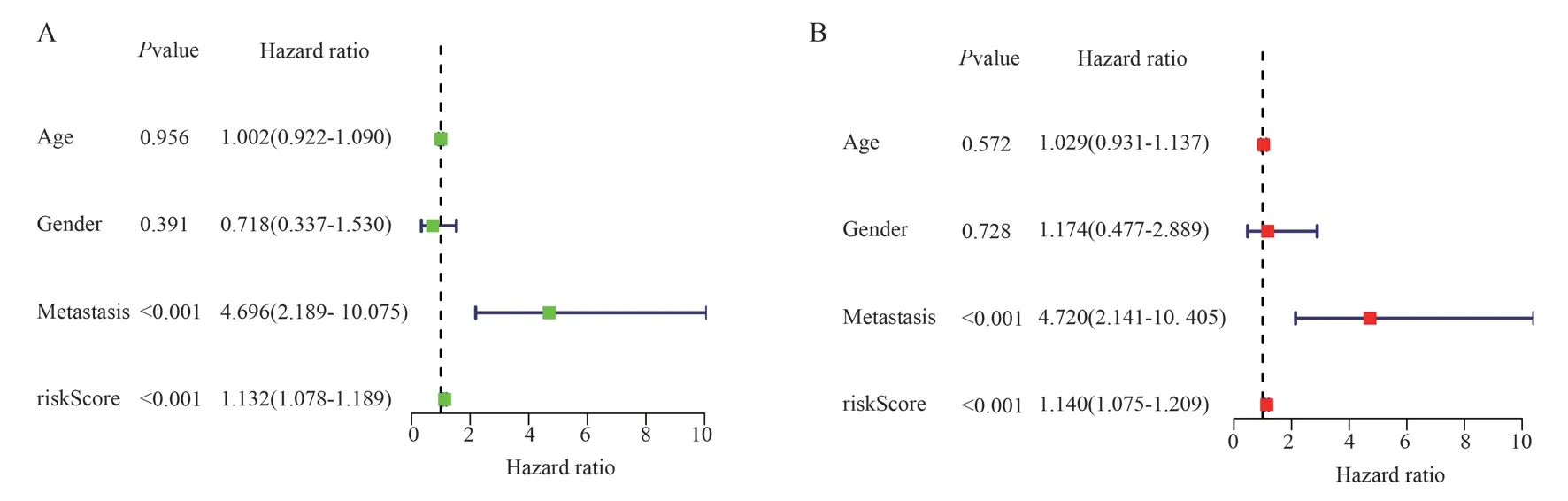
Fig 4 A: univariate Cox regression for clinical characteristics and risk score; B: Multivariate Cox regression analysis
3.4 Construction and validation of Nomogram model
A nomogram model was constructed to predict 1, 3 and 5-year survival of patients with OS based on clinical characteristics,including risk score, age, sex, and metastasis (figure 5A).The calibration curve showed that the overall survival predicted by nomograms was in good agreement with the actual overall survival(figure 5B).We also added nomograms and plotted ROC curves predicting 5-year survival, which showed that nomograms had the highest AUC value (AUC = 0.852) and had some clinical value(figure 5C).
3.5 ssGSEA results for high and low risk groups
We investigated the relationship between different risk groups and infiltrating tumor immune cells and immune function by SSGSEA.We found that the vast majority of immune cells and immune function differed between the high-and low-risk groups, and that both immune cells and immune function scores were higher in the low-risk group than in the high-risk group.Immune cells in the low-risk group(include B cells, CD8+ T cells, DCs, Macrophages,Neutrophils, NK cells, pDCs, T helper cells, Tfh, Th1 cells, Th2 cells, TIL, Treg)(Figure 6A)and immunologic function(APC co inhibition, APC co stimulation, CCR, Check-point, Cytolytic activity,HLA, inflammation-promoting, MHC class I, Parainflammation,T Cell co-inhibition, T Cell co-stimulation, Type_I_IFN_Reponse)(Figure 6B) significant climb.It is suggested that cuproptosis is closely related to tumor immunity and immune cells and functions may be inhibited in high risk group.
Fig 5 A: Nomogram models of risk score versus clinical characteristics predicted 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival of patients with OS (“*” for P < 0.05, “**”for P < 0.01, “***” for P< 0.001) ; B: calibration curve tests for consistency between actual and predicted results.C: ROC curve of 5-year overall survival for patients with OS assessed by nomogram, risk score, and clinical characteristics

Fig 6 A: ssGSEA showed differential analysis of 16 immune cells in the high-and low-risk group; B: SSGSEA showed differential analysis of 13 immune functions in the high-and low-risk group.(“*” stands for P < 0.05, “**” stands for P < 0.01, “***” stands for P < 0.001).
4.Discussion
Cuproptosis is a newly discovered form of copper-dependent regulation of cell death.The imbalance of intracellular copper homeostasis can affect the growth and proliferation of cancer cells[15].Previous studies have shown that cell apoptotic process is closely related to tumors, such as apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis and so on[16].Therefore, further research on cuproptosis may lead to new solutions for cancer treatment.
The LncRNA class is non-protein-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at various levels, including histone modifications, transcription, and post-transcriptional regulation[17].It is estimated that there are over 60,000 lncrnas in humans, and the number of lncrnas is still growing rapidly[18].So far, only a handful of lncRNA functions have been annotated[19].Dysregulated lncrnas are widely involved in the pathogenesis of cancer, including cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and anti-drug resistance[20].Moreover, a subset of lncrnas have been identified as biomarkers of tumor diagnosis and prognosis.Deng et al demonstrated that the LncRNA RBM5-AS1 was significantly increased in OS tissues and cell lines.Furthermore, knockdown of RBM5-AS1 significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells in vitro[21].Huang Q et al found that LncRNA BE503655 was overexpressed in human OS tissues and OS cell lines, and that knockdown of LncRNA BE503655 could inhibit OS cell proliferation and invasion; Its function depends on the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in OS cells[22].The LncRNA CBR3-AS1 has been found to be oncogenic in regulating OS cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and is an independent poor prognostic factor in patients with OS[23].These results suggest that lncrnas not only act as biomarkers of OS, but also are closely related to the prognosis of OS.
In this study, 108 differential cuproptosis-related lncrnas were obtained by Pearson correlation coefficient and differential analysis.85 patients with osteosarcoma were divided into training group and validation group according to the ratio of 1:1.In the training group,the prognostic model including 3 lncrnas was constructed using univariate Cox, Lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression,it is verified in the verification group and the total sample group.Survival analysis, ROC, independent prognostic analysis and calibration curve validation were used to evaluate the predictive performance of the model.
Our prognostic model consists of three lncrnas, including AC124798.1, AC090152.1, and AC090559.1.Of these, AC124798.1 was a risk factor for poor prognosis in osteosarcoma, and AC090152.1 and AC090559.1 were protective factors.We found that these 3 lncrnas were associated with multiple tumor outcomes,reflecting to some extent the reliability of our findings.AC124798.1 is associated with survival in patients with breast and pancreatic cancer and is an important prognostic protective factor for both[24,25].AC090152.1 is considered as a prognostic biomarker of liver cancer[26].Wang Z et.alwas found AC090152.1 not only to be a poor prognostic factor for RCC, but also to be positively correlated with immune cell populations such as T cells and negatively correlated with neutrophil and endothelial cells[27].AC090559.1 is closely related to iron death, autophagy, necrotic apoptosis and coke death,and can be used as a prognostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma and osteosarcoma[28-31].At present, there are few studies on lncrnas in OS, and the relationship between lncrnas and OS is still unclear.Infiltrating immune cells and immune function in the tumor microenvironment play a crucial role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression[32].We performed a differential analysis of 16 immune cell infiltrates and 13 immune functions across the different risk groups, showing that 13 immune cells and 12 immune functions were suppressed in both the high-risk groups.The immune microenvironment of OS consists mainly of T lymphocyte and macrophages, in addition to B lymphocyte and mast cells[33].CD8+T cells are considered to be one of the major drivers of antitumor immunity[34], Can be directly lysed and cleared of cancer cells[35].Research Indicates[36], In triple-negative breast cancer, a high level of CD8 + T cells is associated with a good prognosis.Tfh(follicular helper T cells) is also closely associated with antitumor immunity, and patients with higher Tfh cell infiltration in breast cancer also have higher survival rates[37].It is of great significance to further study the mechanisms of various immune cells and their functions in tumor microenvironment, and to find out the ways to improve the anti-tumor ability of the immune system.
There are also many inadequacies in this study.First, although the prognostic model we constructed was confirmed in internal data,we need more clinical data for further validation.Secondly, the prognostic model of this study was established and validated by public database.Besides our data analysis, experimental validation is still needed.
Authors’ Contribution
Professor Qin Gang provided the idea for the paper, FAN carried out the data analysis, research design and manuscript writing, and so Su guowai and Xiao Shifu selected the chip for the paper Liu Junliang, Li Weicai and Wu Guangtao are responsible for data collation and literature review.
Conflict of interest statement: all authors have no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年16期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年16期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- TCM Intervention on Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy
- Research progress on the correlation between intestinal microflora disorder and liver disease
- Research progress on the effects of phthalates on reproductive health of childbearing population and their offspring
- Study on pharmacodynamics and mechanism of nano-Kuiyangye in treating radiation esophagitis in rats
- Effect of glycyrrhetinic acid on Th1/Th2 balance in cough variant asthma mice
- Efficacy and safety of oral Chinese patent medicine combined with sacubitril/valsartan in the treatment of chronic heart failure: A Metaanalysis
